Содержание
- 2. HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
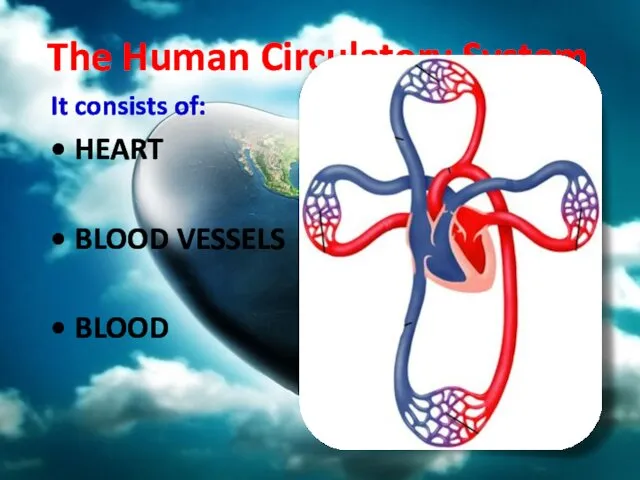
- 4. The Human Circulatory System It consists of: HEART BLOOD VESSELS BLOOD
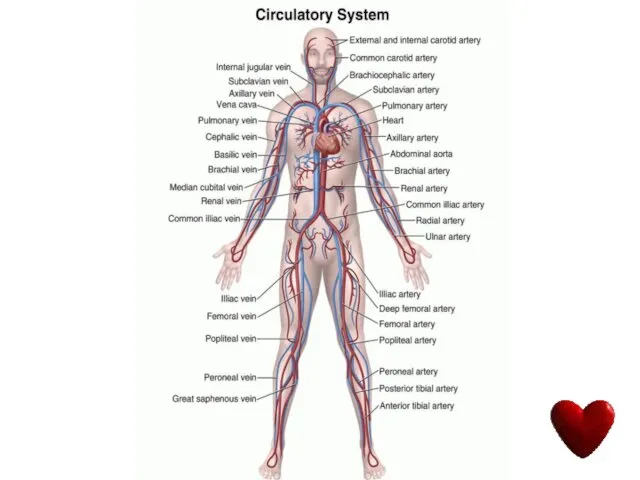
- 6. The human circulatory system functions like a network of highways. It transports materials around the body.
- 7. IT TRANSPORTS: Oxygen and Carbon dioxide Digested and absorbed food or nutrients Hormones, vitamins and minerals
- 8. Functions of human circulatory system It plays an important role in gas exchange Supply body cells
- 9. HEART FACTS: About 250-340 grams, In your life time, pumps about 300 million liter of blood,
- 10. Main structure of the heart The heart is made of a special type of muscle called
