Содержание
- 2. Функции соединительных тканей 1. Опорная (капсулы органов, сухожилии, фасции, скелет) 2. Трофическая (обмен веществ между кровью
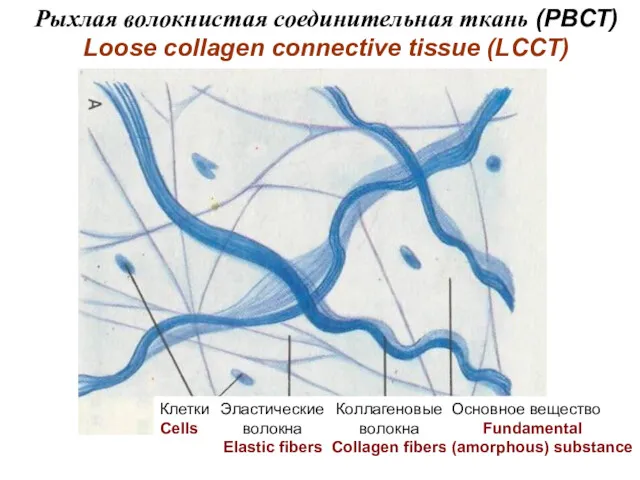
- 3. Рыхлая волокнистая соединительная ткань (РВСТ) Loose collagen connective tissue (LCCT) Клетки Cells Эластические волокна Elastic fibers
- 4. The fundamental (amorphous) substance – a gel colloid system from water, salts and organic substances: glycoproteins,
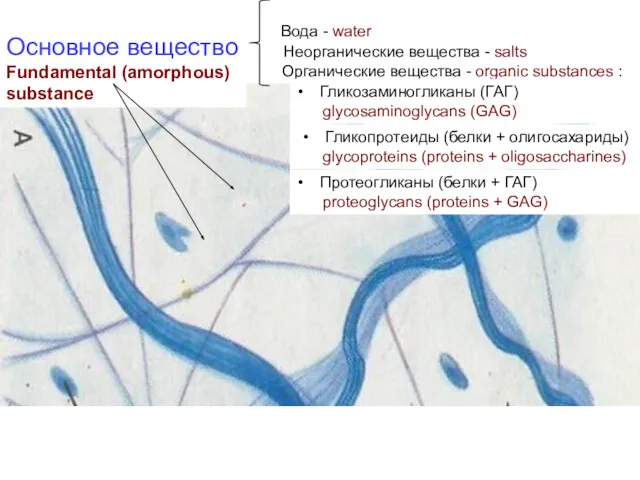
- 5. Основное вещество Fundamental (amorphous) substance Неорганические вещества - salts Вода - water Органические вещества - organic
- 6. 1 группа – хондроитинсульфаты А,В,С 2 группа – дерматансульфаты 3 группа – кератансульфаты 4 группа –
- 7. Hyaluronic acid is hydrophilic, well connects water, stimulates a metabolism, phagocytosis, duplication and mobility of cells.
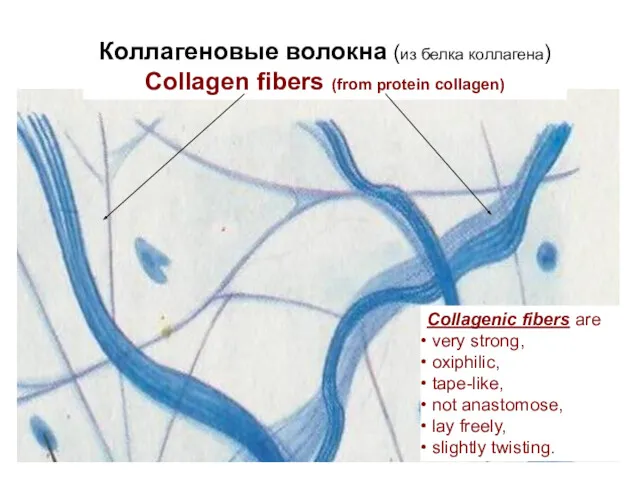
- 8. Коллагеновые волокна (из белка коллагена) Collagen fibers (from protein collagen) Collagenic fibers are very strong, oxiphilic,
