Содержание
- 2. Agenda Test Design and Implementation process Example Test Case Management tools
- 3. Test Design Process
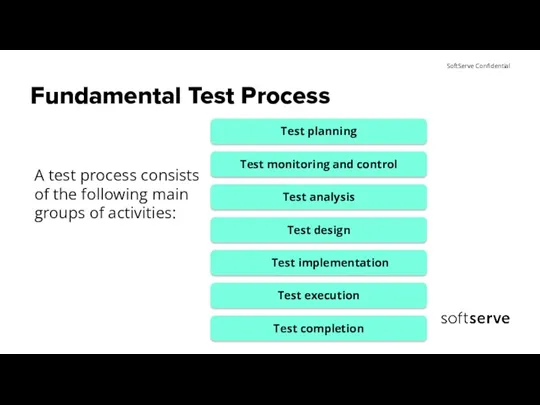
- 4. Fundamental Test Process A test process consists of the following main groups of activities:
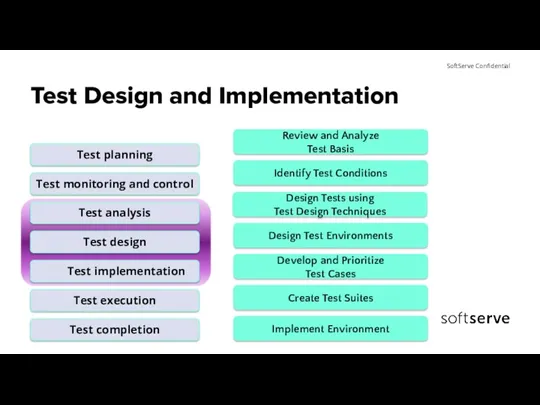
- 5. Test Design and Implementation
- 6. Example Driving test is an analogy for testing. We will use it to illustrate the Test
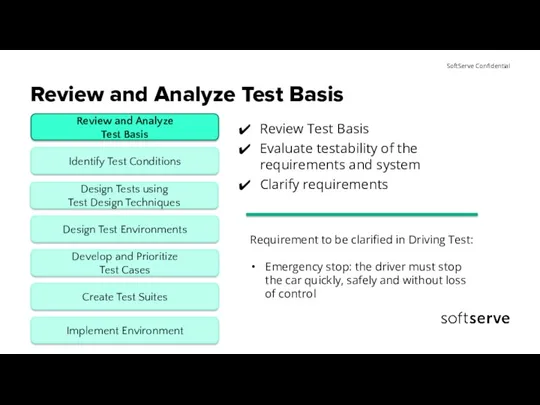
- 7. Review and Analyze Test Basis Review Test Basis Evaluate testability of the requirements and system Clarify
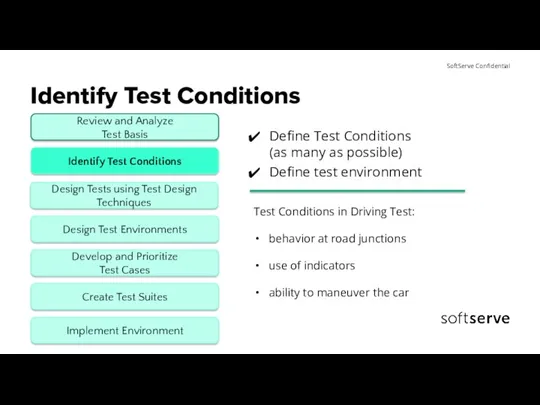
- 8. Identify Test Conditions Define Test Conditions (as many as possible) Define test environment Test Conditions in
- 9. Design Tests Define Tests for defined Conditions Tests for ‘behavior at road junctions’ Test Conditions in
- 10. Design Test Environments Design the test environment set-up and identify any required infrastructure and tools. Test
- 11. Test Case for test condition 'junctions': take the route down Mayfield Road to the junction with
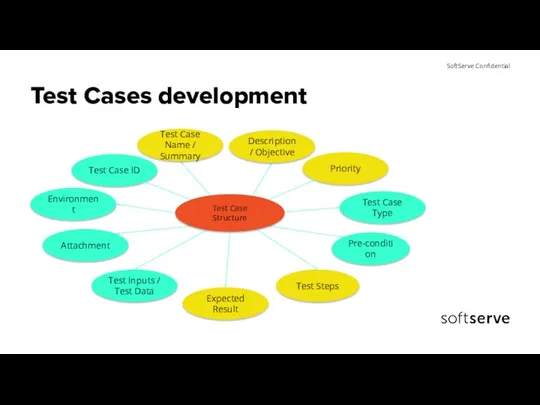
- 12. Test Cases development
- 13. Why Test Cases? Testing efficiency: be ready to test once the code is ready Early bug
- 14. Create Test Suites Group Test Cases logically for Test Execution Create a Test Execution Schedule Test
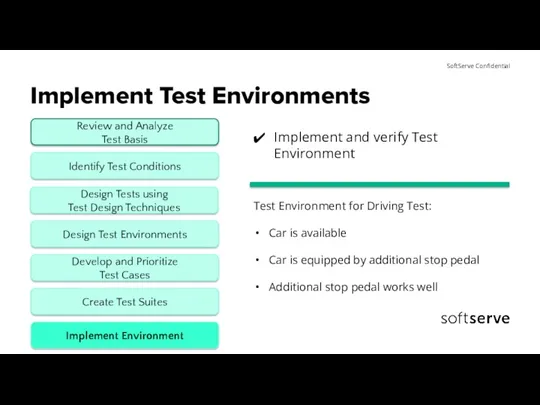
- 15. Implement Test Environments Implement and verify Test Environment Test Environment for Driving Test: Car is available
- 16. Test Design and Implementation Example
