Содержание
- 2. POLYSEMY in English Questions for discussion: 1. Sources/causes of polysemy. 2. Semantic structure of polysemantic words.
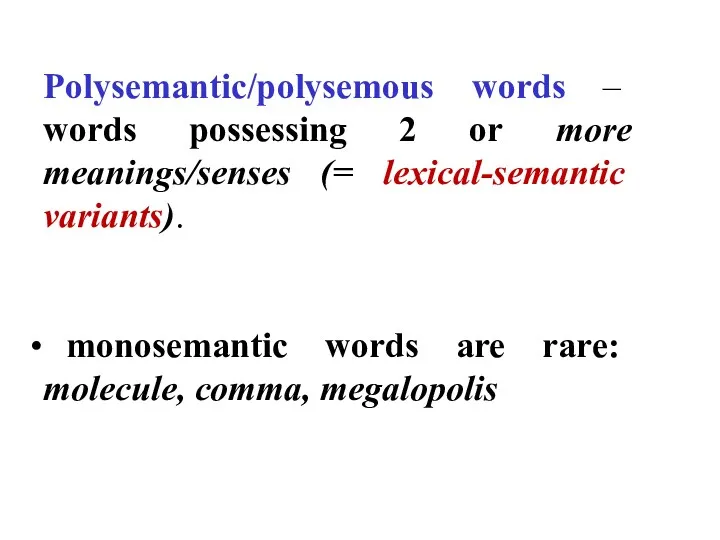
- 3. Polysemantic/polysemous words – words possessing 2 or more meanings/senses (= lexical-semantic variants). monosemantic words are rare:
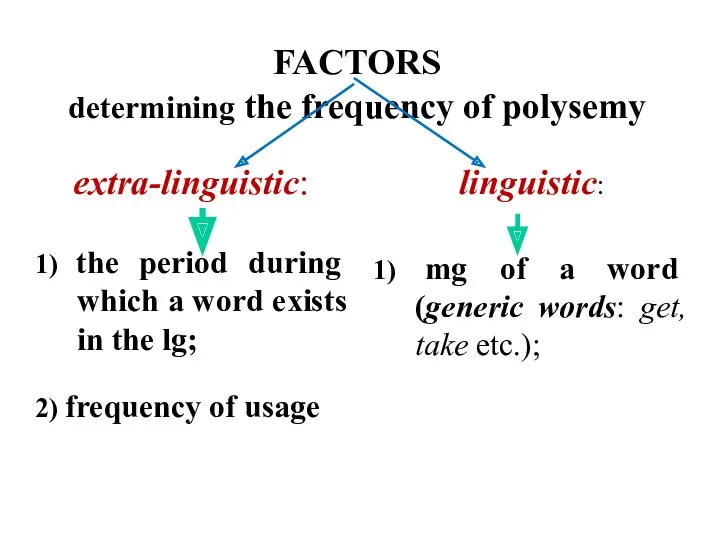
- 4. FACTORS determining the frequency of polysemy extra-linguistic: 1) the period during which a word exists in
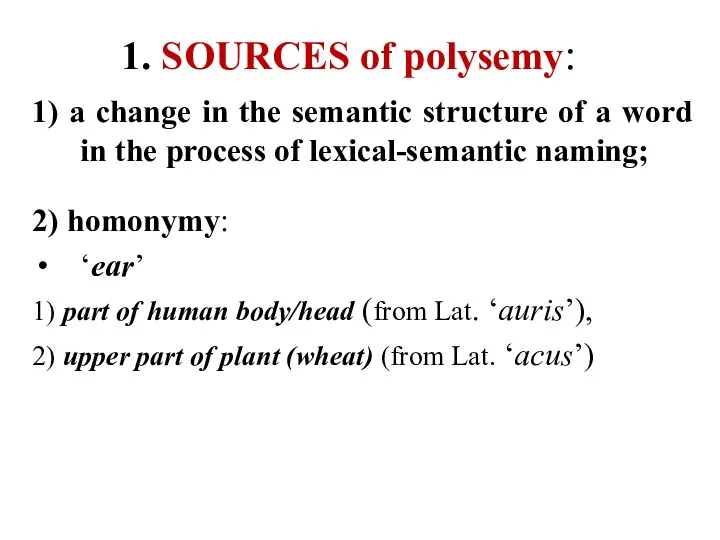
- 5. 1. SOURCES of polysemy: 1) a change in the semantic structure of a word in the