- 9. Collagenic fibers are constructed of tropocollagen-protein which consists of triplets of amino-acids - in each triplet
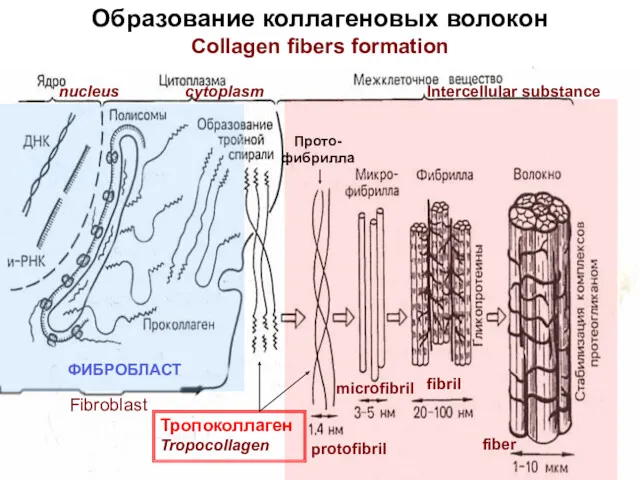
- 10. ФИБРОБЛАСТ Тропоколлаген Tropocollagen Прото- фибрилла Образование коллагеновых волокон Collagen fibers formation Fibroblast nucleus cytoplasm Intercellular substance
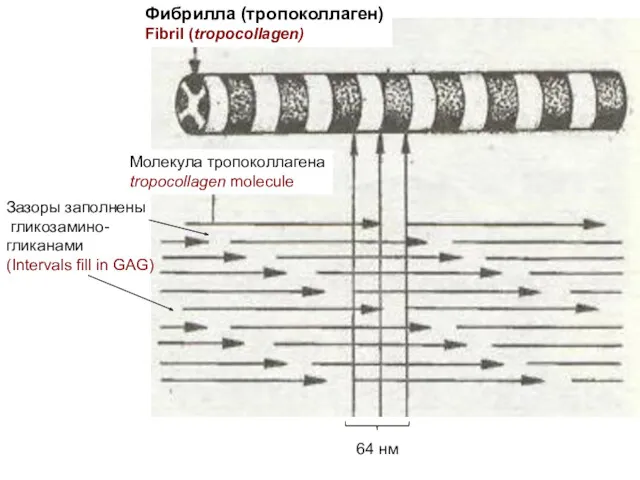
- 11. Фибрилла (тропоколлаген) Fibril (tropocollagen) Молекула тропоколлагена tropocollagen molecule Зазоры заполнены гликозамино- гликанами (Intervals fill in GAG)
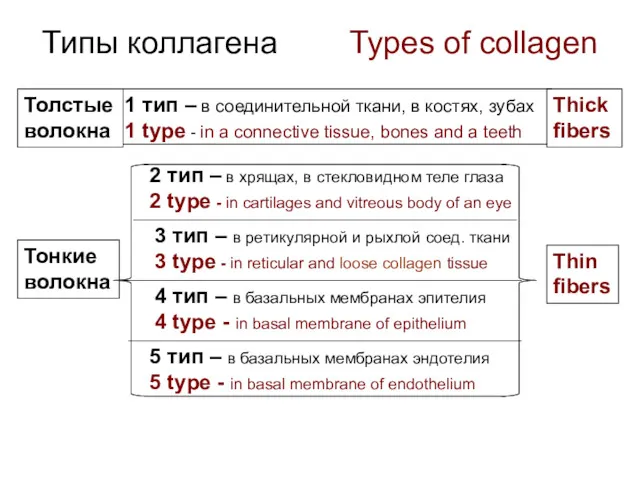
- 12. Типы коллагена Types of collagen 1 тип – в соединительной ткани, в костях, зубах 1 type
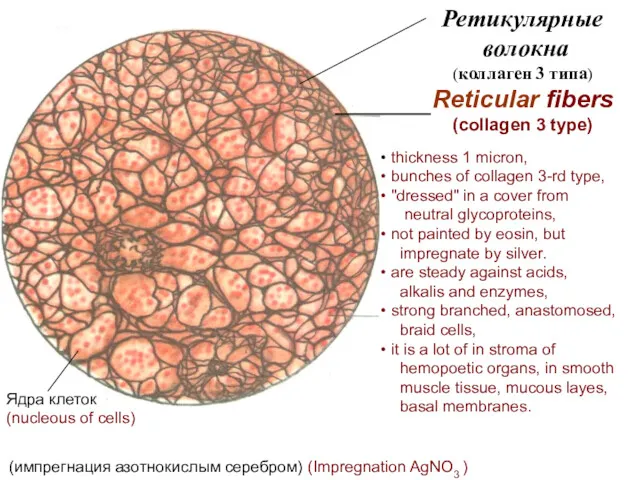
- 13. Ретикулярные волокна (коллаген 3 типа) Reticular fibers (collagen 3 type) Ядра клеток (nucleous of cells) (импрегнация
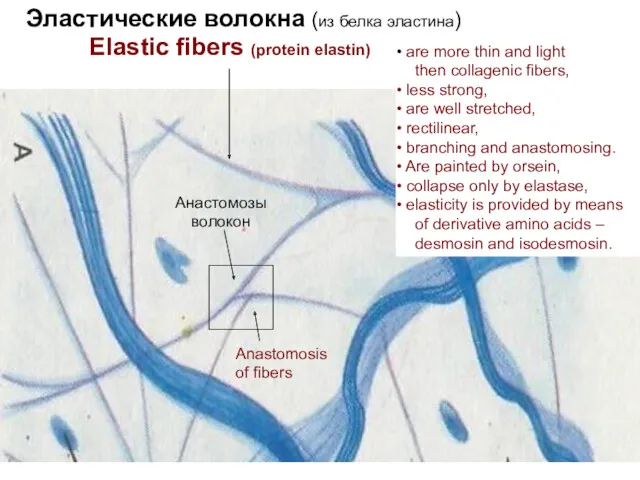
- 14. Эластические волокна (из белка эластина) Анастомозы волокон Elastic fibers (protein elastin) Anastomosis of fibers are more