- 17. Requirements: User Registration Page Business Value: I, as an Administrator user, should be able to create
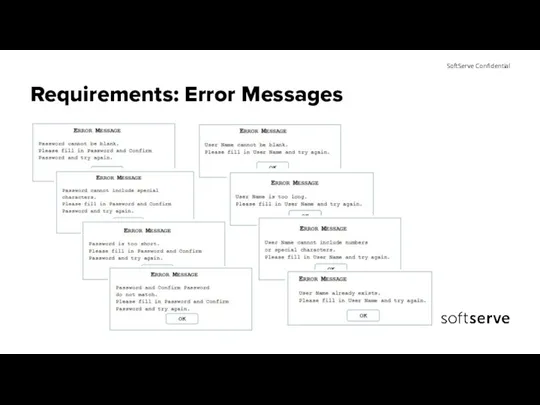
- 18. Requirements: Error Messages
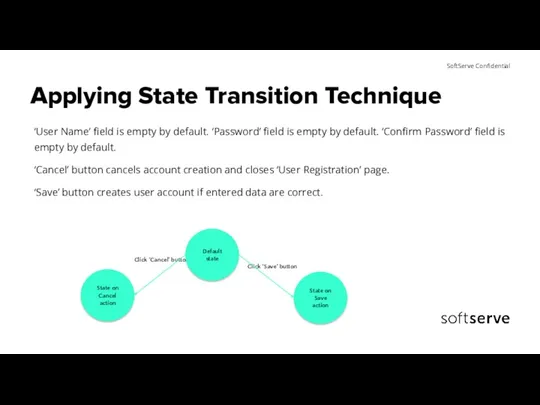
- 19. Applying State Transition Technique ‘User Name’ field is empty by default. ‘Password’ field is empty by
- 20. Applying State Transition Technique
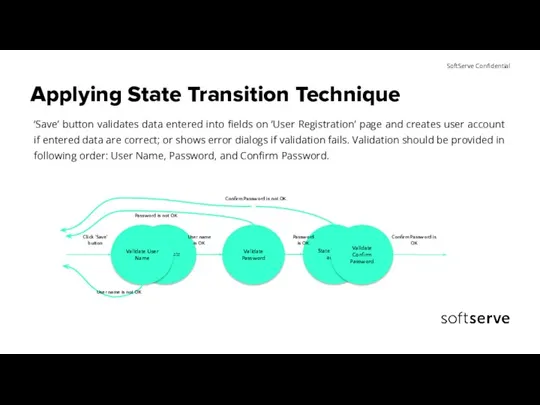
- 21. Applying State Transition Technique ‘Save’ button validates data entered into fields on ‘User Registration’ page and
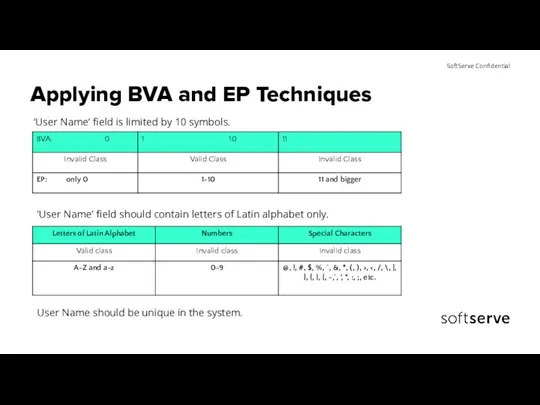
- 22. Applying BVA and EP Techniques ‘User Name’ field is limited by 10 symbols. ‘User Name’ field
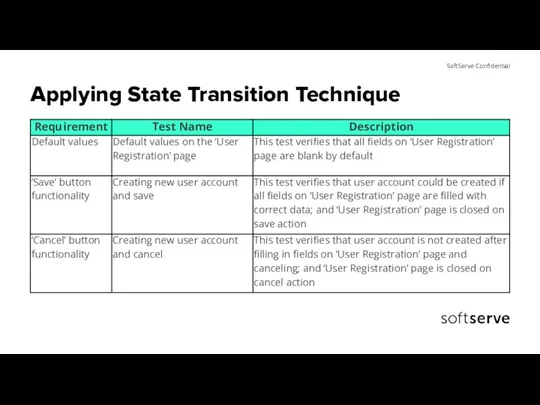
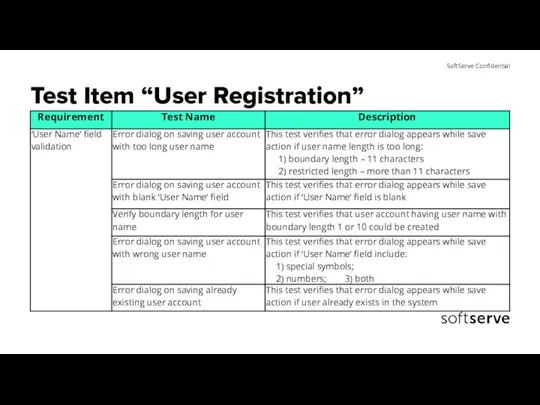
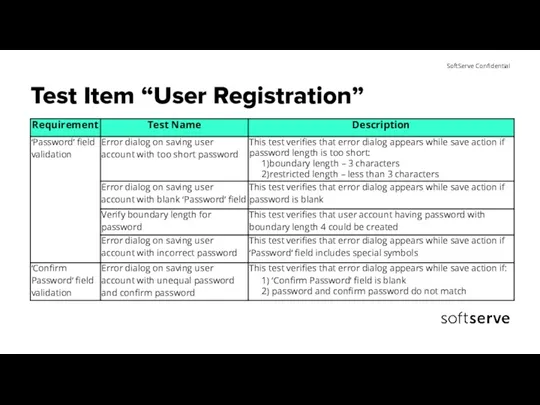
- 23. Test Item “User Registration”
- 24. Test Item “User Registration”
- 25. Test Case for ‘Confirm Password’ field validation Test Design Test Case Example 1 – Test Data
- 26. Test case Example 1 Pros suitable to use when test case is a candidate for automation
- 27. Test case Example 2 Pros easy to maintain one test case can be executed with different
- 28. Test case Example 3 Pros easy to maintain data data in separate document are better structured
- 29. Tips and Tricks Write test cases for all requirements Write test cases with necessary detail level
- 30. Test Case Management Tools
- 31. Test Case Management Tools Test Case Management Tool – A tool that provides support to the
- 32. Test Case Management Tools Test Case Management Tool can have one or more of the following
- 33. Revision History
- 35. Скачать презентацию



















