- Главная
- Английский язык
- Methods in behavioral genetics

Содержание
- 2. In karyotype one half of chromosomes comes from one parent and the second one from the
- 3. As far as genetic information in sister chromosomes is identical and linear so genes, which are
- 4. Alleles and Genes https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pv3Kj0UjiLE
- 5. The set of parental gene alleles is important to understanding of offspring genotype and phenotype. Monohybrids
- 6. The Mendel rules had been discovered in experiments with strict dominance – recessivity gene relationships. After
- 7. Autosomal dominant traits in human - white curl over the forehead, - coarse and straight hair
- 8. Autosomal recessive traits in human - soft and straight hair, - negative rhesus factor, - intaste
- 9. Sex-linked traits in human - Pigment xeroderma - a disease in which, under the influence of
- 10. Monohybrid and one-trait crosses 1. A blue-eyed woman being a spouse of a brown-eyed man has
- 11. Dihybrid and two-trait crosses 1. A father with curly hair (dominant trait) and without freckles, and
- 12. Thank you for your attention
- 14. Скачать презентацию
In karyotype one half of chromosomes comes from one parent and
In karyotype one half of chromosomes comes from one parent and
Parental chromosomes compose a pairs in which both components have the same size, a centromere localization and a gene sequence.
The majority of the pairs consists mainly of body genes and have a name of autosomes.
The pair of sex chromosomes is partially an exception of this rule because of their differences in their size and amount of genes.
In addition, the gene set of the heterochromosomes is not the same due to their forming history, which includes an extensive mutation in the Y progenitor.
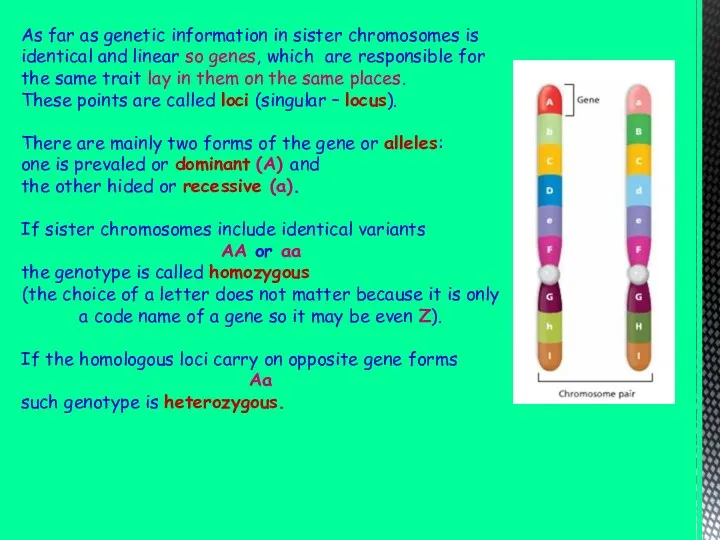
As far as genetic information in sister chromosomes is identical and
As far as genetic information in sister chromosomes is identical and
These points are called loci (singular – locus).
There are mainly two forms of the gene or alleles:
one is prevaled or dominant (A) and
the other hided or recessive (a).
If sister chromosomes include identical variants
AA or aa
the genotype is called homozygous
(the choice of a letter does not matter because it is only a code name of a gene so it may be even Z).
If the homologous loci carry on opposite gene forms
Aa
such genotype is heterozygous.
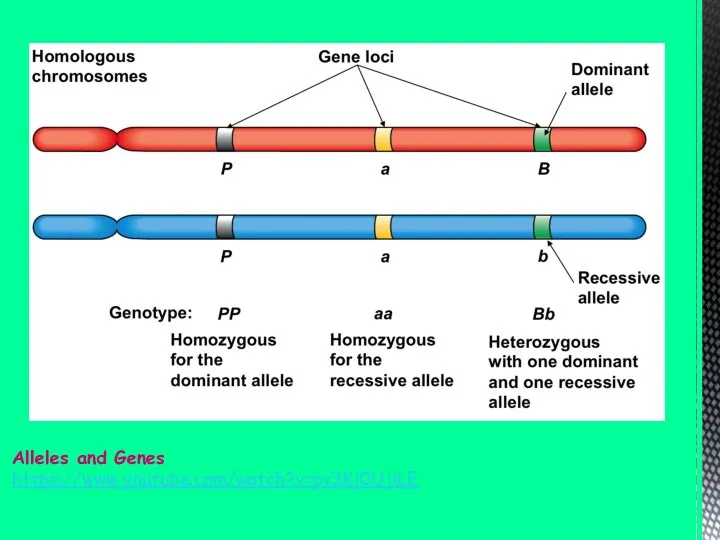
Alleles and Genes
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pv3Kj0UjiLE
Alleles and Genes
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pv3Kj0UjiLE
The set of parental gene alleles is important to understanding of
The set of parental gene alleles is important to understanding of
Monohybrids and the Punnett Square Guinea Pigs
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i-0rSv6oxSY
Dihybrid and Two-Trait Crosses
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qIGXTJLrLf8
If the described gene is localized in autosome the type of inheritance is autosomal and the majority of human genes belong it.
Accordingly to an allele form there are autosomal dominant and recessive types.
Some genes responsible for body properties could be found in sex chromosomes therefore they correlate with sexual belonging. The amount of such ones depends on the size of the heterochromosome. As far as X chromosome is much more larger than Y it includes a majority of such genes.
