Содержание
- 2. GLOBALIZATION Lecture overview 1 Manifestations of Globalization Measuring Globalization Understanding the Global Economy Financial Globalization The
- 3. What is Globalization? 1 Globalization (or globalisation) is the process of international integration arising from the
- 4. Manifestations of Globalization 1 Pros: Supporters of globalization argue that it has the potential to make
- 5. Manifestations of Globalization 1 Pros: 4. It also provides poor countries, through infusions of foreign capital
- 6. Manifestations of Globalization 1 Pros: 9. There is cultural intermingling and each country is learning more
- 7. Manifestations of Globalization 1 Pros: 14. Sharing technology with developing nations will help them progress. True
- 8. Manifestations of Globalization 1 Cons: The general complaint about globalization is that it has made the
- 9. Manifestations of Globalization 1 Cons: • Large multi-national corporations have the ability to exploit tax havens
- 10. Manifestations of Globalization 1 Cons: • Some experts think that globalization is also leading to the
- 11. Manifestations of Globalization 1 • The anti-globalists also claim that globalization is not working for the
- 12. Manifestations of Globalization 1 Some conclusions: Global trends don't affect everybody, in the same way. Global
- 13. 5 Major Manifestations of Globalization: 1 Increased cross-border activity Supra-national organizations and forums (UN, WB, IMF,
