Содержание
- 2. Outline Understanding PPPs- what they are; key structures; perspectives Forms of partnerships: the PPP spectrum How
- 3. PPP: What is it? Medium to long term relationship between the public sector and the partners
- 4. PPP: What is it? It is about creating, nurturing and sustaining an effective relationship between the
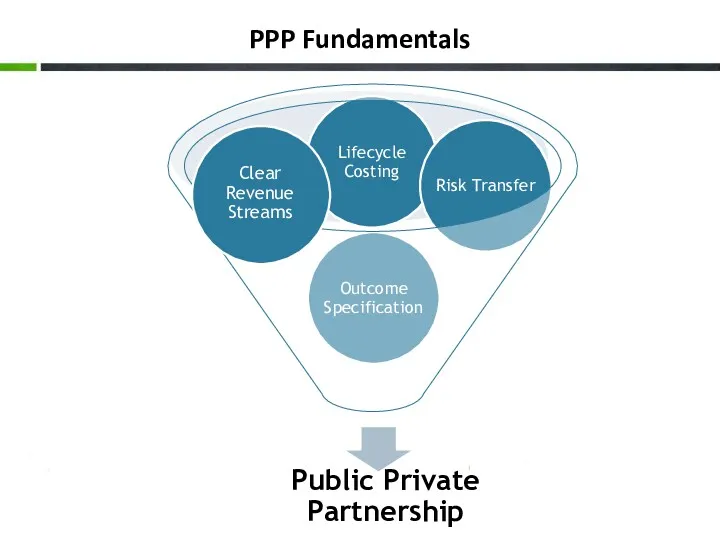
- 5. PPP Fundamentals
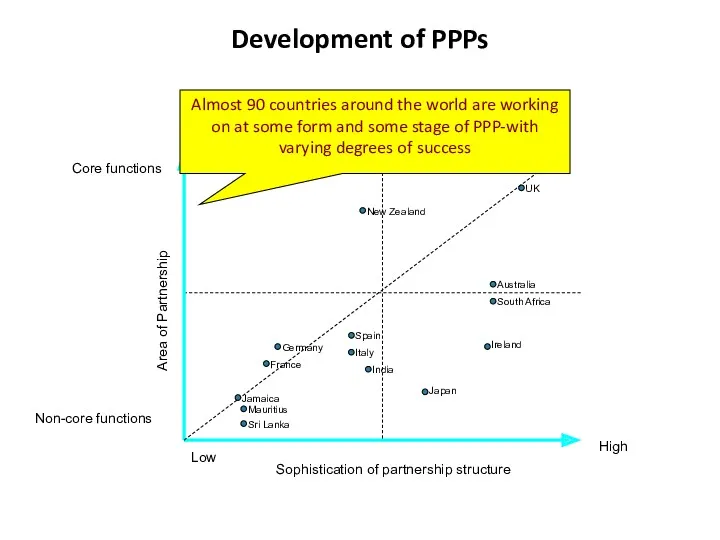
- 6. Development of PPPs Sophistication of partnership structure Low High Area of Partnership Non-core functions Core functions
- 7. Key structures Designed to maximize the use of Private Sector Skills Risk placed where it can
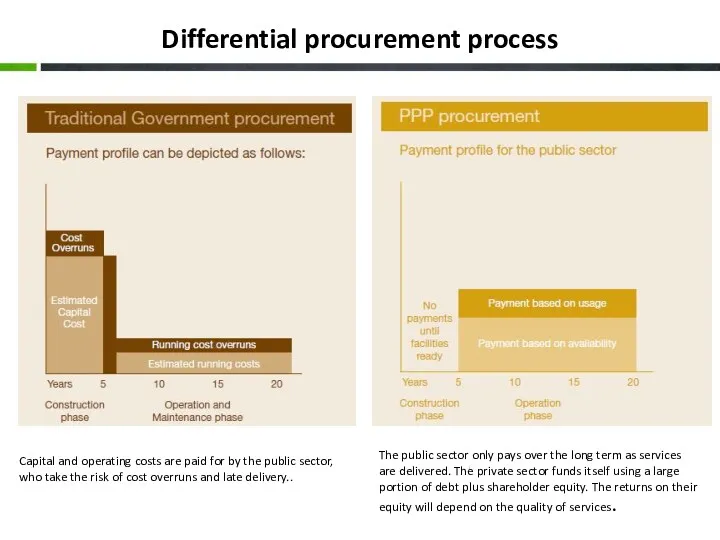
- 8. Differential procurement process Capital and operating costs are paid for by the public sector, who take
- 9. Perspectives PPPs cannot be a solution for every challenge that public sector faces with regard to
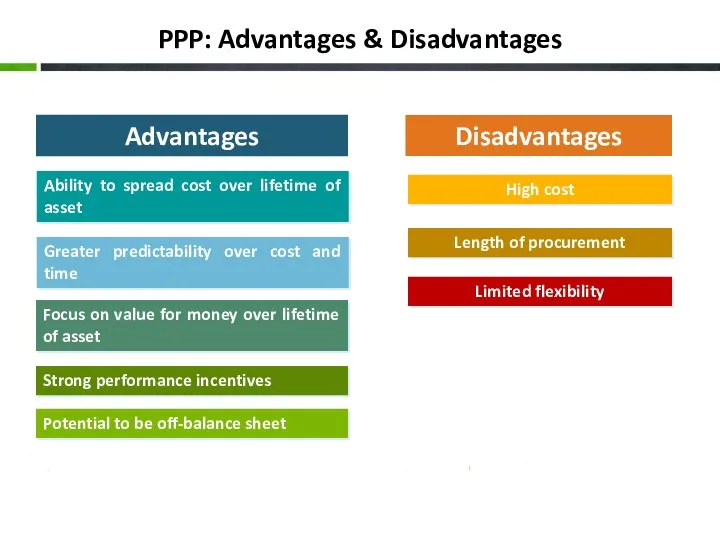
- 10. PPP: Advantages & Disadvantages Advantages Disadvantages Ability to spread cost over lifetime of asset Greater predictability
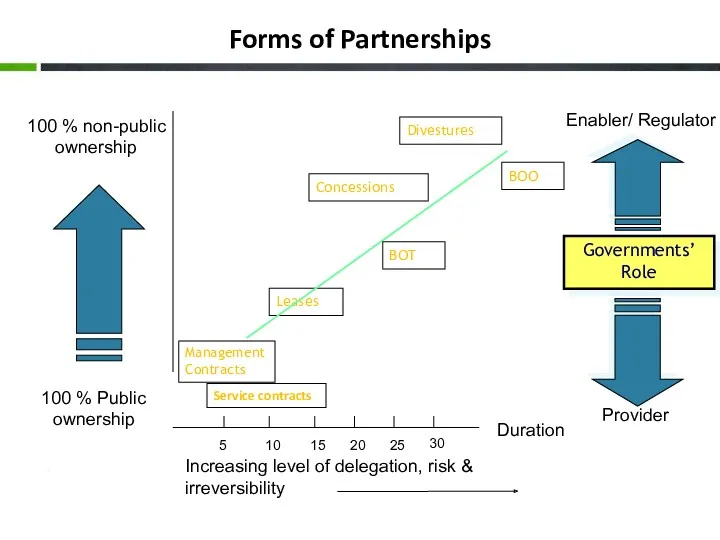
