Содержание
- 2. Megacities - Cities with 10 million residents or more.
- 3. Metropolitan Area A metropolitan area is a densely populated core area together with adjacent communities. .The
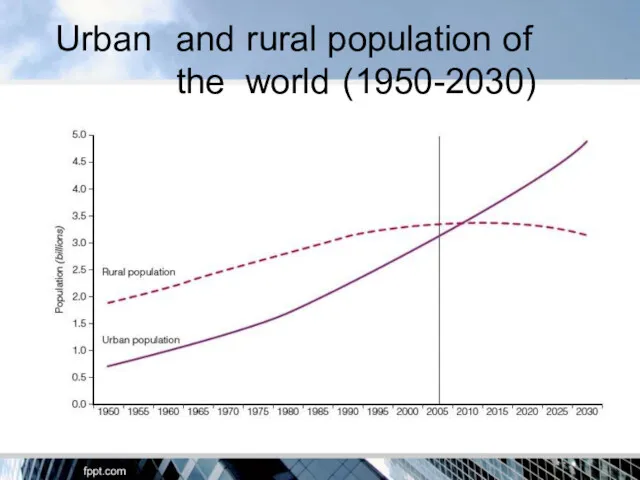
- 4. Urban and rural population of the world (1950-2030)
- 5. Causes of Urban Growth ϖBetter food supply ϖGood medical care ϖEducation ϖJobs ϖEntertainment ϖSpecialization of professions
- 6. Functionalist View Focuses on how changes in one aspect of the social system affect other aspects
- 7. Functionalist View The development of urban areas is functional for societal development. Urbanization is also dysfunctional,
- 8. Functionalist View There are different theories: Concentric-zone theory Demographic transition theory Multiple-nuclei theory
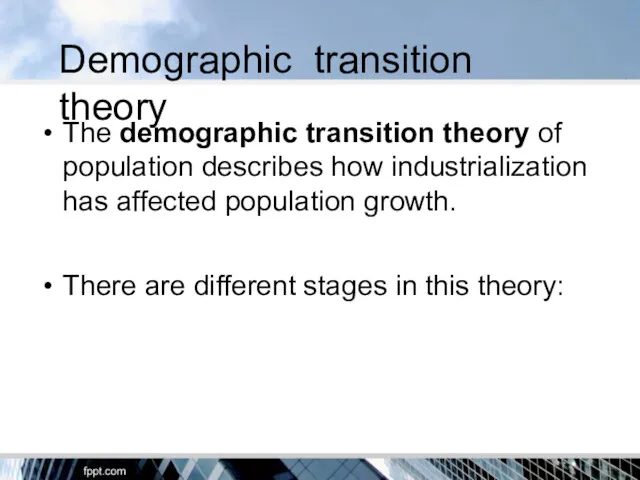
- 9. Demographic transition theory The demographic transition theory of population describes how industrialization has affected population growth.
- 10. Stage 1: Preindustrial Societies - little population growth, high birth rates offset by high death rates.
- 11. Stage 3: Advanced Industrialization and Urbanization - very little population growth occurs, birth rates and death
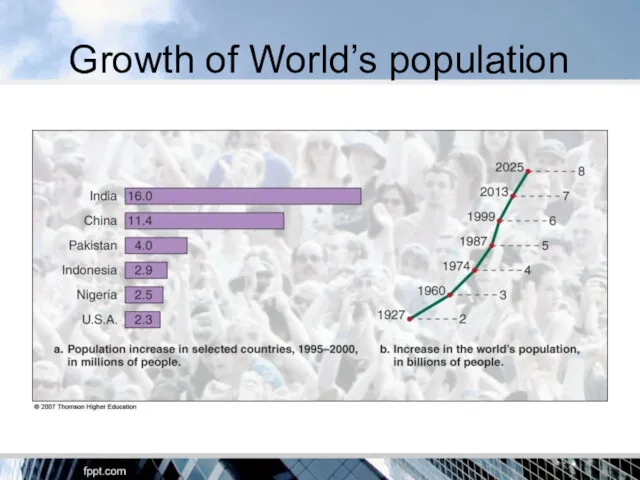
- 12. Growth of World’s population
- 13. Symbolic View Simmel’s view of city life The intensity of city life causes people to become
- 14. Conflict View Emphasizes the role of power, wealth and profit motive in development of urban areas.
- 15. Conflict View The capitalist class chooses locations for skyscrapers and housing projects, limiting individual choices by
- 16. New Urban Sociology An approach to urbanization that considers the interplay of local, national, and worldwide
- 18. Скачать презентацию












 Навчання вимови у школі
Навчання вимови у школі What`s the letter?
What`s the letter? New Year in Great Britain
New Year in Great Britain Toys
Toys Сложное предложение
Сложное предложение A system of courts of law for the administration of justice. (Unit 10)
A system of courts of law for the administration of justice. (Unit 10) Kid's box 1. Unit 1. Hello!
Kid's box 1. Unit 1. Hello! My family
My family Free time activities
Free time activities How to gtow a garden
How to gtow a garden Алфавит и цифры
Алфавит и цифры The present perfect tense
The present perfect tense Проект Мое любимое животное 3 класс
Проект Мое любимое животное 3 класс The Renal Transplant Patient
The Renal Transplant Patient Speaking Games (тренажёр)
Speaking Games (тренажёр) Lecture 6. Word-building (part 2 )
Lecture 6. Word-building (part 2 ) Great minds. (Module 3)
Great minds. (Module 3) ¿Qué es esto? Что это?
¿Qué es esto? Что это? Do you have the same hobby?
Do you have the same hobby? US presidential election
US presidential election Present Real Conditionals. Условные предложения настоящего времени (истинные условия)
Present Real Conditionals. Условные предложения настоящего времени (истинные условия) Подготовка к ОГЭ. Пробник. Christmas and New Year
Подготовка к ОГЭ. Пробник. Christmas and New Year Possessive case of the nouns. Present Simple Tense Test
Possessive case of the nouns. Present Simple Tense Test How much do you know about - game
How much do you know about - game Intonation
Intonation Teen Activities
Teen Activities Pronunciation of vowels (2)
Pronunciation of vowels (2) Тo be етістігі
Тo be етістігі