Содержание
- 2. What is a science? Science (from the Latin word scientia, meaning "knowledge") is a systematic enterprise
- 3. The earliest roots of science can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3500
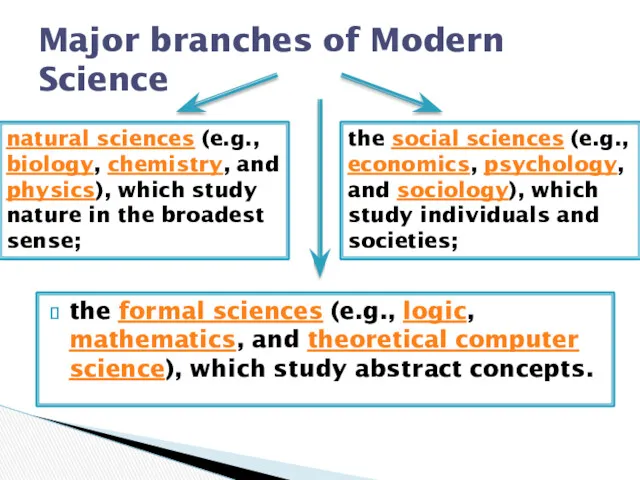
- 4. the formal sciences (e.g., logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science), which study abstract concepts. Major branches
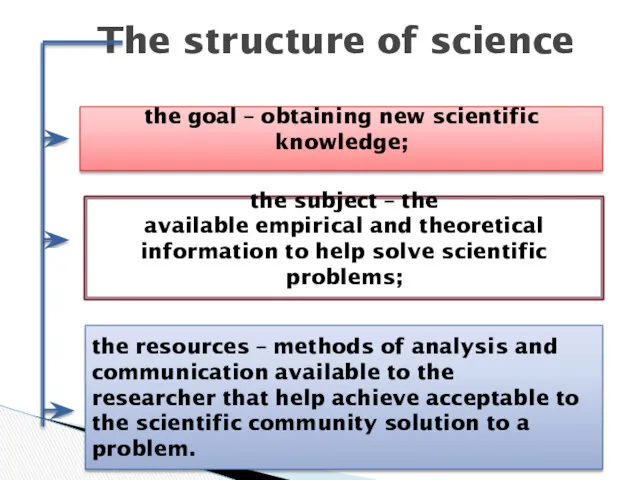
- 5. The structure of science the goal – obtaining new scientific knowledge; the subject – the available
- 6. 2) as a discipline that emerged during the second half of the XX-th century in response
- 7. 1) the general socio-cultural background of a particular historical epoch; 2) gnosiological, epistemological, and methodological studies;
- 9. Скачать презентацию




 Основы философии. Русская философия
Основы философии. Русская философия Жаһандық проблемалар және болашақ мәселесі. Футурология
Жаһандық проблемалар және болашақ мәселесі. Футурология Рождение новой европейской науки
Рождение новой европейской науки Динамика общественного развития
Динамика общественного развития Бердяев Николай Александрович. Русский философ
Бердяев Николай Александрович. Русский философ Социальная философия и историософия
Социальная философия и историософия Философские проблемы естествознания
Философские проблемы естествознания Философия и общественные науки в Новое и Новейшее время
Философия и общественные науки в Новое и Новейшее время Познание как деятельность. Истина и ее критерии
Познание как деятельность. Истина и ее критерии Русская философия
Русская философия Предмет логики. Человеческое мышление и его особенности. Понятие о законах и формах мышления
Предмет логики. Человеческое мышление и его особенности. Понятие о законах и формах мышления Человек в обществе
Человек в обществе Социальная философия
Социальная философия Духовная сфера
Духовная сфера Мораль. Нравственность. Долг. Совесть
Мораль. Нравственность. Долг. Совесть Координаты вектора в пространстве. Скалярное произведение векторов
Координаты вектора в пространстве. Скалярное произведение векторов Философия как разновидность мировоззрения
Философия как разновидность мировоззрения Философия Средневековья. Лекция 3
Философия Средневековья. Лекция 3 Потребности человека. (Обществознание, 6 класс)
Потребности человека. (Обществознание, 6 класс) Постструктурализм
Постструктурализм Философия средних веков
Философия средних веков ХХ ғ. Батыс Еуропа философиясы
ХХ ғ. Батыс Еуропа философиясы Конфуций
Конфуций Э.Г.Юдин методология құрылымы
Э.Г.Юдин методология құрылымы Начало цивилизации
Начало цивилизации Подготовка к ЕГЭ. Познание
Подготовка к ЕГЭ. Познание Смысл жизни
Смысл жизни Эссе по обществознанию. Критерии оценивания (ЕГЭ)
Эссе по обществознанию. Критерии оценивания (ЕГЭ)