Содержание
- 2. 2 approaches to word meaning Meaning and Notion Types of Word Meaning Types of Morpheme Meaning
- 3. Semantics branch of linguistics which studies meaning of words and word equivalents
- 4. 2 Approaches to Word Meaning The Referential Approach The Functional Approach
- 5. Referential Approach essence of meaning => interdependence between words and things or concepts they denote distinguishes
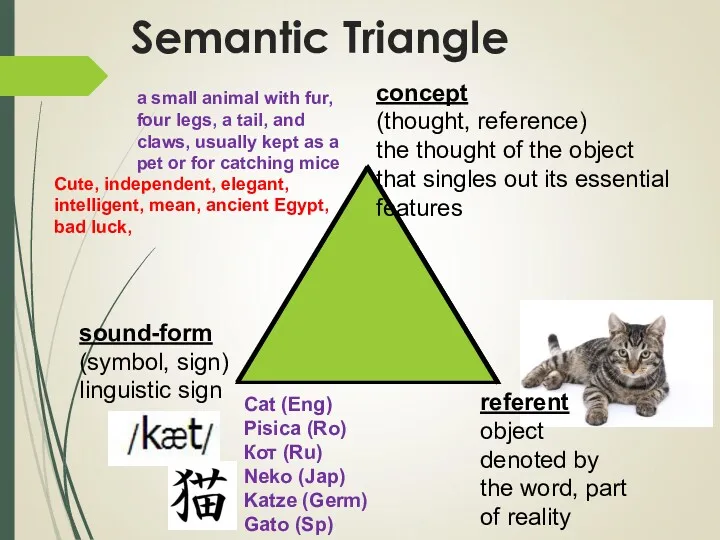
- 6. Semantic Triangle concept (thought, reference) the thought of the object that singles out its essential features
- 8. Meaning and Sound-form are not identical different sound-forms MAY convey one and the same mng cat
- 9. nearly identical sound-forms may have different meanings in different languages e.g. [kot] English – a small
- 10. even considerable changes in sound-form do not affect the meaning e.g. OE lufian [luvian] – love
- 11. What’s a “cat”? concept is a category of human cognition concept is abstract and reflects the
- 12. identical concepts may have different semantic structures in different languages e.g. concept “a building for human
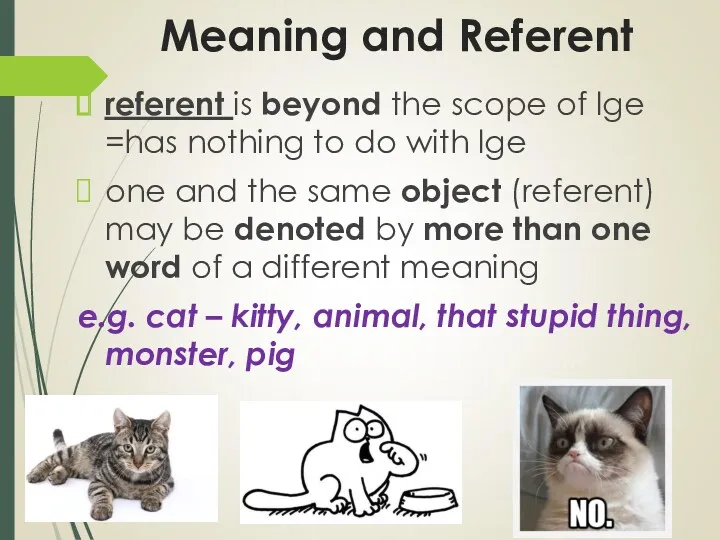
- 13. Meaning and Referent referent is beyond the scope of lge =has nothing to do with lge
- 14. Один иностранец путешествовал по российским глубинкам, и в одной из деревушек увидел, как бабка гусей гоняет,
- 15. angel
- 16. Meaning a component of a word through which a concept is communicated, in this way giving
- 17. Functional Approach studies the functions of a word in speech meaning of a word is studied
- 18. Notion denotes the reflection in the mind of real objects and phenomena in their relations Notion
- 19. Lexical Meaning and Notion Notions are always emotionally neutral as they are a category of thought.
