Содержание
- 2. Background ◦The overproduction ◦Over intensification of agriculture …because the EU price floor is higher than the
- 3. Target
- 4. Method and theory ① ⊡We assume that all the surplus food was dumped on the world
- 5. Method and theory ② ⊡Every farmer in the world market wants to sell at the EU
- 6. Method and theory ③ ⊡As the result of reforms, the consumers’ surplus: a+b ⊡EU farmers lose:
- 8. Скачать презентацию
Background
◦The overproduction
◦Over intensification of agriculture
…because the EU price floor is
Background
◦The overproduction
◦Over intensification of agriculture
…because the EU price floor is
Serious reforms started from 1990s
For examples,
⊡EU farmers---less than 5 percent of all the population in the 1970s (almost same as today’s)
⊡Most of money goes to the largest farm owners
…because the direct payment was linked to the amount of money each farm got.
These issues apparently appeared from 1970s
⊡The farm sector‘s political strength
⊡The conflicts between the members
⊡The historical background
⇒These factors made it difficult to implement the reforms.
Thus, CAP had to find the different approach from the just eliminating the price floors
Target
Target
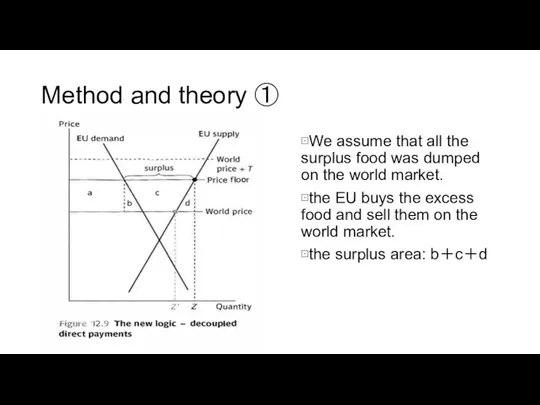
Method and theory ①
⊡We assume that all the surplus food was
Method and theory ①
⊡We assume that all the surplus food was
⊡the EU buys the excess food and sell them on the world market.
⊡the surplus area: b+c+d
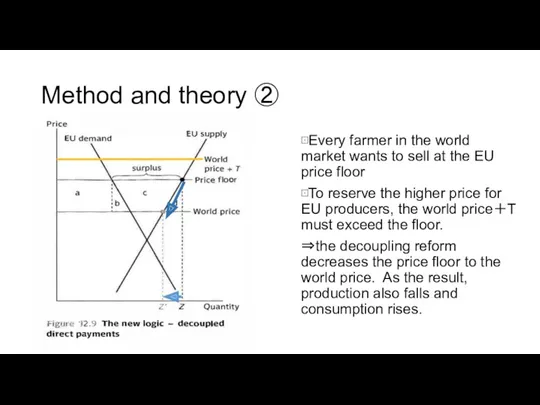
Method and theory ②
⊡Every farmer in the world market wants to
Method and theory ②
⊡Every farmer in the world market wants to
⊡To reserve the higher price for EU producers, the world price+T must exceed the floor.
⇒the decoupling reform decreases the price floor to the world price. As the result, production also falls and consumption rises.
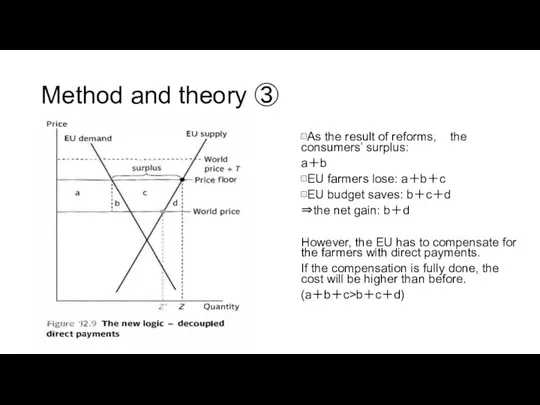
Method and theory ③
⊡As the result of reforms, the consumers’ surplus:
a+b
⊡EU
Method and theory ③
⊡As the result of reforms, the consumers’ surplus:
a+b
⊡EU
⊡EU budget saves: b+c+d
⇒the net gain: b+d
However, the EU has to compensate for the farmers with direct payments.
If the compensation is fully done, the cost will be higher than before.
(a+b+c>b+c+d)

 Теория потребительского выбора
Теория потребительского выбора Экономика Санкт-Петербурга
Экономика Санкт-Петербурга Стратегия социально-экономического развития муниципального образования муниципального района Удорский на период до 2020 года
Стратегия социально-экономического развития муниципального образования муниципального района Удорский на период до 2020 года Системный анализ и управление устойчивым развитием сложных систем (магистерская программа)
Системный анализ и управление устойчивым развитием сложных систем (магистерская программа) Экономика Древней Индии
Экономика Древней Индии Государственное управление трудовыми ресурсами. Трудовой потенциал общества
Государственное управление трудовыми ресурсами. Трудовой потенциал общества Устойчивое управление лесами: опыт зарубежных стран
Устойчивое управление лесами: опыт зарубежных стран урок экономики Расчет издержек и эффективности деятельности фирмы в 11 классе (профильный уровень)
урок экономики Расчет издержек и эффективности деятельности фирмы в 11 классе (профильный уровень) Инфляция: виды, причины, последствия
Инфляция: виды, причины, последствия Анализ экономических показателей на основе применения метода динамических рядов
Анализ экономических показателей на основе применения метода динамических рядов Стратегии социально-экономического развития макрорегионов РФ
Стратегии социально-экономического развития макрорегионов РФ Основные фонды
Основные фонды Компьютерные технологии 1С
Компьютерные технологии 1С Нормы естественной убыли продовольственных товаров
Нормы естественной убыли продовольственных товаров Поддержка кадрового потенциала в АПК. Закрепление молодых специалистов в сельскохозяйственном производстве
Поддержка кадрового потенциала в АПК. Закрепление молодых специалистов в сельскохозяйственном производстве Равновесие на денежном рынке
Равновесие на денежном рынке Методы комплексной оценки финансово-хозяйственной деятельности
Методы комплексной оценки финансово-хозяйственной деятельности Глобальная проблема бедности и отсталости
Глобальная проблема бедности и отсталости Фирмы в экономике, или КАК разбогатеть
Фирмы в экономике, или КАК разбогатеть Денежные знаки Великобритании
Денежные знаки Великобритании Особенности товарного рынка. Понятие инфраструктуры рынка. Основные элементы инфраструктурного рынка
Особенности товарного рынка. Понятие инфраструктуры рынка. Основные элементы инфраструктурного рынка Управление конкурентноспособностью
Управление конкурентноспособностью Прогноз места России в мировой экономике к 2030 г
Прогноз места России в мировой экономике к 2030 г Оценка эффективности инноваций
Оценка эффективности инноваций Региональная экономика
Региональная экономика Основы теории предельной полезности
Основы теории предельной полезности Государственная поддержка
Государственная поддержка Экономическое обоснование капиталовложений в строительство завода по производству ячеистого бетона автоклавного твердения
Экономическое обоснование капиталовложений в строительство завода по производству ячеистого бетона автоклавного твердения