Содержание
- 2. After the Soviet Union was over the Russian economy went through a lot of changes. It
- 3. The main industry - It is still an exports of natural gas and oil that are
- 4. Shipbuilding Shipbuilding has been very well developed in Russia for a long time. There are over
- 5. Automobile industry We also have a developed automobile industry. For example, our AvtoVAZ is the biggest
- 6. Light industry - Light industry plays an important role in our economy too. Such industries as
- 7. - A continuation of old methods raises the specter of worsening traffic congestion and pollution in
- 8. - The Japanese economy was in an unprecedented boom at that time. - Economic policy has
- 9. Ukraine’s economy is set to grow fast driven by exports that are up by one quarter,
- 10. Ecological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, or eco-economics, is both a transdisciplinary and an interdisciplinary field of academic
- 11. Ecological economics was founded in the 1980s as a modern discipline on the works of and
- 13. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
After the Soviet Union was over the Russian economy went through
After the Soviet Union was over the Russian economy went through
a lot of changes. It had a long way of reformations, several world’s crisis and right now it’s a global system of market economy.
Слайд 3
The main industry
- It is still an exports of natural gas
The main industry
- It is still an exports of natural gas
and oil that are extracted in Western Siberia. Besides our country has a lot of coal and iron ore as well as diamonds.
- We export not only natural resources we have. We get a lot of money from selling weapons and military pattern spare parts, microelectronics, pharmaceutical and nanotechnological products.
- We export not only natural resources we have. We get a lot of money from selling weapons and military pattern spare parts, microelectronics, pharmaceutical and nanotechnological products.
Слайд 4
Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding has been very well developed in Russia for a
Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding has been very well developed in Russia for a
long time. There are over 1000 manufactures that design and repair ships of different kinds and tonnage. Most of these manufactures are located in Saint Petersburg, Severodvinsk, Nizhni Novgorod and in Kaliningrad region.
Слайд 5
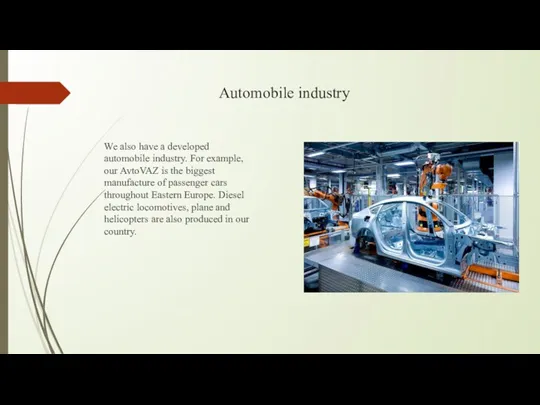
Automobile industry
We also have a developed automobile industry. For example, our
Automobile industry
We also have a developed automobile industry. For example, our
AvtoVAZ is the biggest manufacture of passenger cars throughout Eastern Europe. Diesel electric locomotives, plane and helicopters are also produced in our country.
Слайд 6
Light industry
- Light industry plays an important role in our
Light industry
- Light industry plays an important role in our
economy too. Such industries as textiles, clothing production and leather production are also very developed.
- No doubt agriculture, food industry, ferrous and non-ferrous metal industry are very important as well. Our country is one of the largest producers of aluminium and nickel and our wheat production is several times bigger than in the USA and of course, our sweets are well known across the world.
- No doubt agriculture, food industry, ferrous and non-ferrous metal industry are very important as well. Our country is one of the largest producers of aluminium and nickel and our wheat production is several times bigger than in the USA and of course, our sweets are well known across the world.
Слайд 7
- A continuation of old methods raises the specter of worsening
- A continuation of old methods raises the specter of worsening
traffic congestion and pollution in the biggest cities if migration continues to outpace policy makers’ plans.
- The country's economy depends on agriculture.
- “If you do not focus on big cities with concentrated populations, China will become an ecological catastrophe,” he said.
The country is in a bad economic state.
