Содержание
- 2. Acronyms IT Information Technology BLT Bacon, Lettuce & Tomato SSADM Structured Systems Analysis & Design Method
- 3. Unit 11: Systems analysis & design SSADM Tools & Techniques Overview
- 4. Learning Outcomes Task 1 – Principles of systems analysis & design Produce a report describing the
- 5. Typical Tools and Techniques used in SSADM Activity diagrams Context diagrams Data Flow Diagrams Entity relationship
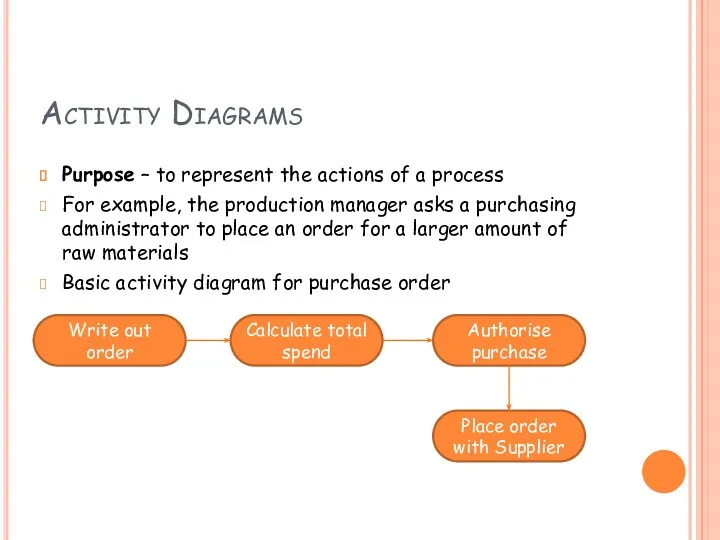
- 6. Activity Diagrams Purpose – to represent the actions of a process For example, the production manager
- 7. Activity Diagrams - Tasks Create activity diagrams for the following examples;- Making a cup of tea
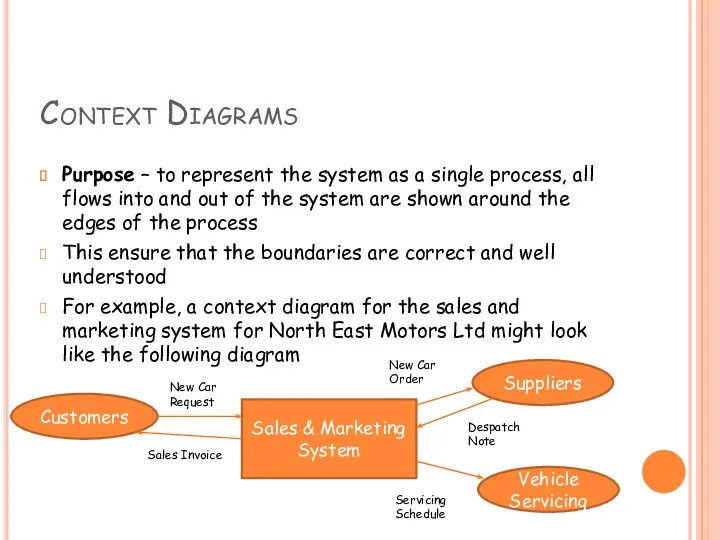
- 8. Context Diagrams Purpose – to represent the system as a single process, all flows into and
- 9. Context Diagrams - Tasks Create context diagrams for the following examples;- A customer bring a car
- 10. Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) Purpose :- To represent the information flows of a system The diagrams
- 11. Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) For example, the production manager asks a purchasing administrator to place an
- 12. Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERD) Also referred to as a Logical Data Model or Logical Data Structure
- 13. ERD Diagrams - Tasks Create Entity Relationship Diagrams for the following examples;- A customer buying a
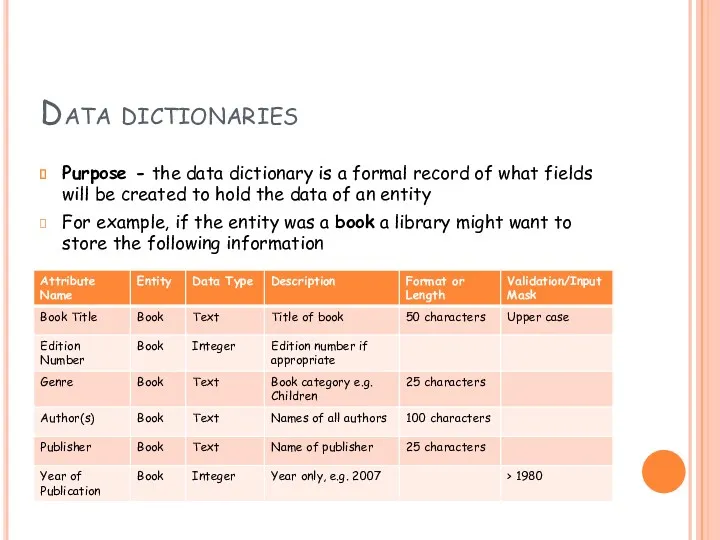
- 14. Data dictionaries Purpose - the data dictionary is a formal record of what fields will be
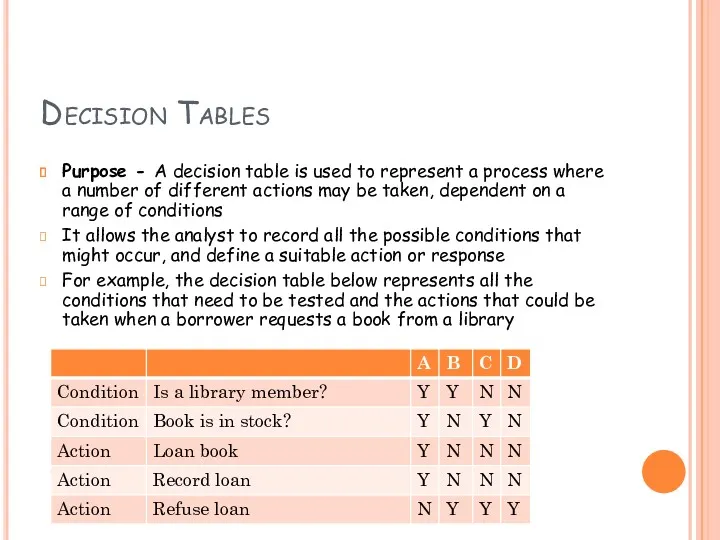
- 15. Decision Tables Purpose - A decision table is used to represent a process where a number
- 16. Decision Tables - Tasks Create Decision Table for the following example;- The process you go through
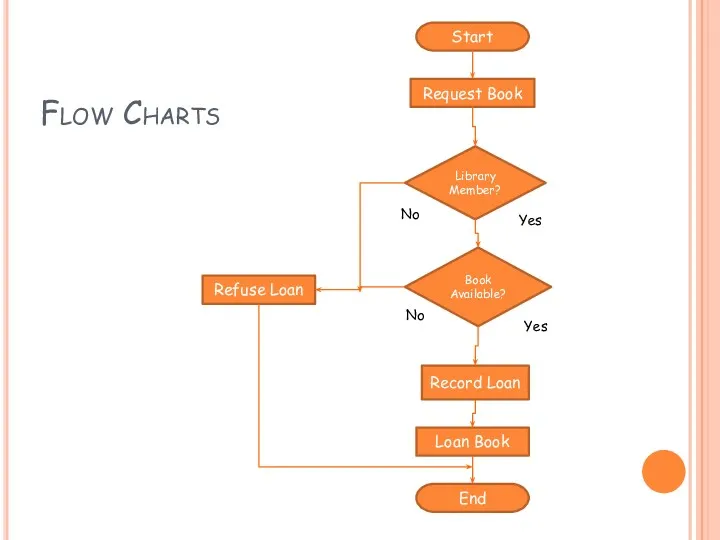
- 17. Flow Charts Purpose :– A flow chart shows how steps in a process fit together and
- 18. Flow Charts Start Request Book Refuse Loan Record Loan Loan Book End Library Member? Book Available?
- 19. Flow Chart- Tasks Create Flow Chart for the following example;- The process you go through while
- 20. Structured English Purpose – to give the analyst the ability to represent a process as a
- 21. Structured English- Tasks Create Structured English for the following example;- The process you go through while
- 22. Non-diagrammatic Techniques Relational data analysis Requirements definition Function definition Formulation of options Specification prototyping
- 24. Скачать презентацию















 Простейшая (каскадная) модель жизненного цикла ПО. Техническое задание. Требования к содержанию и оформлению
