Слайд 2

Introduction
Ideally, all terms designating a concept should be
unambiguous (having a
unique relationship between form and concept) and
monosemantic (a one concept - one term relationship) with that concept in a given specialized language.
Слайд 3

Introduction
4th principle:
a concept is referred to by one term and
one term only designates one concept.
Слайд 4

Introduction
In reality, however, this is not always the case.
The principle
one designation - one concept,
does not always occur in practice.
Слайд 5
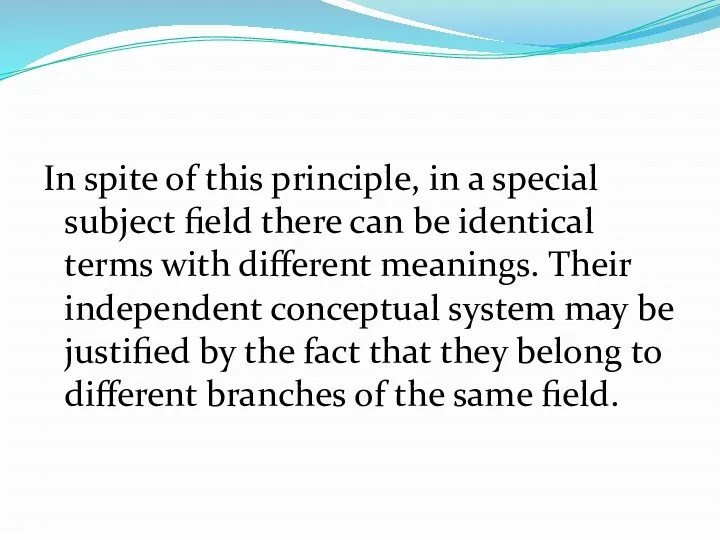
In spite of this principle, in a special subject field there
can be identical terms with different meanings. Their independent conceptual system may be justified by the fact that they belong to different branches of the same field.
Слайд 6
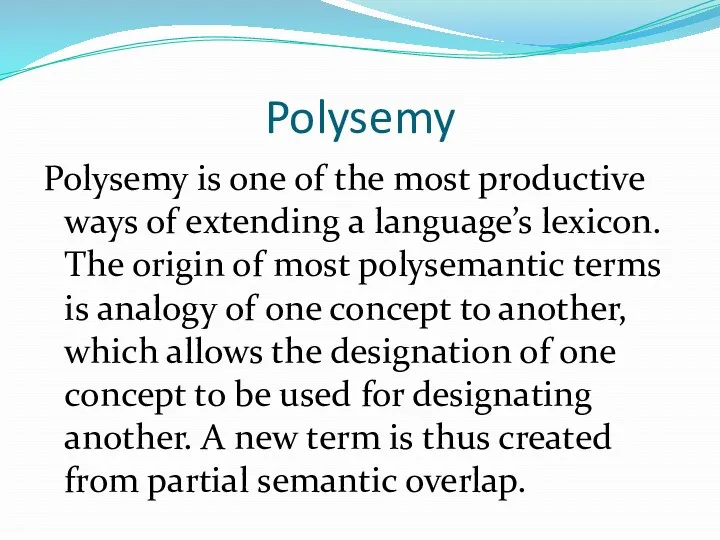
Polysemy
Polysemy is one of the most productive ways of extending a
language’s lexicon. The origin of most polysemantic terms is analogy of one concept to another, which allows the designation of one concept to be used for designating another. A new term is thus created from partial semantic overlap.
Слайд 7

Definition of Polysemy
A word having several meanings is called polysemantic, and
the ability of words to have more than one meaning is described by the term polysemy.
Слайд 8

