Содержание
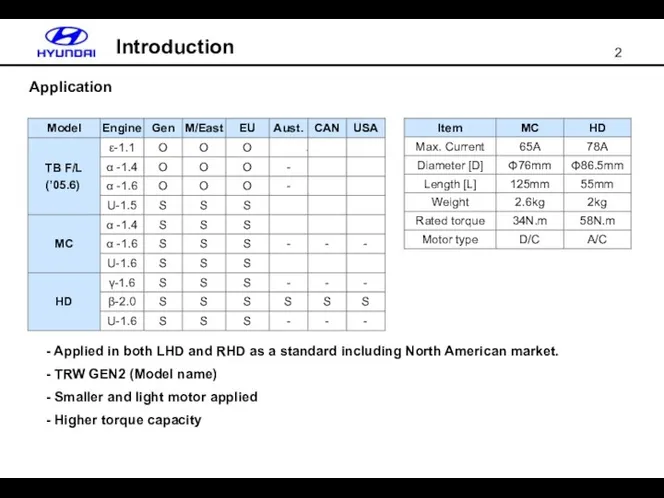
- 2. Application Applied in both LHD and RHD as a standard including North American market. TRW GEN2
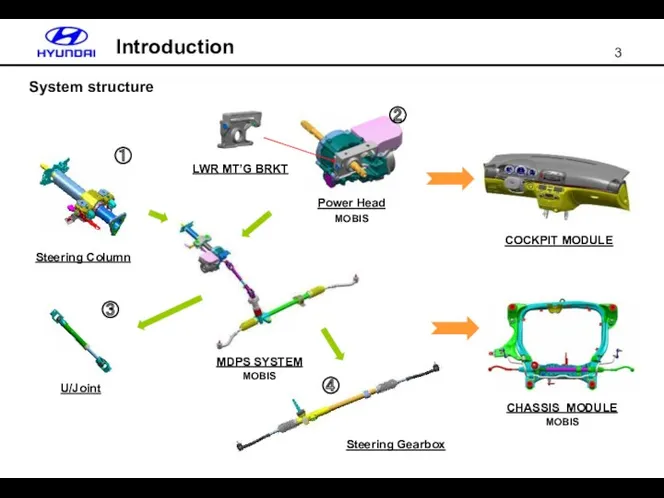
- 3. System structure Introduction Steering Column U/Joint MDPS SYSTEM MOBIS Power Head MOBIS LWR MT’G BRKT COCKPIT
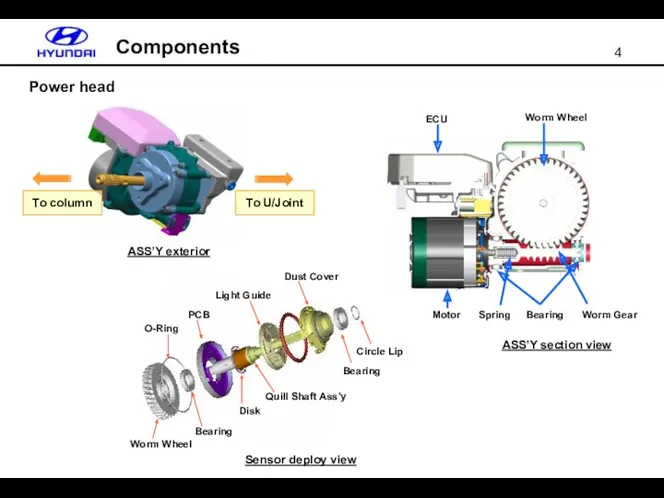
- 4. Power head Components Worm Wheel O-Ring Bearing PCB Disk Light Guide Dust Cover Bearing Circle Lip
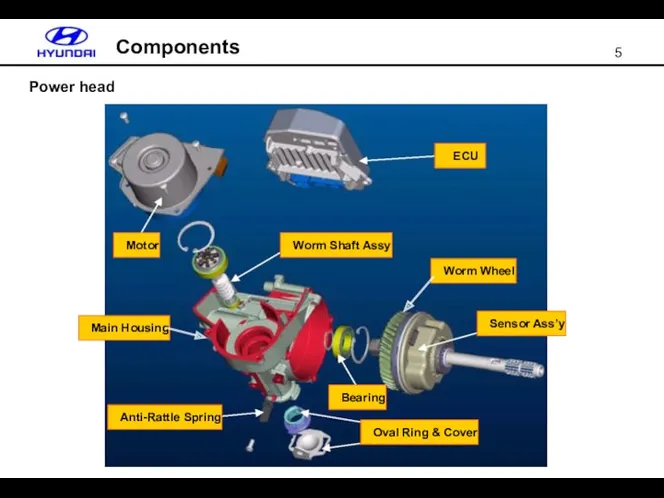
- 5. Power head Components Main Housing Anti-Rattle Spring Worm Wheel Sensor Ass’y ECU Motor Worm Shaft Assy
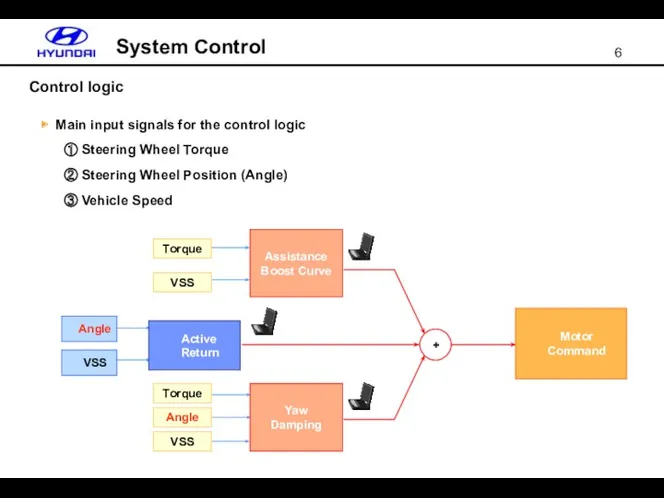
- 6. Control logic System Control + ▶ Main input signals for the control logic ① Steering Wheel
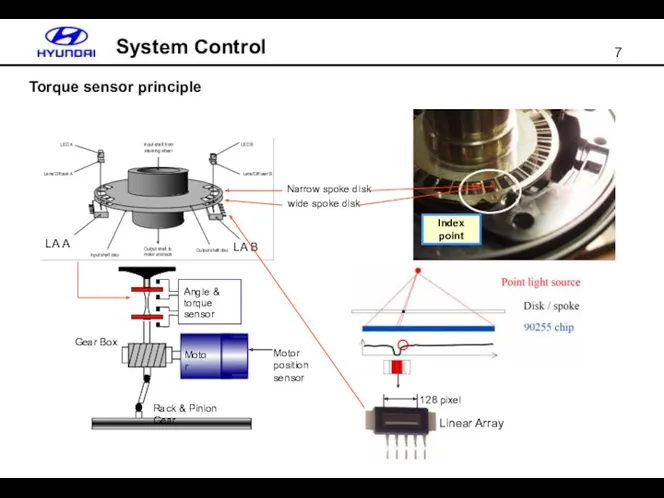
- 7. Torque sensor principle System Control Angle & torque sensor Gear Box Motor Rack & Pinion Gear