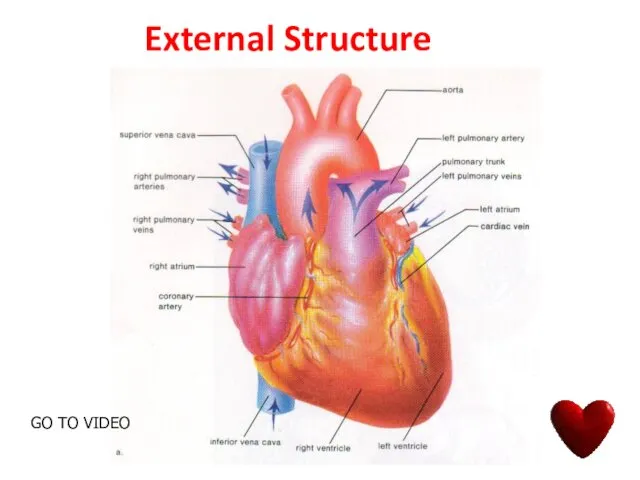
- 11. External Structure GO TO VIDEO
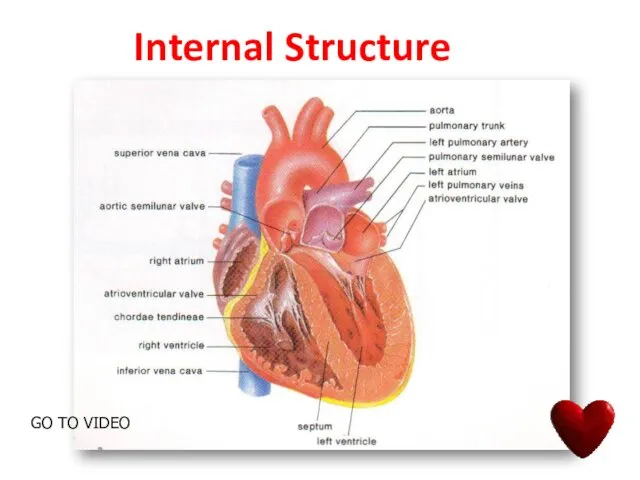
- 12. Internal Structure GO TO VIDEO
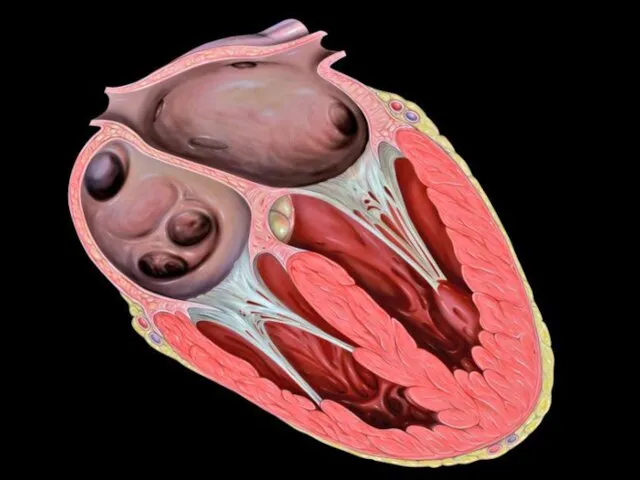
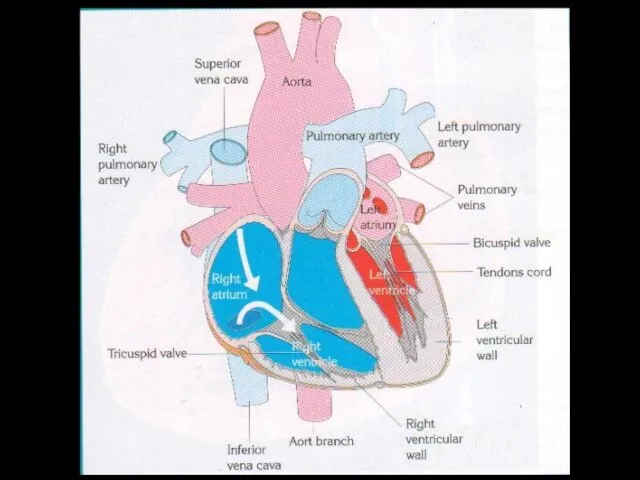
- 15. Internal Structure Of The Heart The heart consists of four chambers : The two upper chambers
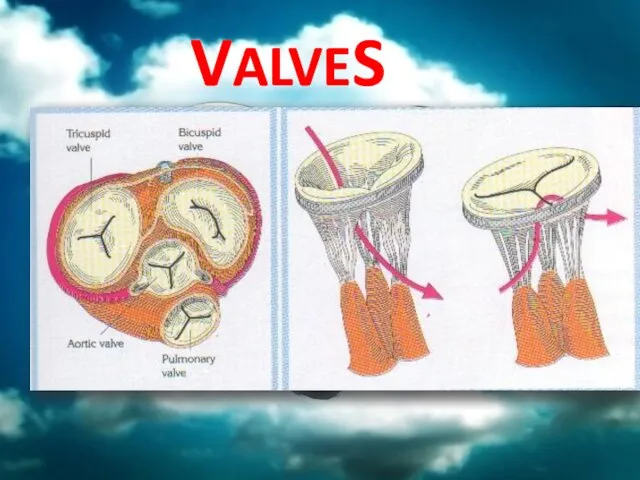
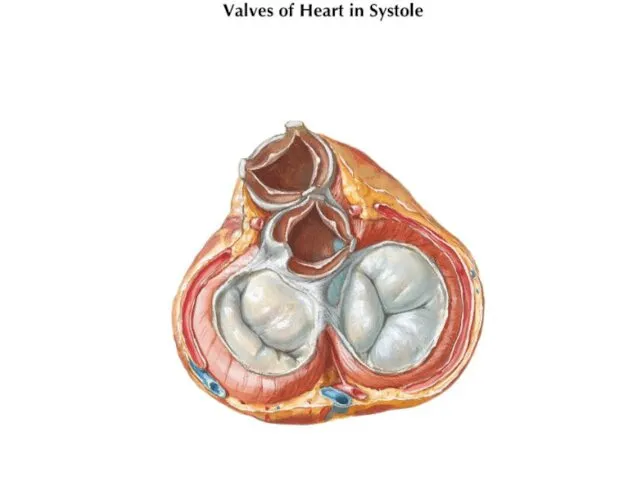
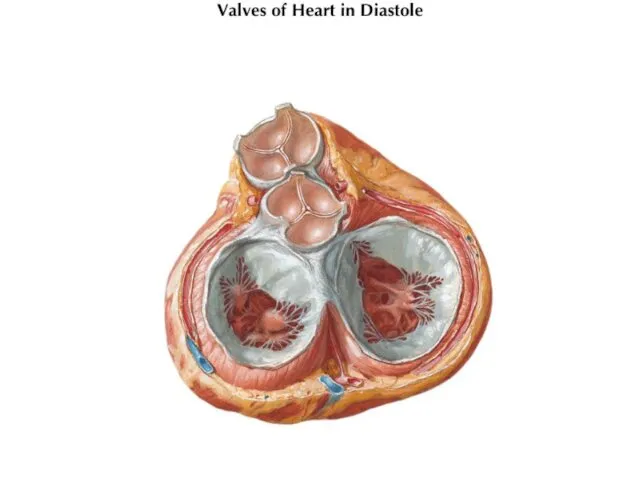
- 16. VALVES
- 17. Semilunar Valves Semilunar valves are found between the arteries and the ventricles. They prevent the blood
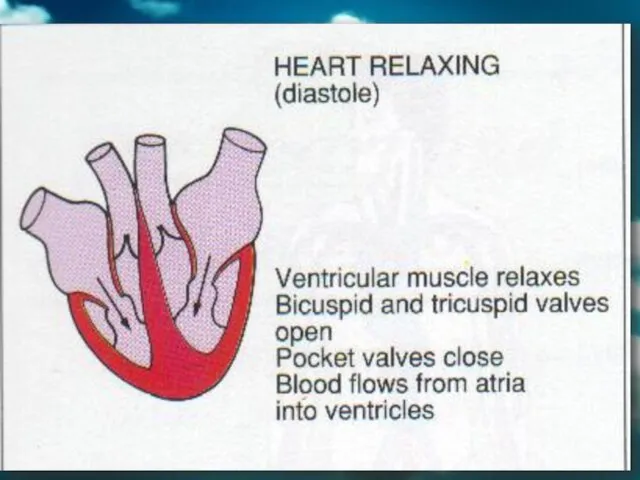
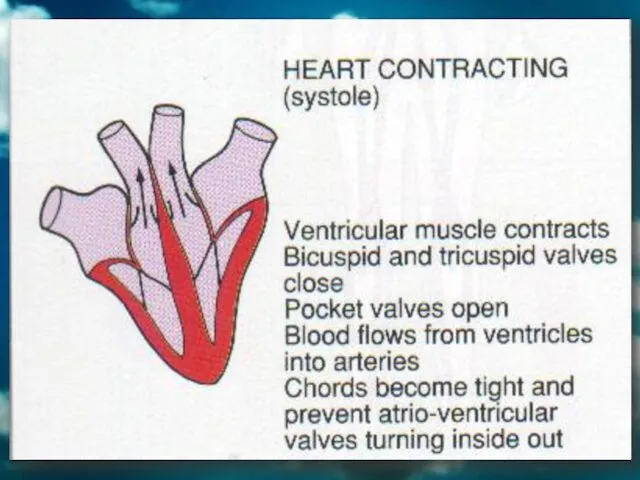
