Содержание
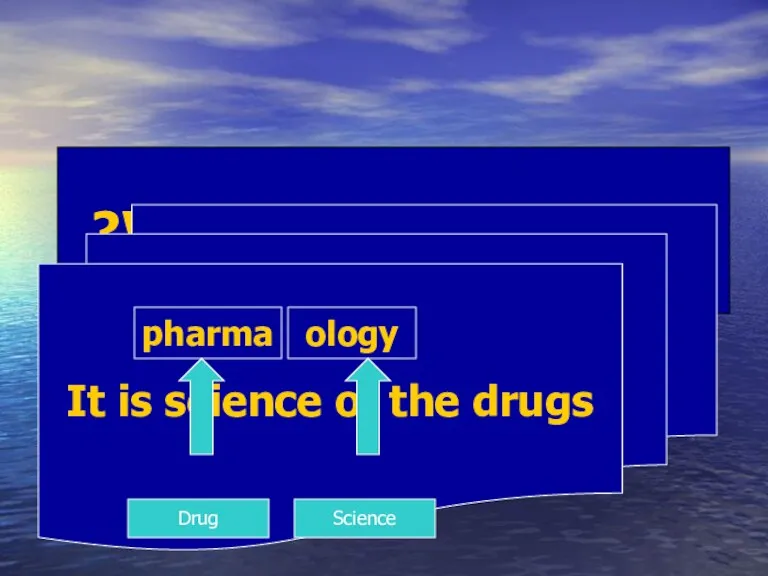
- 2. What is pharmacology? It is science of the drugs pharma ology Drug Science
- 3. What is Drug? It is the chemical that affect physiological body function through interaction with receptors
- 4. It is the chemical that affect physiological body function through interaction with receptors What is Drug?
- 5. A Response
- 6. Forces involved in D-R interaction Covalent bonds Ionic bonds Hydrogen bonds Vander waals bonds
- 7. Forces involved in D-R interaction Covalent bonds Ionic bonds Hydrogen bonds Vander waals bonds
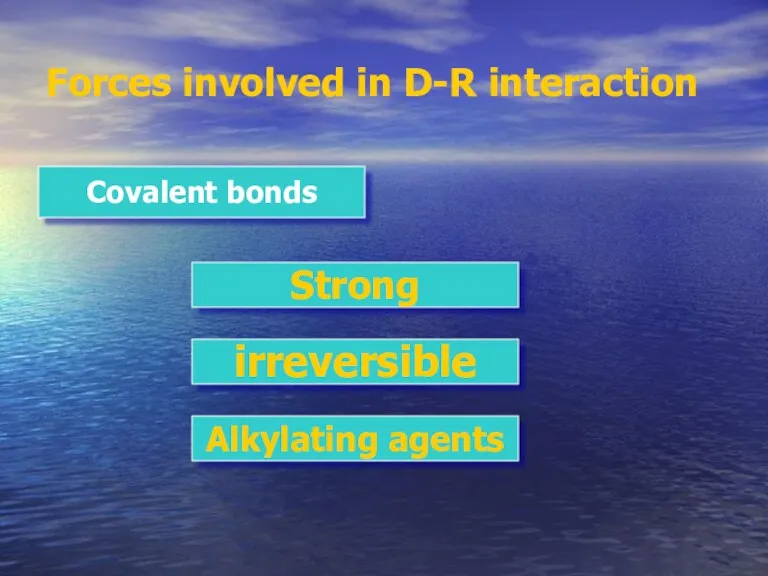
- 8. Forces involved in D-R interaction Covalent bonds Strong irreversible Alkylating agents
- 9. Forces involved in D-R interaction Covalent bonds Ionic bonds Hydrogen bonds Vander waals bonds
- 10. Forces involved in D-R interaction Ionic bonds common Affected by pH
- 11. Forces involved in D-R interaction Covalent bonds Ionic bonds Hydrogen bonds Vander waals bonds
- 12. Forces involved in D-R interaction Hydrogen bonds ?
- 13. Forces involved in D-R interaction Covalent bonds Ionic bonds Hydrogen bonds Vander waals bonds
- 14. Forces involved in D-R interaction Vander waals bonds ?
