Содержание
- 2. WATER ECONOMY - sector of the economy, dealing with accounting, planning and management of complex use,
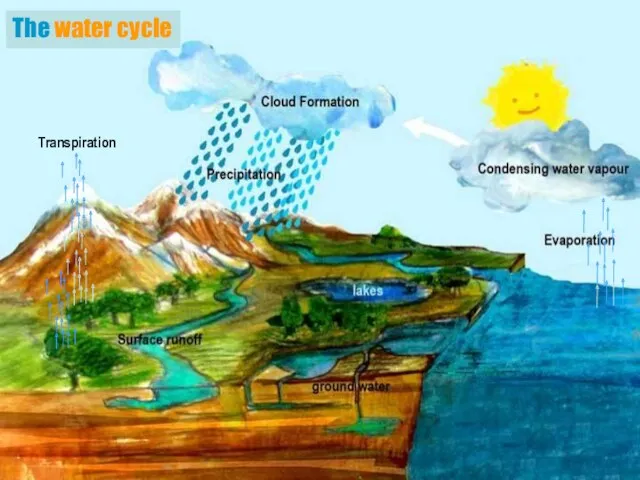
- 3. The water cycle Transpiration
- 4. Water Resources . Uses of water include agricultural, industrial, household, recreational and environmental activities. Virtually all
- 5. Fresh water is renewable resources like soil and air. The worlds is supplied by clean and
- 6. Water resources are divided: Water resources are divisible into two distinct categories : the surface-water resources
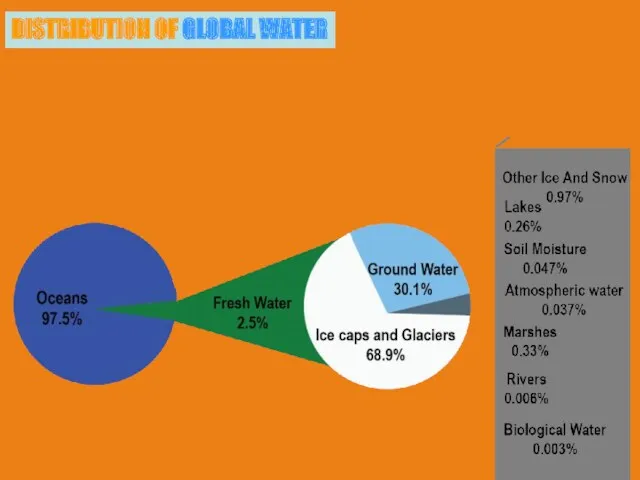
- 7. DISTRIBUTION OF GLOBAL WATER
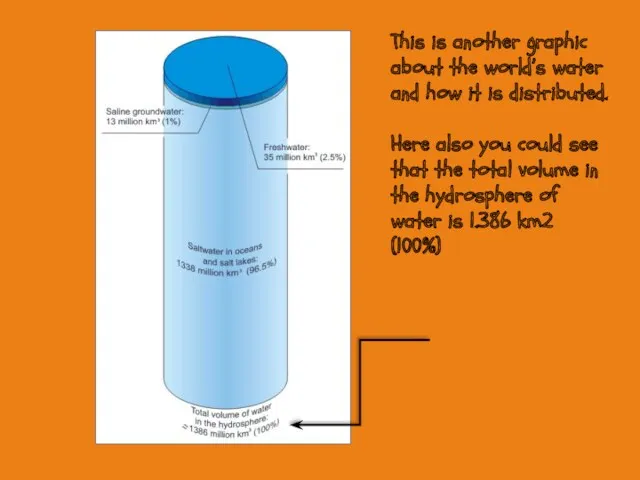
- 8. This is another graphic about the world’s water and how it is distributed. Here also you
- 9. If all the world’s water could fit into a bucket Water available for drinking would be
- 10. Mismatch between regions of large population and available freshwater resources Fresh Water Stress By 2025 2
- 11. Sources of Fresh Water Surface water: Surface water is water in a river, lake or fresh
- 12. Ground Water: Sub-surface water, or groundwater, is fresh water located in the pore space of soil
- 13. Frozen Water: Several schemes have been proposed to make use of icebergs as a water source,
- 14. How do people use Water Resources? Household Personal Use Recreational activities Washing dishes Fill the car
- 15. The total amount of water in the world is the same, but there are more people
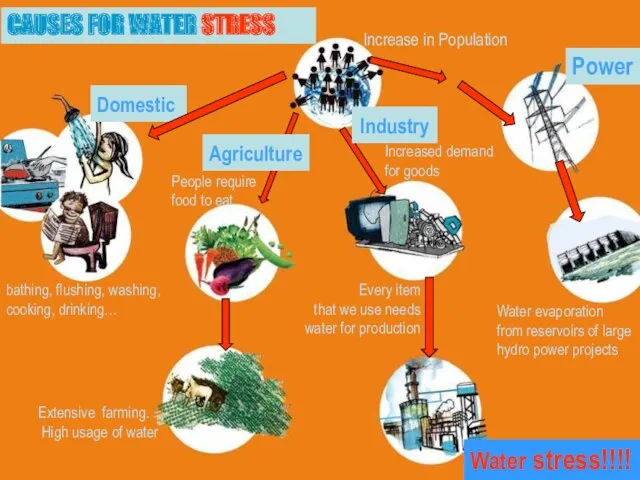
- 16. Every item that we use needs water for production CAUSES FOR WATER STRESS Water evaporation from
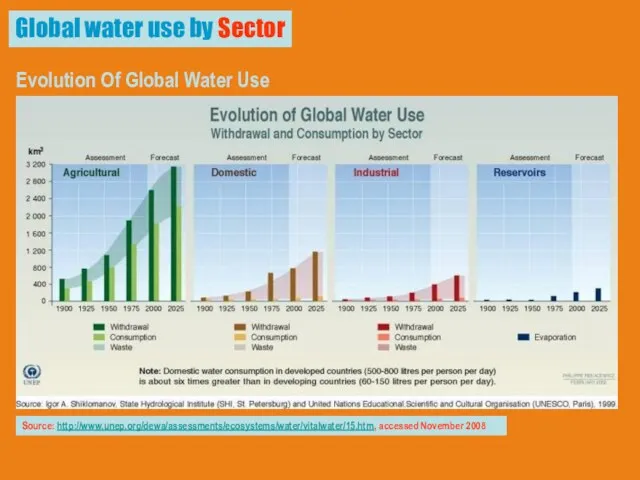
- 17. Global water use by Sector Evolution Of Global Water Use Withdrawal And Consumption By Sector Source:
- 18. Uses of water Agricultural: It is estimated that 69% of worldwide water use is for irrigation,
- 19. India, with more than a billion people, needs a lot of water to grow food for
- 20. Household: It is estimated that 15% of worldwide water use is for household purposes. These include
- 21. Run off from agricultural fields Untreated municipal sewage Air pollutants Dissolve in rainwater It’s not just
