Содержание
- 2. Chapter 4 Emotions and Moods
- 3. After studying this chapter you should be able to: Differentiate between emotions and moods. Discuss whether
- 4. Why Were Emotions Excluded from OB Study? Historically, emotions in the workplace were thought to be
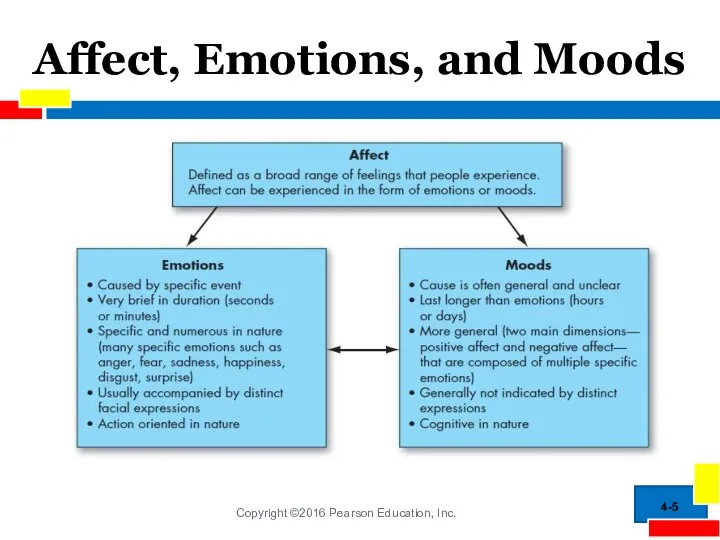
- 5. Affect, Emotions, and Moods 4- Copyright ©2016 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 6. The Basic Emotions Six universal emotions Anger Fear Sadness Happiness Disgust Surprise 4-
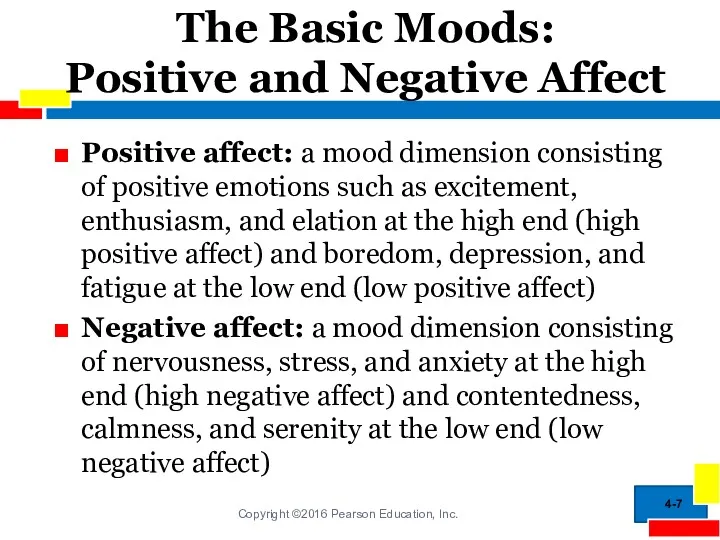
- 7. The Basic Moods: Positive and Negative Affect Positive affect: a mood dimension consisting of positive emotions
- 8. Experiencing Moods and Emotions Positive moods are somewhat more common than negative moods Positivity offset: at
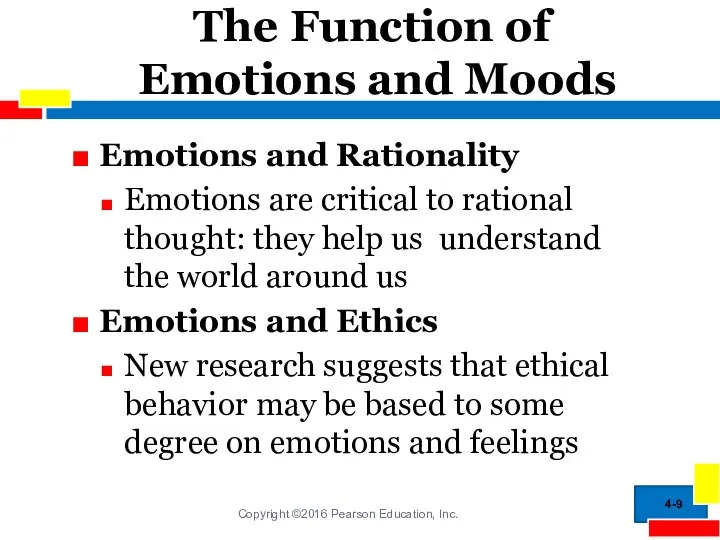
- 9. The Function of Emotions and Moods Emotions and Rationality Emotions are critical to rational thought: they
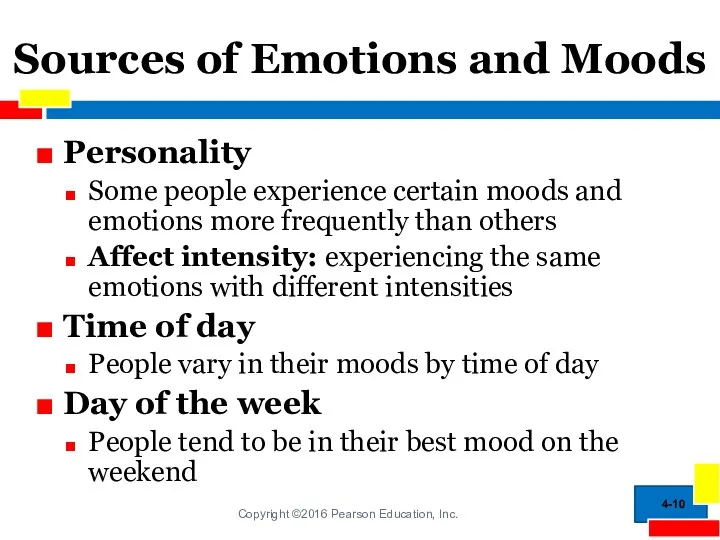
- 10. Sources of Emotions and Moods Personality Some people experience certain moods and emotions more frequently than
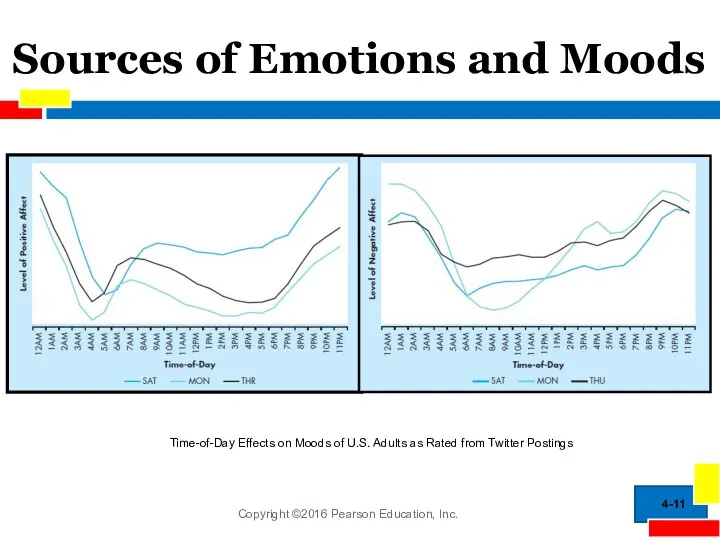
- 11. Sources of Emotions and Moods 4- Time-of-Day Effects on Moods of U.S. Adults as Rated from
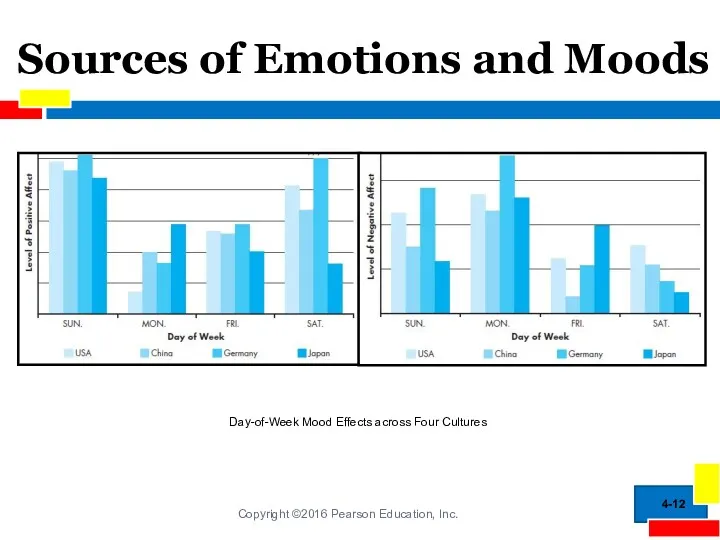