- 21. The heart pumps blood into the body. Relaxation of heart is known as diastole. Contraction of
- 24. Heart beating 3D video
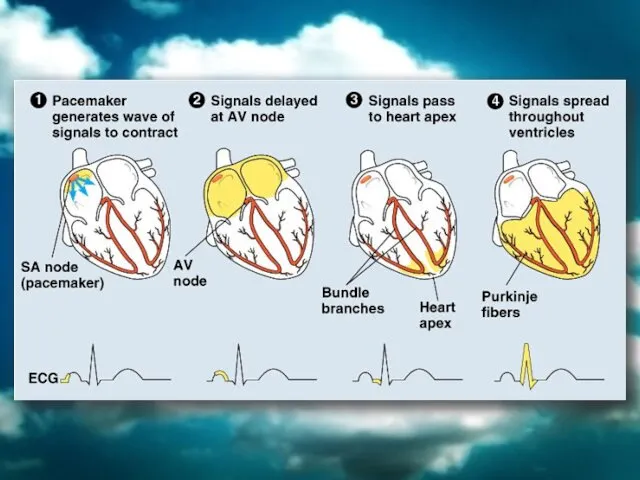
- 25. Heartbeat is controlled by autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system stimulates the sinoatrial node and
- 27. Heart Rate Parasympathetic nerves reduces the heart rate. Sympathetic nervs speed up the heart rate. Acetylcholine
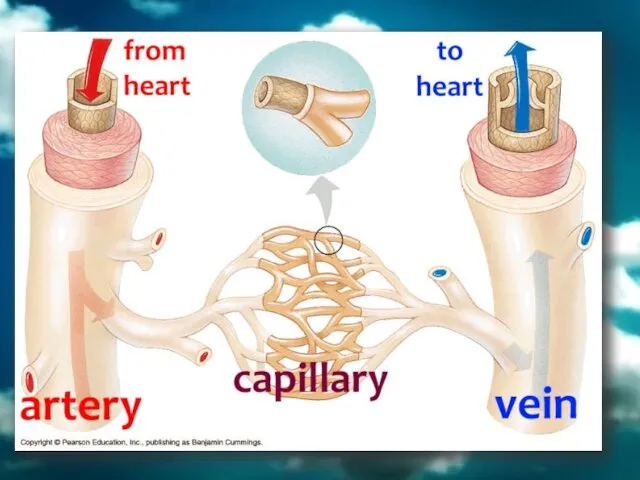
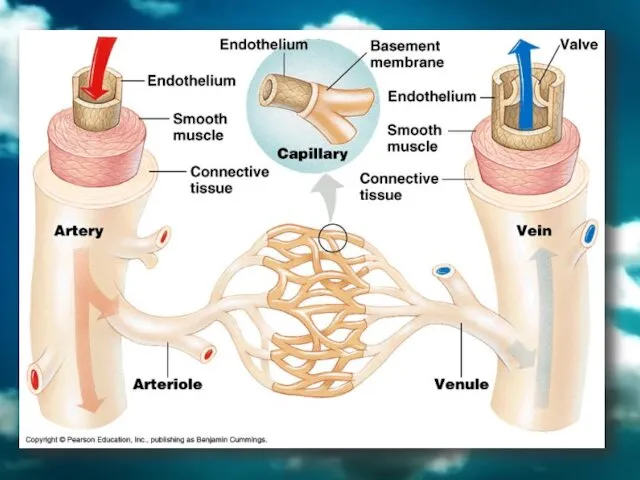
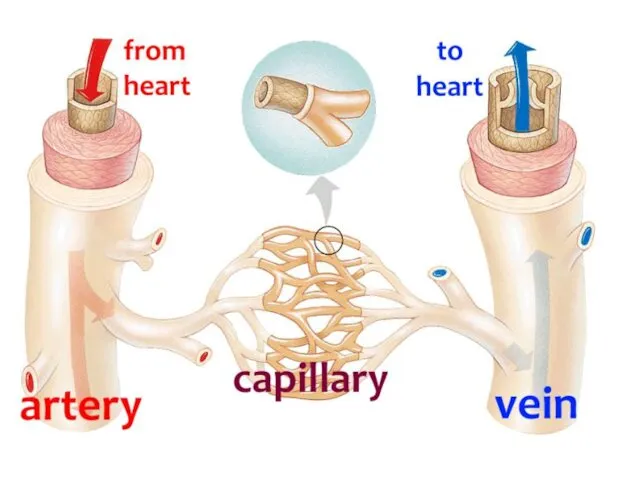
- 28. BLOOD VESSELS There are 3 types of vessels in our body. These are; ARTERIES VEINS CAPILLARIES`
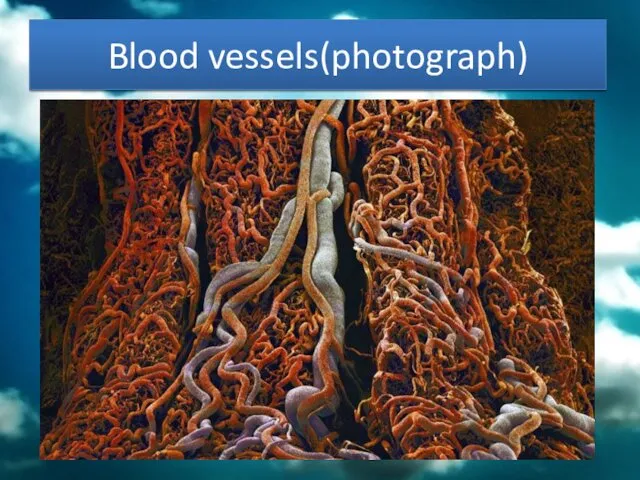
- 30. Blood vessels(photograph)