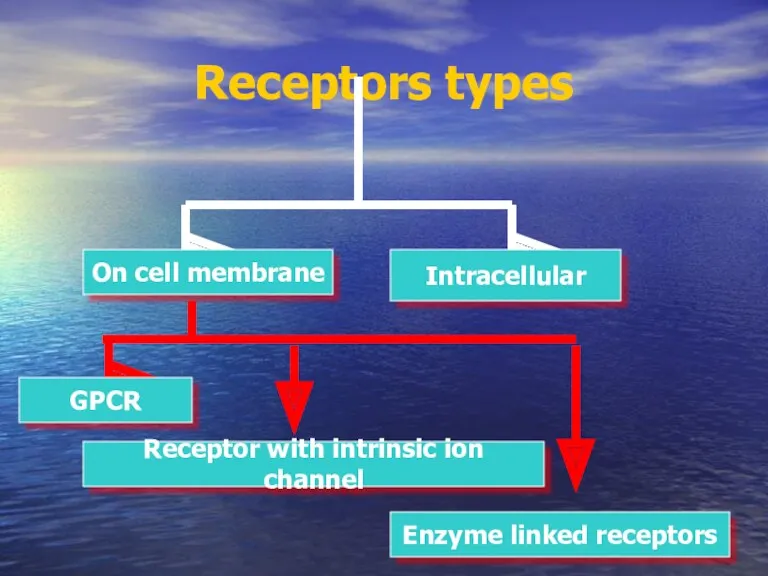
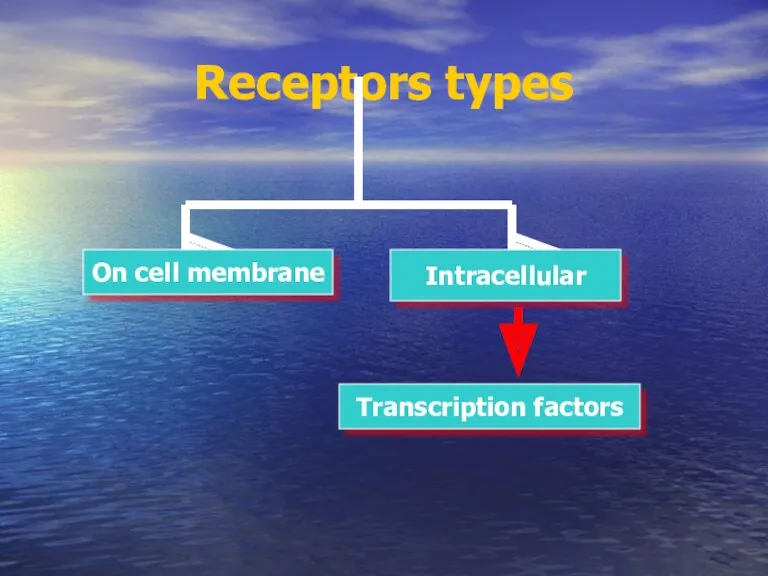
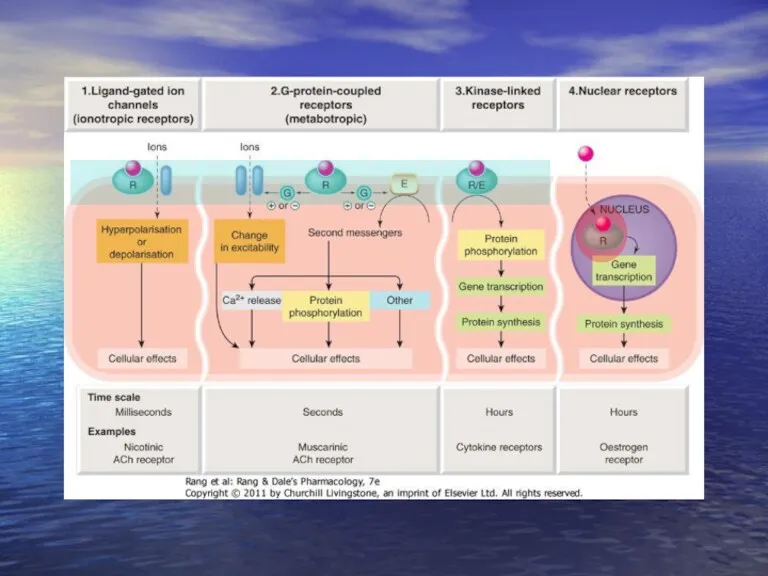
- 15. Receptors types On cell membrane Intracellular Receptor with intrinsic ion channel GPCR Enzyme linked receptors
- 16. Receptors types On cell membrane Intracellular Transcription factors
- 18. Drug-Receptor Interaction D + R DR k1 K1 is association rate constant
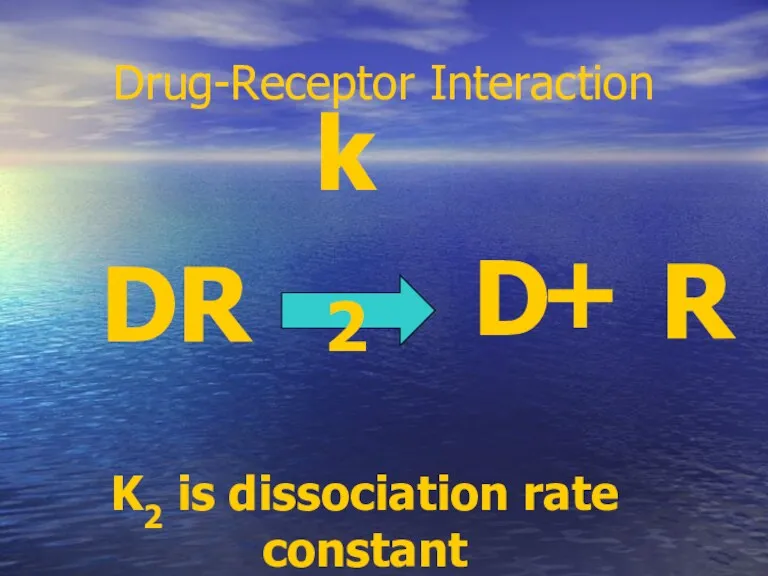
- 19. Drug-Receptor Interaction D + R DR k2 K2 is dissociation rate constant
- 20. Drug-Receptor Interaction D + R DR k1 k2 At equilibrium
- 21. Drug-Receptor Interaction [D] [R] [DR] k1 k2 = At equilibrium
- 22. Drug-Receptor Interaction [D] [R] [DR] k1 k2 = At equilibrium
- 23. Drug-Receptor Interaction k2 k1 = [R] [D] [DR] kd Kd (dissociation equilibrium constant) is conc. of