- 12. Sources of Emotions and Moods 4- Day-of-Week Mood Effects across Four Cultures
- 13. More Sources Weather No impact according to research Stress Increased stress worsens moods Social Activities Physical,
- 14. Even More Sources Exercise Mildly enhances positive mood Age Older people experience negative emotions less frequently
- 15. Emotional Labor Emotional labor: an employee’s expression of organizationally desired emotions during interpersonal transactions at work
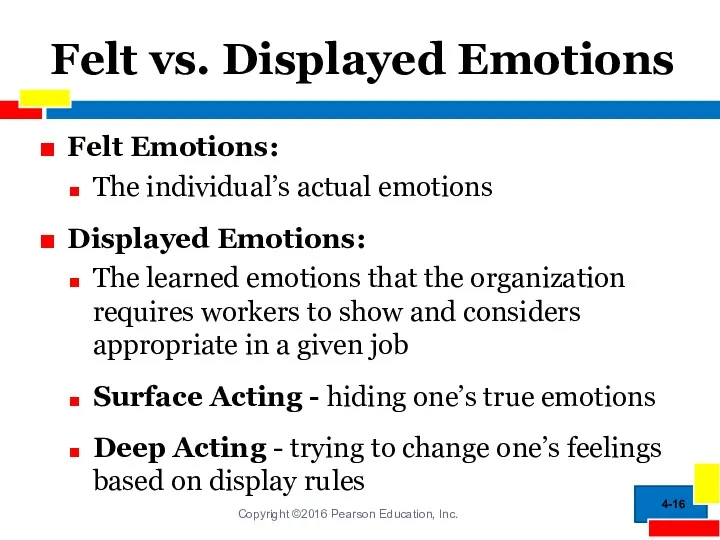
- 16. Felt vs. Displayed Emotions Felt Emotions: The individual’s actual emotions Displayed Emotions: The learned emotions that
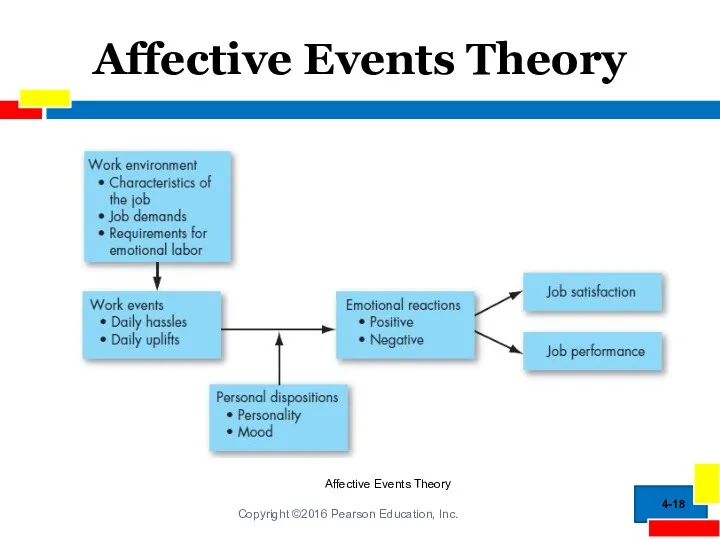
- 17. Affective Events Theory How do emotions and moods influence job performance and satisfaction? Affective events theory
- 18. Affective Events Theory 4- Affective Events Theory
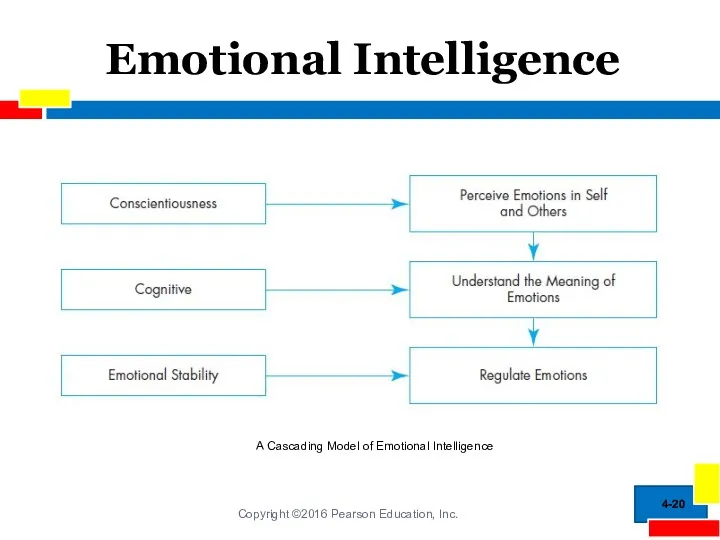
- 19. Emotional Intelligence Emotional intelligence: a person’s ability to: Perceive emotions in the self and others Understand
- 20. Emotional Intelligence 4- A Cascading Model of Emotional Intelligence
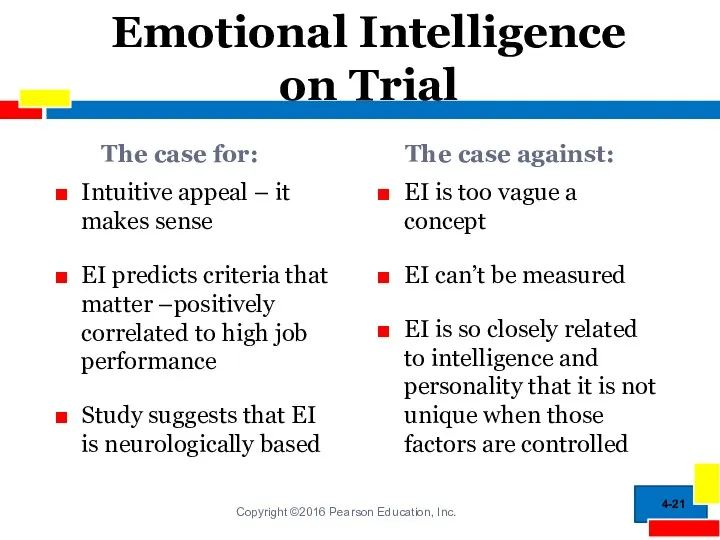
- 21. Emotional Intelligence on Trial The case for: Intuitive appeal – it makes sense EI predicts criteria
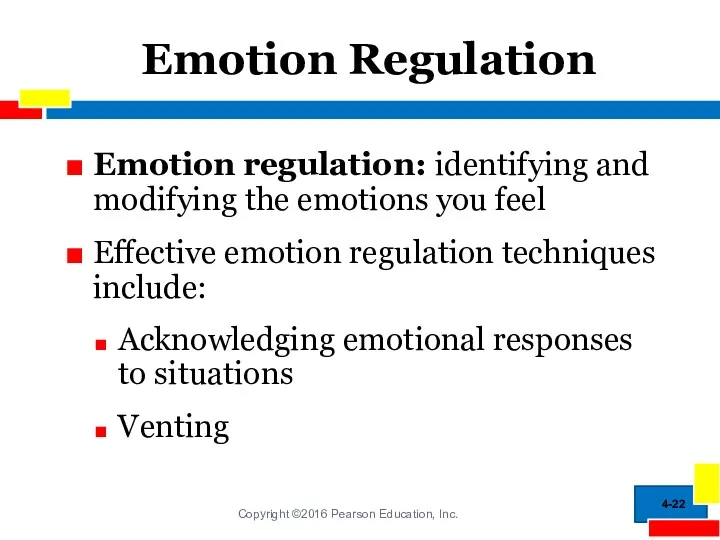