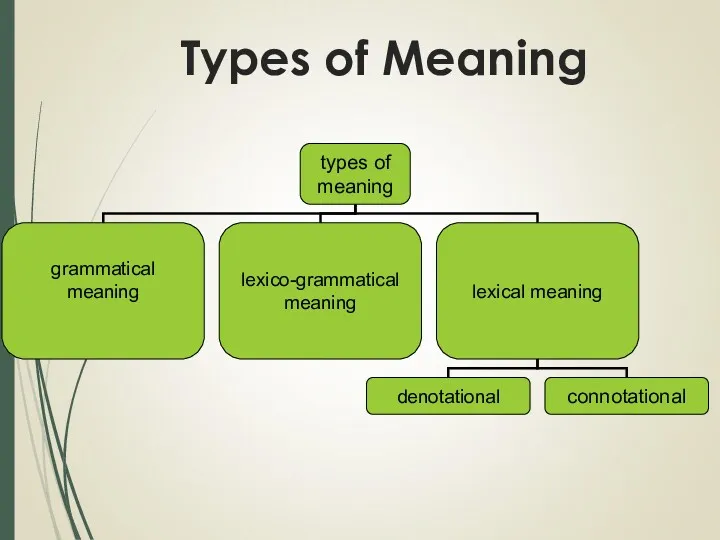
- 20. Types of Meaning
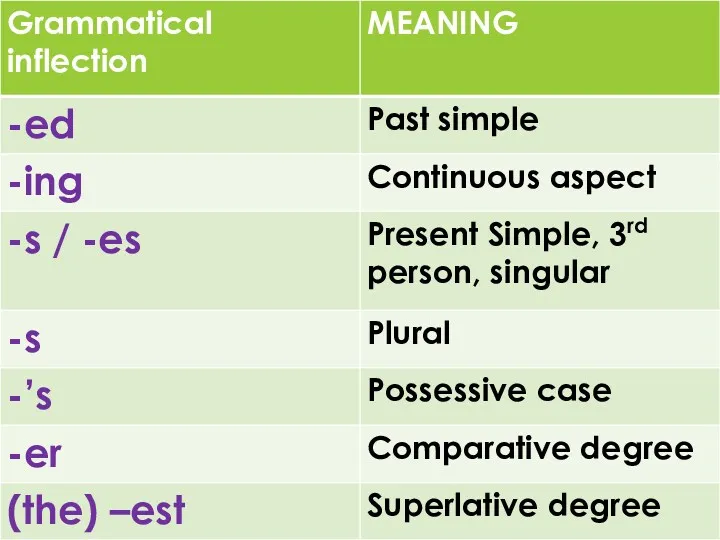
- 21. Grammatical Meaning component of meaning recurrent in identical sets of individual forms of different words e.g.
- 23. Lexico-grammatical meaning Name of all the meanings of words belonging to a lexico-grammatical class e.g. action
- 24. Lexical Meaning component of meaning proper to a word as a linguistic unit met in all
- 25. Morphemes have lexical mng differential mng functional mng distributional mng
- 26. Lexical Meaning in Morphemes root-morphemes that are homonymous to words possess lexical meaning e.g. boy –
- 27. Lexical Meaning in Morphemes has denotational and connotational components e.g. –ly, -like, -ish – denotational meaning
- 28. Differential Meaning a semantic component that serves to distinguish one word from all others containing identical
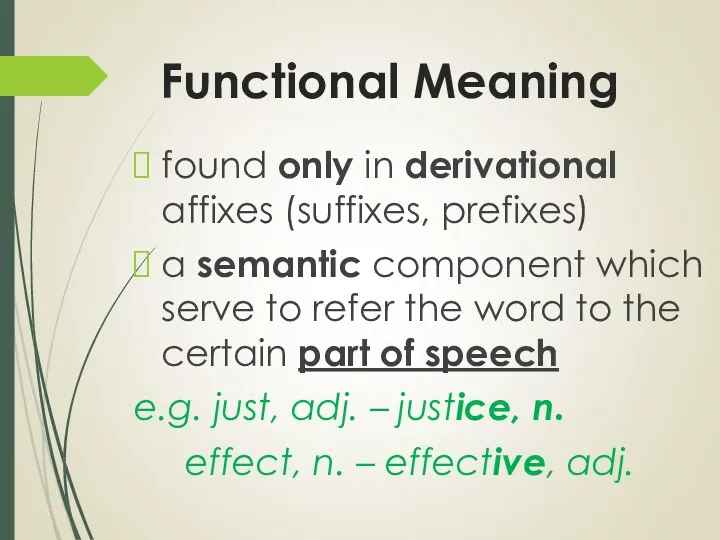
- 29. Functional Meaning found only in derivational affixes (suffixes, prefixes) a semantic component which serve to refer
- 31. Скачать презентацию























 Past Tences
Past Tences Academic english
Academic english Test assignments
Test assignments Total Physical Response на уроках английского языка
Total Physical Response на уроках английского языка Road safety
Road safety The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland Tag-questions (разделительные вопросы)
Tag-questions (разделительные вопросы) Case law in the United States
Case law in the United States Colours and numbers. Game
Colours and numbers. Game About monitors
About monitors Словарь: Закон и преступление
Словарь: Закон и преступление Глагол Have got (иметь)
Глагол Have got (иметь) Private school in UK
Private school in UK Independent work. Fractures
Independent work. Fractures Притяжательный падеж существительных
Притяжательный падеж существительных Работа со словарями
Работа со словарями Party animals
Party animals Money in man`s life
Money in man`s life Jobs. Guess the professions
Jobs. Guess the professions Spotlight 4. To be present past future
Spotlight 4. To be present past future Official symbols of Sudan
Official symbols of Sudan Feedback
Feedback Food 5
Food 5 Job hunting
Job hunting My pet Tell about your pet
My pet Tell about your pet Карманные деньги. Shopping
Карманные деньги. Shopping Present Simple and Present Continuous
Present Simple and Present Continuous Professions
Professions