- 24. kd It is a measure of drug affinity Its units is conc. units Drug A Drug
- 25. Important concepts Affinity Efficacy potency
- 26. Affinity The ability of the drug to bind to the receptor Measured by Kd Both agonist
- 27. Efficacy It is the ability of the drugs to elicit pharmacological effect Measured by Emax Agonist
- 28. potency The ability of the drug to produce response at lower conc. Measured by ED50
- 29. The drug may be Agonist Antagonist Partial agonist
- 30. Agonist Has affinity and efficacy IA=1
- 31. Antagonist Has affinity but no efficacy IA=0
- 32. Partial agonist Has affinity and efficacy IA=0-1
- 33. antagonism Physical Chemical Physiological Pharmacokinetic pharmacodynamic
- 34. Chemical antagonism One drug reacts chemically with an active drug to form an inactive compound, It
- 35. Physiological antagonism 2 drugs act on different sites in the same or different system. a- Intended
- 36. Pharmacokinetic antagonism (ADME) a- Intended ? forced alkaline diuresis in management of barb Poisoning. b- Incidental
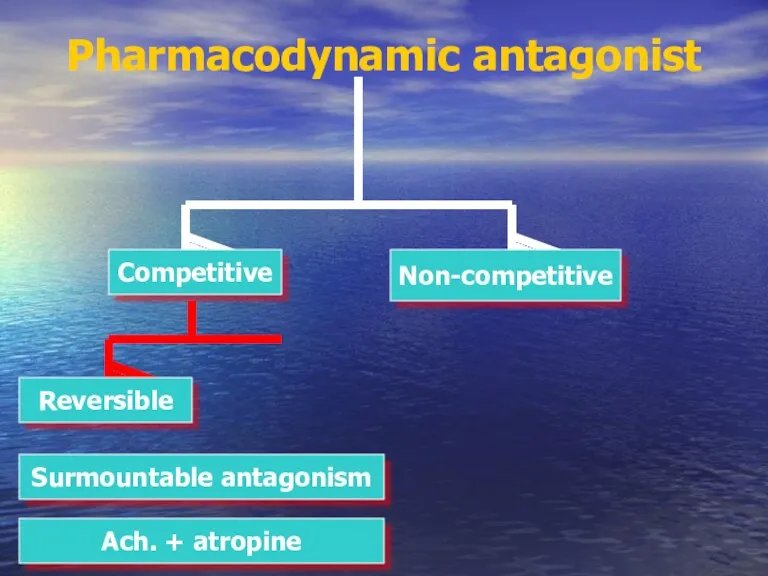
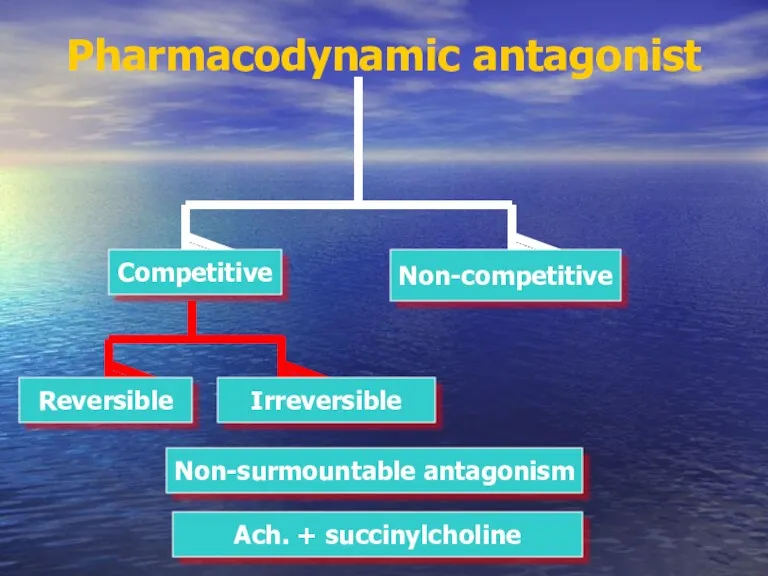
- 37. Pharmacodynamic antagonist Competitive Non-competitive Reversible Surmountable antagonism Ach. + atropine
- 38. Pharmacodynamic antagonist Competitive Non-competitive Irreversible Reversible Non-surmountable antagonism Ach. + succinylcholine
- 39. An A X
- 40. A X An
- 41. Dose-Response Curve What ? Types ?
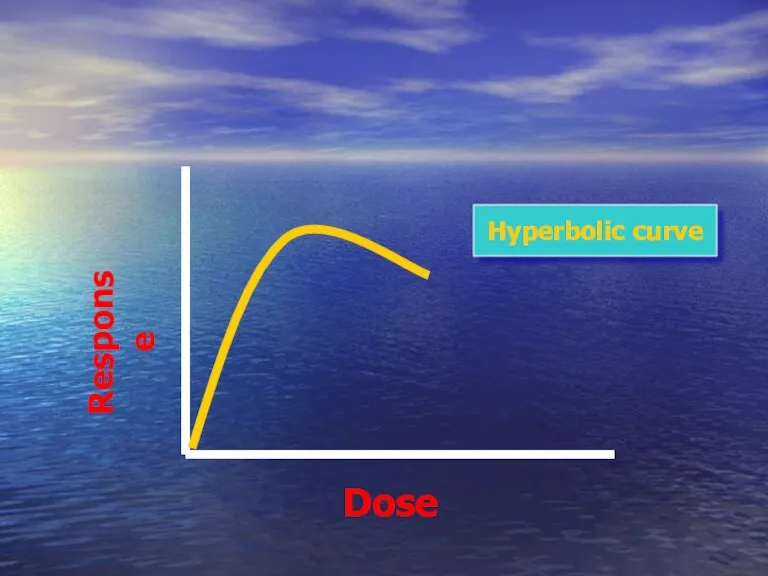
- 42. Dose Response Hyperbolic curve
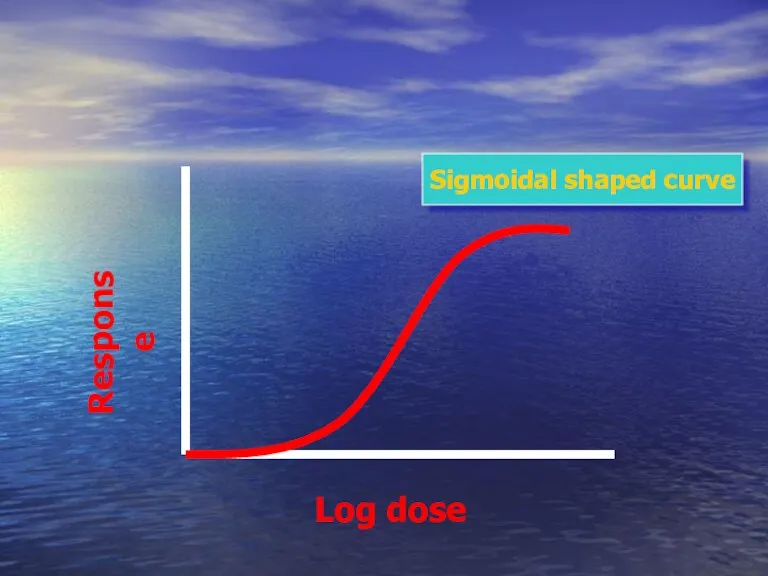
- 43. Log dose Response Sigmoidal shaped curve
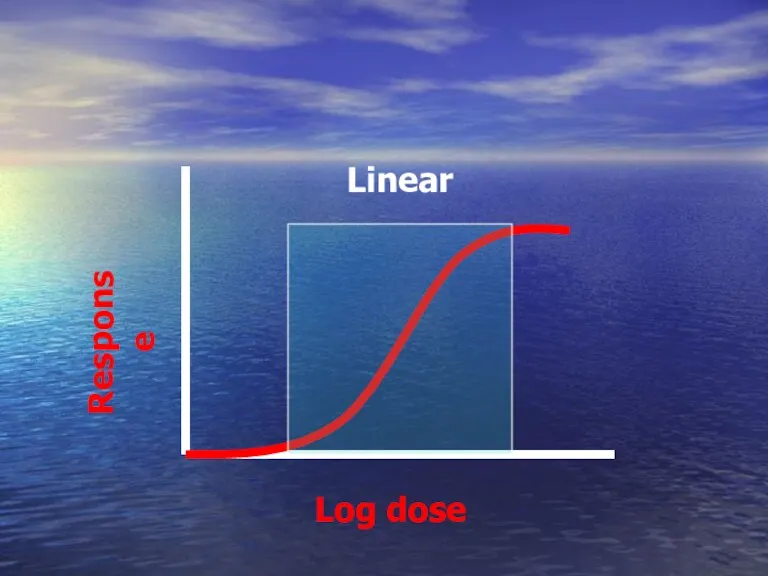
- 44. Log dose Response Linear
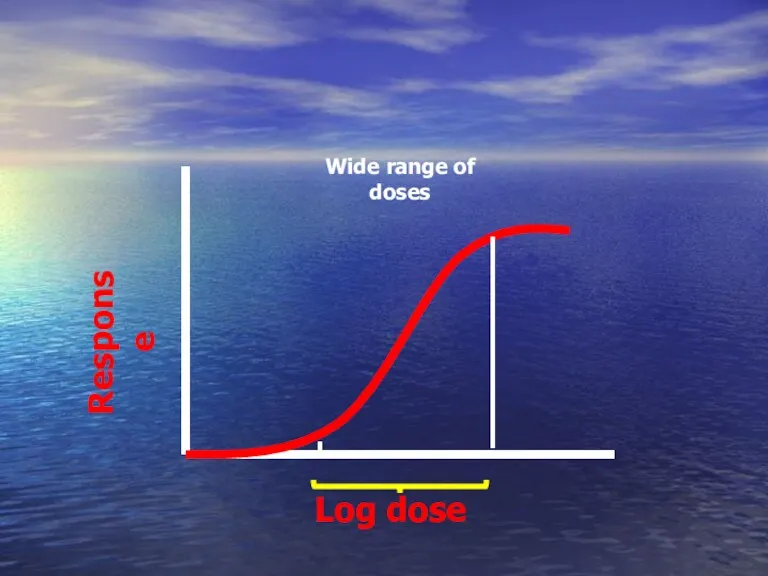