- 32. 1. Arteries Arteries carry blood away from heart to the different tissues of the body. Artery
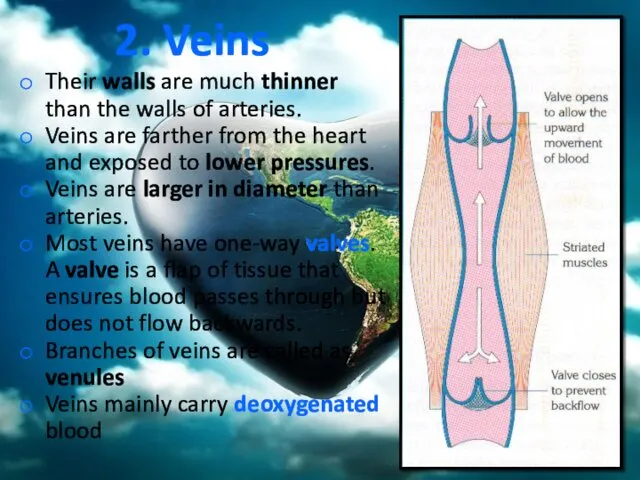
- 33. 2. Veins Their walls are much thinner than the walls of arteries. Veins are farther from
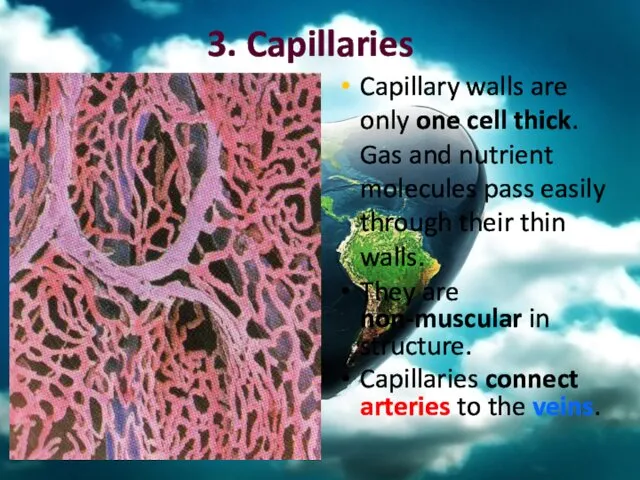
- 35. 3. Capillaries Capillary walls are only one cell thick. Gas and nutrient molecules pass easily through
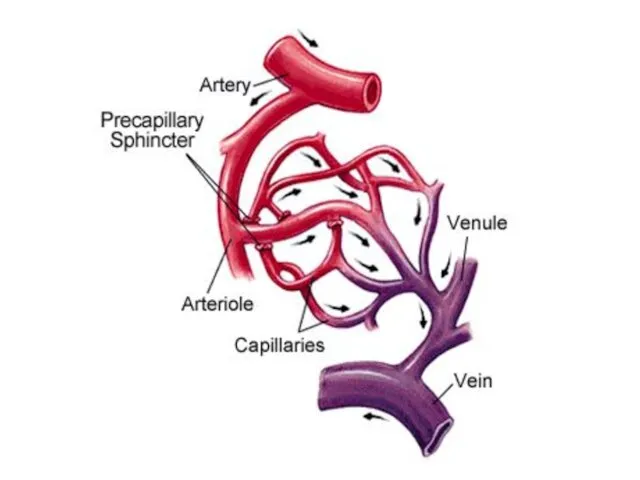
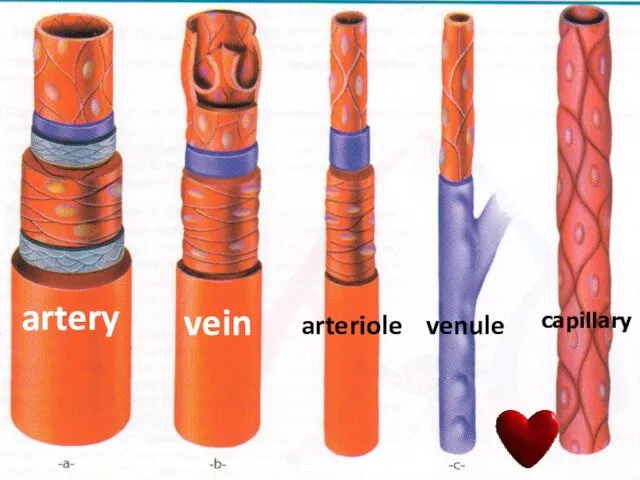
- 38. artery vein arteriole venule capillary
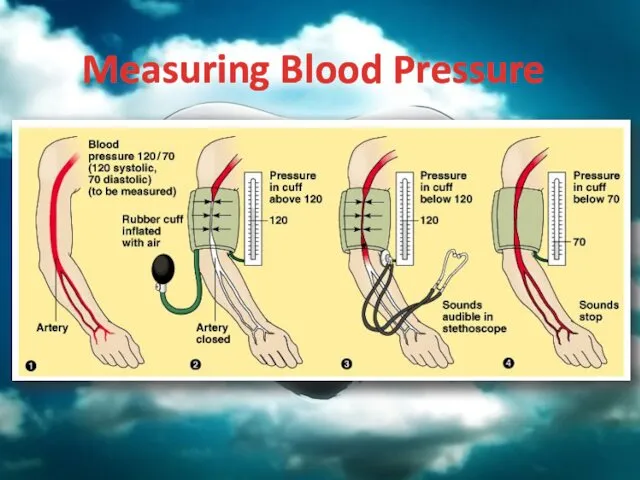
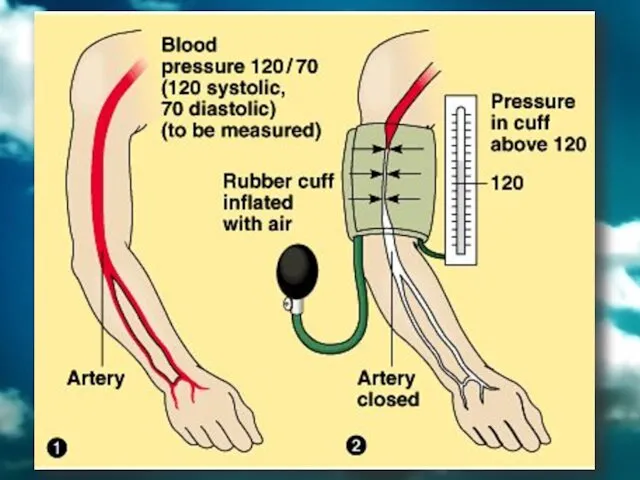
- 39. Blood Pressure Blood exerts pressure on the walls of vessels during circulation Blood pressure increases when
