Содержание
- 2. Skeletal System Skeletal system is the supportive and protective system of organisms There 2 types of
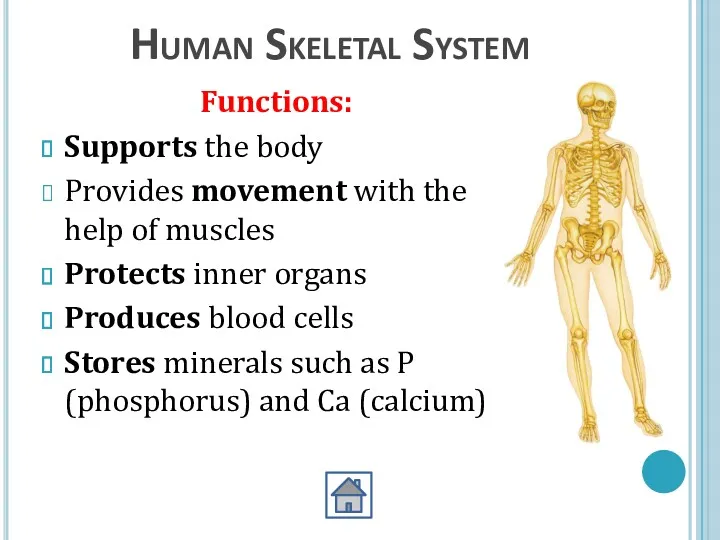
- 3. Human Skeletal System Functions: Supports the body Provides movement with the help of muscles Protects inner
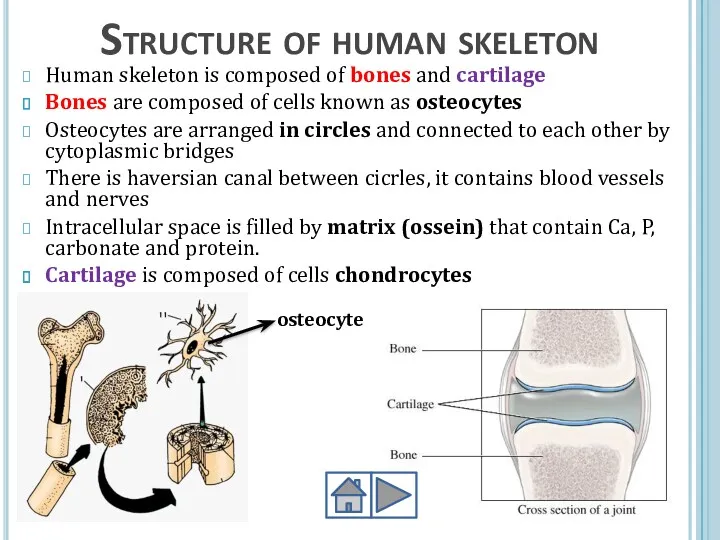
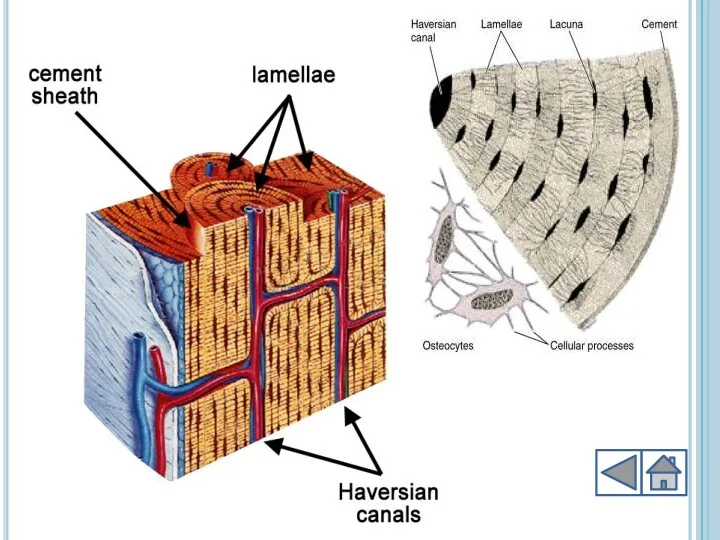
- 4. Structure of human skeleton Human skeleton is composed of bones and cartilage Bones are composed of
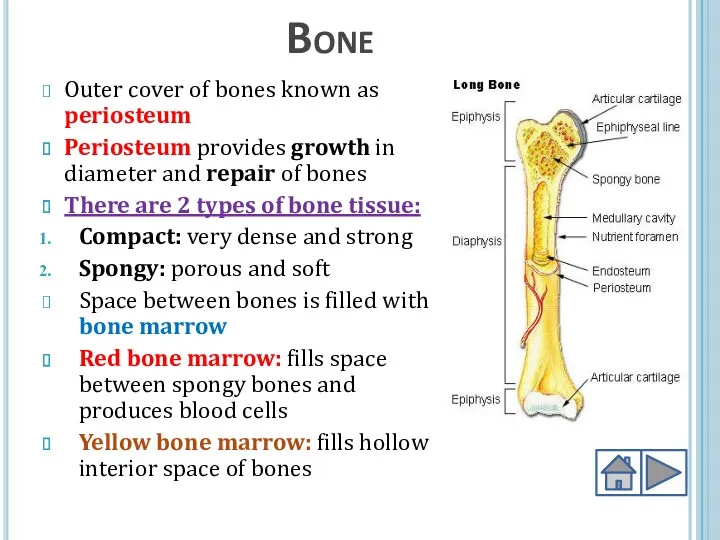
- 6. Bone Outer cover of bones known as periosteum Periosteum provides growth in diameter and repair of
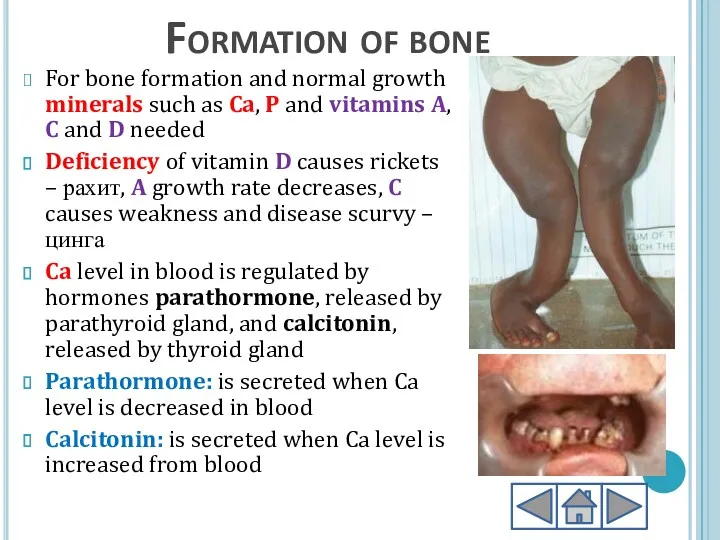
- 7. Formation of bone For bone formation and normal growth minerals such as Ca, P and vitamins
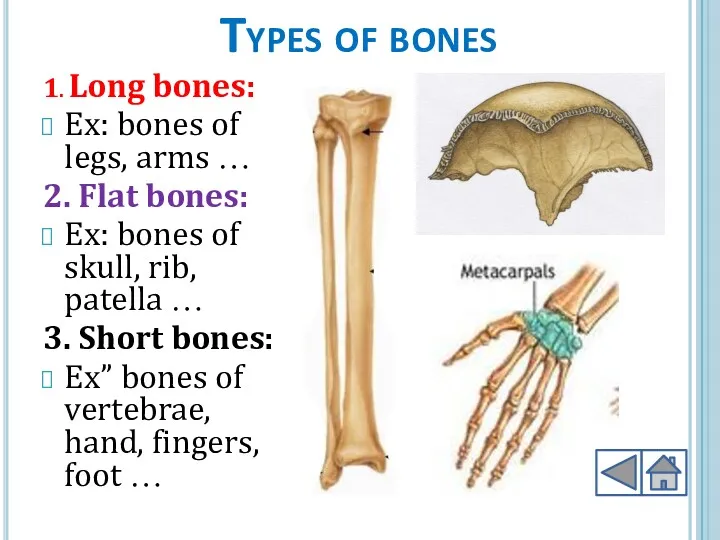
- 8. Types of bones 1. Long bones: Ex: bones of legs, arms … 2. Flat bones: Ex:
