Содержание
- 2. Project plan : 1. Form of government (Monarchy, Republic). 2. Form of state territorial structure (Unitary
- 3. 1. Form of government (Monarchy, Republic). A government is a system of order for a nation,
- 4. What form of government is Republic? Republic, form of government in which a state is ruled
- 5. features of government republic : - a form of government in which the people or their
- 6. types of government republic : - Presidential republics with an executive presidency separate from the legislature.
- 7. What form of government is monarchy ? A monarchy is a form of government in which
- 8. features of government monarchy : Functions of monarchies. A monarchy consists of distinct but interdependent institutions—a
- 9. types of government monarchy : There are two types of monarchies: constitutional and absolute. Constitutional monarchies
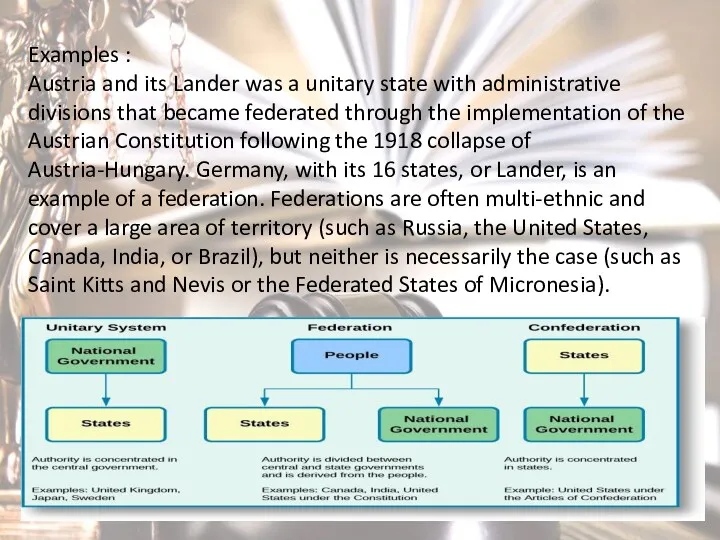
- 11. 2. Form of state territorial structure (Unitary state, Federation, Confederation) . Territorial structure means the special
- 12. Unitary state - Unitary state, a system of political organization in which most or all of
- 13. In France, the classic example of a centralized administrative system, some members of local government are
- 14. A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union
- 15. Examples : Austria and its Lander was a unitary state with administrative divisions that became federated
- 16. Confederation A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups
- 17. The characteristics of confederations also are highlighted by distinguishing them from federations: -No Authority to Legislate
- 18. 3. Political regime (Democracy, Non-Democracy) . Democracy is based on the idea of deliberation and negotiation.
- 19. Democracy political regime democratic features: According to American political scientist Larry Diamond, democracy consists of four
- 20. Types : - Direct democracy. - Representative democracy. - Constitutional democracy. - Monitory democracy.
- 21. Example : Democracy in the United States The United States is a representative democracy. This means
- 22. Non-Democracy political regime non-democratic features - There is no free and fair elections. - There is
- 23. Types : Non-Democratic Governments: Monarchy, Oligarchy, Technocracy, and Theocracy. Some nondemocratic governments can be classified into
- 24. Example : Top Five NON-DEMOCRATIC countries: 1 . Saudi Arabia This is a prominent example of
- 26. Скачать презентацию






















 Меры уголовно-процессуального принуждения
Меры уголовно-процессуального принуждения Федеративная Республика Германии
Федеративная Республика Германии Общая собственность и порядок защиты права собственности. Защита неимущественных прав
Общая собственность и порядок защиты права собственности. Защита неимущественных прав Понятие трудового права
Понятие трудового права Системы документации. Требования к оформлению служебных документов
Системы документации. Требования к оформлению служебных документов Правовое положение общества с ограниченной ответственностью
Правовое положение общества с ограниченной ответственностью 20_Договор коммерческой концессии
20_Договор коммерческой концессии Школа правовых знаний. Судебный процесс (игровая модель)
Школа правовых знаний. Судебный процесс (игровая модель) Профессиональная преступность
Профессиональная преступность Әкімшілік құқық
Әкімшілік құқық Административная ответственность специалистов, ответственных за проведение закупок
Административная ответственность специалистов, ответственных за проведение закупок Основные принципы создания положительного впечатления о компании и ее работниках
Основные принципы создания положительного впечатления о компании и ее работниках Кедендік одақ
Кедендік одақ Вопросы взаимодействия с общественностью и средствами массовой информации в судах Липецкой области
Вопросы взаимодействия с общественностью и средствами массовой информации в судах Липецкой области Договор транспортной экспедиции
Договор транспортной экспедиции Социальное партнерство
Социальное партнерство Организация работы с документами, содержащими конфиденциальную информацию
Организация работы с документами, содержащими конфиденциальную информацию Конституція України. Конституційний лад в Україні. Конституційне право. Організація і здійснення державної влади в Україні
Конституція України. Конституційний лад в Україні. Конституційне право. Організація і здійснення державної влади в Україні Вопросы совершенствования организации учета электрической энергии
Вопросы совершенствования организации учета электрической энергии Происхождение государства. Основные концепции
Происхождение государства. Основные концепции Основные правила сертификации продукции. Схемы сертификации продукции
Основные правила сертификации продукции. Схемы сертификации продукции Підстави звільнення від кримінальної відповідальності
Підстави звільнення від кримінальної відповідальності Герб России
Герб России Подпрограмма Создание благоприятных условий для развития рынка недвижимости
Подпрограмма Создание благоприятных условий для развития рынка недвижимости Антимонопольное регулирование в цифровую эпоху
Антимонопольное регулирование в цифровую эпоху Судебная система Российской Федерации
Судебная система Российской Федерации Контрактная система: осуществление закупок
Контрактная система: осуществление закупок Правовая охрана окружающей среды городов и других населенных пунктов
Правовая охрана окружающей среды городов и других населенных пунктов