- 11. Forms of Partnerships Duration Increasing level of delegation, risk & irreversibility Service contracts Management Contracts Leases
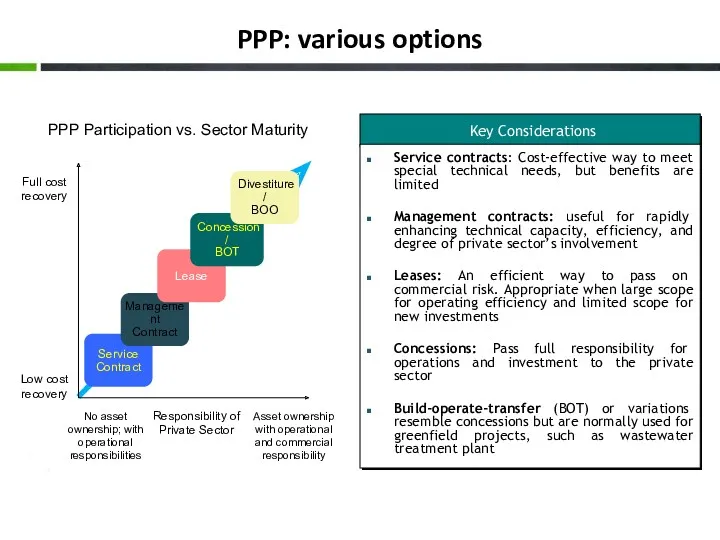
- 12. PPP: various options PPP Participation vs. Sector Maturity Responsibility of Private Sector Asset ownership with operational
- 13. Service Agreement Public sector employ private sector to assist in running certain aspects of their utility
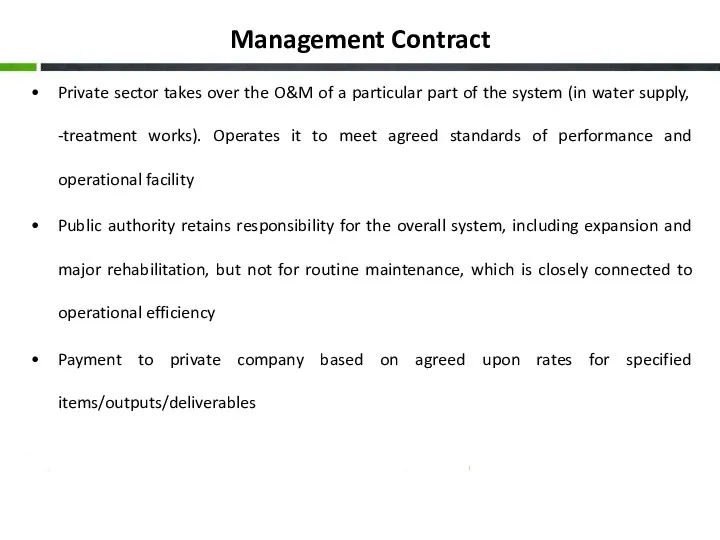
- 14. Management Contract Private sector takes over the O&M of a particular part of the system (in
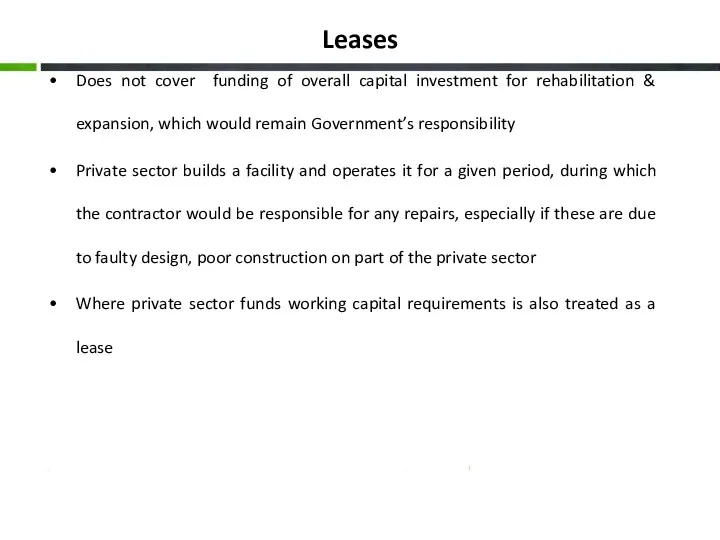
- 15. Leases Does not cover funding of overall capital investment for rehabilitation & expansion, which would remain
- 16. Concessions The Concessionaire finances the investment costs Concessionaire gets revenue from users/customers on a pre-defined tariff
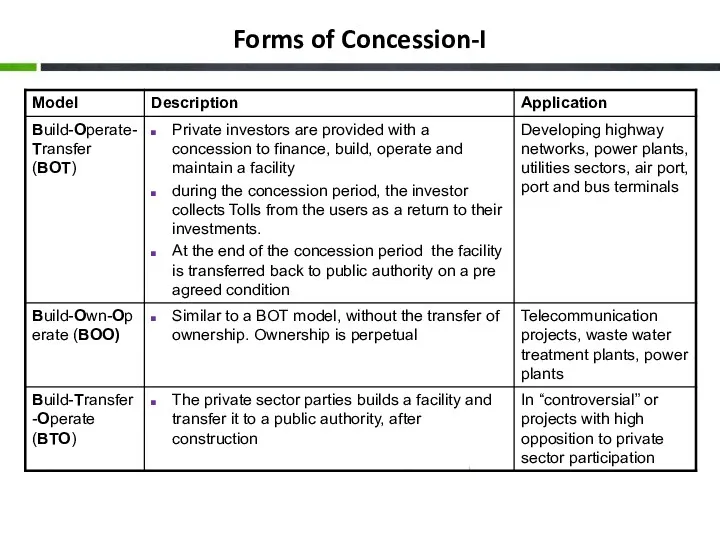
- 17. Forms of Concession-I
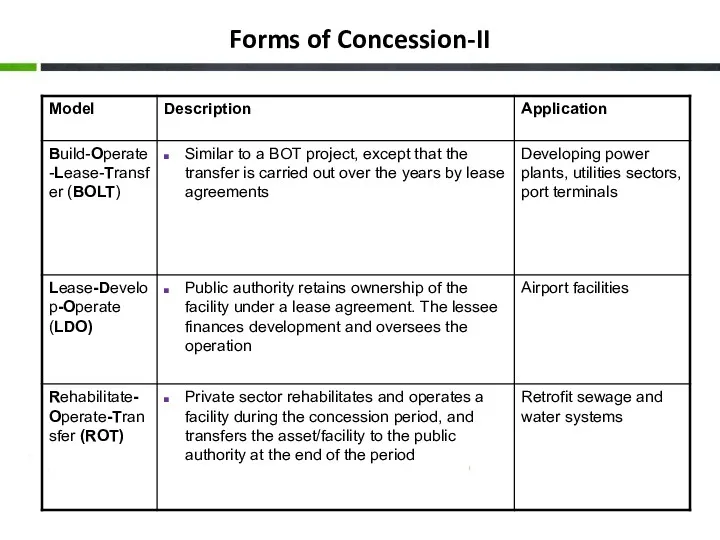
- 18. Forms of Concession-II
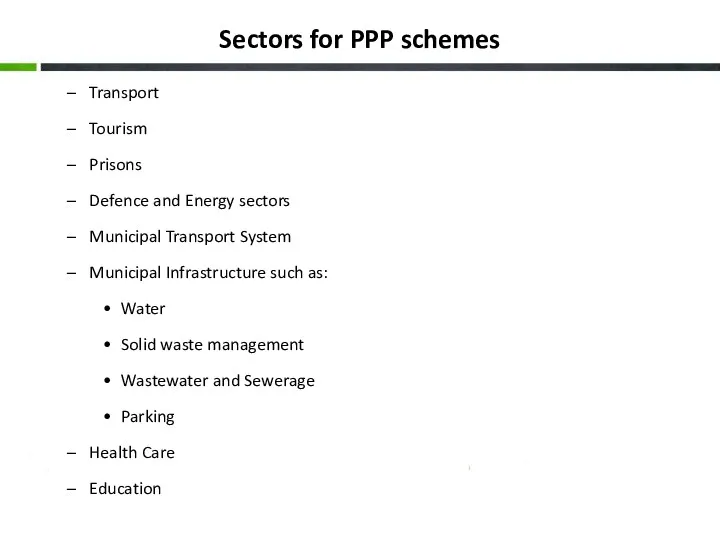
- 19. Sectors for PPP schemes Transport Tourism Prisons Defence and Energy sectors Municipal Transport System Municipal Infrastructure