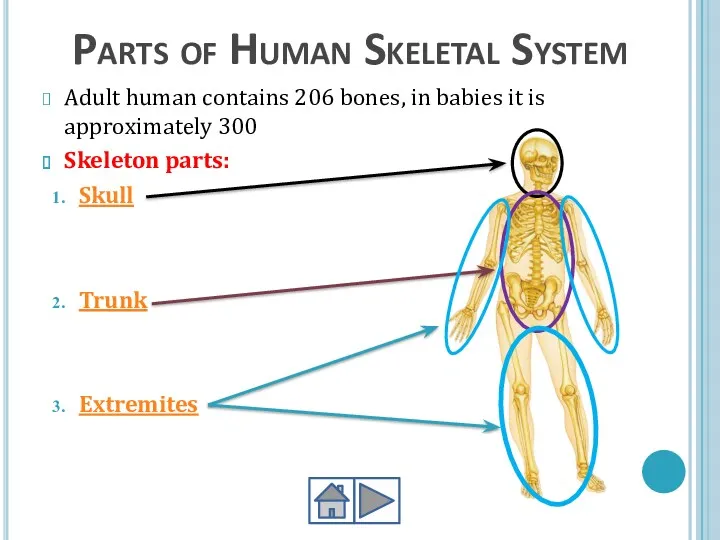
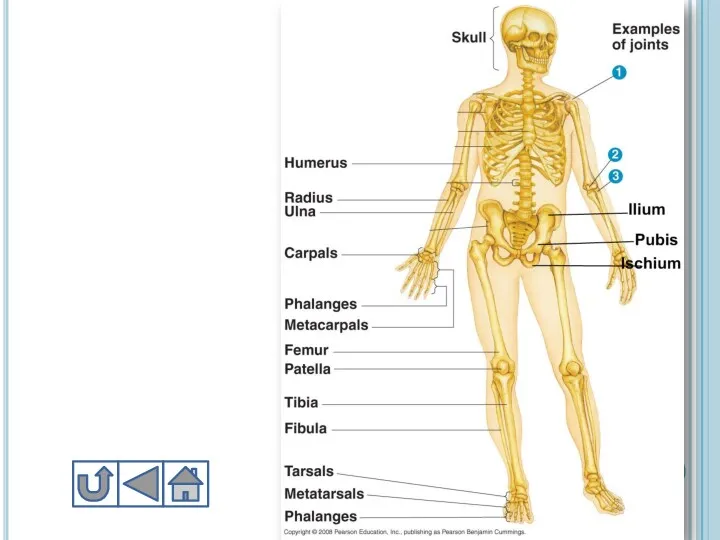
- 9. Parts of Human Skeletal System Adult human contains 206 bones, in babies it is approximately 300
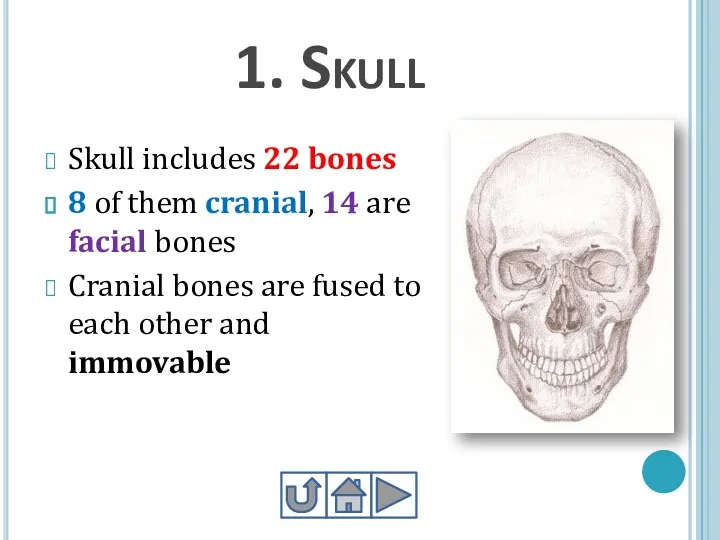
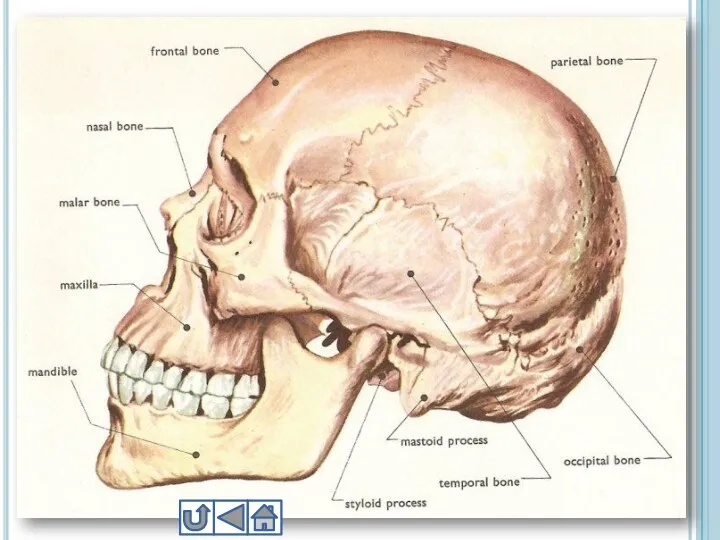
- 10. 1. Skull Skull includes 22 bones 8 of them cranial, 14 are facial bones Cranial bones
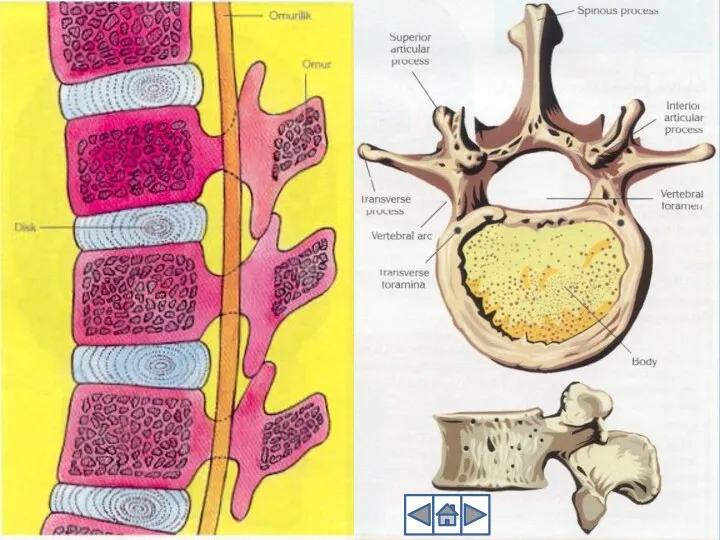
- 12. 2. Trunk Trunk includes vertebral column, ribs, sternum, pelvic girdle and pectoral girdle Vertebral column: Vertebral
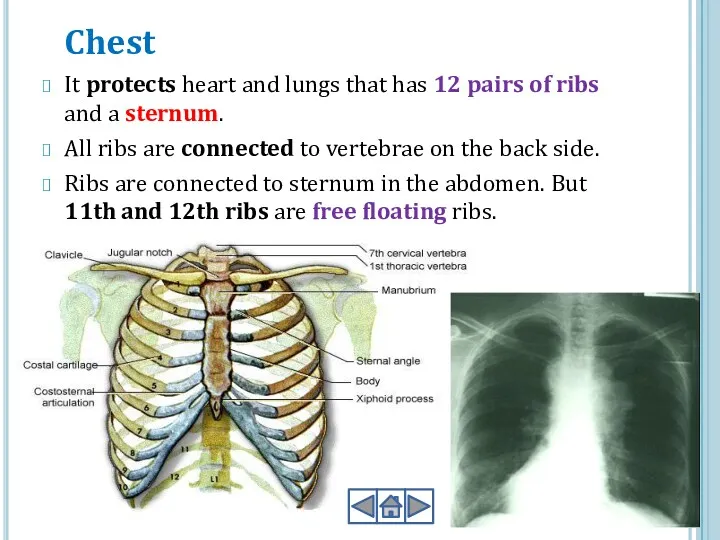
- 14. Chest It protects heart and lungs that has 12 pairs of ribs and a sternum. All
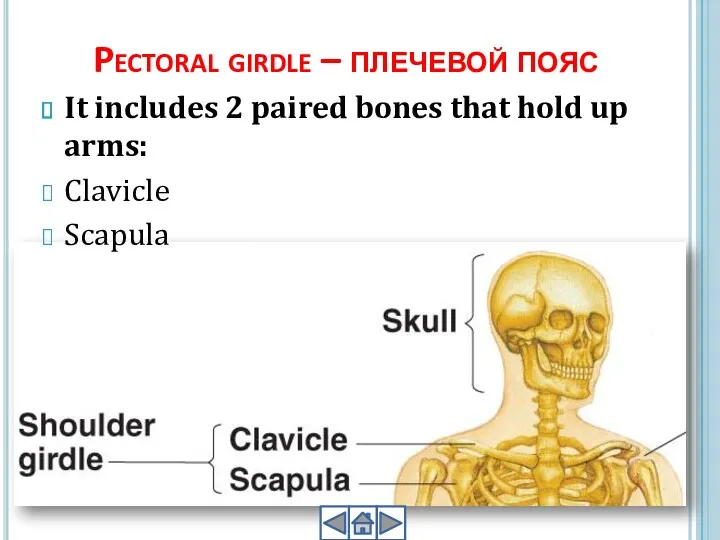
- 15. Pectoral girdle – плечевой пояс It includes 2 paired bones that hold up arms: Clavicle Scapula