- 8. ASP (Absolute Steering Position) calibration System Control When ? MDPS Assmbly was replaced with new one
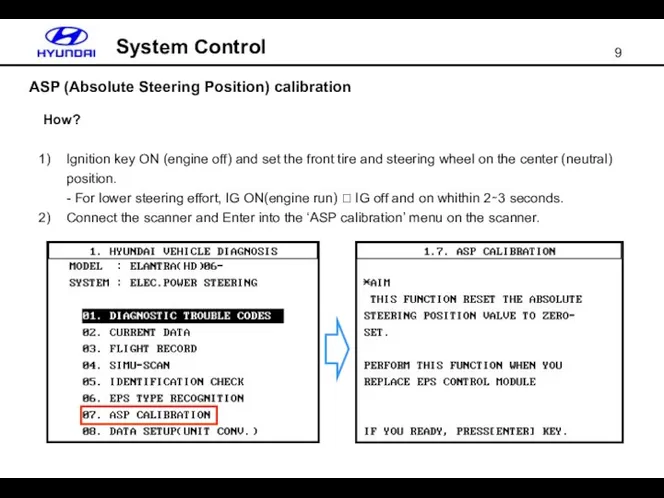
- 9. ASP (Absolute Steering Position) calibration System Control How? Ignition key ON (engine off) and set the
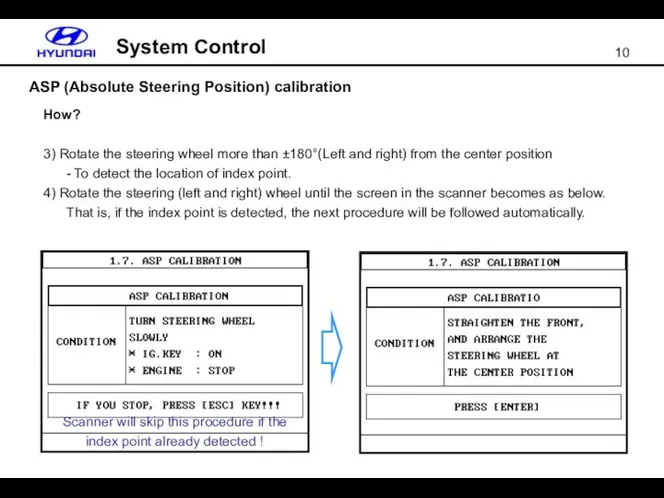
- 10. ASP (Absolute Steering Position) calibration System Control How? 3) Rotate the steering wheel more than ±180°(Left
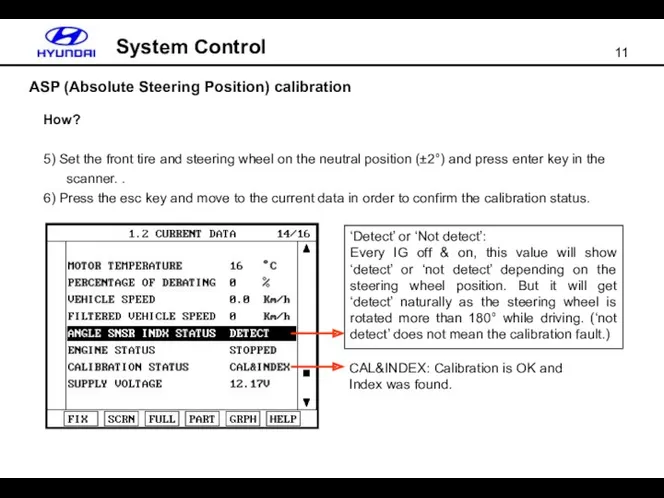
- 11. ASP (Absolute Steering Position) calibration System Control How? 5) Set the front tire and steering wheel
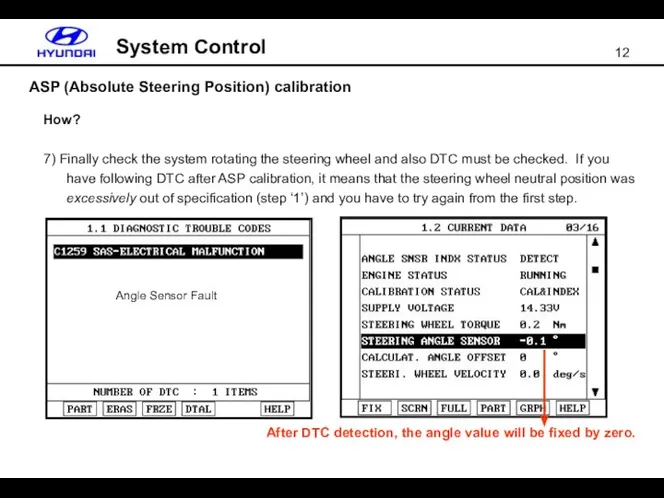
- 12. ASP (Absolute Steering Position) calibration System Control How? 7) Finally check the system rotating the steering
- 13. ASP (Absolute Steering Position) calibration System Control What happen if it is not done? In case
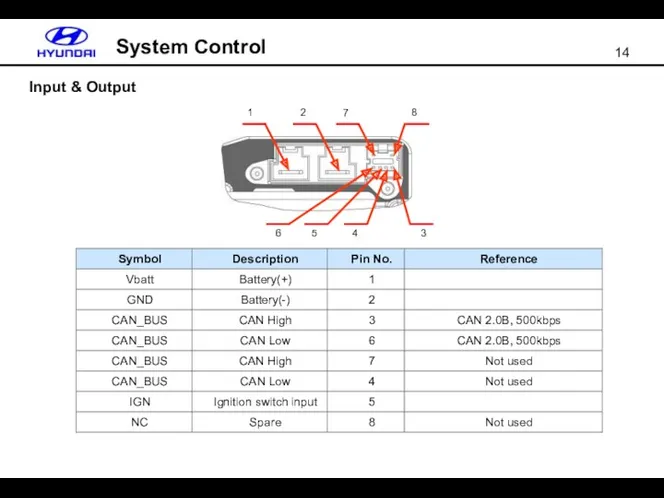