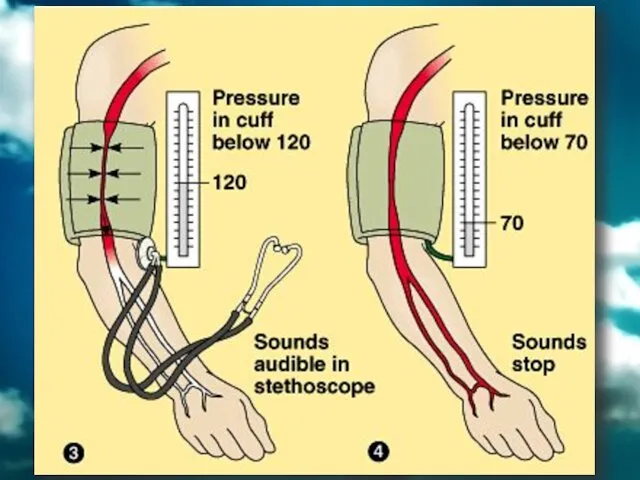
- 40. Measuring Blood Pressure
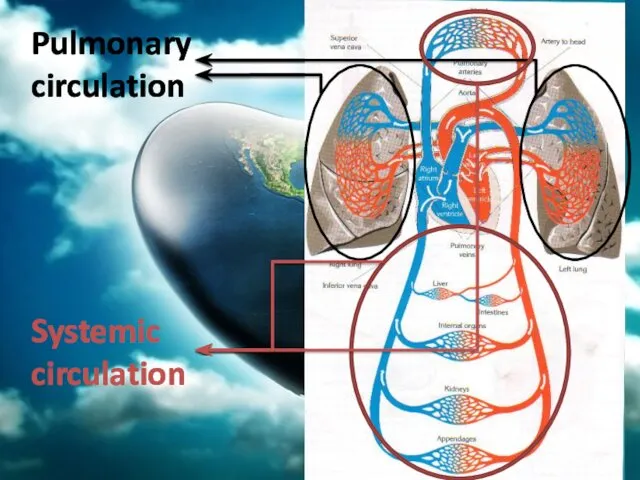
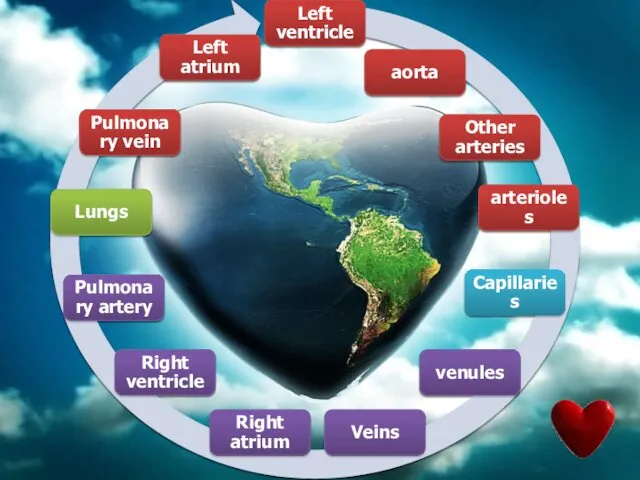
- 43. Blood Circulation There two types of circulation in human body: 1. Pulmonary Circulation: Oxygen poor blood
- 44. Pulmonary circulation Systemic circulation
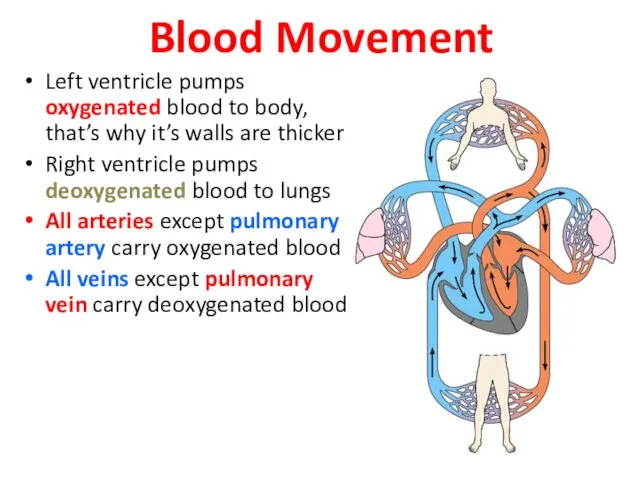
- 46. Blood Movement Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to body, that’s why it’s walls are thicker Right
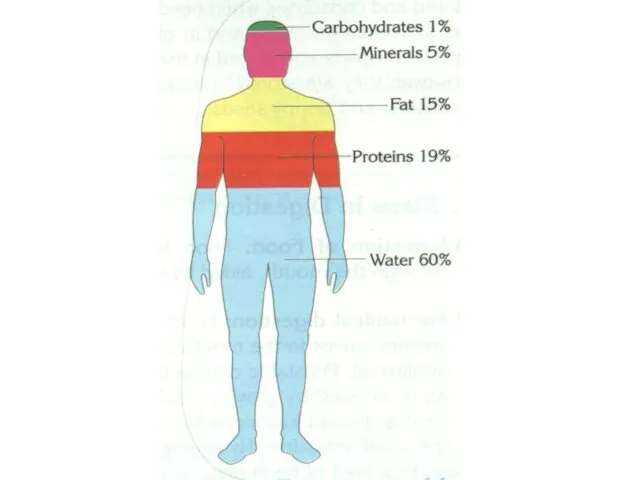
- 48. BLOOD Blood is a type of tissue that formed by mesoderm layer of embryo. An adult
- 49. FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD Transport of materials Hormone transport Homeostasis Immune response Blood Clotting