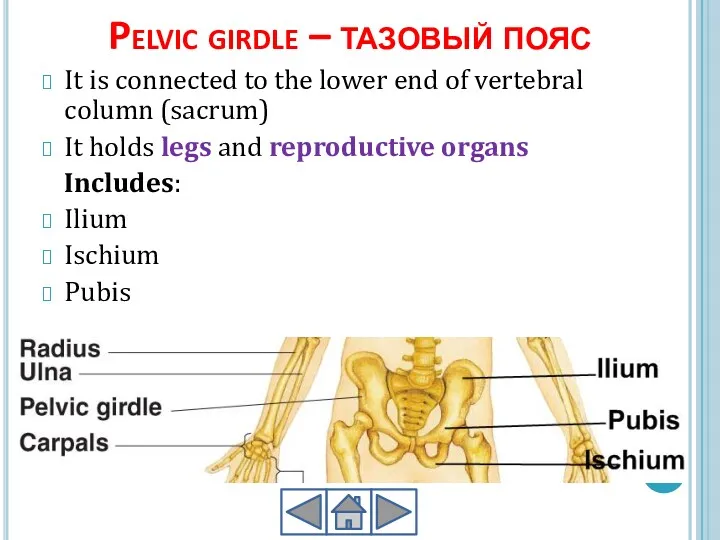
- 16. Pelvic girdle – тазовый пояс It is connected to the lower end of vertebral column (sacrum)
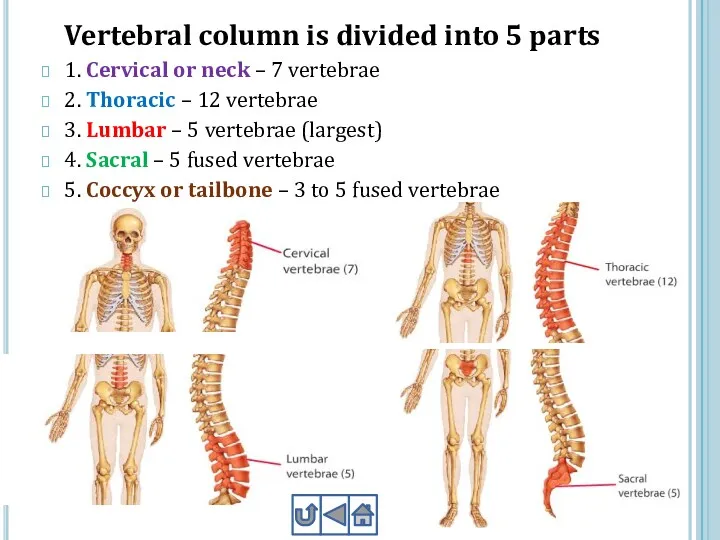
- 17. Vertebral column is divided into 5 parts 1. Cervical or neck – 7 vertebrae 2. Thoracic
- 18. 3. Extremites - конечности Extremites in other words appendages include upper extremites and lower extremites a.
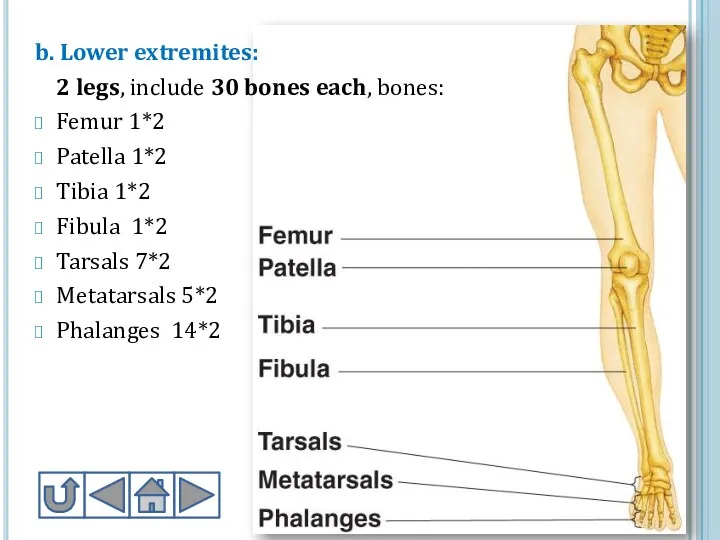
- 19. b. Lower extremites: 2 legs, include 30 bones each, bones: Femur 1*2 Patella 1*2 Tibia 1*2
- 21. Joints Joint forms the junction between two or more bones There are three types of joints;
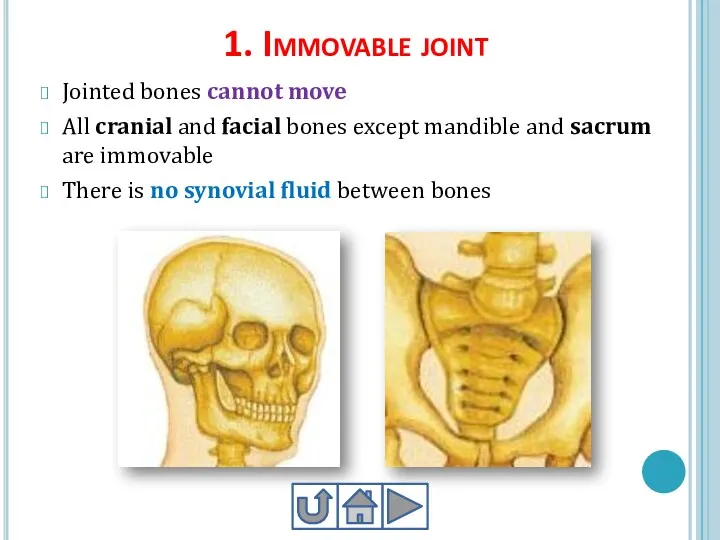
- 22. 1. Immovable joint Jointed bones cannot move All cranial and facial bones except mandible and sacrum
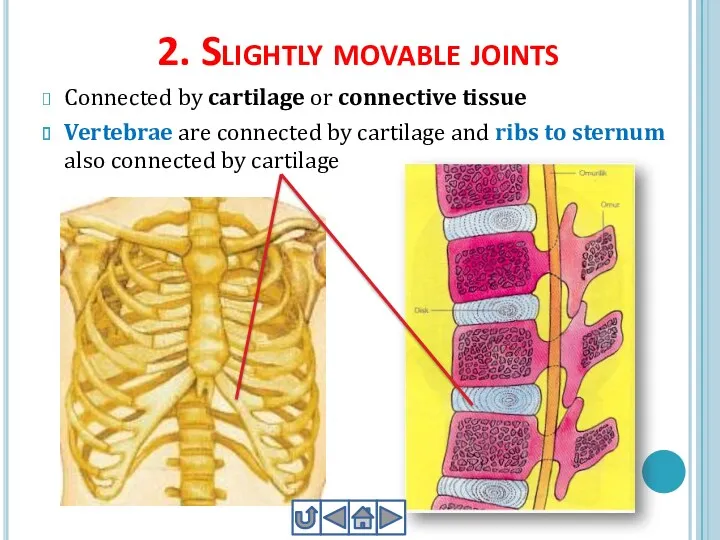