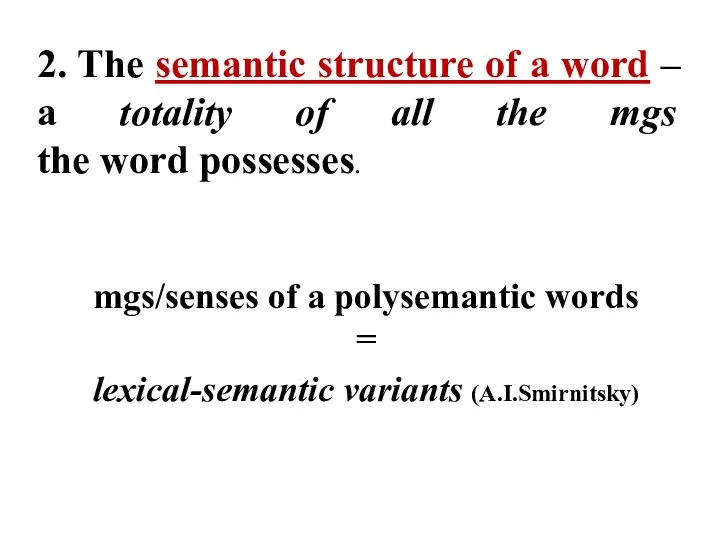
- 6. 2. The semantic structure of a word – a totality of all the mgs the word
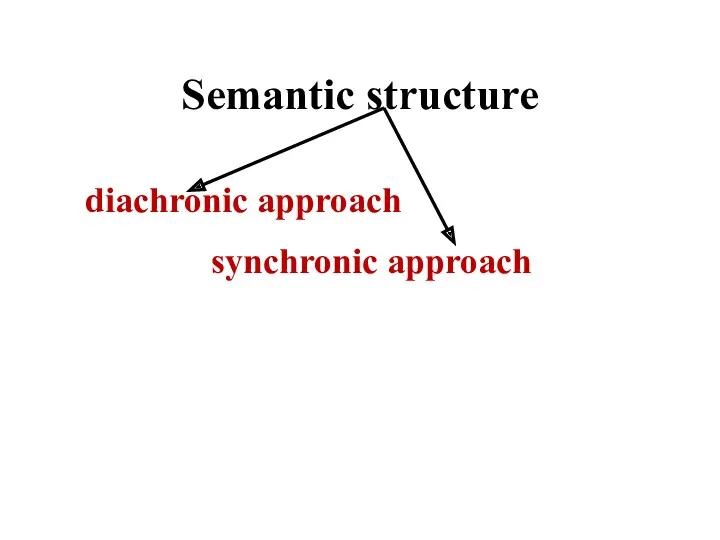
- 7. Semantic structure diachronic approach synchronic approach
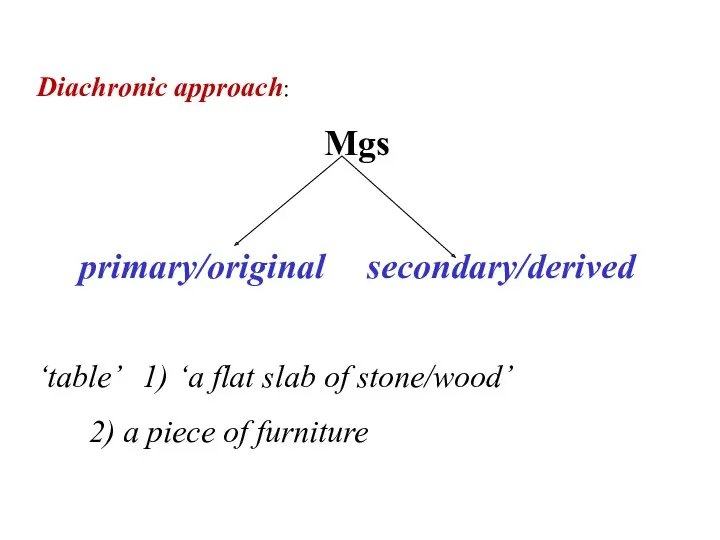
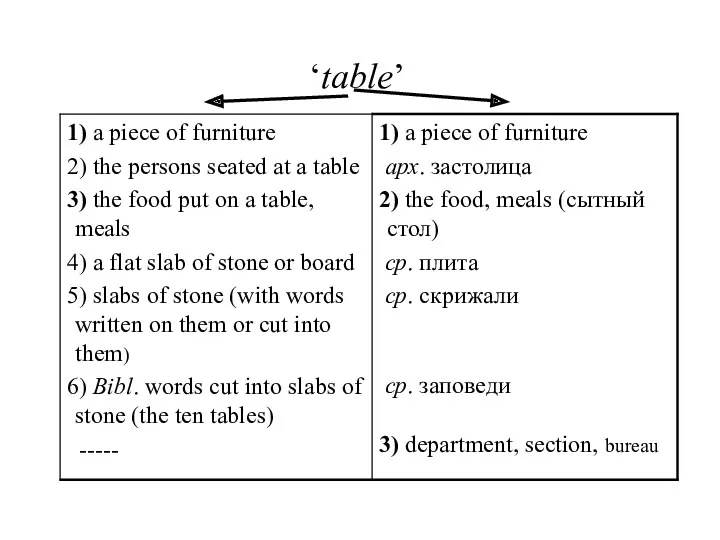
- 8. Diachronic approach: Mgs primary/original secondary/derived ‘table’ 1) ‘a flat slab of stone/wood’ 2) a piece of
- 9. Synchronically: polysemy – coexistence of different mgs of the same word in a certain historical period