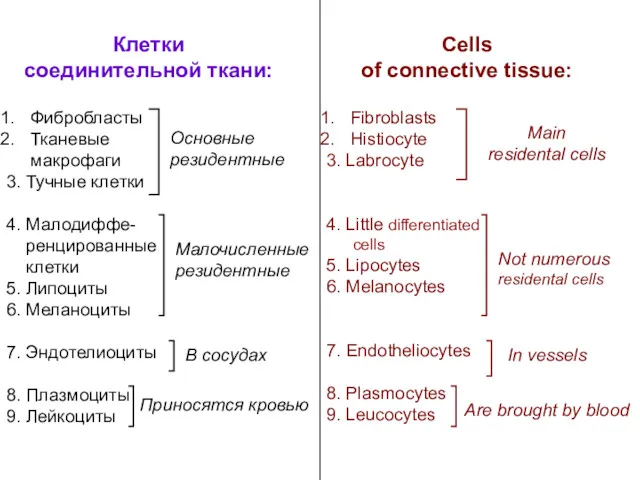
- 15. Клетки соединительной ткани: Фибробласты Тканевые макрофаги 3. Тучные клетки 4. Малодиффе- ренцированные клетки 5. Липоциты 6.
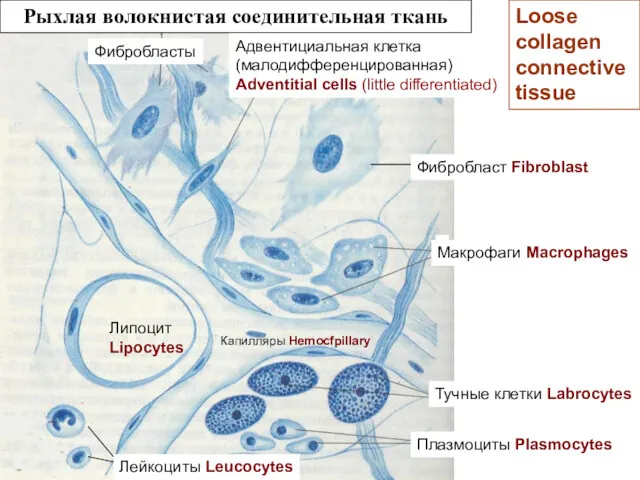
- 16. Рыхлая волокнистая соединительная ткань Тучные клетки Labrocytes Липоцит Lipocytes Плазмоциты Plasmocytes Лейкоциты Leucocytes Капилляры Hemocfpillary Адвентициальная
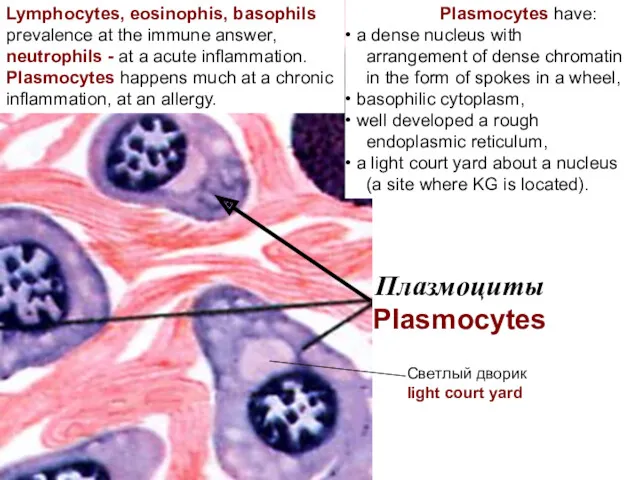
- 17. Плазмоциты Plasmocytes Светлый дворик light court yard Lymphocytes, eosinophis, basophils prevalence at the immune answer, neutrophils
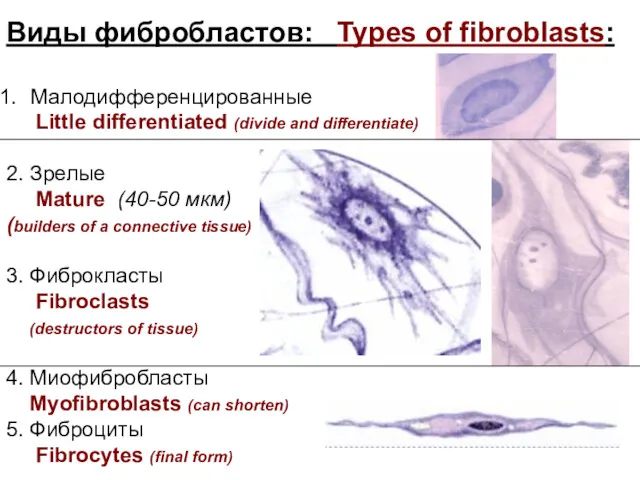
- 18. Виды фибробластов: Types of fibroblasts: Малодифференцированные Little differentiated (divide and differentiate) 2. Зрелые Mature (40-50 мкм)
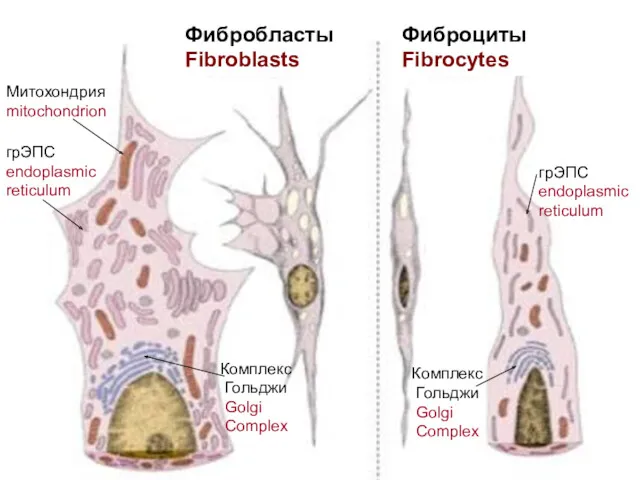
- 19. Фибробласты Fibroblasts Фиброциты Fibrocytes Митохондрия mitochondrion грЭПС endoplasmic reticulum Комплекс Гольджи Golgi Complex Комплекс Гольджи Golgi
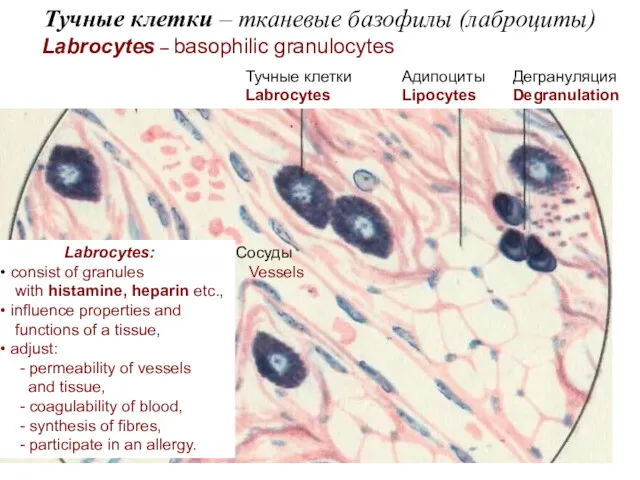