- 23. 2. Slightly movable joints Connected by cartilage or connective tissue Vertebrae are connected by cartilage and
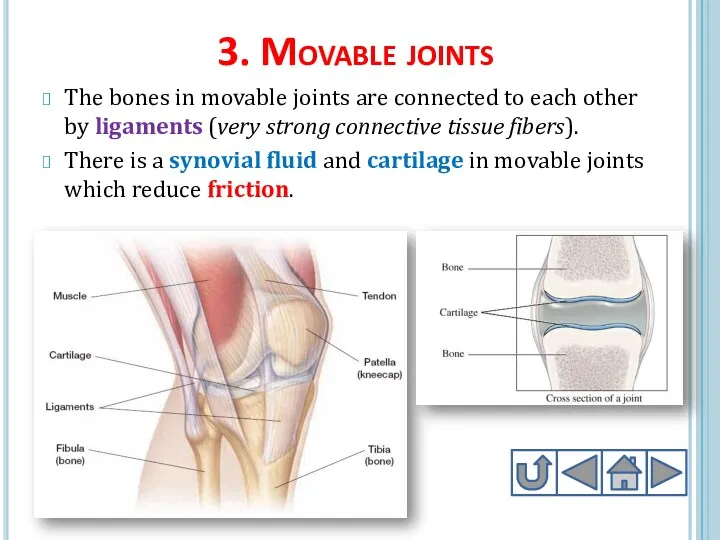
- 24. 3. Movable joints The bones in movable joints are connected to each other by ligaments (very
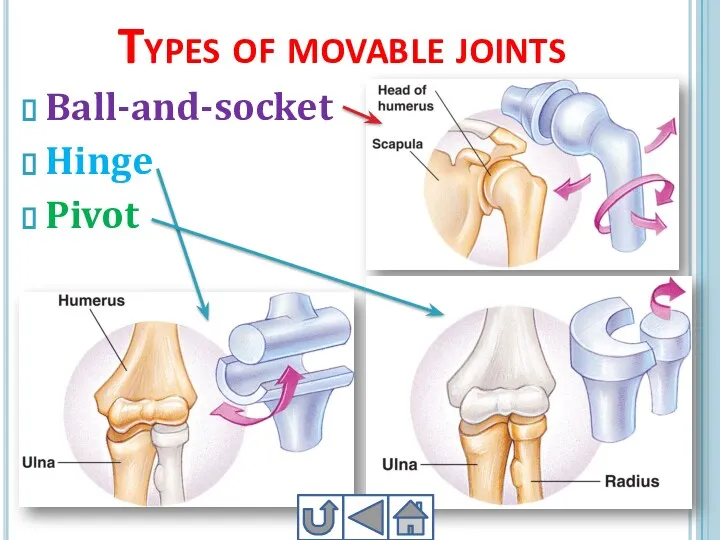
- 25. Types of movable joints Ball-and-socket Hinge Pivot
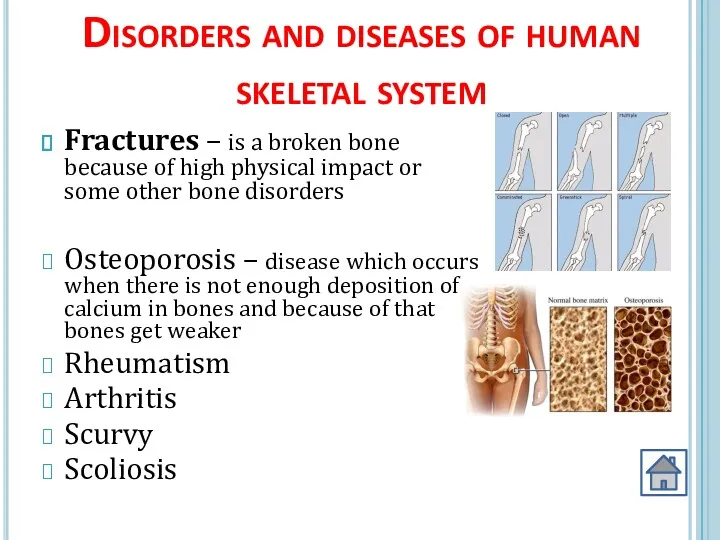
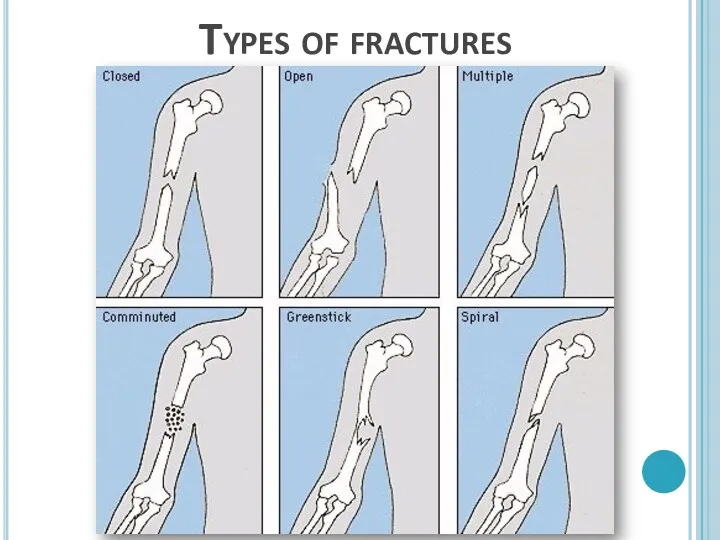
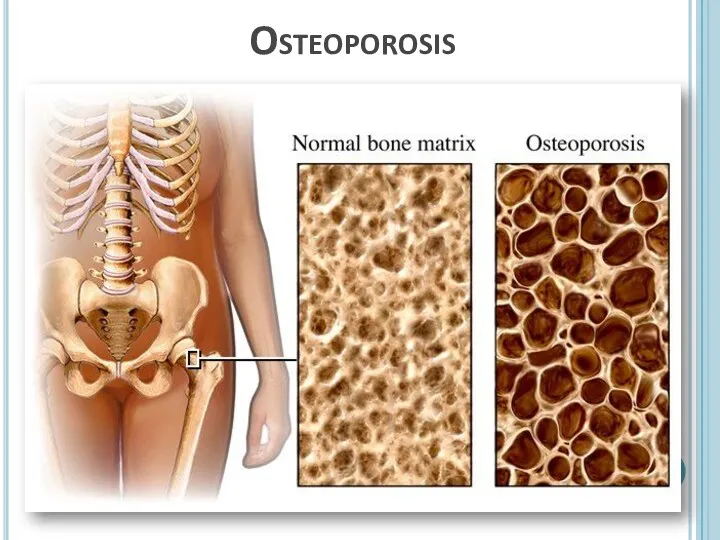
- 26. Disorders and diseases of human skeletal system Fractures – is a broken bone because of high
- 27. Types of fractures
- 28. Osteoporosis
- 29. Muscular system Muscular system helps in the movement of body, inner organs and also helps in
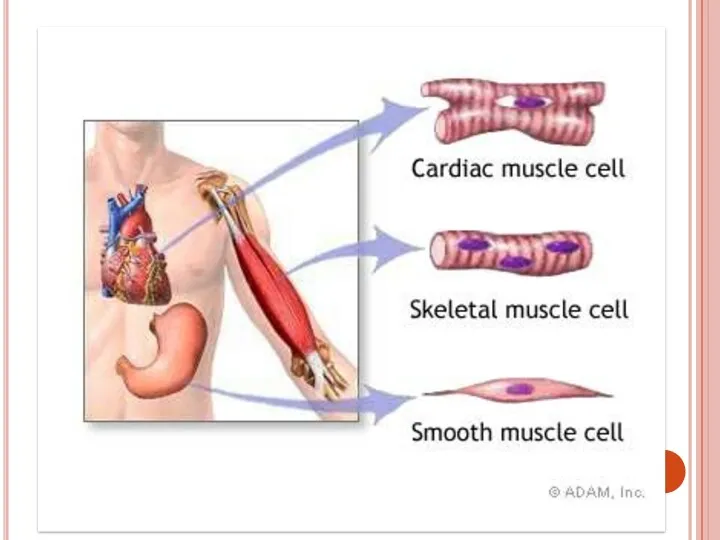
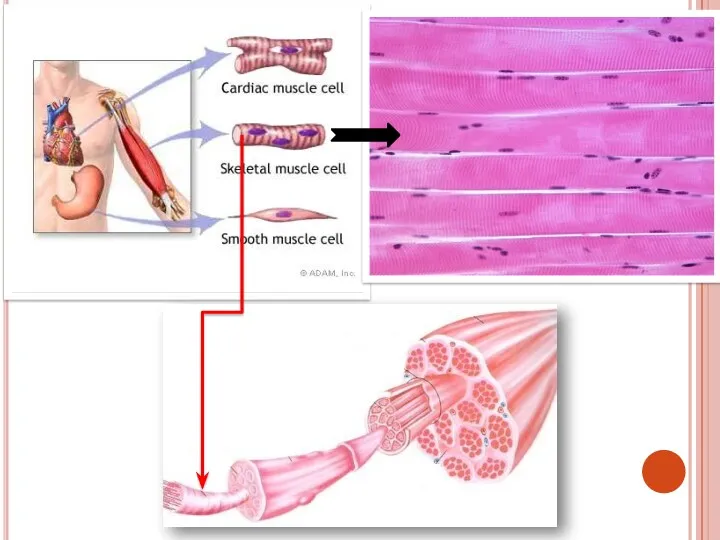