Простейшая (каскадная) модель жизненного цикла ПО. Техническое задание. Требования к содержанию и оформлению Финансовая отчетность для владельца бизнеса. 1С:Управление небольшой фирмой 8
Финансовая отчетность для владельца бизнеса. 1С:Управление небольшой фирмой 8 СУБД MySQL PHP. Лекція №7
СУБД MySQL PHP. Лекція №7 Профессия: Оператор компьютерного набора
Профессия: Оператор компьютерного набора Знакомство с языком программирования Python. Ввод. Вывод. Оператор присваивания
Знакомство с языком программирования Python. Ввод. Вывод. Оператор присваивания Устройство компьютера. Схема устройства компьютера
Устройство компьютера. Схема устройства компьютера Лидар. Сбор входных данных
Лидар. Сбор входных данных Рекурсия
Рекурсия Программирование разветвляющихся алгоритмов
Программирование разветвляющихся алгоритмов Фейковые новости и как их отличать от настоящих
Фейковые новости и как их отличать от настоящих Как создать свой сайт
Как создать свой сайт Берсерк. Самоучитель
Берсерк. Самоучитель Миркомир. Игра
Миркомир. Игра Предметно-ориентированные информационные системы
Предметно-ориентированные информационные системы Розробка системи обміну повідомленнями для Twitter, на базі мобільних технологій
Розробка системи обміну повідомленнями для Twitter, на базі мобільних технологій Эффективные инструменты визуализации учебной информации
Эффективные инструменты визуализации учебной информации Тестирование программного обеспечения. Основы реляционных баз данных. Работа с SQL. (Урок 6)
Тестирование программного обеспечения. Основы реляционных баз данных. Работа с SQL. (Урок 6) Логические выражения и таблицы истинности. Логика
Логические выражения и таблицы истинности. Логика Что такое Unity и Vuforia
Что такое Unity и Vuforia Хранение и предварительная обработка больших наборов данных с помощью Tensor Flow
Хранение и предварительная обработка больших наборов данных с помощью Tensor Flow Турбопоиск. Предложение для компании “Концепт-Строй”
Турбопоиск. Предложение для компании “Концепт-Строй” Кодирование звуковой информации. Представление информации в компьютере
Кодирование звуковой информации. Представление информации в компьютере Математичне програмування. Задачі оптимізації. Задача лінійного програмування. Лекція 5
Математичне програмування. Задачі оптимізації. Задача лінійного програмування. Лекція 5 Внешние устройства компьютера
Внешние устройства компьютера История развития вычислительной техники
История развития вычислительной техники Проектирование реляционных баз данных
Проектирование реляционных баз данных Графический редактор PAINT
Графический редактор PAINT Методы анализа сложности рекурсивных алгоритмов
Методы анализа сложности рекурсивных алгоритмов