- 50. BLOOD COMPONENTS Blood contain 2 main parts. These are: Blood Plasma Blood cells
- 51. Blood Plasma Plasma is liquid part of blood. It includes water (90%) and dissolved proteins. It
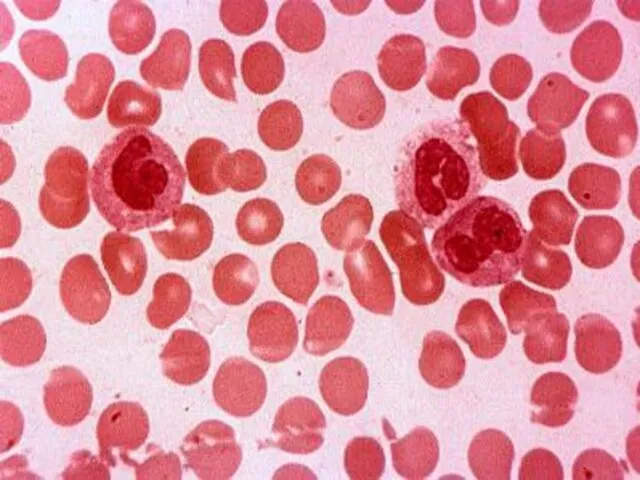
- 53. Blood Cells There are three types of blood cells: Erythrocytes (=Red Blood Cells) Leucocytes (=White Blood
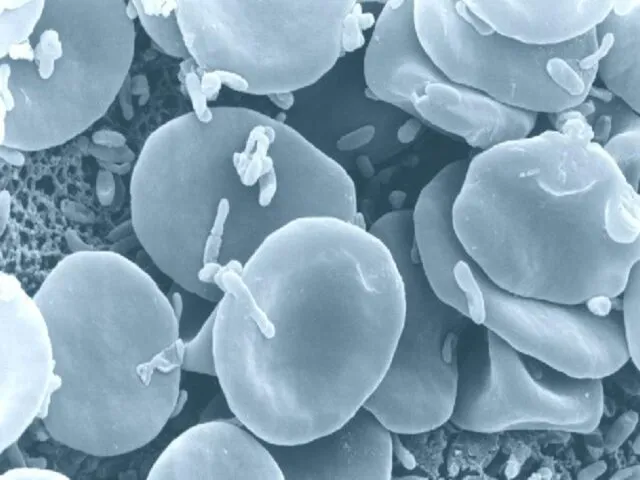
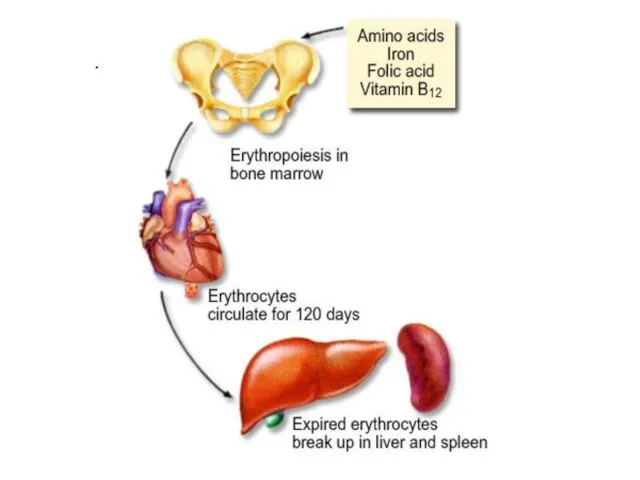
- 55. There are approximately 5 to 5,5 million of erythrocytes per cubic millimeter of blood. The major
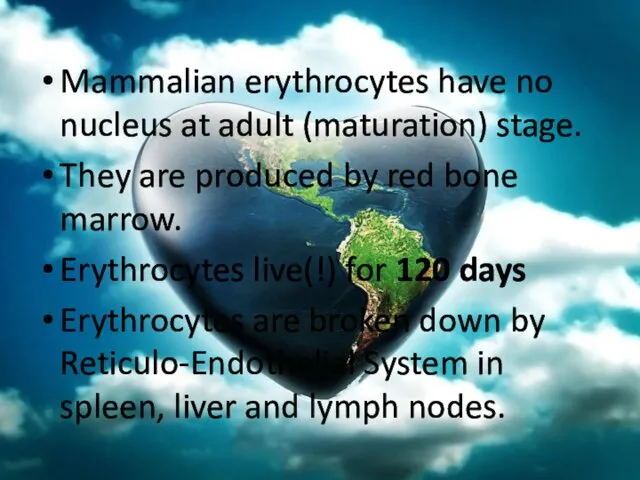
- 56. Mammalian erythrocytes have no nucleus at adult (maturation) stage. They are produced by red bone marrow.