- 31. Types of muscular tissue There are 3 types of muscular tissue, they are: Smooth muscle Skeletal
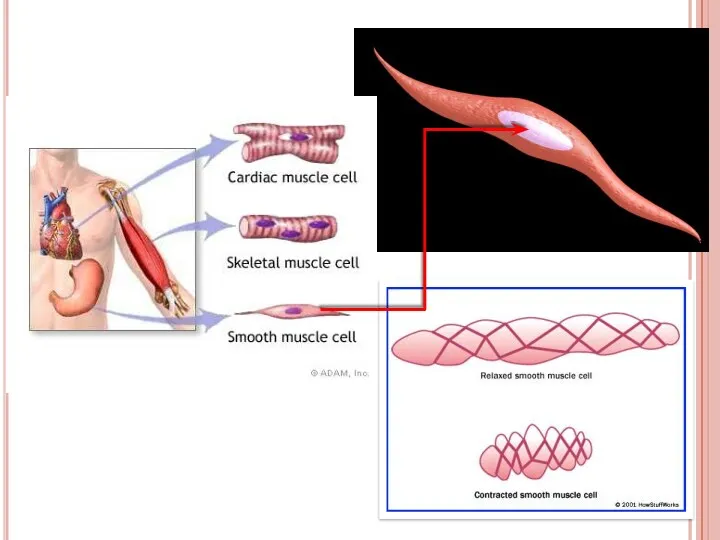
- 33. 1. Smooth muscle Each cell is long, sharp-ended with a single central nucleus Smooth muscles generally
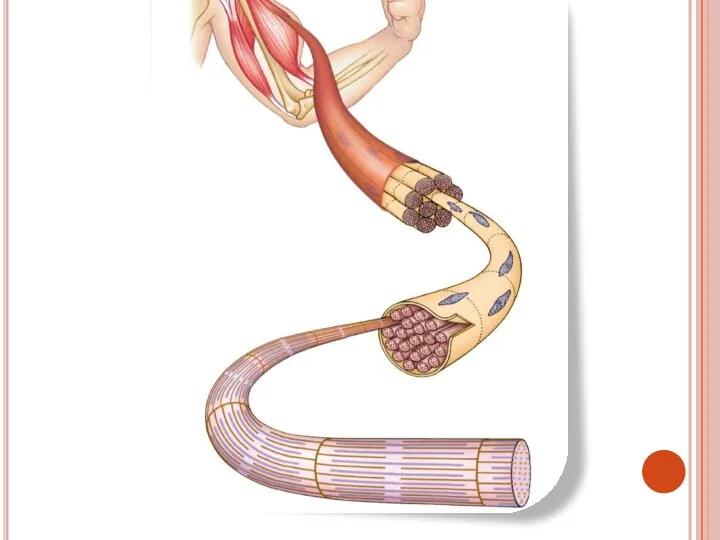
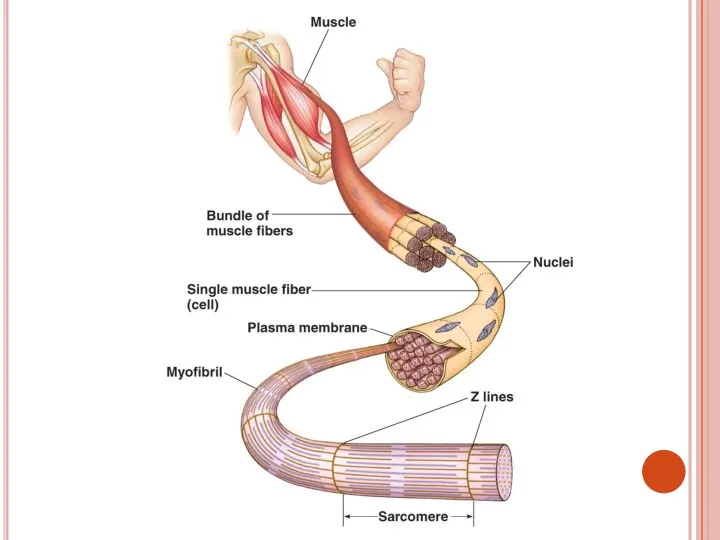
- 35. 2.Skeletal or striated muscle Cells are long, cylindrical and multinuclear, i.e. have many nucleuses They are
- 37. Skeletal muscles cover the skeleton They provide movement of skeleton and by that body It is
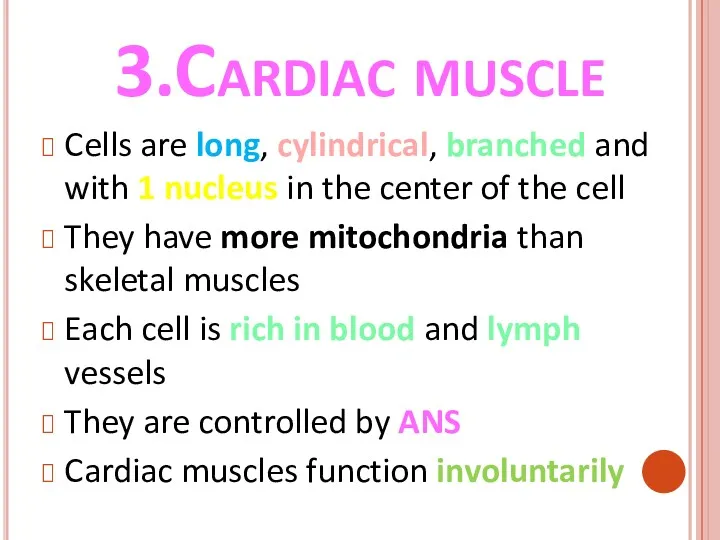
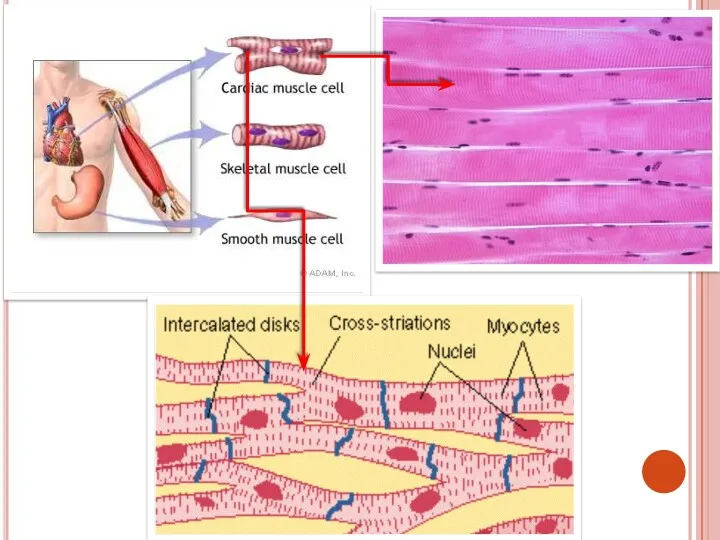
- 39. 3.Cardiac muscle Cells are long, cylindrical, branched and with 1 nucleus in the center of the
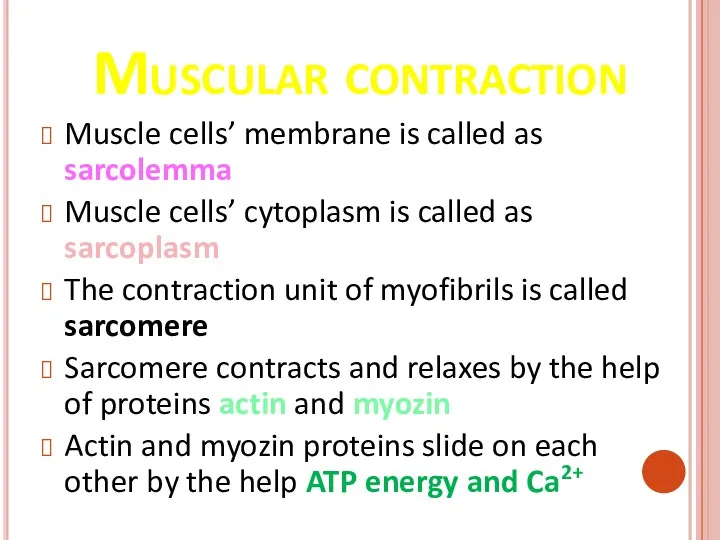
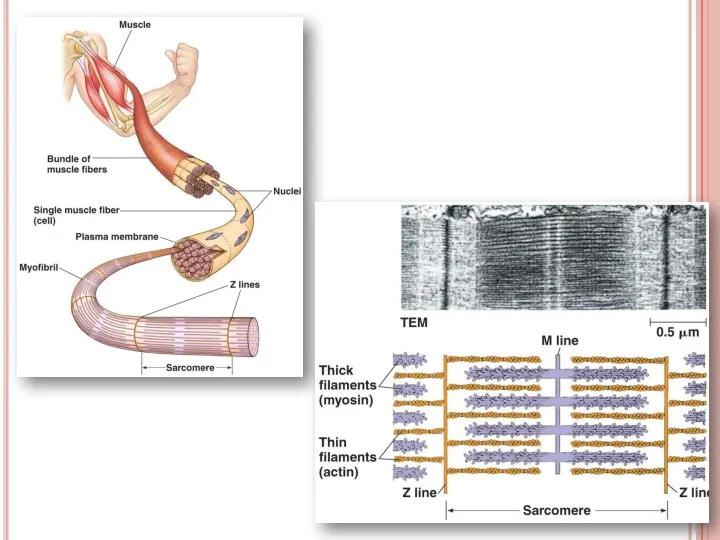
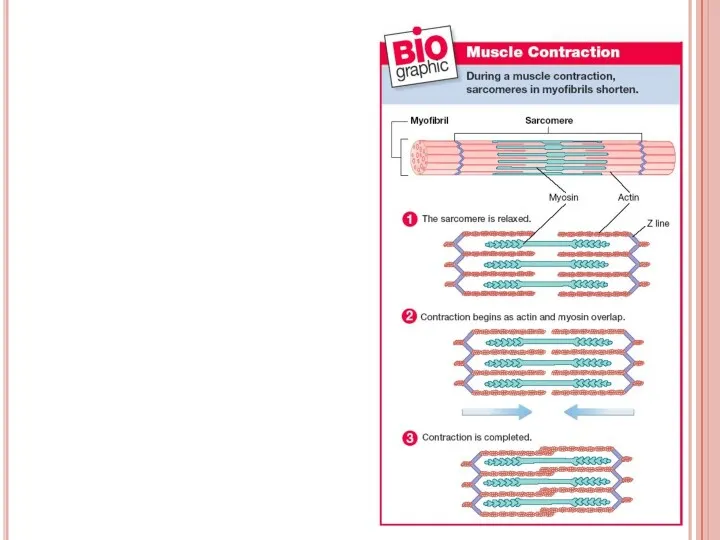