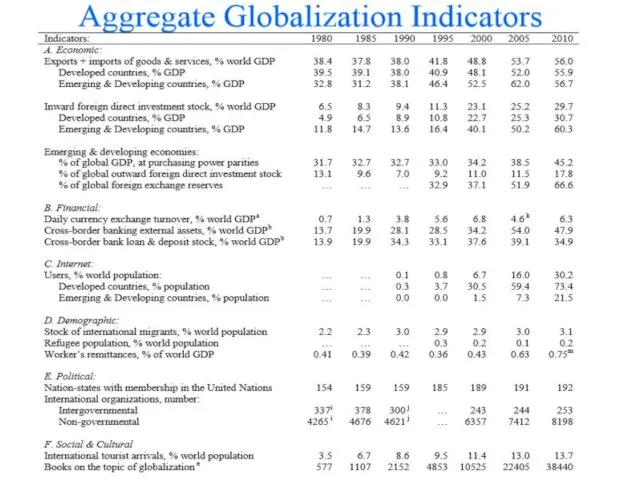
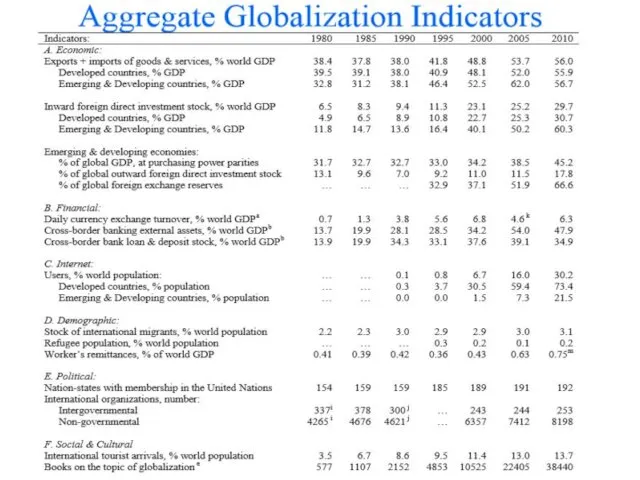
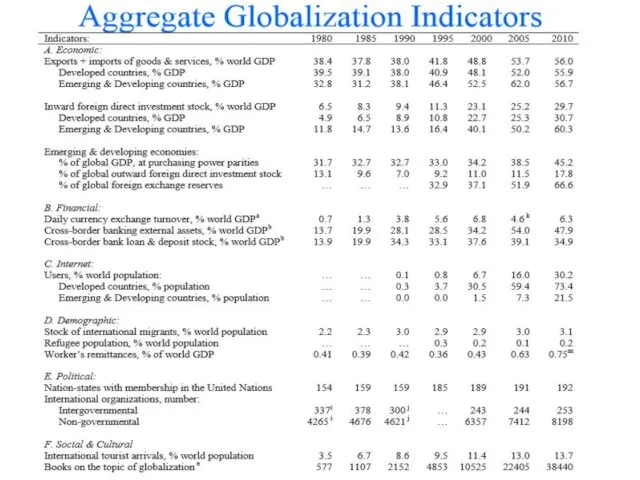
- 14. Measuring Globalization Two Approaches to Measurement: Aggregate indicators, such as level of trade, level of cross
- 15. 2
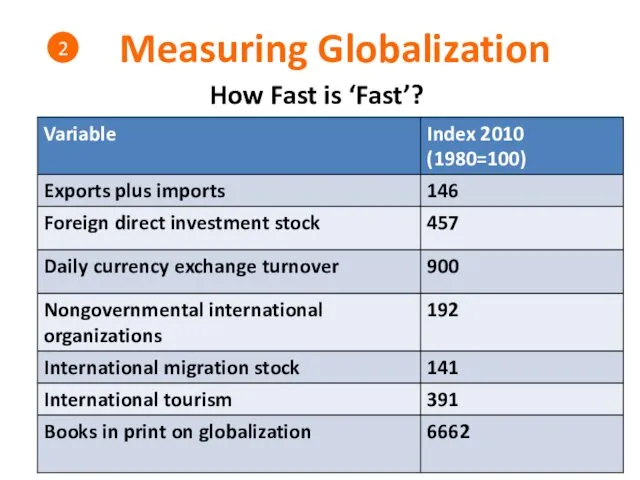
- 16. Measuring Globalization How Fast is ‘Fast’? 2
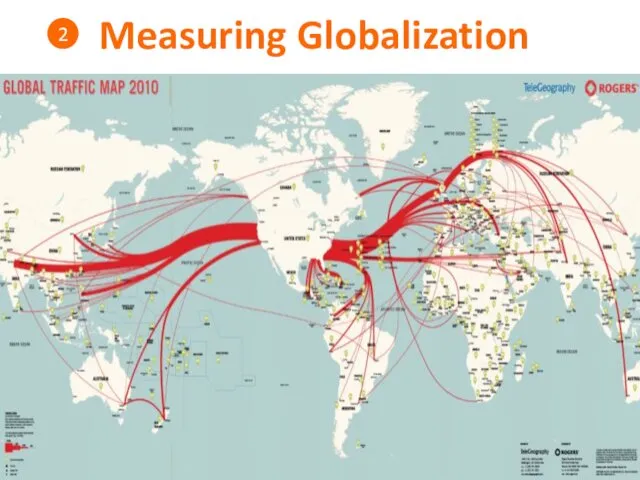
- 17. Measuring Globalization 2
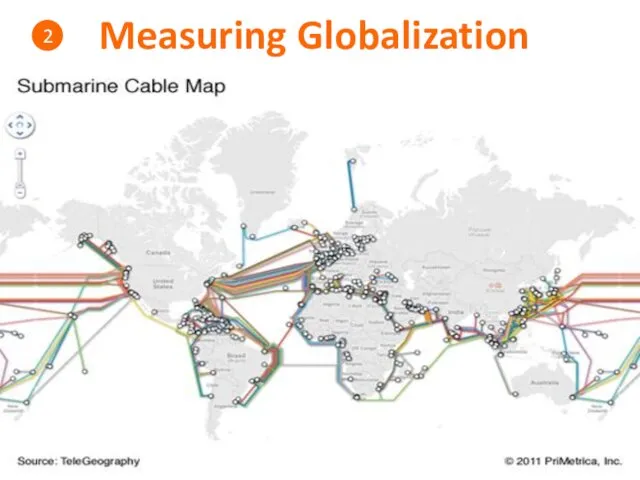
- 18. Measuring Globalization 2
- 19. Measuring Globalization 2 Definitions: Gross Domestic Product: The total value of goods and services produced in
- 20. Measuring Globalization 2 Simple Calculations: Ratio • Ratio: one number divided by another. – Example: The
- 21. Measuring Globalization 2 Simple Calculations: Rate • Rate: is the pace or rhythm at which a
- 22. Measuring Globalization 2 Simple Calculations: Index Number • Index number: reveals the change in a magnitude
- 23. Measuring Globalization 2 Simple Calculations: Proportion • Proportion: A measure of a part with respect to
- 24. Measuring Globalization 2 Large Numbers In this class, we will use the U.S. convention of numbers:
- 25. Understanding the Global Economy 3 To what extent International trade. Foreign investment. Multinational firms. have become
- 26. Understanding the Global Economy 3 International Trade • Cross-border flows of goods & services. • Why