Its mercantile currency policy in a beggar-thy-neighbor approach, environmental degradation, and disdain for human rights and the rule of law generally are the obvious reflections of its despotism.
Nobody can deny the fact the world economy revolves around the American economy.
Another black-swan disaster (another nuclear accident a la Fukushima or a major environmental catastrophe laid at the feet of fracking) would be a boon to Russia's markets.
Japan is a service economy, in which services account for more than 50% of the GNP.
Meanwhile, Haiti's ecological and demographic conditions posed huge development challenges that have never been overcome.
The country's economy was dislocated by the war.
What we can say is that all of the happiest countries emphasize equality, solidarity, democratic accountability, environmental sustainability, and strong public institutions.
- The country's economy depends on agriculture.
- “If you do not focus on big cities with concentrated populations, China will become an ecological catastrophe,” he said.
The country is in a bad economic state.
Its mercantile currency policy in a beggar-thy-neighbor approach, environmental degradation, and disdain for human rights and the rule of law generally are the obvious reflections of its despotism.
Nobody can deny the fact the world economy revolves around the American economy.
Another black-swan disaster (another nuclear accident a la Fukushima or a major environmental catastrophe laid at the feet of fracking) would be a boon to Russia's markets.
Japan is a service economy, in which services account for more than 50% of the GNP.
Meanwhile, Haiti's ecological and demographic conditions posed huge development challenges that have never been overcome.
The country's economy was dislocated by the war.
What we can say is that all of the happiest countries emphasize equality, solidarity, democratic accountability, environmental sustainability, and strong public institutions.
Слайд 8
- The Japanese economy was in an unprecedented boom at that
- The Japanese economy was in an unprecedented boom at that
time.
- Economic policy has also contributed to their current condition as trade agreements and an over-valued dollar promoted auto imports, and incoherent energy and environmental policy stifled innovation.
- Although the economy has stabilized and grown in the last two quarters, it remains fragile.
- Climate change looms as this century's primary long-term environmental challenge.
Until then, economic development will be stalled and a handful of oligarchic empires will continue strangling the country.
As the US, China, and many other nations now realize, climate change is much more than an environmental issue.
- Economic policy has also contributed to their current condition as trade agreements and an over-valued dollar promoted auto imports, and incoherent energy and environmental policy stifled innovation.
- Although the economy has stabilized and grown in the last two quarters, it remains fragile.
- Climate change looms as this century's primary long-term environmental challenge.
Until then, economic development will be stalled and a handful of oligarchic empires will continue strangling the country.
As the US, China, and many other nations now realize, climate change is much more than an environmental issue.
Слайд 9
Ukraine’s economy is set to grow fast driven by exports that
Ukraine’s economy is set to grow fast driven by exports that
are up by one quarter, construction by almost as much, and retail sales by 8 percent in the first half of 2017.
Facing the sharp end of the stick are the seven million Niger delta peasants, who bear the brunt of the violence, environmental devastation, and social anarchy that Big Oil produces wherever it sets up its drilling rigs.
Слайд 10
Ecological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, or eco-economics, is both a transdisciplinary and
Ecological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, or eco-economics, is both a transdisciplinary and
an interdisciplinary field of academic research addressing the interdependence and coevolution of human economies and natural ecosystems, both intertemporally and spatially. By treating the economy as a subsystem of Earth's larger ecosystem, and by emphasizing the preservation of natural capital, the field of ecological economics is differentiated from environmental economics, which is the mainstream economic analysis of the environment. One survey of German economists found that ecological and environmental economics are different schools of economic thought, with ecological economists emphasizing strong sustainability and rejecting the proposition that physical (human-made) capital can substitute for natural capital (see the section on weak versus strong sustainability below).