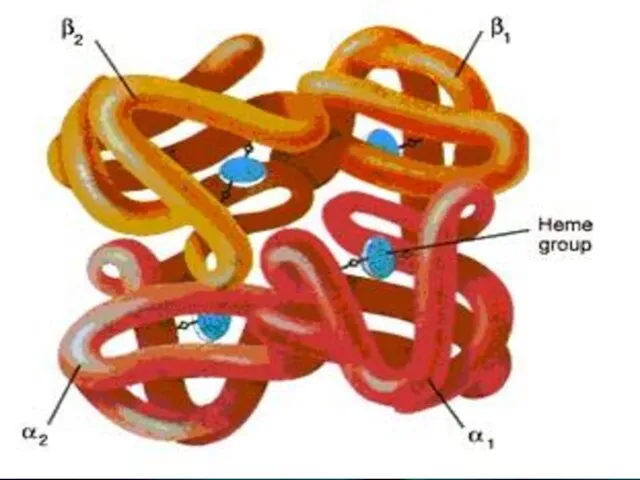
- 60. HEMOGLOBIN Erythrocytes are filled with hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is iron (Fe) containing pigment. It gives red color
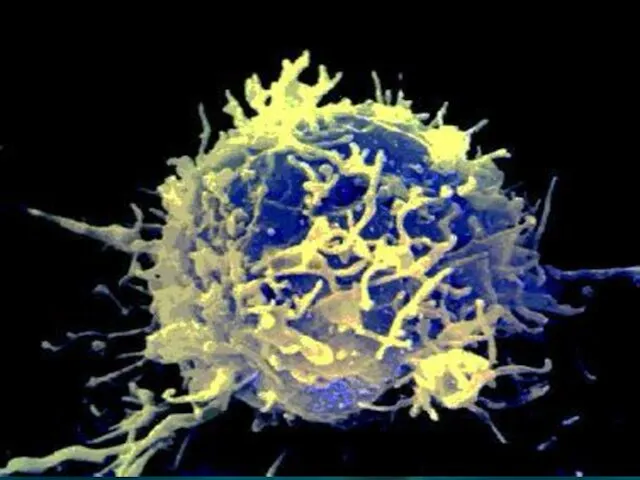
- 63. LEUCOCYTES Leucocytes protect the body from infections. They are produced by red bone marrow and lymph
- 64. Normally there are only 6000 to 8000 leucocytes per cubic millimeter of blood. When there is
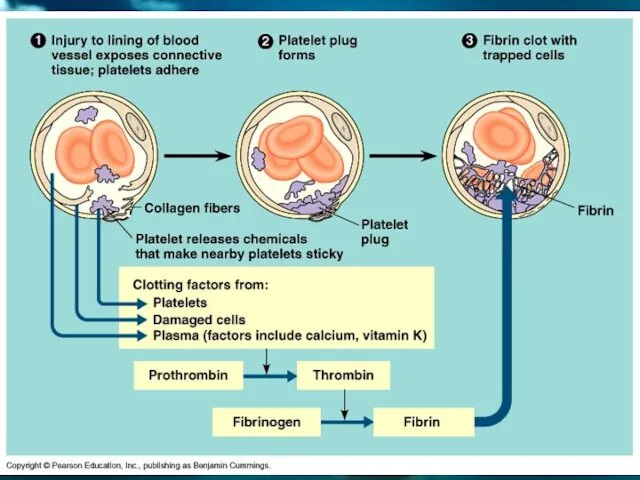
- 67. PLATELETS Platelets are produced by bone marrow. They play major role in blood clotting. Blood clotting
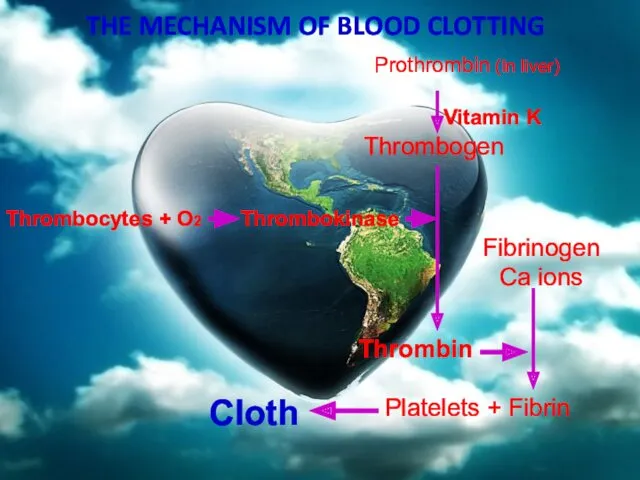
- 68. THE MECHANISM OF BLOOD CLOTTING Prothrombin (In liver) Vitamin K Thrombogen Thrombocytes + O2 Thrombokinase Thrombin
- 71. Diseases related to circulatory system Anemia Leukemia Arteriosclerosis
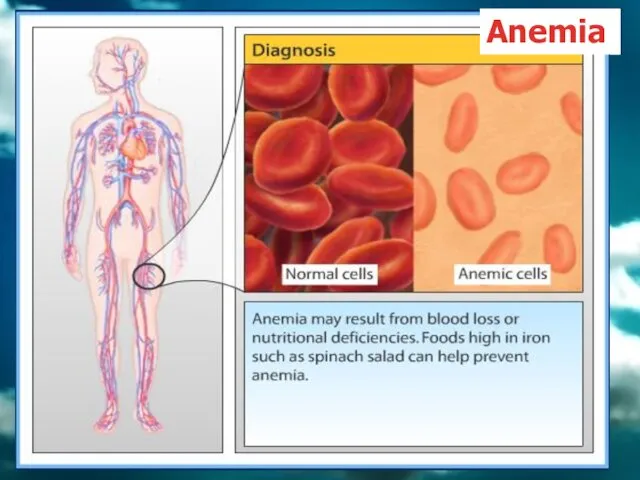
- 72. Anemia
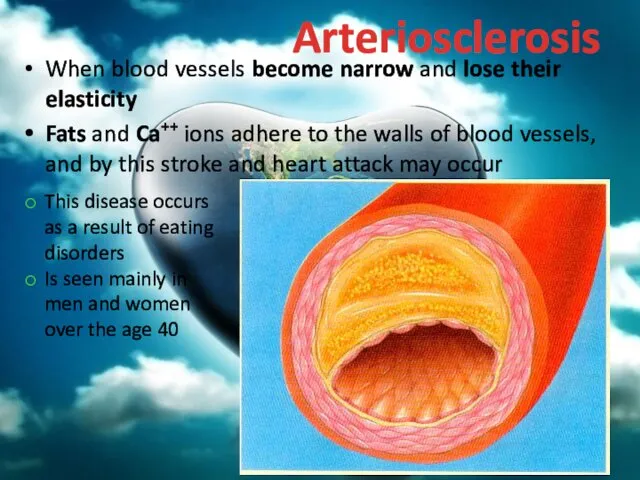
- 73. Arteriosclerosis When blood vessels become narrow and lose their elasticity Fats and Ca++ ions adhere to
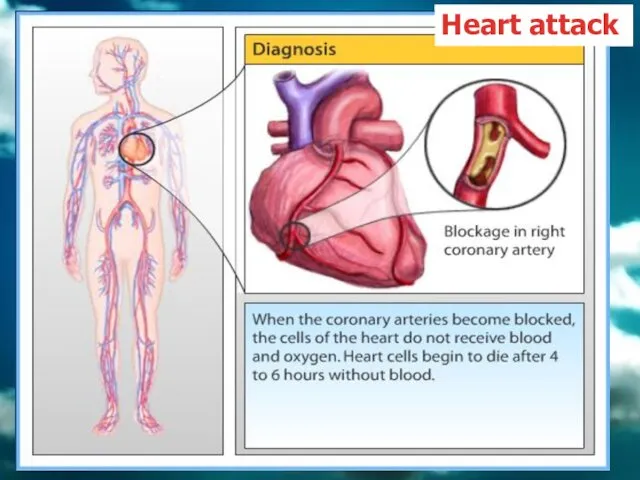
- 74. Heart attack
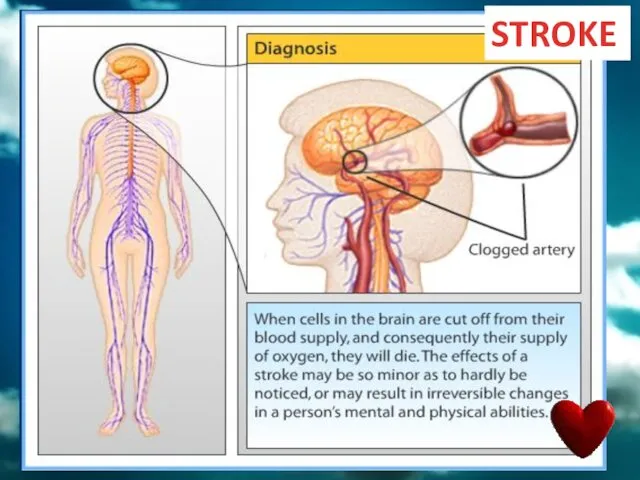
- 75. STROKE
- 76. TRUE or FALSE Open circulatory system is a characteristic for vertebrates. FALSE Red blood cells are
- 77. Hemoglobin is carbohydrate FALSE The right sides of the heart have oxygenated blood and left sides
- 78. Fill in the blanks ………... Is placed in the chest cavity between lungs, it has four
- 79. Cardiovascular system Duration 3 week (3x2=6 hours) The function of cardiovascular system Human cardiovascular system Heart
- 80. LEARNING OBJECTIVES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AFTER THE STUDENTS HAVE STUDIED THESE SUBJECTS THEY SHOULD BE
- 82. Скачать презентацию




































 Влияние физических факторов на микроорганизмы
Влияние физических факторов на микроорганизмы Артерии большого и малого круга кровообращения