- 20. Тучные клетки – тканевые базофилы (лаброциты) Labrocytes – basophilic granulocytes Тучные клетки Labrocytes Адипоциты Lipocytes Дегрануляция
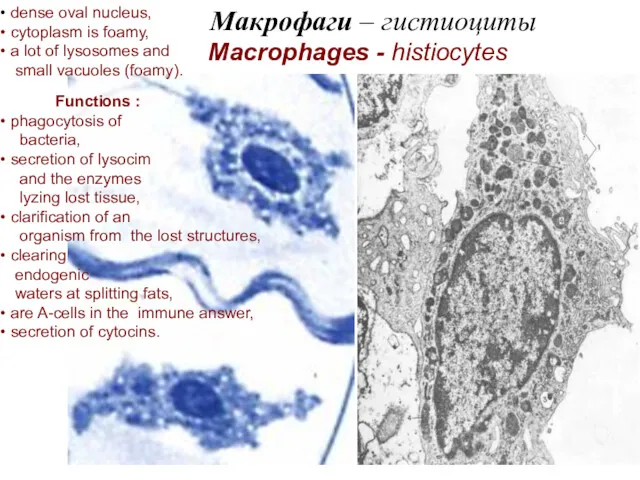
- 21. Макрофаги – гистиоциты Macrophages - histiocytes dense oval nucleus, cytoplasm is foamy, a lot of lysosomes
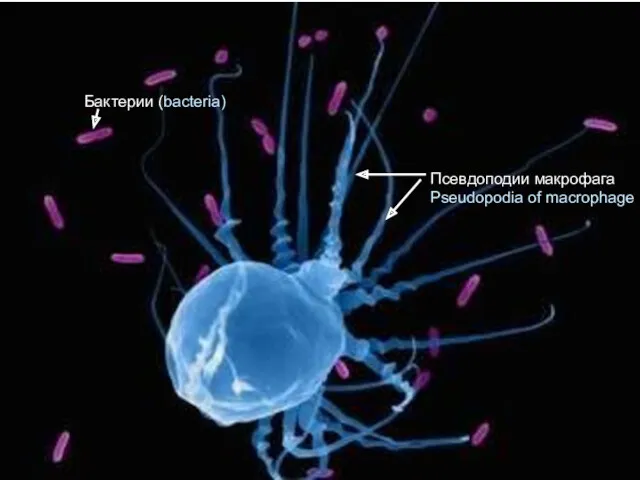
- 22. Бактерии (bacteria) Псевдоподии макрофага Pseudopodia of macrophage
- 23. Мононуклеарная фагоцитарная система Гистиоциты Альвеолярные макрофаги лёгких Звёздчатые клетки Купфера печени Береговые клетки лимфоузлов Макрофаги ретикулярной
- 25. Скачать презентацию






 Female culex
Female culex Гели косметические
Гели косметические Поле и его обитатели
Поле и его обитатели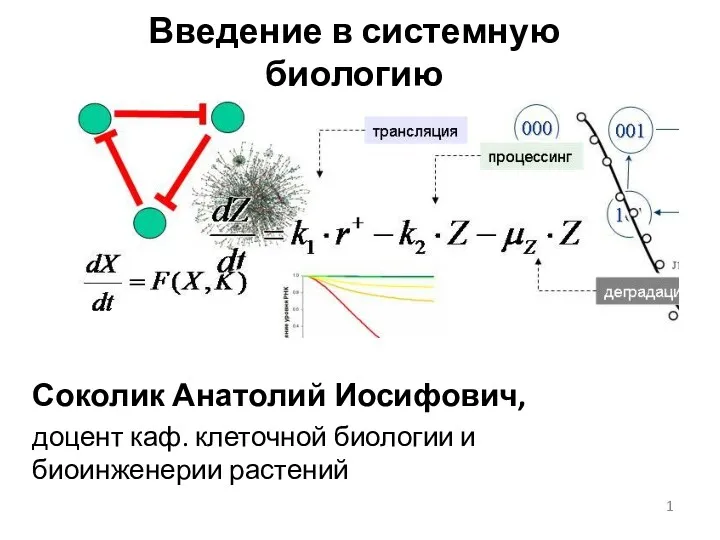 Особенности экспериментальных данных в биологии, применение математических методов, технологий
Особенности экспериментальных данных в биологии, применение математических методов, технологий Пищеварение в толстом кишечнике, Физиология печени, Всасывание, Пищевое поведение