 Mustn’t, must, can’t
Mustn’t, must, can’t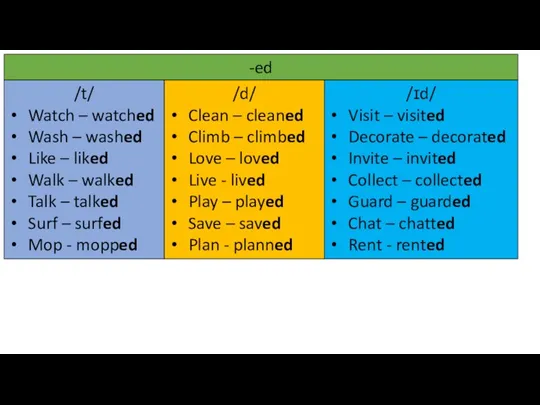 Past simple
Past simple Calendar 2019
Calendar 2019 Welcome to the year 2020-2021
Welcome to the year 2020-2021 Manager of the restaurant
Manager of the restaurant Устная и письменная части ЕГЭ по английскому языку: стратегии подготовки
Устная и письменная части ЕГЭ по английскому языку: стратегии подготовки Grammar Study
Grammar Study Direct and reported speech (Прямая и косвенная речь)
Direct and reported speech (Прямая и косвенная речь) English online. Lesson 2
English online. Lesson 2 Uncountable Nouns. Неисчисляемые существительные.
Uncountable Nouns. Неисчисляемые существительные. Урок по английскому языку в 3 классе по теме Еда
Урок по английскому языку в 3 классе по теме Еда Food
Food Sergey Yesenin Monument
Sergey Yesenin Monument Food 5
Food 5 Имя прилагательное (The Adjective)
Имя прилагательное (The Adjective) Demonstrative pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns My own game. Categories
My own game. Categories Active voice and Passive voice
Active voice and Passive voice Have got/ has got
Have got/ has got Cartoons
Cartoons Communicative Language Teaching Plan
Communicative Language Teaching Plan Opposite adjectives
Opposite adjectives The Geography Outlook of the UK
The Geography Outlook of the UK Времена действительного залога в английском языке
Времена действительного залога в английском языке Introduction to shipping
Introduction to shipping Passive Voice - Страдательный Залог
Passive Voice - Страдательный Залог Singular and plurals
Singular and plurals I cook meat
I cook meat