- 23. Скачать презентацию















 Основы экологии
Основы экологии Ландшафный дизайн школьного двора
Ландшафный дизайн школьного двора Пластик и его переработка
Пластик и его переработка Экология. Подготовка к ЕГЭ
Экология. Подготовка к ЕГЭ альернативные источники энергии
альернативные источники энергии Оцінка хімічної обстановки
Оцінка хімічної обстановки Байкальский заповедник
Байкальский заповедник Классный час ООПТ
Классный час ООПТ Воздушный шар – опасная радость
Воздушный шар – опасная радость Заповедники России
Заповедники России Влияние добычи полезных ископаемых на окружающую среду
Влияние добычи полезных ископаемых на окружающую среду Специфічні забруднення водойм та роль мікроорганізмів в його ліквідації
Специфічні забруднення водойм та роль мікроорганізмів в його ліквідації Природные ресурсы и охрана природы
Природные ресурсы и охрана природы Экологические проблемы лесопользования и их решени
Экологические проблемы лесопользования и их решени Акция Спаси дерево
Акция Спаси дерево Чистый город начинается с тебя
Чистый город начинается с тебя Вода. Её химические и физические свойства. Гигиеническое и экологическое значение. (8)
Вода. Её химические и физические свойства. Гигиеническое и экологическое значение. (8) Как влияют свалки на здоровье человека
Как влияют свалки на здоровье человека Павловск прошлое, заповедное настоящее и экологическое будущее
Павловск прошлое, заповедное настоящее и экологическое будущее Экосистемы. Лекция 8
Экосистемы. Лекция 8 Техногенные катастрофы
Техногенные катастрофы Биопластик – жизнь без мусора
Биопластик – жизнь без мусора Охорона повітря від забруднення
Охорона повітря від забруднення Экологическое состояние реки Инсар
Экологическое состояние реки Инсар Вода. Её химические и физические свойства. Гигиеническое и экологическое значение
Вода. Её химические и физические свойства. Гигиеническое и экологическое значение Биосфера
Биосфера Команда Орден неравнодушных в экологическом квесте Другая планета
Команда Орден неравнодушных в экологическом квесте Другая планета Природное сообщество
Природное сообщество