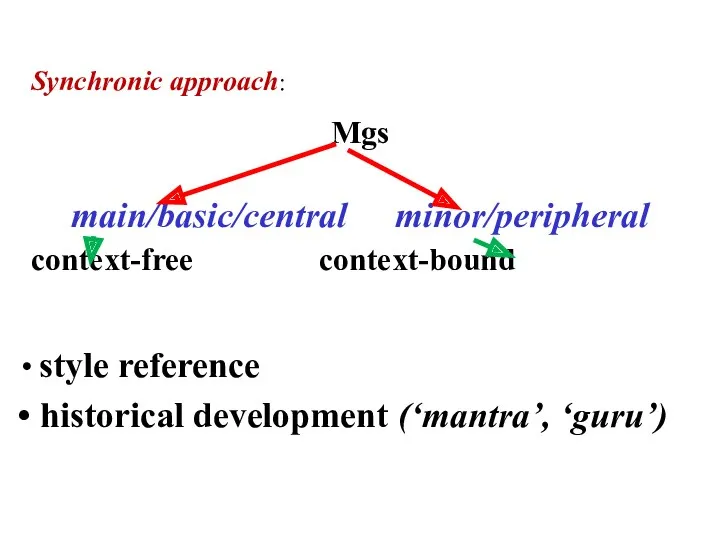
- 10. Synchronic approach: Mgs main/basic/central minor/peripheral context-free context-bound style reference historical development (‘mantra’, ‘guru’)
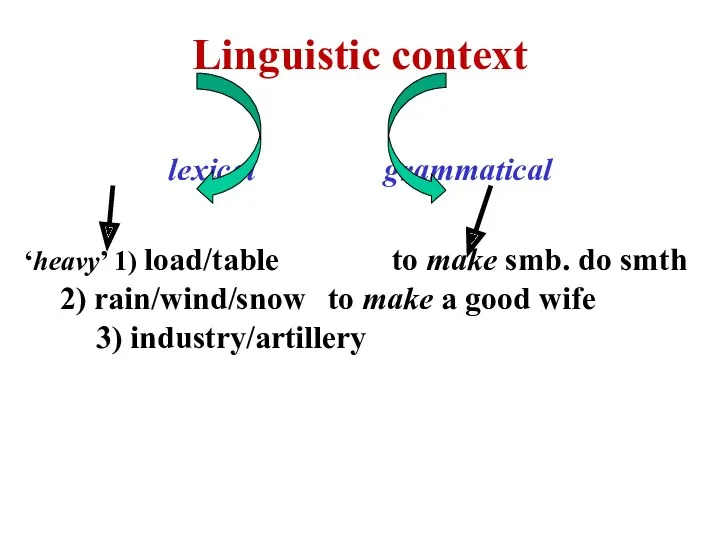
- 11. 3. Polysemy & context CONTEXT– the minimal stretch of speech determining each individual mg of the
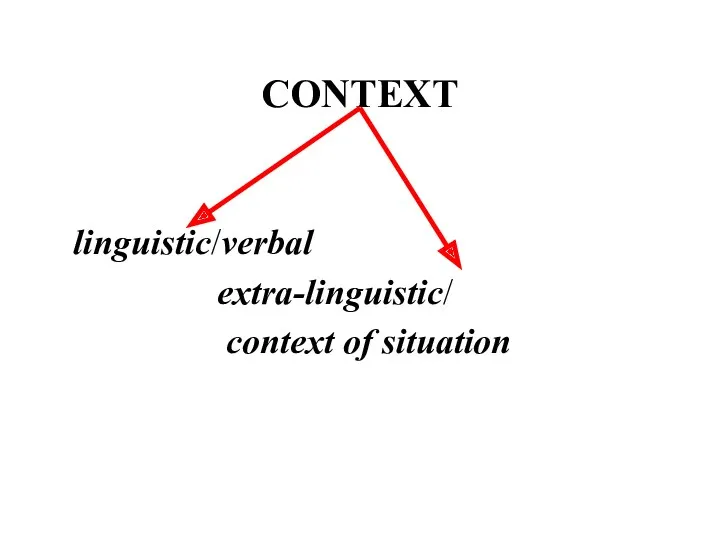
- 12. CONTEXT linguistic/verbal extra-linguistic/ context of situation
- 13. Linguistic context lexical grammatical ‘heavy’ 1) load/table to make smb. do smth 2) rain/wind/snow to make