- 27. Understanding the Global Economy 3 Absolute Advantage Theory Adam Smith (“The Wealth of Nations”, 1776) “If
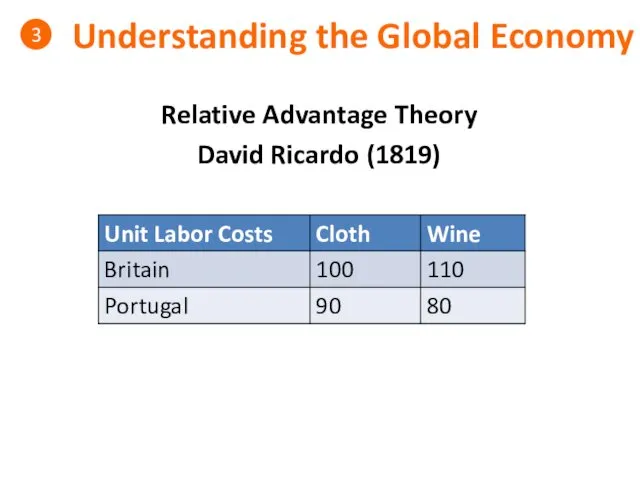
- 28. Understanding the Global Economy 3 Relative Advantage Theory David Ricardo (1819)
- 29. Understanding the Global Economy 3 Other Considerations: • Transportation costs. • Other costs of trade. •
- 30. Understanding the Global Economy 3 Other Considerations: • Transportation costs. • Other costs of trade. •
- 31. 2
- 32. Understanding the Global Economy 3 The Multinational Enterprise (MNE) A company with operations in at least
- 33. Understanding the Global Economy 3 How Important are MNEs? • There are 104,000 MNEs in the
- 34. Understanding the Global Economy 3 Multinationals as “Citizens of the World” “The Tommy Hilfiger Corporation [is]
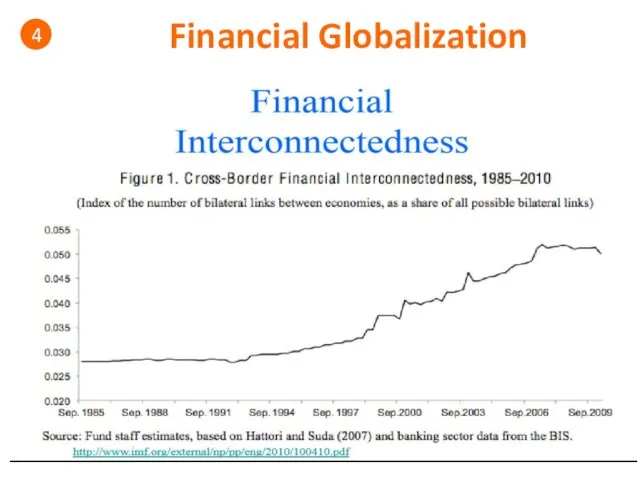
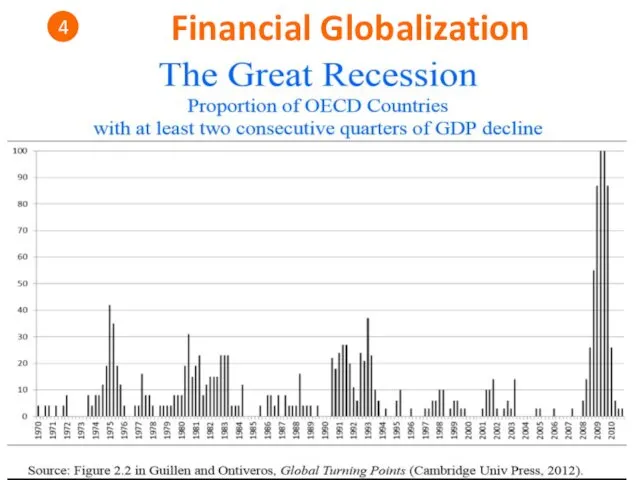
- 35. Financial Globalization 4 Financial globalization & Financial interconnectedness • Foreign portfolio investment - represents passive holdings
- 36. 2
- 37. Financial Globalization 4
- 38. Financial Globalization 4
- 39. Financial Globalization 4
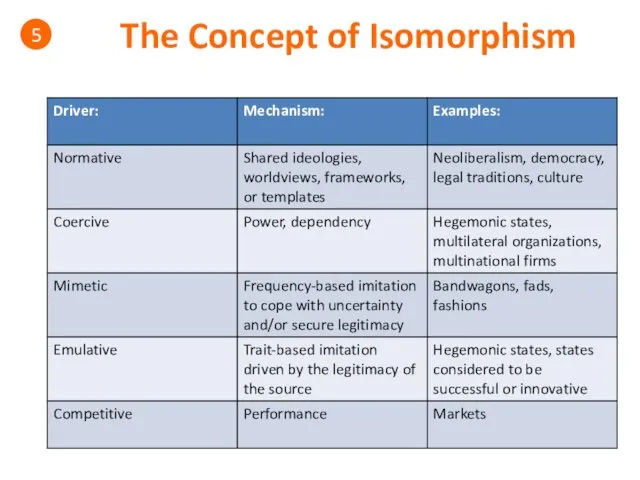
- 40. The Concept of Isomorphism 5 Isomorphism • Is the tendency of actors, organizations or other types
- 41. The Concept of Isomorphism 5 Examples of Isomorphism • The modern nation-state. • The ministry of
- 42. The Concept of Isomorphism 5 Drivers of Isomorphism:
- 43. The Concept of Isomorphism 5 • Certain countries are more exposed to isomorphic pressures: – Dependent
- 44. The Paradoxes of Globalization 6 Three Major Global Paradoxes: Paradox of predictability: – The global system
- 45. The Paradoxes of Globalization 6 Three Major Global Paradoxes: 2. Paradox of coupling: – Tight coupling
- 46. The Paradoxes of Globalization 6 Three Major Global Paradoxes: 3. Paradox of differentiated convergence: – Isomorphic
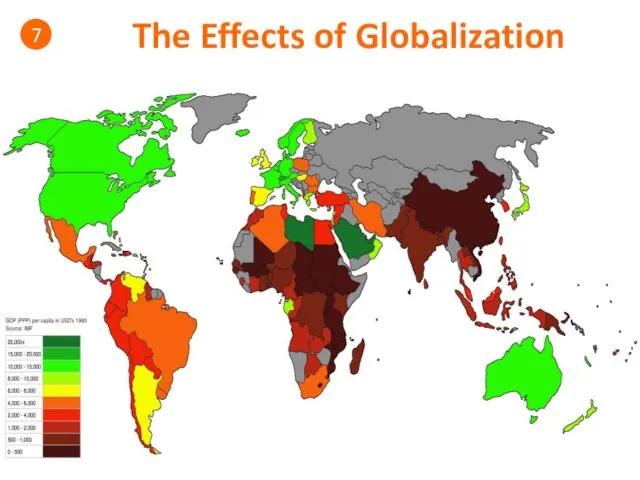
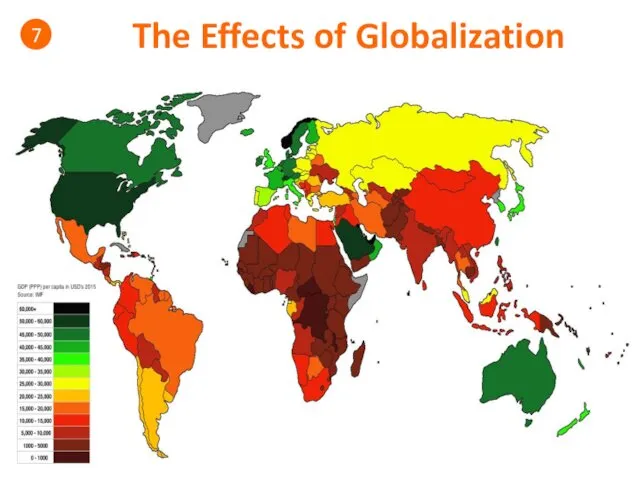
- 47. The Effects of Globalization 7 Discussion Questions: • Is there more or less inequality in the
- 48. The Effects of Globalization 7
- 49. The Effects of Globalization 7
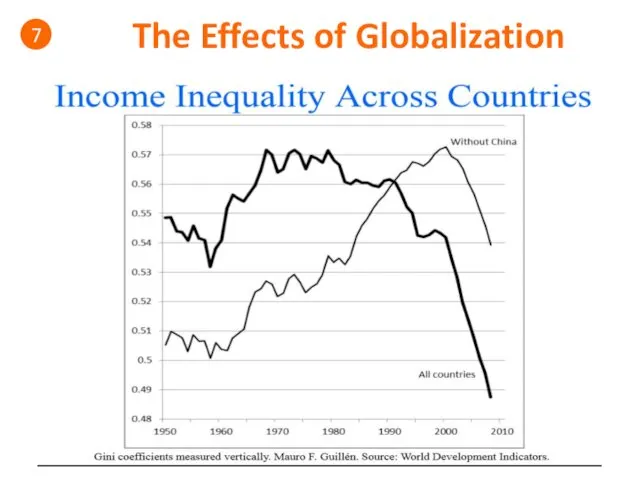
- 50. The Effects of Globalization 7 Gini Coefficient: Gini coefficient measures the extent to which the distribution
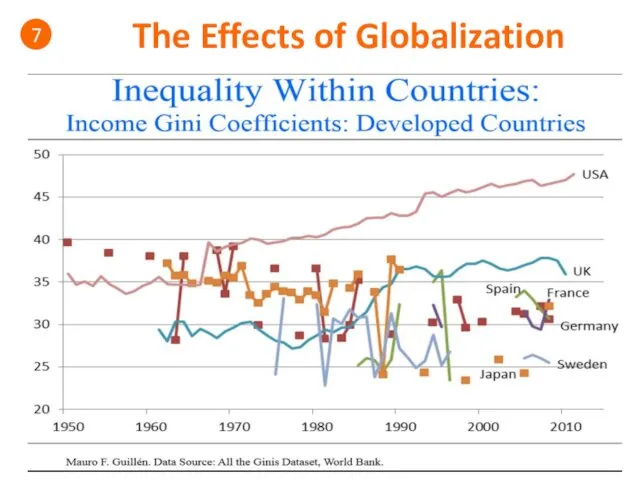
- 51. The Effects of Globalization 7
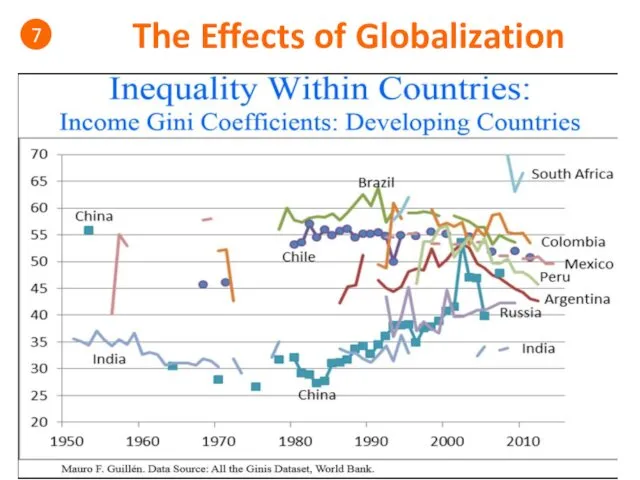
- 52. The Effects of Globalization 7
- 53. The Effects of Globalization 7
- 54. The Effects of Globalization 7 Discussion Questions/Food for Thought Winners & Losers?
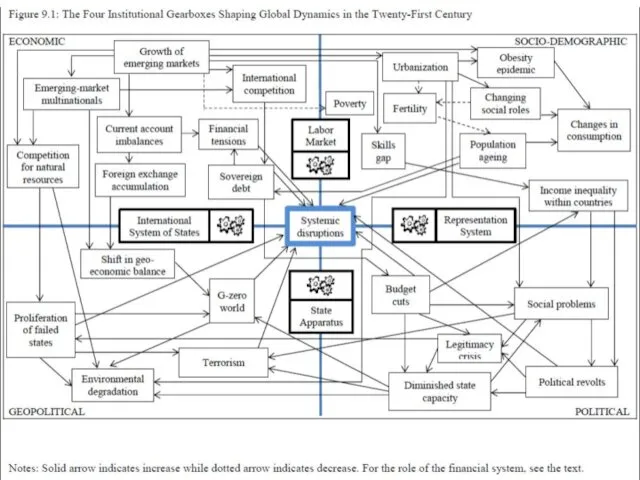
- 55. Tensions in the Global Landscape 8 Key Tensions: • They occur at the border between the
- 56. Tensions in the Global Landscape 8 Key Institutions: • Labor market • Political representation system •
