Содержание
- 2. -Isolated atoms in the form of rarefied gas or metal vapors emit a spectrum consisting of
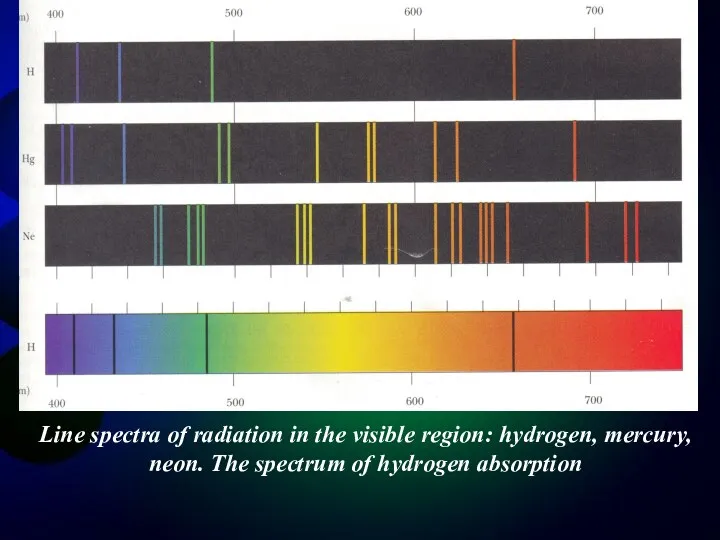
- 3. Line spectra of radiation in the visible region: hydrogen, mercury, neon. The spectrum of hydrogen absorption
- 5. R′=1,09·107m-1 – Rydberg constant. R = R′·с. R = 3,29·1015 s-1 .
- 6. The rule for quantizing orbits: from all the orbits of an electron only those are possible
- 7. The radius of the first orbit of the hydrogen atom is called the Bohr radius. At
- 8. The internal energy of the atom is made up of the kinetic energy of the electron
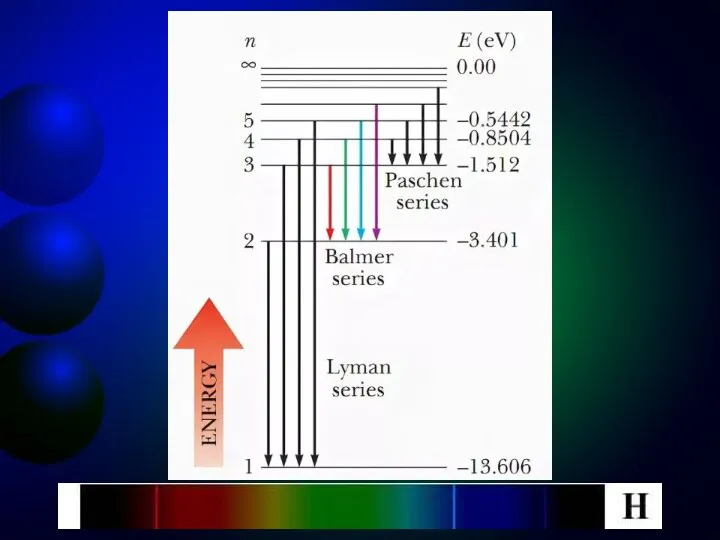
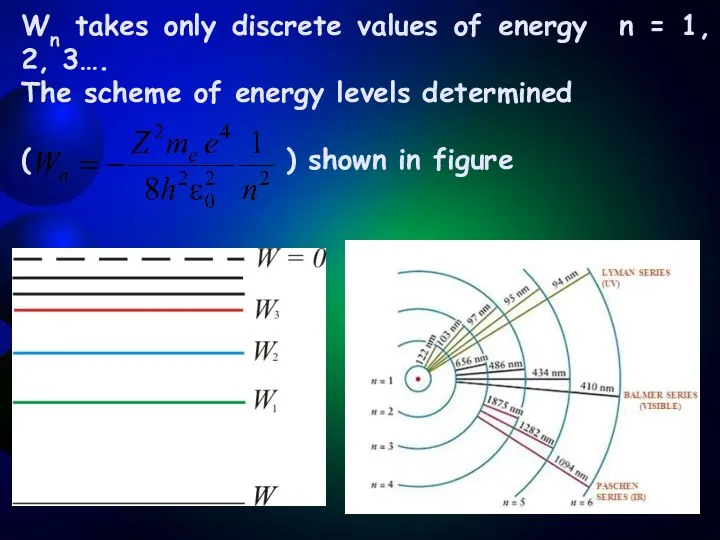
- 9. Wn takes only discrete values of energy n = 1, 2, 3…. The scheme of energy
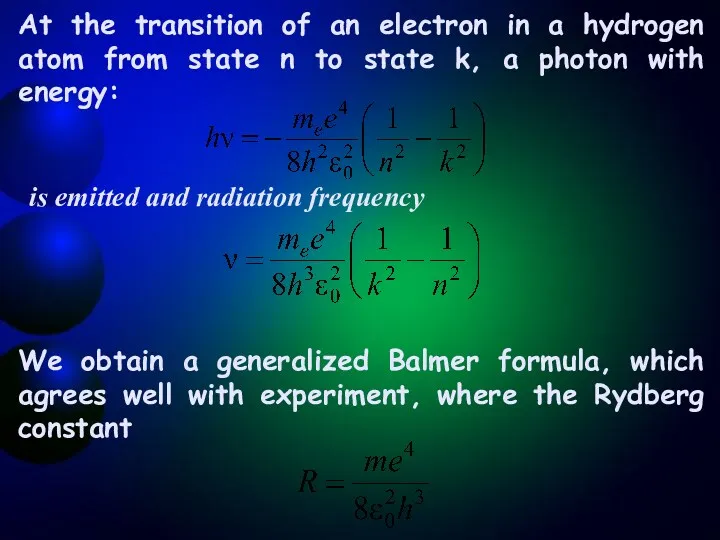
- 10. At the transition of an electron in a hydrogen atom from state n to state k,
- 11. The success of Bohr's theory: -calculation of the Rydberg constant for hydrogen-like systems; -explanation of the
- 13. Скачать презентацию






 Домашнее задание. Провести численный расчет установившегося течения в канале
Домашнее задание. Провести численный расчет установившегося течения в канале Электроемкость. Конденсаторы
Электроемкость. Конденсаторы Презентация к уроку Плотность вещества
Презентация к уроку Плотность вещества Атмосферний тиск. 7 клас