- 45. Log dose Response Wide range of doses
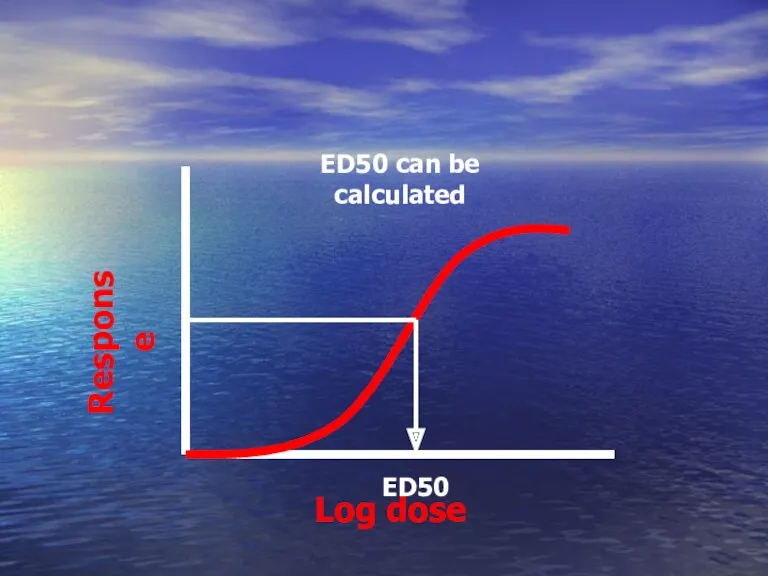
- 46. Log dose Response ED50 can be calculated ED50
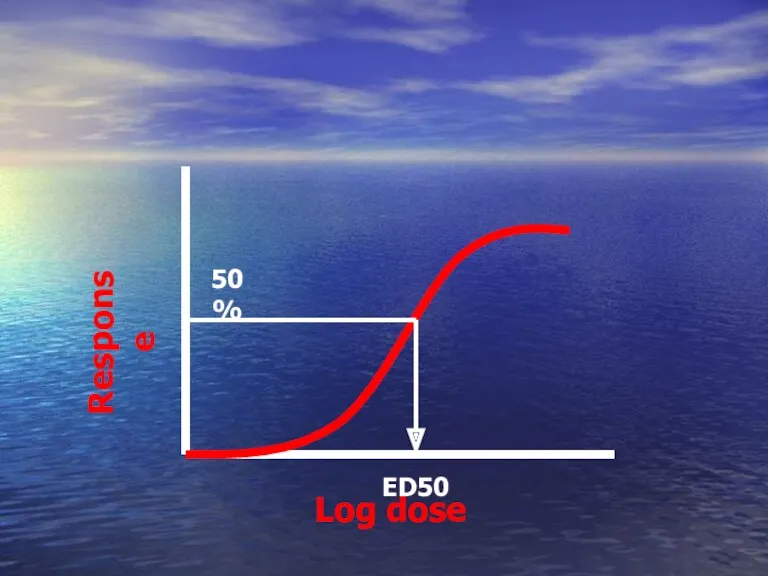
- 47. Graded DRC Depends on graded response ED50 ? The dose that give 50% of maximal response
- 48. Log dose Response ED50 50%
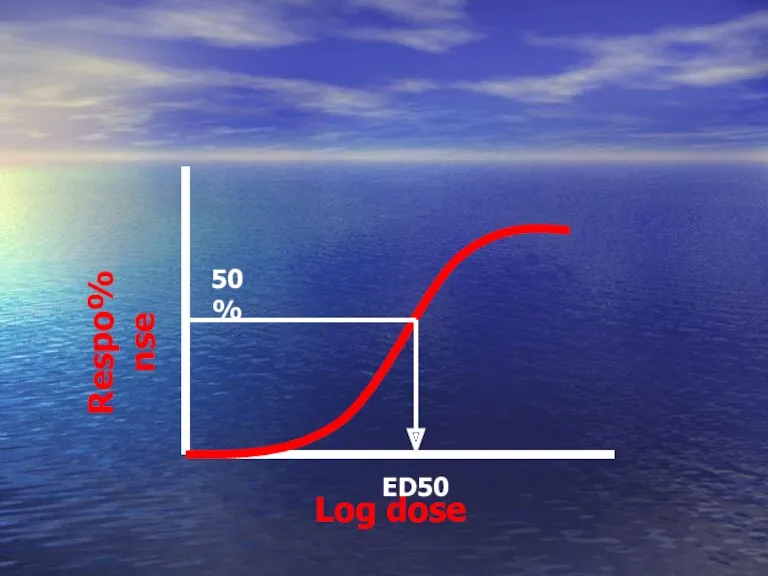
- 49. Quantal DRC Depends on quantal response ED50 ? The dose that give response in 50% of
- 50. Log dose %Response ED50 50%
- 51. ED50 Compare between potencies of two drugs Drug A Drug B Has higher ED50 than Which
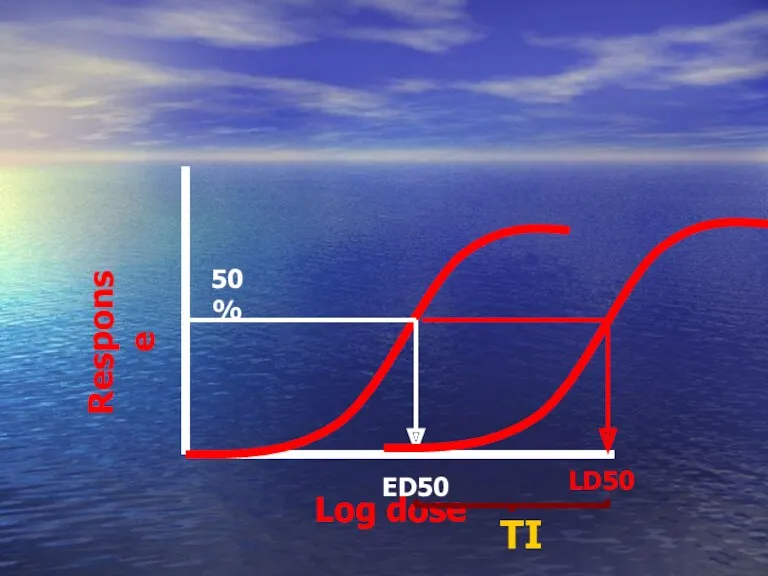
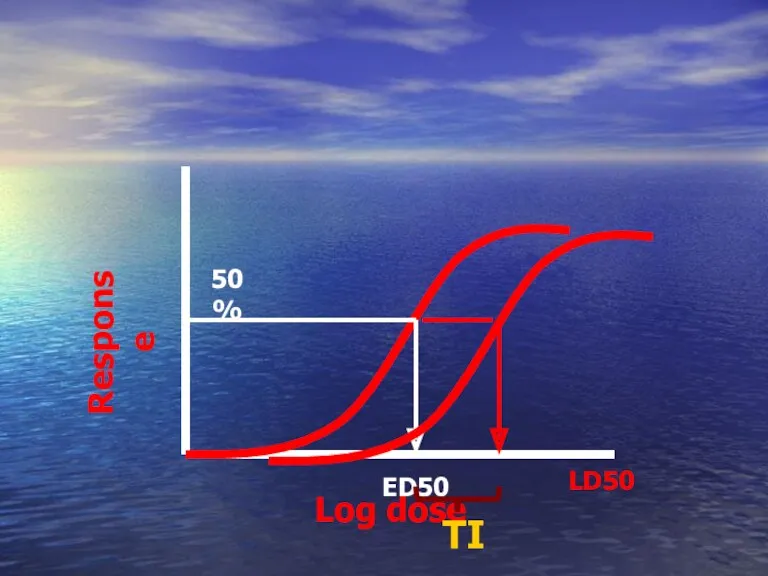
- 52. ED50 Calculation of the therapeutic index TI LD50 = Is a measure of drug safety ED50
- 53. Log dose Response ED50 50% LD50 TI
- 54. Log dose Response ED50 50% LD50 TI
- 55. Drug A Drug B Has higher TI than Which one is more safer ?