- 14. Extra-linguistic context the mg is determined by the actual speech situation in which this word is
- 15. Polysemy: a linguistic universal a source of ambiguity in a lg pun: -- You missed my
- 16. 4. Correlative words. Correlative/correlated words – words of different lgs, similar in lexical mg (esp. in
- 18. ‘table’
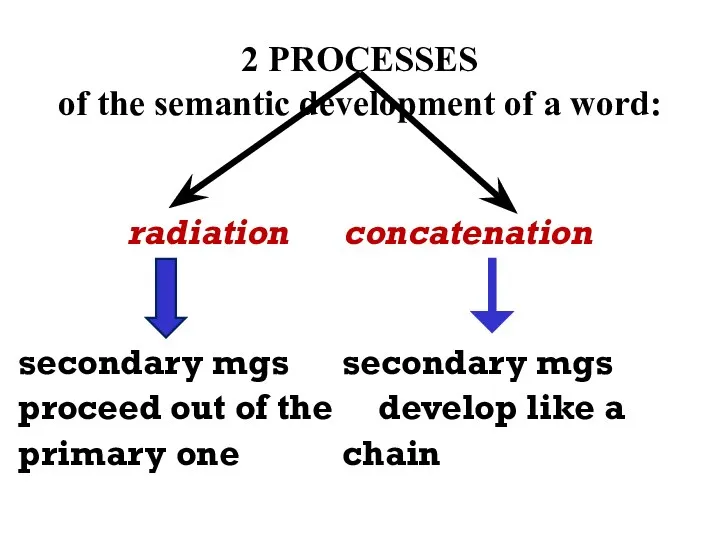
- 19. 2 PROCESSES of the semantic development of a word: radiation concatenation secondary mgs secondary mgs proceed
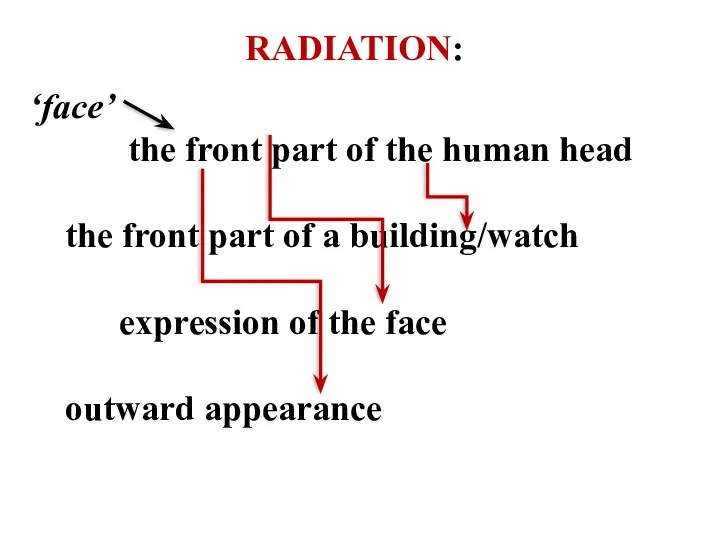
- 20. RADIATION: ‘face’ the front part of the human head the front part of a building/watch expression