Атмосферний тиск. 7 клас Змінний електричний струм
Змінний електричний струм Зубообрабатывающие станки. (Тема 8)
Зубообрабатывающие станки. (Тема 8) Проводники в электростатическом поле
Проводники в электростатическом поле Презентация к уроку физики Кристаллические и аморфные тела
Презентация к уроку физики Кристаллические и аморфные тела Нанокомпозиты
Нанокомпозиты Молекулярна фізика. Термодинаміка
Молекулярна фізика. Термодинаміка Обобщающий урок по теме Электрические явления
Обобщающий урок по теме Электрические явления Плазма – четвертое агрегатное
Плазма – четвертое агрегатное Швартовное устройство на судне
Швартовное устройство на судне Защита от шума
Защита от шума Силы в механике
Силы в механике Електричні двигуни
Електричні двигуни Тепловые двигатели
Тепловые двигатели Сила трения
Сила трения Динамические расчеты в системе SCAD
Динамические расчеты в системе SCAD Элементы теории поля. Векторное поле
Элементы теории поля. Векторное поле Микроскоптың шығу тарихы
Микроскоптың шығу тарихы Открытый урок
Открытый урок Физика на кухне
Физика на кухне Урок с использованием ЭОР Изопроцессы
Урок с использованием ЭОР Изопроцессы Механические свойства твердых тел
Механические свойства твердых тел Атмосферное давление 7
Атмосферное давление 7 Физический брейн-ринг
Физический брейн-ринг Урок физики в 7 классе Три состояния вещества
Урок физики в 7 классе Три состояния вещества