- 41. Muscular contraction Muscle cells’ membrane is called as sarcolemma Muscle cells’ cytoplasm is called as sarcoplasm
- 45. Скачать презентацию








 Основные методы селекции животных
Основные методы селекции животных Рефлекторный принцип деятельности ЦНС. Возбуждение и торможение. Функции нейронов и нейроглии. Физиология рецепторов
Рефлекторный принцип деятельности ЦНС. Возбуждение и торможение. Функции нейронов и нейроглии. Физиология рецепторов Презентация к уроку биологии в 9 классе Развитие жизни на Земле
Презентация к уроку биологии в 9 классе Развитие жизни на Земле Болезни овощей и фруктов
Болезни овощей и фруктов Всероссийская акция Серая шейка
Всероссийская акция Серая шейка Основные особенности растительной клетки
Основные особенности растительной клетки Заказник Урочище Берикпара, Южный Алтай
Заказник Урочище Берикпара, Южный Алтай Выделение у животных
Выделение у животных Тип членистоногие
Тип членистоногие Традиційна біотехнологія
Традиційна біотехнологія Атлас млекопитающих Москвы и Подмосковья
Атлас млекопитающих Москвы и Подмосковья Презентация к уроку Папоротникообразные .
Презентация к уроку Папоротникообразные . Дикие животные наших лесов
Дикие животные наших лесов Плаун тәрізділер бөлімі
Плаун тәрізділер бөлімі Отличие человека от животного
Отличие человека от животного Растительный белок: свойства, факты, источники
Растительный белок: свойства, факты, источники Әр түрлі мөлшердегі минералды тыңайтқыштардың қант қызылшасының өнімділігіне әсерін анықтау барысындағы суреттер
Әр түрлі мөлшердегі минералды тыңайтқыштардың қант қызылшасының өнімділігіне әсерін анықтау барысындағы суреттер Общие признаки животных
Общие признаки животных Как классифицируют живые организмы
Как классифицируют живые организмы Основы молекулярной генетики
Основы молекулярной генетики Как появился человек на Земле
Как появился человек на Земле Системная биология: предмет, инструменты, экспериментальные методы
Системная биология: предмет, инструменты, экспериментальные методы Белки. Функции белков
Белки. Функции белков Птицы. Отряд воробьинообразные
Птицы. Отряд воробьинообразные Презентация Моллюски
Презентация Моллюски Лист. Внешнее и внутреннее строение листа
Лист. Внешнее и внутреннее строение листа Carbohydrate Metabolism I: Aerobic oxidation of glucose. Anaerobic Glycolysis. Gluconeogenesis
Carbohydrate Metabolism I: Aerobic oxidation of glucose. Anaerobic Glycolysis. Gluconeogenesis Строение клетки
Строение клетки