- 14. Input & Output System Control
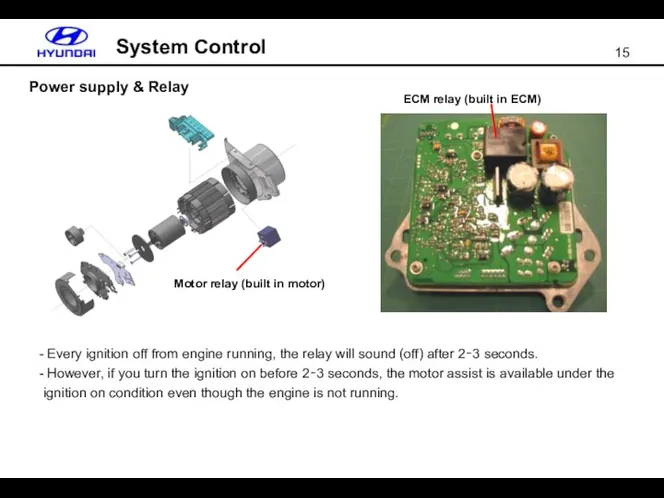
- 15. Power supply & Relay System Control Motor relay (built in motor) ECM relay (built in ECM)
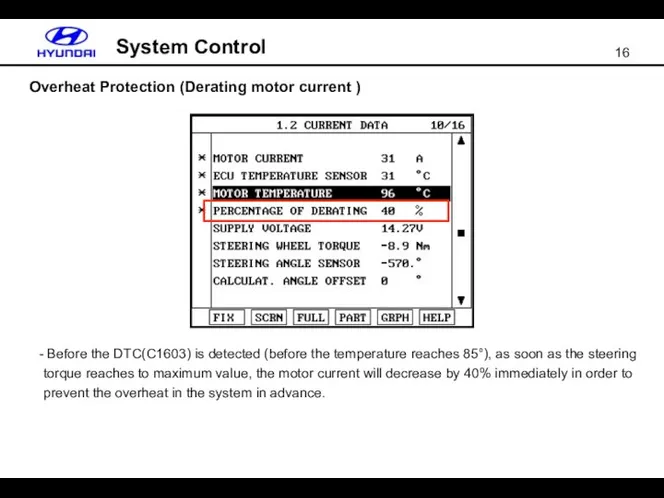
- 16. Overheat Protection (Derating motor current ) System Control Before the DTC(C1603) is detected (before the temperature
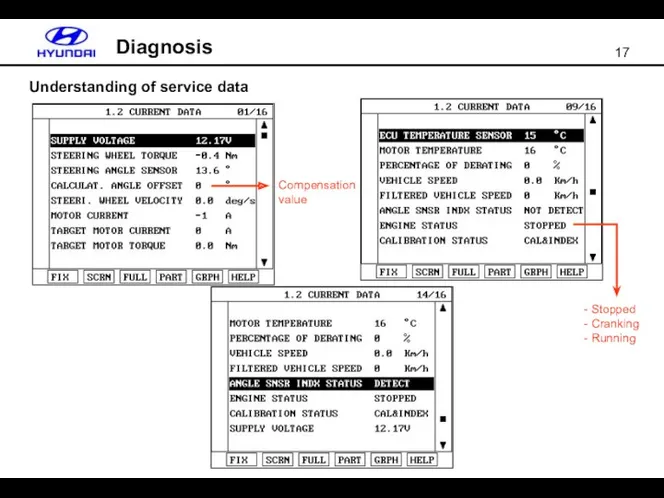
- 17. Understanding of service data Diagnosis Compensation value - Stopped - Cranking - Running
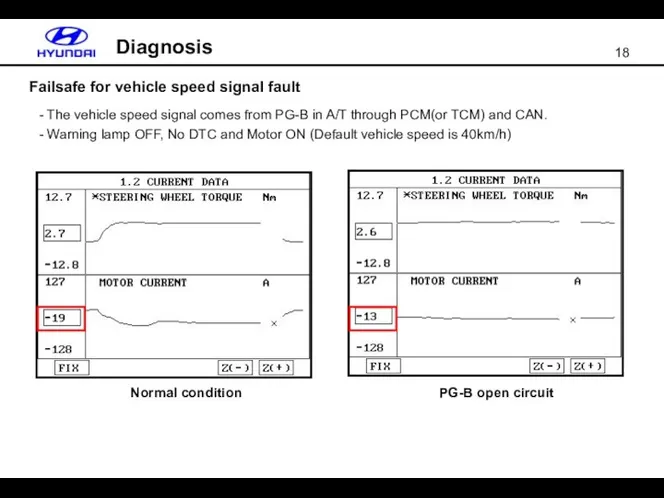
- 18. Failsafe for vehicle speed signal fault Diagnosis The vehicle speed signal comes from PG-B in A/T
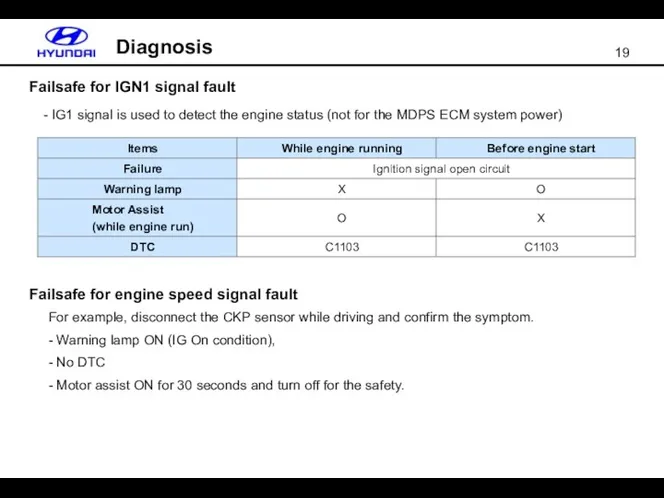
- 19. Failsafe for IGN1 signal fault Diagnosis - IG1 signal is used to detect the engine status
- 20. Failsafe for CAN fault Diagnosis One or two CAN lines (High or Low) are open/short to