Слайд 11
Ecological economics was founded in the 1980s as a modern discipline
Ecological economics was founded in the 1980s as a modern discipline
on the works of and interactions between various European and American academics (see the section on History and development below). The related field of green economics is in general a more politically applied form of the subject.[4][5]
According to ecological economist Malte Michael Faber [de], ecological economics is defined by its focus on nature, justice, and time. Issues of intergenerational equity, irreversibility of environmental change, uncertainty of long-term outcomes, and sustainable development guide ecological economic analysis and valuation.[6] Ecological economists have questioned fundamental mainstream economic approaches such as cost-benefit analysis, and the separability of economic values from scientific research, contending that economics is unavoidably normative, i.e. prescriptive, rather than positive or descriptive.[7] Positional analysis, which attempts to incorporate time and justice issues, is proposed as an alternative.[8][9] Ecological economics shares several of its perspectives with feminist economics, including the focus on sustainability, nature, justice and care values.[10]
According to ecological economist Malte Michael Faber [de], ecological economics is defined by its focus on nature, justice, and time. Issues of intergenerational equity, irreversibility of environmental change, uncertainty of long-term outcomes, and sustainable development guide ecological economic analysis and valuation.[6] Ecological economists have questioned fundamental mainstream economic approaches such as cost-benefit analysis, and the separability of economic values from scientific research, contending that economics is unavoidably normative, i.e. prescriptive, rather than positive or descriptive.[7] Positional analysis, which attempts to incorporate time and justice issues, is proposed as an alternative.[8][9] Ecological economics shares several of its perspectives with feminist economics, including the focus on sustainability, nature, justice and care values.[10]









 Спрос. Предложение. Рыночное равновесие
Спрос. Предложение. Рыночное равновесие Валовой внутренний продукт (ВВП) и другие показатели, рассчитываемые на основе ВВП
Валовой внутренний продукт (ВВП) и другие показатели, рассчитываемые на основе ВВП Персонал предприятия
Персонал предприятия Message president of the republic of Kazakhstan - the nation leader na Nazarbayev the people of Kazakhstan strategy
Message president of the republic of Kazakhstan - the nation leader na Nazarbayev the people of Kazakhstan strategy Основные средства предприятия
Основные средства предприятия Экономический кризис 1929-1933 год
Экономический кризис 1929-1933 год Экономическая теория
Экономическая теория Інфраструктурний компонент проекту. Програма ЄС Підтримка політики регіонального розвитку України”. Місто Волинь
Інфраструктурний компонент проекту. Програма ЄС Підтримка політики регіонального розвитку України”. Місто Волинь Неоклассические теории международной торговли
Неоклассические теории международной торговли Открытое акционерное общество КАМАЗ. 7 видов потерь
Открытое акционерное общество КАМАЗ. 7 видов потерь Ринок чорної металургії
Ринок чорної металургії Қазақстанның саласындағы инвестициялық хал-ахуалдың проблемалары мен перспективаларыпроблемаларын талқылау
Қазақстанның саласындағы инвестициялық хал-ахуалдың проблемалары мен перспективаларыпроблемаларын талқылау Субъекты и объекты международных экономических отношений
Субъекты и объекты международных экономических отношений Международные организации
Международные организации Краткий обзор Ассоциации ИТК ИТЭ ТО
Краткий обзор Ассоциации ИТК ИТЭ ТО Демография современного мира
Демография современного мира Interdependence and the Gains from Trade
Interdependence and the Gains from Trade Основы теории производства
Основы теории производства Международные экономические отношения
Международные экономические отношения Еңбек нарығы. Еңбек тәртібі
Еңбек нарығы. Еңбек тәртібі Распределение доходов
Распределение доходов Трудовые ресурсы предприятия
Трудовые ресурсы предприятия Деньги и их роль в экономике
Деньги и их роль в экономике Государственная кадровая политика
Государственная кадровая политика Предмет макроэкономики
Предмет макроэкономики Принципы функционирования рыночной экономики
Принципы функционирования рыночной экономики Специализация Санкт-Петербурга
Специализация Санкт-Петербурга Фінансові результати діяльності торговельного підприємства. (Лекція 14)
Фінансові результати діяльності торговельного підприємства. (Лекція 14)