- 20. How to decide on Options? Depends on: Public policy considerations Goals of the government Expectations from
- 21. The key is… To spell out a clear partnership process, backed by a strong policy and
- 22. What are the key challenges? Internalising PPP process within the public sector Preparing the PPP environment
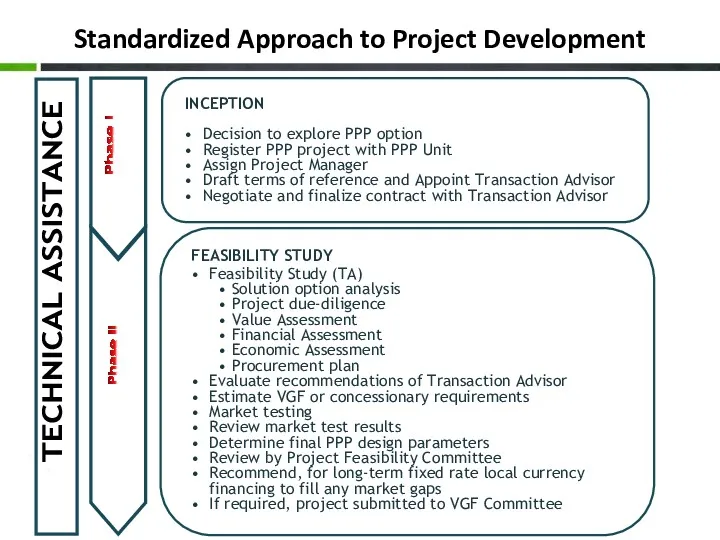
- 23. Standardized Approach to Project Development TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE Phase II Phase I
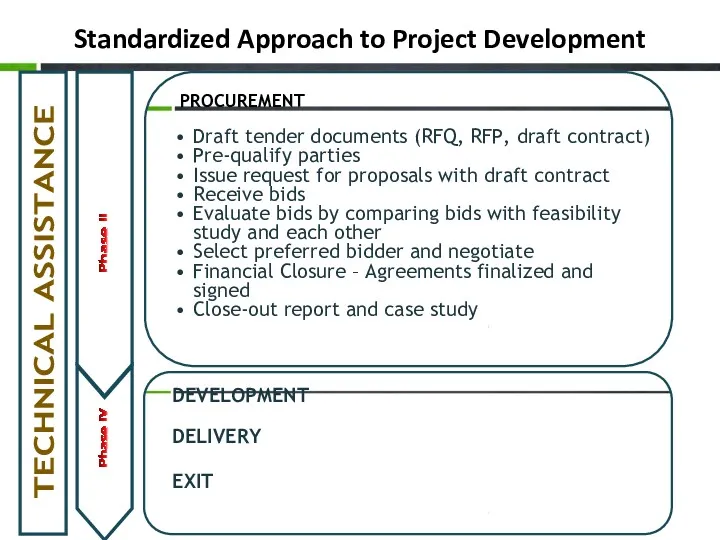
- 24. Standardized Approach to Project Development DEVELOPMENT DELIVERY EXIT PROCUREMENT Draft tender documents (RFQ, RFP, draft contract)
- 26. Скачать презентацию









 Выпускная работа. Обоснование перспектив развития предприятия Фортуна Крым Трейд
Выпускная работа. Обоснование перспектив развития предприятия Фортуна Крым Трейд Ценообразование на монополизированном рынке
Ценообразование на монополизированном рынке Безработица. Трудоспособное и нетрудоспособное население
Безработица. Трудоспособное и нетрудоспособное население Методы ABC, XYZ. Задача на знание метода ABC
Методы ABC, XYZ. Задача на знание метода ABC Макроэкономика. Сущность макроэкономики, ее основные цели