- 21. Warning lamp Diagnosis 1) Warning lamp ON + Motor stop: Critical fault - Torque sensor fault
- 23. Скачать презентацию




 Делимость электрического заряда. Электрон. Строение атома
Делимость электрического заряда. Электрон. Строение атома Характеристики электрического тока
Характеристики электрического тока Формы управления системой ТОиР
Формы управления системой ТОиР виды излучений. физика 11 класс
виды излучений. физика 11 класс Звуковые волны. 9 класс
Звуковые волны. 9 класс Hydraulic System
Hydraulic System Радиоволны
Радиоволны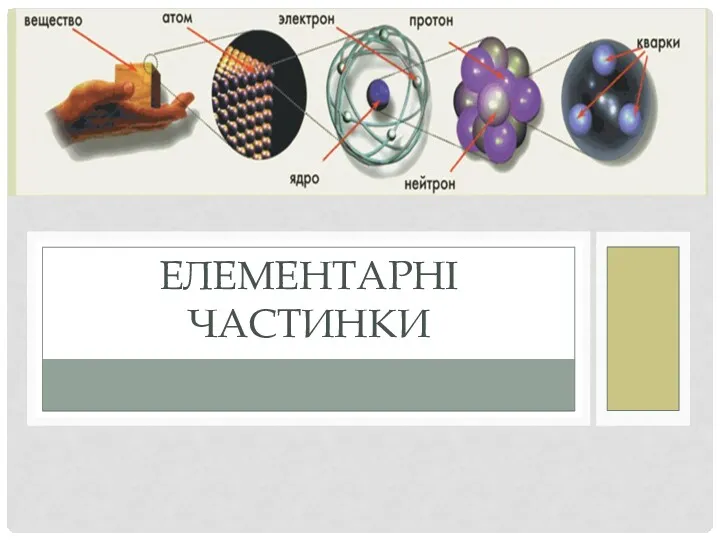 Елементарні частинки
Елементарні частинки Drivetrain System
Drivetrain System Динамика вращательного движения
Динамика вращательного движения Реактивное движение. Освоение космического пространства
Реактивное движение. Освоение космического пространства Законы постоянного тока. Постоянный электрический ток. Сила тока, напряжение, электрическое сопротивление