- 21. CONCATENATION: ‘crust’ hard outer part of bread hard part of anything (a pie/cake etc) harder layer
- 22. HOMONYMY in English Questions for discussion: 1) Sources of homonymy 2) Classification of homonyms 3) Polysemy
- 23. Homonyms – words identical in sound-form but different in mg
- 24. SOURCES of homonymy: change in pronunciation & spelling (‘I’ from ‘ic’ & ‘eye’ from ‘eae’); borrowings
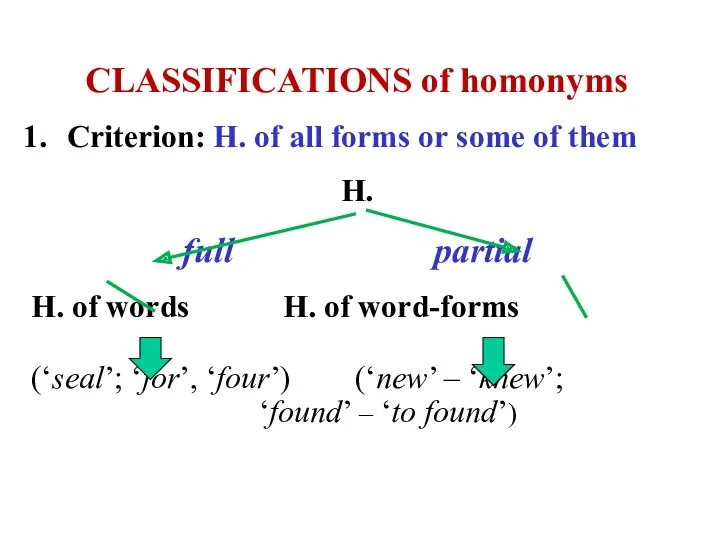
- 25. CLASSIFICATIONS of homonyms Criterion: H. of all forms or some of them H. full partial H.
