Содержание
- 2. 1. The money supply and methods of its measurement. Demand for money. Money supply (money mass)
- 3. 1. The money supply and methods of its measurement. Demand for money. MONETARY BASE – is
- 4. 1. The money supply and methods of its measurement. Demand for money. Bank reserves consist of
- 5. 1. The money supply and methods of its measurement. Demand for money. Money supply of Ukraine:
- 6. 1. The money supply and methods of its measurement. Demand for money. To measure the money
- 7. The structure of the money supply in Ukraine, 2020. М3=1476,8 bln.UAH (100 %) М2=1473,9 bln.UAH (99,8
- 8. 1. The money supply and methods of its measurement. Demand for money. The quantitative theory of
- 9. 1. The money supply and methods of its measurement. Demand for money. Monetization in the economy
- 10. 1. The money supply and methods of its measurement. Demand for money. The main factor of
- 11. The level of monetization in Ukraine 2014-2018 Quite low values of the coefficient of monetization of
- 12. THE LEVEL OF MONETIZATION IN DIFFERENT COUNTRIES GERMANY ±89% JAPAN ±180% ±18% INDIA RUSSIA ±43% The
- 13. Demand for money and the factors that determine it Operational or transactional demand for money (M1)
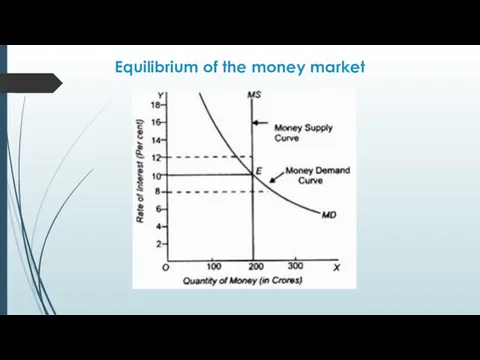
- 14. Equilibrium of the money market Ms Md A M
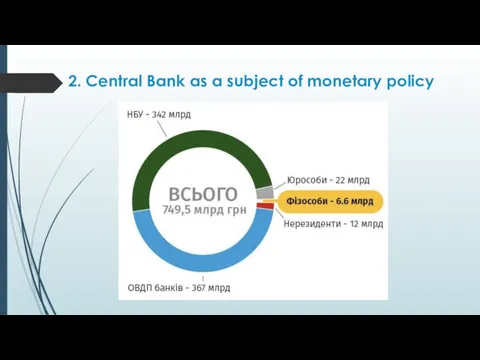
- 15. 2. Central Bank as a subject of monetary policy CENTRAL BANK - is a monopolized and
- 16. 2. Central Bank as a subject of monetary policy The main functions of the central bank:
- 17. 2. Central Bank as a subject of monetary policy There are several main monetary policy instruments
- 18. 2. Central Bank as a subject of monetary policy There are several main monetary policy instruments
- 19. 2. Central Bank as a subject of monetary policy
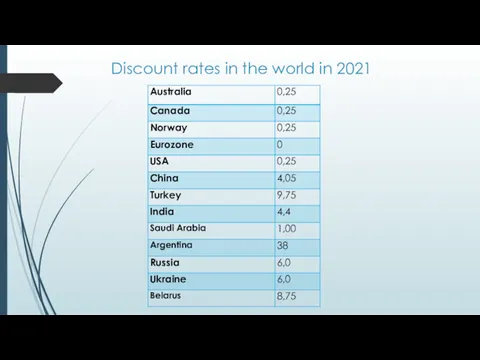
- 20. Discount rates in the world in 2021
- 21. 3. The essence of monetary policy, its strategy MONETARY POLICY – consists of the actions of
- 22. 3. The essence of monetary policy, its strategy MONETARY TRANSMISSION MECHANISM - is a chain of
- 23. NBU and monetary policy in Ukraine The discount interest rate is 6% from October 23, 2020.
- 24. 3. The essence of monetary policy, its strategy Monetarist model of monetary transmission mechanism At the
- 25. 3. The essence of monetary policy, its strategy TYPES OF MONETARY POLICY EXPANSIONARY (STIMULATING) MONETARY POLICY
- 26. 3. The essence of monetary policy, its strategy TYPES OF MONETARY POLICY CONTRACTIONARY (RESTRICTIVE) MONETARY POLICY
- 27. The use of monetary policy instruments
- 28. 3. The essence of monetary policy, its strategy Keynesian model of monetary transmission mechanism according to
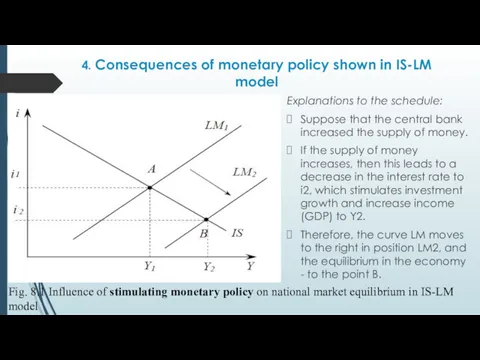
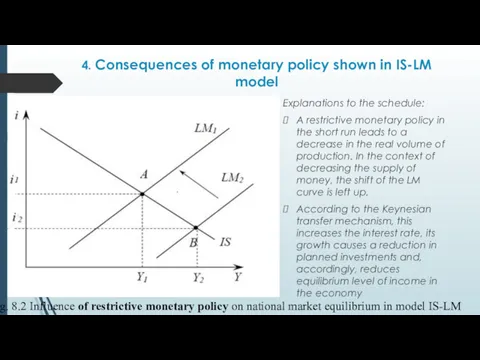
- 29. 4. Consequences of monetary policy shown in IS-LM model Explanations to the schedule: Suppose that the
- 30. 4. Consequences of monetary policy shown in IS-LM model Explanations to the schedule: A restrictive monetary
- 31. 4. Consequences of monetary policy shown in IS-LM model Conclusions of the analysis: Stimulating monetary policy
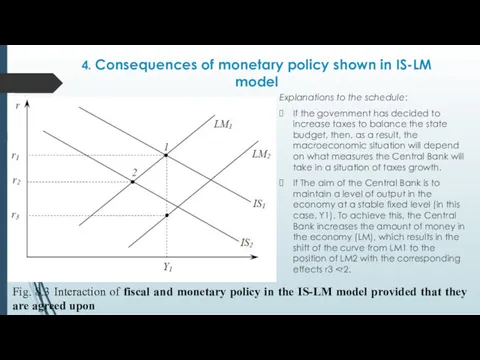
- 32. 4. Consequences of monetary policy shown in IS-LM model Explanations to the schedule: If the government
- 33. 4. Consequences of monetary policy shown in IS-LM model Explanations to the schedule: If the government
