Содержание
- 2. LECTURE No. 7 BASIC METHODS OF STUDYING NANOSTRUCTURED MATERIALS
- 3. INTRODUCTION The importance of the studying methods of nanostructured materials. Various techniques for detecting, measuring and
- 4. OBJECTIVES To describe how to characterize nanomaterials.
- 5. OUTLINE Electronic Microscopy Spectral methods of research Scanning Probe Test Methods
- 6. Electronic Microscopy Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- 7. Electronic Microscopy Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Measures: particle size and characterization. Sample preparation: Sample preparation is
- 8. Electronic Microscopy Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Measures particle size and characterization. Sample: conductive or sputter coated.
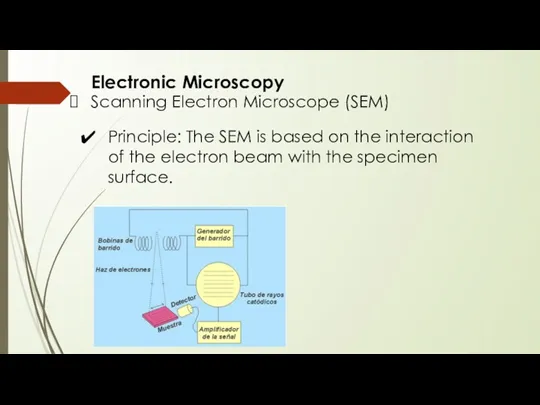
- 9. Electronic Microscopy Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Principle: The SEM is based on the interaction of the
- 10. Electronic Microscopy Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- 11. Spectral methods of research Electronic Auger Spectroscopy (AES) Analytical technique used specifically in the study of
- 12. Spectral methods of research Secondary ion mass spectroscopy Analyze the composition of solid surfaces and thin
- 13. Spectral methods of research Laser microprobe analysis It uses a focused laser for microanalysis. It employs
- 14. Scanning Probe Test Methods The most widely used in the field of nanomaterials and nanotechnology. The
- 15. Scanning Probe Test Methods The cost and size of probe microscopes are usually much lower than
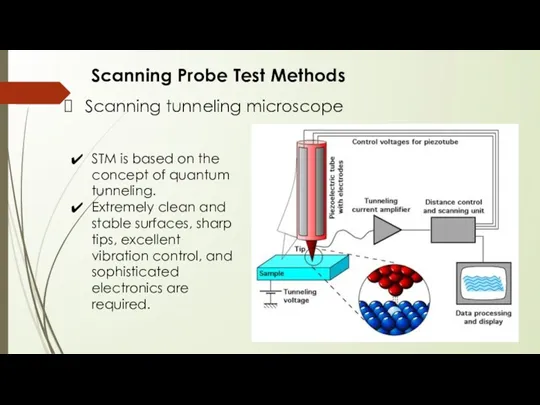
- 16. Scanning Probe Test Methods Scanning tunneling microscope STM is based on the concept of quantum tunneling.
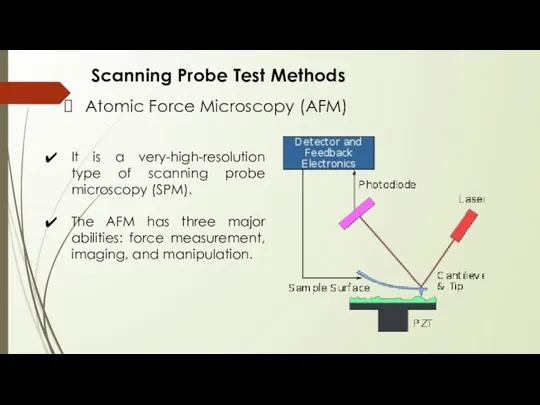
- 17. Scanning Probe Test Methods Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) It is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe
- 18. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Dynamic light scattering (DLS) Nanoparticle Surface Area Monitor (NSAM) Condensation Particle Counter (CPC)
- 19. Control questions What are the key parameters in the physical characterization of nanostructured materials? Describe the
- 21. Скачать презентацию















 Винтовые поверхности и изделия с резьбой. Крепежные изделия