Identification of polysemic expressions in terminology is difficult, if not impossible,
without a sufficient knowledge of the subject field and without a reasonable context available which helps delineate the topic, a branch of SpF, text-type, etc.
Слайд 9
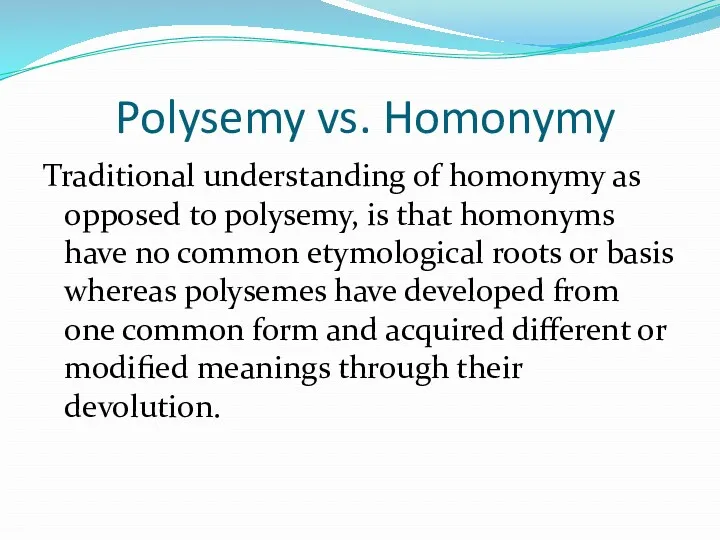
Polysemy vs. Homonymy
Traditional understanding of homonymy as opposed to polysemy,
is that homonyms have no common etymological roots or basis whereas polysemes have developed from one common form and acquired different or modified meanings through their devolution.
Слайд 10

Homonyms
Are terms that have the same form but represent entirely different
concepts. It is far more frequent in terminology than in the general lexicon. This is explained by the fact that in terminology each subject filed is considered a closed domain.
Слайд 11

Synonymy in Terminology
Broadly speaking two units designating the same concepts are
synonyms.
Even though theoretically a concept is expressed by a single designation, in reality there are alternative designations for a single concept and the designations of two different concepts can coincide even within the same subject field.
Слайд 12

Thus, terminology only considers synonyms to be semantically equivalent units that
belong to the same historical language and to the same formal register.
Synonyms for a single concept, however, do not always correspond to absolute equivalents, but rather manifest a range of possible cases.
Слайд 13

True synonyms
are terms that designate the same concept and that
can be used interchangeably in all contexts.
derived word = derivative
word-building = word-formation
substantive = noun
Слайд 14

Quasi-synonyms / near-synonyms
are terms that designate the same concept but that
are not interchangeable because of differences in usage depending on communication situations.
fridge / refrigerator
measles / rubeolla
football / soccer
Слайд 15

Pseudo-synonyms / false synonyms
designate different, although often closely related, concepts.
chair
/ stool
law / statute / ordinance /act
Слайд 16

Antonyms
are pairs of words whose meanings are the opposites of
one another, exactly as antonym is opposite to synonym
explosion / implosion
seropositive / seronegative
constitutional / unconstitutional
Слайд 17

Hyperonymy-hyponymy
Hyperonymy and hyponymy are semantic relations of lexical units deriving from
a hierarchical classification of the referents they represent.
Слайд 18

A hyperonym
is a word whose meaning contains the meanings of
other words (hyponyms) or, from the ontological dimension point of view, a hyperonym represents a referent, of which there are several kinds (the name of each kind is a hyponym).
Слайд 19

A hyponym
is a word whose meaning is contained in the
meaning of another word (hyperonym), this means, a hyponym represents a referent that is a certain type of a hierarchically superior referent in a sorting of referents.


















 My favorite group Twenty Øne Piløts
My favorite group Twenty Øne Piløts Фразеология английского языка. (Лекция 5)
Фразеология английского языка. (Лекция 5) The subjunctive mood. Формы сослагательного наклонения
The subjunctive mood. Формы сослагательного наклонения Halloween chant activities with music
Halloween chant activities with music Irregular plurals
Irregular plurals Computers of the future
Computers of the future Time to travel, USA
Time to travel, USA Halloween riddles
Halloween riddles Around the town
Around the town Семья. Основные задачи
Семья. Основные задачи Vocabulary and Grammar
Vocabulary and Grammar Match the types of stories to their descriptions
Match the types of stories to their descriptions Conditional sentences
Conditional sentences Pacific coastline
Pacific coastline Madame Tussauds
Madame Tussauds London
London Zero conditional. Present simple
Zero conditional. Present simple Types of sentences
Types of sentences My favorite sportsman
My favorite sportsman Modern technology
Modern technology The Pomor Family
The Pomor Family Длительные времена (Времена группы Continuous)
Длительные времена (Времена группы Continuous) Выражение благодарности в английском языке
Выражение благодарности в английском языке Артикли a, an
Артикли a, an This-that-these-those
This-that-these-those Amazing creatures
Amazing creatures Австралийский вариант английского языка
Австралийский вариант английского языка Alphabet. Английский алфавит
Alphabet. Английский алфавит