- 59. Скачать презентацию








































 Запуск VAPE CNPT SHIFT в СПП РФ
Запуск VAPE CNPT SHIFT в СПП РФ Введение в бизнес. Основы международного бизнеса
Введение в бизнес. Основы международного бизнеса Развитие предпринимательства
Развитие предпринимательства Цветочный магазин Цветочная Россия
Цветочный магазин Цветочная Россия Теория фирмы и предпринимательской деятельности
Теория фирмы и предпринимательской деятельности Комерційна пропозиція Бонус, ТОВ Тернопільелектропостач
Комерційна пропозиція Бонус, ТОВ Тернопільелектропостач Магазин фермерских продуктов Farmer’s barn
Магазин фермерских продуктов Farmer’s barn Сеть салонов нумизматики Я нумизмат. Бизнес на деньгах
Сеть салонов нумизматики Я нумизмат. Бизнес на деньгах Слагаемые успеха в бизнесе
Слагаемые успеха в бизнесе Коммерческое предложение для ООО Делика
Коммерческое предложение для ООО Делика Бизнес-планирование в социокультурной сфере
Бизнес-планирование в социокультурной сфере Школа социального предпринимательства
Школа социального предпринимательства Инвестиционный проект: сущность, этапы и стадии разработки, принципы формирования. Тема 2
Инвестиционный проект: сущность, этапы и стадии разработки, принципы формирования. Тема 2 Assessment of the tourism function in region development
Assessment of the tourism function in region development Разработка комплекса мероприятий по совершенствованию технологий обслуживания VIP-гостей гостиницы Холидей Инн Лесная