Винтовые поверхности и изделия с резьбой. Крепежные изделия Зубчатые передачи
Зубчатые передачи Моменты импульса (угловые моменты). Часть вторая
Моменты импульса (угловые моменты). Часть вторая Градуировка спектроскопа
Градуировка спектроскопа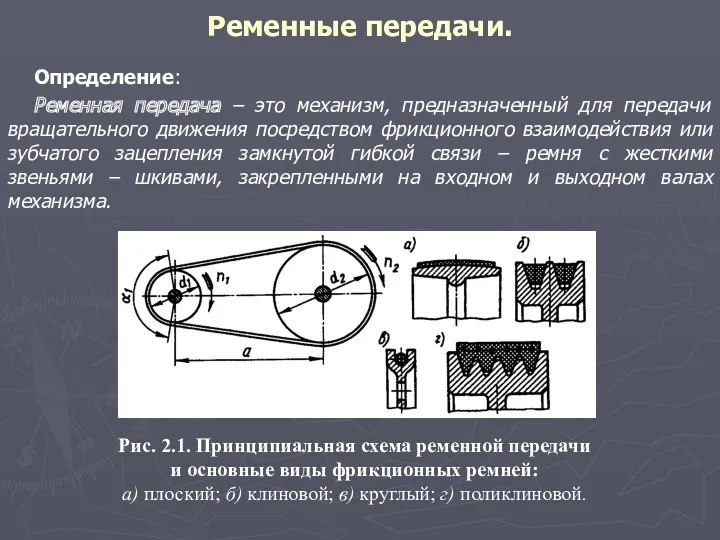 Ременные передачи
Ременные передачи Количество теплоты
Количество теплоты Источники оптического импульсного когерентного излучения для информационных систем II. Полупроводниковые лазеры
Источники оптического импульсного когерентного излучения для информационных систем II. Полупроводниковые лазеры Разработка лаборатории по ремонту и диагностики топливных систем дизельных двигателей
Разработка лаборатории по ремонту и диагностики топливных систем дизельных двигателей Техническое диагностирование автомобильной техники
Техническое диагностирование автомобильной техники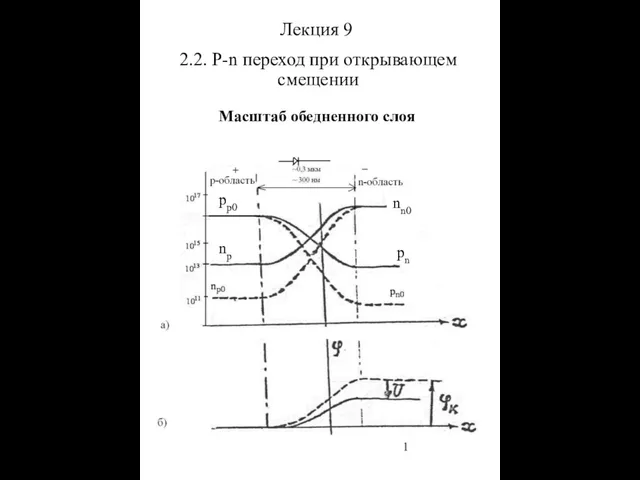 P-n переход при открывающем смещении. Масштаб обедненного слоя
P-n переход при открывающем смещении. Масштаб обедненного слоя Тепломассообмен. Конвекция
Тепломассообмен. Конвекция Кинематика материальной точки. Физические модели
Кинематика материальной точки. Физические модели Основы физической реабилитации
Основы физической реабилитации Физические и геологические основы сейсморазведки
Физические и геологические основы сейсморазведки Колебания в неживой и живой природе. Урок 11
Колебания в неживой и живой природе. Урок 11 Презентация. Законы Ньютона
Презентация. Законы Ньютона Презентация по теме Механические колебания
Презентация по теме Механические колебания Работа, кинетическая энергия
Работа, кинетическая энергия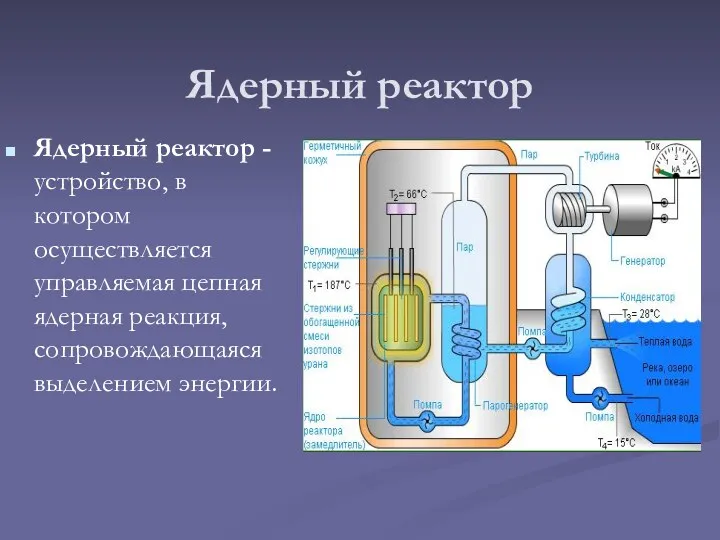 Ядерный реактор
Ядерный реактор Проводниковые материалы
Проводниковые материалы Осесимметричные тонкостенные оболочки. Лекция 12
Осесимметричные тонкостенные оболочки. Лекция 12 Выяснение условия равновесия рычага
Выяснение условия равновесия рычага Открытия М.В. Ломоносова в области физики и астрономии
Открытия М.В. Ломоносова в области физики и астрономии Масса вещества. Плотность
Масса вещества. Плотность Электрическая цепь и ее элементы
Электрическая цепь и ее элементы Migrating from Streams to GoldenGate12c
Migrating from Streams to GoldenGate12c Электроразведка. Методы профилирования
Электроразведка. Методы профилирования Управляемость автомобиля. Лекция № 11
Управляемость автомобиля. Лекция № 11