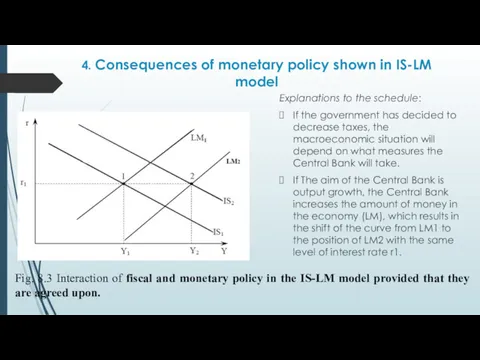
- 34. 4. Consequences of monetary policy shown in IS-LM model Explanations to the schedule: If the government
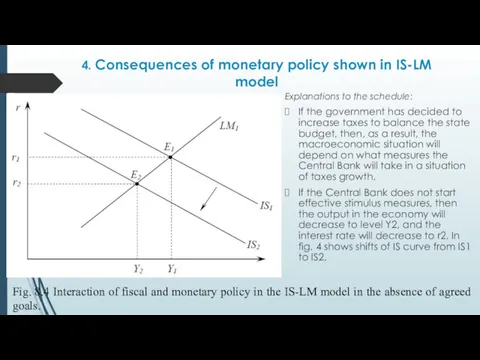
- 35. 4. Consequences of monetary policy shown in IS-LM model Conclusions of the analysis: if the government
- 36. 5. NBU and Monetary Policy in Ukraine The main directions of monetary policy in Ukraine at
- 38. Скачать презентацию



























 Гостевая лекция для KFSA. Практические аспекты макроэкономического моделирования
Гостевая лекция для KFSA. Практические аспекты макроэкономического моделирования Анализ деятельности предприятия: методология
Анализ деятельности предприятия: методология Технология обработки экономической информации
Технология обработки экономической информации Обгрунтування вибору постачальників товарів торговельного підприємства
Обгрунтування вибору постачальників товарів торговельного підприємства Введение в микроэкономику
Введение в микроэкономику Теория спроса и предложения
Теория спроса и предложения Логистикалық үрдісті ақпаратпен қамтамасыз ету
Логистикалық үрдісті ақпаратпен қамтамасыз ету Развитие кредитования юридических лиц
Развитие кредитования юридических лиц Неоклассические теории международной торговли
Неоклассические теории международной торговли Тектонічна будова, рельєф і корисні копалини Африки
Тектонічна будова, рельєф і корисні копалини Африки Инструменты государственной финансовой поддержки сельского хозяйства
Инструменты государственной финансовой поддержки сельского хозяйства Государственно – частное партнерство (ГЧП). Лекция №11
Государственно – частное партнерство (ГЧП). Лекция №11 Глобальна економічна політика. (Лекція 7)
Глобальна економічна політика. (Лекція 7) Системы управления крупнейших городов. (Тема 4)
Системы управления крупнейших городов. (Тема 4) Демографический кризис
Демографический кризис II заседание Ассоциации молодых депутатов в Янаульском районе
II заседание Ассоциации молодых депутатов в Янаульском районе Динамика народонаселения в мире и России. Демографические проблемы
Динамика народонаселения в мире и России. Демографические проблемы История развития пищевой промышленности России
История развития пищевой промышленности России Кафедра устойчивого инновационного развития. Системный анализ и управление устойчивым развитием сложных систем. Лекции
Кафедра устойчивого инновационного развития. Системный анализ и управление устойчивым развитием сложных систем. Лекции Виды и формы бизнеса. 7 класс
Виды и формы бизнеса. 7 класс ВВП России и других стран в таблицах и графиках
ВВП России и других стран в таблицах и графиках Рыночная конкуренция. (Тема 6)
Рыночная конкуренция. (Тема 6) Семейный бюджет
Семейный бюджет Система товарно-денежных отношений рынок
Система товарно-денежных отношений рынок Комитет по развитию предпринимательства и потребительского рынка Санкт-Петербурга
Комитет по развитию предпринимательства и потребительского рынка Санкт-Петербурга Предпринимательская деятельность (обществознание, 8 класс)
Предпринимательская деятельность (обществознание, 8 класс) Сұраныс пен ұсыныс теориясының негіздері
Сұраныс пен ұсыныс теориясының негіздері урок экономики Расчет издержек и эффективности деятельности фирмы в 11 классе (профильный уровень)
урок экономики Расчет издержек и эффективности деятельности фирмы в 11 классе (профильный уровень)