Разработка комплекса мероприятий по совершенствованию технологий обслуживания VIP-гостей гостиницы Холидей Инн Лесная Меры поддержки для малого и среднего бизнеса
Меры поддержки для малого и среднего бизнеса Бизнес-план Антикафе
Бизнес-план Антикафе Организация работы структурного подразделения ресторана первого класса Традиция (горячий цех)
Организация работы структурного подразделения ресторана первого класса Традиция (горячий цех) Отели и рестораны Kempinski
Отели и рестораны Kempinski Совершенствование организации работы службы приема, размещения и выписки в гостиничном бизнесе на примере ООО Брайтон
Совершенствование организации работы службы приема, размещения и выписки в гостиничном бизнесе на примере ООО Брайтон Проект частного Детского сада Sun School, в г. Москва
Проект частного Детского сада Sun School, в г. Москва Бизнес-проект: создание платформы Collab
Бизнес-проект: создание платформы Collab Бизнес модель. Построение бизнес-модели
Бизнес модель. Построение бизнес-модели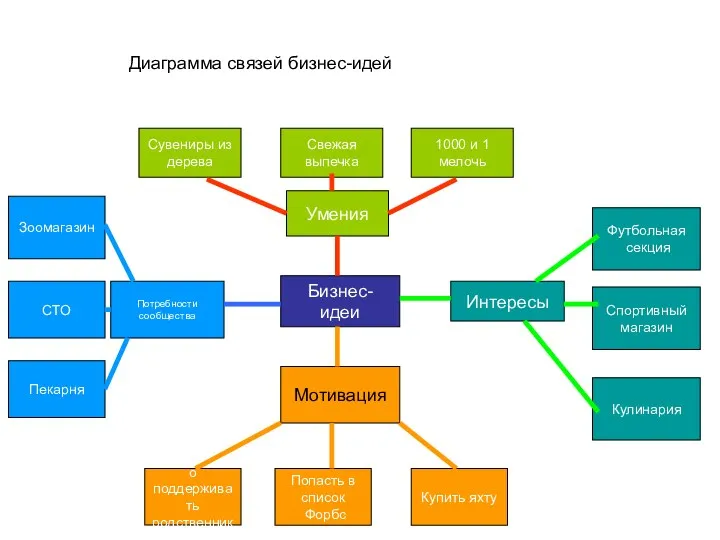 Диаграмма связей бизнес-идей
Диаграмма связей бизнес-идей Салауат ватаны - туристический аграрно-этнографический комплекс спорта и отдыха
Салауат ватаны - туристический аграрно-этнографический комплекс спорта и отдыха Фреш-бар Vitamin. Бизнес-идея
Фреш-бар Vitamin. Бизнес-идея Тернопільські бізнес-леді
Тернопільські бізнес-леді Игровой клуб “Monster Kill”
Игровой клуб “Monster Kill”