Punnett Squares and Sex-Linked Traits
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h2xufrHWG3E
The Mendel rules had been discovered in experiments with strict dominance
The Mendel rules had been discovered in experiments with strict dominance
After Mendel there were found out another gene interactions.
Multiple Alleles (ABO Blood Types) and Punnett Squares
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9O5JQqlngFY
Incomplete Dominance, Codominance, Polygenic Traits, and Epistasis!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YJHGfbW55l0
Autosomal dominant traits in human
- white curl over the forehead,
- coarse
Autosomal dominant traits in human
- white curl over the forehead,
- coarse
- hitch-hicker’s thumb - Habsburg’s lip - lower lip, protruding forward, lower lip, sagging and half-open mouth, - polydactyly - multi-pitched, when there are from six or more fingers, - brachydactyly (short bones) - underdevelopment of the distal phalanges of the fingers, - arachnodactyly - highly elongated spider fingers, - familial hypercholesterolemia - a cholesterol metabolic disorder, an increase in its blood pressure in the blood. Accompanied by the development of atherosclerosis and risk of heart attack. - Recklinghausen’s disease or neurofibromatosis – caused by defective form of neurofibrin, which is needed for normal function in many human cell types. Results in skin lesions of various manifestations. - Otospongiosis - manifested in adults with progressive deafness. - Achondroplasia - dwarfism. - Marfan’s disease - hereditary disease characterized by a systemic lesion of the connective tissue.
- Huntington’s chorea disease - occurs in an adult, manifests as impaired movement and progressed dementia
Autosomal recessive traits in human
- soft and straight hair,
- negative rhesus
Autosomal recessive traits in human
- soft and straight hair,
- negative rhesus
- Galactosemia - accumulation in the blood of galactose, which inhibits the absorption of glucose and has a toxic effect on the function of the liver, the brain, the lens of the eye. This disease is manifested by a lag in physical and mental development, severe damage to the liver, nervous system, eyes and other organs.
- Albinism – the absence of melanin pigment in body tissues. - Tay-Sachs’ disease - is associated with a sharp increase in the cells of the brain, as well as the liver and spleen of the gangliosides, due to the deficiency of hexosaminidase A in the body. Mental changes are progressing. Gradually muscle hypotension develops, limb paralysis occurs
Sex-linked traits in human
- Pigment xeroderma - a disease in which,
Sex-linked traits in human
- Pigment xeroderma - a disease in which,
- Epidermolysis bullosa - blistering after mechanical injuries of the skin. - General color blindness - the complete absence of color vision. Of great importance for medical practice is the study of blood groups that depend on antigens located on the surface of red blood cells. - Duchenne muscle dystrophy - progressive muscle weakness is founded exeptionally in boys. - Hemophilia A and B – blood coagulation disorder, which is manifested mainly in men.
Monohybrid and one-trait crosses
1. A blue-eyed woman being a spouse of
Monohybrid and one-trait crosses
1. A blue-eyed woman being a spouse of
2. Cousins had got married. The wife was able to roll the tongue into a tube. The feature was absent from the husband. From this marriage was born a child who is unable to roll the tongue. Try to found the genotypes o fall family members.
3. In humans classical haemophilia is a recessive trait linked to the X chromosome.
In a family one of spouses has a blood with normal coagulation but they have a son, who was born with haemophilia. What is the probability of the illness in the second son?
Dihybrid and two-trait crosses
1. A father with curly hair (dominant trait)
Dihybrid and two-trait crosses
1. A father with curly hair (dominant trait)
Try to reveal the genotypes of the parents and their children.
2. In humans myopia (M) or short sight dominates over normal vision, and brown eyes (B) do over blue.
The only child of myopic brown-eyed parents has blue eyes and normal sight. Set the genotypes of all the family members.
3. The brown-eyed woman, whose father has saw colours well, has blue eyes and sufferes from color blindness, gets married a blue-eyed man with common eyesight. What offspring could be expected from this pair, if it is known that the brown eye gene is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, and the color blindness gene is a recessive and linked to the X chromosome?
Thank you for your attention
Thank you for your attention









 Английский язык на улицах Кемерово
Английский язык на улицах Кемерово Lecture 5. Word-building part-1
Lecture 5. Word-building part-1 Лондон и его достопримечательности
Лондон и его достопримечательности Friendship
Friendship We live in Russia
We live in Russia Past Tenses
Past Tenses Времена в английском языке. Verb Tenses
Времена в английском языке. Verb Tenses Parts of body. Части тела
Parts of body. Части тела Обучение поисковому чтению на уроках английского языка
Обучение поисковому чтению на уроках английского языка Притяжательный падеж в английском языке. Past Simple
Притяжательный падеж в английском языке. Past Simple Recycling is one of the best ways to help protect our environment
Recycling is one of the best ways to help protect our environment How Has the Aral Sea Changed Over Time
How Has the Aral Sea Changed Over Time The wonders of Great Britain
The wonders of Great Britain Procyon Emerald
Procyon Emerald Secure Guard Services in Southern California
Secure Guard Services in Southern California Module 6. Reported Speech
Module 6. Reported Speech The world of hobbies
The world of hobbies Funny food
Funny food Do you want to visit space one day?
Do you want to visit space one day? Kazan - the third capital of Russia
Kazan - the third capital of Russia Fashion in our lifes
Fashion in our lifes Christmas game
Christmas game Модальные глаголы
Модальные глаголы Пассивный залог
Пассивный залог Toys
Toys Super. Simple. Learning
Super. Simple. Learning What are they doing?
What are they doing? Tower Bridge
Tower Bridge