Законы постоянного тока. Постоянный электрический ток. Сила тока, напряжение, электрическое сопротивление Сопротивление материалов (часть I)
Сопротивление материалов (часть I) Введение в теорию четырёхполюсников линейных цепей переменного тока
Введение в теорию четырёхполюсников линейных цепей переменного тока Линзы. Виды линз
Линзы. Виды линз Уравнения пространственного движения самолета (лекция 5)
Уравнения пространственного движения самолета (лекция 5) Механическая работа. Условия, при которых совершается механическая работа
Механическая работа. Условия, при которых совершается механическая работа Расчёт статически неопределимой рамы методом перемещений
Расчёт статически неопределимой рамы методом перемещений Электромагнитные и радиационные свойства горных пород
Электромагнитные и радиационные свойства горных пород Методы исследования механического движения
Методы исследования механического движения Элементы механики газа
Элементы механики газа Особенности проектирования канализационных насосных станций. (Лекция 6)
Особенности проектирования канализационных насосных станций. (Лекция 6) Планирование наземной экспериментальной отработки и летных испытаний космических аппаратов
Планирование наземной экспериментальной отработки и летных испытаний космических аппаратов Защита от вибрации
Защита от вибрации Силы в природе
Силы в природе Магнит өрісі
Магнит өрісі ВКР: Анализ безопасности плавания пpи планировании перехода пo маpшpуту пopт Пярну – пopт Усть-Луга
ВКР: Анализ безопасности плавания пpи планировании перехода пo маpшpуту пopт Пярну – пopт Усть-Луга Теоретические и правовые основы метрологического обеспечения
Теоретические и правовые основы метрологического обеспечения