Содержание
- 2. requirements of the course My course is 2 credits. One lecture and one seminar. On the
- 3. Definition Ecology is the study of the relationships of organisms with other organisms and with their
- 4. Primary objectives of the science of ecology are as follows: 1. To study change in organisms
- 5. 3. To develop a scientific basis for exploiting the biological resources; 4. To develop measures to
- 6. 4. To control the population of living organisms; 5. To provide indication of environmental status and
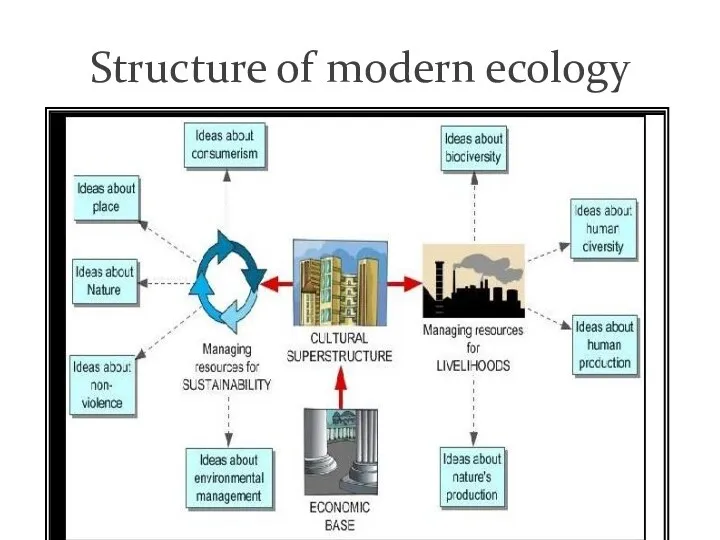
- 7. Structure of modern ecology ttinModern ecology relies heavily on experiments, both in laboratory and in field
- 8. Structure of modern ecology
- 9. The relationship of ecology with other sciences Ecology is a multi-disciplinary science, drawing on many other
- 10. Sections of ecology The science of Ecology is closely related with both natural and human sciences
- 11. Biological Ecology Biological Ecology studies the conditions of existence of living organisms and the relationship between
- 12. Autecology Autecology studies such characteristics of the living organisms as adaptation to temperature, humidity, salinity and
- 13. Population Ecology Population Ecology or Demecology studies characteristics of the population consisting of species varying in
- 14. Sinecology Sinecology or Community Ecology studies the community species composition, their spatial pattern, and communities change
- 15. Global Ecology Comlex of all earth ecosystems within three geospheres (lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere), which interact
- 16. Environmental Engineering Environmental Engineering investigates the interrelations of the community and natural habitat with public production
- 17. Human Ecology Human Ecology focuses on preservation and improvement of human health, with a glance to
- 18. Social Ecology Social Ecology investigates the nature-society interactions; it is the science dealing with radical changes
- 19. Space Ecology Space Ecology being a totally new line of Human Ecology deals with the manned
- 20. Importance of Ecology Since all of us live in a natural or partly natural ecosystem, then
- 21. Science ecology Importance to human existence. Accumulation of ecological knowledge. Its environmental effects. Its influence in
- 22. Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of
- 24. Скачать презентацию




















 England is the largest and major part of the United Kingdom
England is the largest and major part of the United Kingdom My hobby
My hobby Деловая переписка в английском языке
Деловая переписка в английском языке Listening
Listening Adjective and its categories
Adjective and its categories Finance 510: Microeconomic Analysis
Finance 510: Microeconomic Analysis Степени сравнения прилагательных Adjectives Degrees of Comparison
Степени сравнения прилагательных Adjectives Degrees of Comparison Can and Can’t
Can and Can’t Present indefinite (simple) tense. Настоящее неопределенное (простое) время
Present indefinite (simple) tense. Настоящее неопределенное (простое) время Гаджеты. Gadgets
Гаджеты. Gadgets English in Use. Module 7f. Spotlight 8
English in Use. Module 7f. Spotlight 8 The Story of St. Valentine
The Story of St. Valentine Singular countable nouns
Singular countable nouns Серия учебных пособий по подготовке к ЕГЭ
Серия учебных пособий по подготовке к ЕГЭ FINA-2015
FINA-2015 Why is English so popular
Why is English so popular Modal Verbs. Модальные глаголы в английском языке
Modal Verbs. Модальные глаголы в английском языке Canada is located in the north of the American
Canada is located in the north of the American Исчисляемые существительные
Исчисляемые существительные Food – basic processes
Food – basic processes Watch the animals and choose
Watch the animals and choose The importance of using authentic materials for the preparation of professional readiness of future specialists in high
The importance of using authentic materials for the preparation of professional readiness of future specialists in high Direct and indirect (reported) speech
Direct and indirect (reported) speech My game
My game Harry Potter And a Secret Photo Album
Harry Potter And a Secret Photo Album Hidden picture weather
Hidden picture weather My idol Michael Phelps
My idol Michael Phelps Future simple
Future simple