Пищеварение в толстом кишечнике, Физиология печени, Всасывание, Пищевое поведение Термодинамика биологических процессов(new)
Термодинамика биологических процессов(new) Витамины: Мал золотник, да дорог
Витамины: Мал золотник, да дорог Двойное оплодотворение у цветковых растений
Двойное оплодотворение у цветковых растений Тварини - частина живої природи
Тварини - частина живої природи Строение и жизненные циклы первичнополостных червей. Тип nematoda
Строение и жизненные циклы первичнополостных червей. Тип nematoda Методы исследования в биологии
Методы исследования в биологии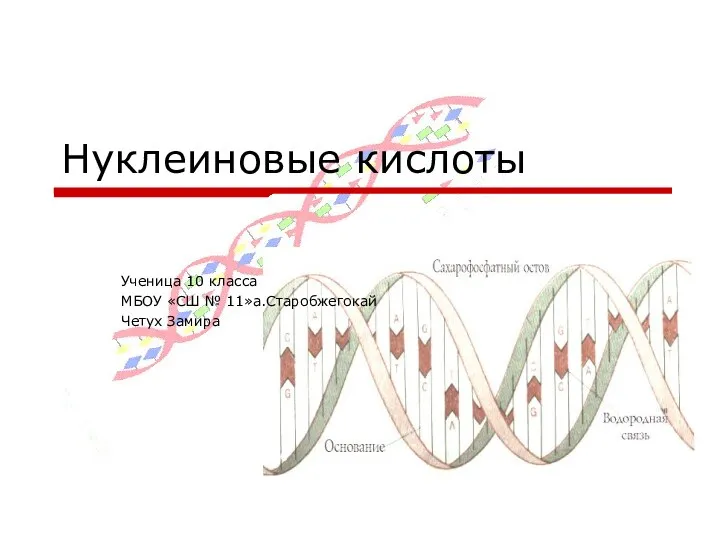 Презентация по биологии ДНК и РНК
Презентация по биологии ДНК и РНК Этапы решения задач по родословной
Этапы решения задач по родословной Cells. Muscle cells
Cells. Muscle cells Развитие опорно-двигательного аппарата
Развитие опорно-двигательного аппарата Бактерии в организме человека
Бактерии в организме человека Сны и сновидения
Сны и сновидения Влияние фитонцидов различных растений на жизнедеятельность колорадского жука