Артерии большого и малого круга кровообращения презентация Цветок
презентация Цветок Организменный уровень жизни, его роль в природе
Организменный уровень жизни, его роль в природе Термин популяция
Термин популяция Кишечнополостные. Губки
Кишечнополостные. Губки Видоизменения листьев
Видоизменения листьев МАТЕМАТИКА и БИОЛОГИЯ ... НА КУХНЕ?
МАТЕМАТИКА и БИОЛОГИЯ ... НА КУХНЕ? Класс Паукообразные. Паукообразные, как и насекомые
Класс Паукообразные. Паукообразные, как и насекомые Способы размножения животных
Способы размножения животных Механизмы влияния гуминовых препаратов на физиолого-биохимические процессы, происходящие в растениях
Механизмы влияния гуминовых препаратов на физиолого-биохимические процессы, происходящие в растениях Комнатные растения (часть 2)
Комнатные растения (часть 2) Рослини і тварини Сумщини занесені до Червоної книги України
Рослини і тварини Сумщини занесені до Червоної книги України 20231130_8_klass_ptitsy._obshchie_priznaki._osobennosti_stroeniya._1
20231130_8_klass_ptitsy._obshchie_priznaki._osobennosti_stroeniya._1 Световая микроскопия. Занятие 1
Световая микроскопия. Занятие 1 Пищевые связи в сообществе
Пищевые связи в сообществе Митохондрия
Митохондрия Женская половая система. (Часть 3)
Женская половая система. (Часть 3) Группы крови. Переливание крови.
Группы крови. Переливание крови. Жабы и лягушки. 2 класс
Жабы и лягушки. 2 класс Законы зависимости организмов от факторов среды
Законы зависимости организмов от факторов среды Периферическая нервная система животных
Периферическая нервная система животных Семейство растений яснотковые
Семейство растений яснотковые В гости к весне (окружающий мир, 2 класс)
В гости к весне (окружающий мир, 2 класс) Лесные жители
Лесные жители Мышечная ткань
Мышечная ткань Размножение многоклеточных животных
Размножение многоклеточных животных Модификационная изменчивость
Модификационная изменчивость