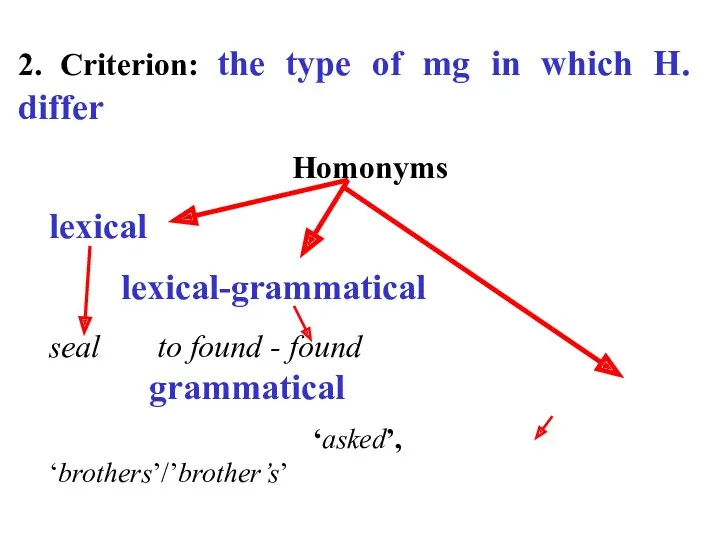
- 26. 2. Criterion: the type of mg in which H. differ Homonyms lexical lexical-grammatical seal to found
- 27. 3. Criterion: type of the coincidence form H. homographs (tear, row) homophones (sea/see; air/heir) perfect H./H.
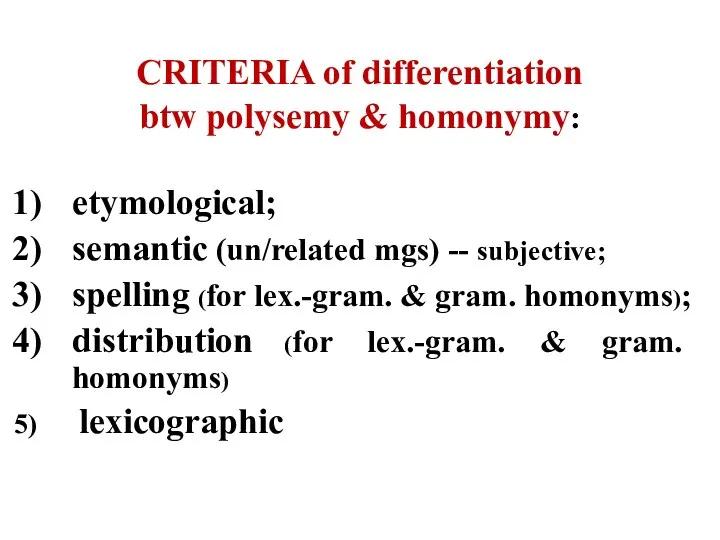
- 28. CRITERIA of differentiation btw polysemy & homonymy: etymological; semantic (un/related mgs) -- subjective; spelling (for lex.-gram.
- 30. Скачать презентацию












 Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey Добро пожаловать на берега Адриатического моря. Специфика лагеря Only English Land
Добро пожаловать на берега Адриатического моря. Специфика лагеря Only English Land Different kinds of sports
Different kinds of sports Word formation. Game
Word formation. Game Present simple. Настоящее простое время
Present simple. Настоящее простое время A shop I would like to have
A shop I would like to have Система вправ для навчання ІМ
Система вправ для навчання ІМ Earth Day - April 22
Earth Day - April 22 Образование множественного числа английских существительных
Образование множественного числа английских существительных The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom Video Modeling
Video Modeling The Passive Voice
The Passive Voice Food and Health
Food and Health ОГЭ. Устная часть. Задание 3
ОГЭ. Устная часть. Задание 3 Intonation
Intonation Tell me about each person in the photos
Tell me about each person in the photos Past present
Past present Fish
Fish What are they going to do?
What are they going to do? Weather
Weather Learn some names of jobs
Learn some names of jobs Sociolinguistic Variation of the English Language
Sociolinguistic Variation of the English Language Begin with an outline or agenda to give a big picture view
Begin with an outline or agenda to give a big picture view Глагол have - has
Глагол have - has Some phrases in English. Topic friends
Some phrases in English. Topic friends Modern building materials
Modern building materials Будущее время
Будущее время Diversity of plants Kingdom Fungi
Diversity of plants Kingdom Fungi