Влияние фитонцидов различных растений на жизнедеятельность колорадского жука Условия, необходимые для прорастания семян
Условия, необходимые для прорастания семян Дәнді дақылдардың вирустық аурулары
Дәнді дақылдардың вирустық аурулары Строение и процессы жизнедеятельности птиц
Строение и процессы жизнедеятельности птиц Огород без химии, или бюджетные удобрения
Огород без химии, или бюджетные удобрения The Link Reaction and Krebs Cycle
The Link Reaction and Krebs Cycle Циклы развития растений
Циклы развития растений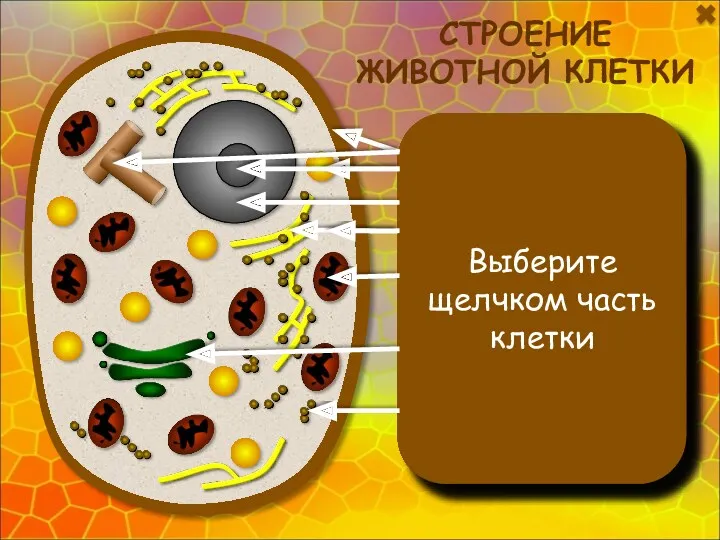 Интерактивная модель по биологии Строение животной клетки для 7 (8) классов
Интерактивная модель по биологии Строение животной клетки для 7 (8) классов Подготовка учащихся к ЕГЭ по биологии
Подготовка учащихся к ЕГЭ по биологии Таксы - охотничья порода собак
Таксы - охотничья порода собак Особенности действия элементарных эволюционных факторов в человеческих популяциях
Особенности действия элементарных эволюционных факторов в человеческих популяциях