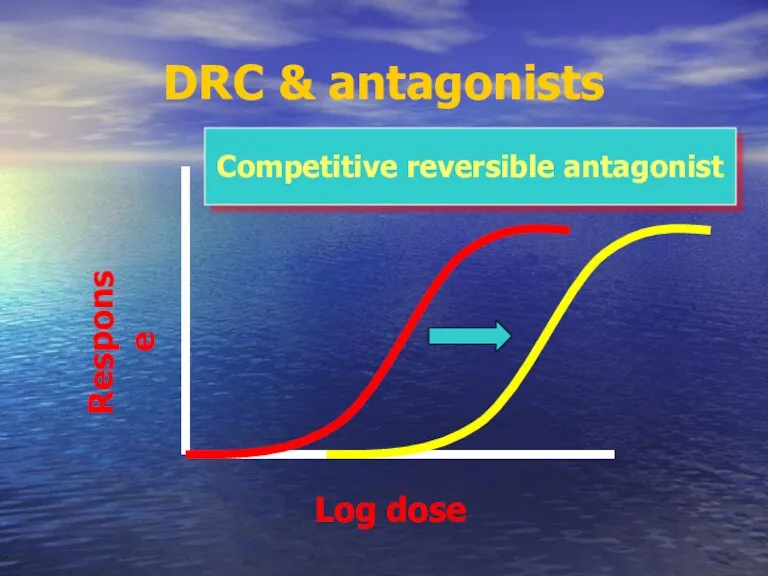
- 56. DRC & antagonists Competitive reversible antagonist Log dose Response
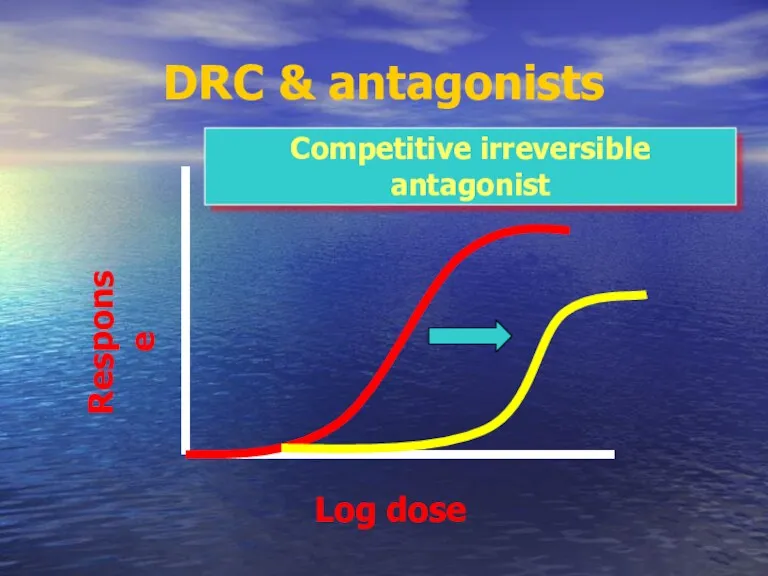
- 57. DRC & antagonists Competitive irreversible antagonist Log dose Response
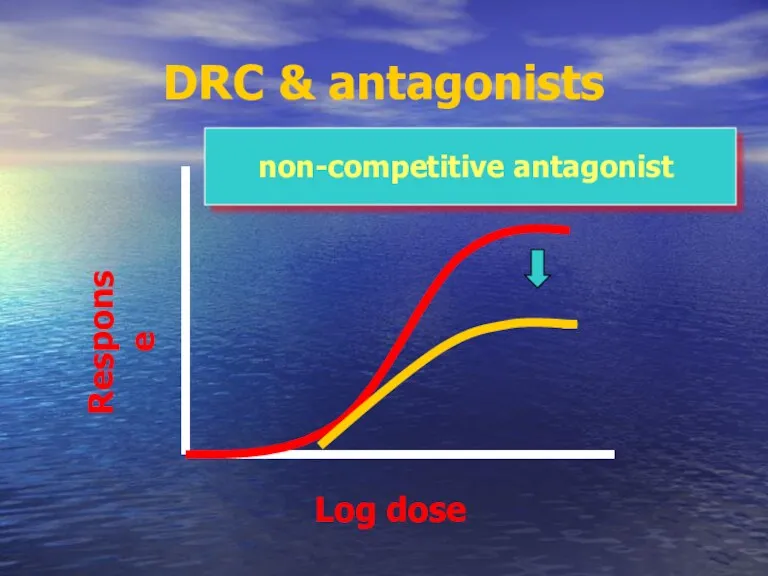
- 58. DRC & antagonists non-competitive antagonist Log dose Response
- 59. Important notes Parrallism Indicate competition
- 60. Important notes Emax Indicate reversibility
- 62. Скачать презентацию












![Drug-Receptor Interaction [D] [R] [DR] k1 k2 = At equilibrium](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/435513/slide-20.jpg)
![Drug-Receptor Interaction [D] [R] [DR] k1 k2 = At equilibrium](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/435513/slide-21.jpg)