- 22. Emotion Regulation Emotion regulation: identifying and modifying the emotions you feel Effective emotion regulation techniques include:
- 23. OB Applications of Emotions and Moods Selection – Employers should consider EI a factor in hiring
- 24. More OB Applications of Emotions and Moods Motivation – Promoting positive moods may give a more
- 25. Even More OB Applications of Emotions and Moods Job Attitudes – Emotions at work get carried
- 26. Implications for Managers Recognize that emotions are a natural part of the workplace and good management
- 27. Summary Differentiated between emotions and moods. Discussed whether emotions are rational and what functions they serve.
- 29. Скачать презентацию













 Past Perfect Tense. Прошедшее действие, совершившееся до определенного момента в прошлом
Past Perfect Tense. Прошедшее действие, совершившееся до определенного момента в прошлом My favorite film (5 class)
My favorite film (5 class) Reported speech
Reported speech Free PPT templates
Free PPT templates The programmer
The programmer Investor Pitch Deck Template
Investor Pitch Deck Template Past Progressive tense. Употребление времени
Past Progressive tense. Употребление времени Викторина для учащихся 6-8 классов Лучший знаток английского языка
Викторина для учащихся 6-8 классов Лучший знаток английского языка Типичные ошибки русскоговорящих в английском
Типичные ошибки русскоговорящих в английском Alina Zagitova – Olympic champion
Alina Zagitova – Olympic champion What do you eat for breakfast
What do you eat for breakfast Future simple tense. Будущее простое время
Future simple tense. Будущее простое время Страдательный залог
Страдательный залог Action verbs (часть 2)
Action verbs (часть 2) International summer camp Shining Russia. Volunteers booklet
International summer camp Shining Russia. Volunteers booklet The Clothes
The Clothes Трансформации, как способ перевода. Грамматические и комплексные трансформации
Трансформации, как способ перевода. Грамматические и комплексные трансформации My pets
My pets Lifestyle. Join us
Lifestyle. Join us Practical pharmacology. Part 1
Practical pharmacology. Part 1 Formal letters
Formal letters Food commodities. Fish, shellfish
Food commodities. Fish, shellfish Этимологический состав лексики английского языка
Этимологический состав лексики английского языка In the village
In the village How to Identify a Shopaholic?
How to Identify a Shopaholic? Говорение. Стратегия выполнения, полный разбор задания, схема ответа
Говорение. Стратегия выполнения, полный разбор задания, схема ответа Magnus's Effect
Magnus's Effect Your wedding package
Your wedding package