Макроэкономика. Сущность макроэкономики, ее основные цели Економічна теорія як наука
Економічна теорія як наука Государственные финансы
Государственные финансы Märkte für Produktionsfaktoren
Märkte für Produktionsfaktoren Общая характеристика направления менеджмент и ее профилей. (Раздел 1)
Общая характеристика направления менеджмент и ее профилей. (Раздел 1) Денежно-кредитная политика государства
Денежно-кредитная политика государства Трудовые ресурсы предприятия: основные понятия, структура, показатели
Трудовые ресурсы предприятия: основные понятия, структура, показатели Организация и проведение массовой оценки объектов недвижимости
Организация и проведение массовой оценки объектов недвижимости Interaction of logical and nominal meanings
Interaction of logical and nominal meanings Научно-техническая безопасность и экономический рост
Научно-техническая безопасность и экономический рост Теоретичні засади податків
Теоретичні засади податків Собственность. Предпринимательство. Издержки производства. Прибыль
Собственность. Предпринимательство. Издержки производства. Прибыль Контроль за соблюдением норм и правил охраны труда. (Лекция 2)
Контроль за соблюдением норм и правил охраны труда. (Лекция 2) Задачи по экономике
Задачи по экономике Экономическая природа фирмы: основные формы деловых предприятий
Экономическая природа фирмы: основные формы деловых предприятий Нематериальные активы (НМА) организации
Нематериальные активы (НМА) организации Экономика. Главные вопросы экономики
Экономика. Главные вопросы экономики Нобелевские премии по экономике
Нобелевские премии по экономике Введение в логистику
Введение в логистику Основные производственные фонды. Понятие и классификация основных фондов
Основные производственные фонды. Понятие и классификация основных фондов Өндіріс факторларының арақатынасы теориясын эмпирикалық тексеру және олардың шектеулілігі мәселесі
Өндіріс факторларының арақатынасы теориясын эмпирикалық тексеру және олардың шектеулілігі мәселесі Неопределенность и риск в процессе реализации инвестиционных проектов
Неопределенность и риск в процессе реализации инвестиционных проектов Неолиберализм. Сущность и особенности неолиберализма
Неолиберализм. Сущность и особенности неолиберализма Комплексный план развития Куединского муниципального округа Пермского края
Комплексный план развития Куединского муниципального округа Пермского края