![Drug-Receptor Interaction k2 k1 = [R] [D] [DR] kd Kd](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/435513/slide-22.jpg)























 There is/ there are
There is/ there are Prefix and sufix
Prefix and sufix Go Getter 2. Unit 3
Go Getter 2. Unit 3 Speaking Games (тренажёр)
Speaking Games (тренажёр) Travel and leisure
Travel and leisure Presentation Template
Presentation Template Types of translation
Types of translation Education in Kazakhstan
Education in Kazakhstan Функции и спряжение глаголов to be, to have
Функции и спряжение глаголов to be, to have Тип Членистоногие
Тип Членистоногие Clothes vocabulary review 4
Clothes vocabulary review 4 Reported speech
Reported speech Present Perfect Continuous. Употребление
Present Perfect Continuous. Употребление Язык массовой коммуникации и перевод текстов СМИ. Лекция 5
Язык массовой коммуникации и перевод текстов СМИ. Лекция 5 Present Continuous. Утверждение
Present Continuous. Утверждение Play the card game “What is missing”
Play the card game “What is missing” Буквосочетание th. Числительные (numbers)
Буквосочетание th. Числительные (numbers) Creation of Hollywood
Creation of Hollywood Healthy Habits
Healthy Habits Choosing a Career. My Future Profession
Choosing a Career. My Future Profession Fina championship
Fina championship Methods of planning training work in the classroom
Methods of planning training work in the classroom Lesson 23. Travelling. Packing a luggage
Lesson 23. Travelling. Packing a luggage Present Simple. Утверждение. Отрицание
Present Simple. Утверждение. Отрицание Hello world technologies
Hello world technologies Introduction, style, science
Introduction, style, science Calendar 2019
Calendar 2019 Can you....?
Can you....?