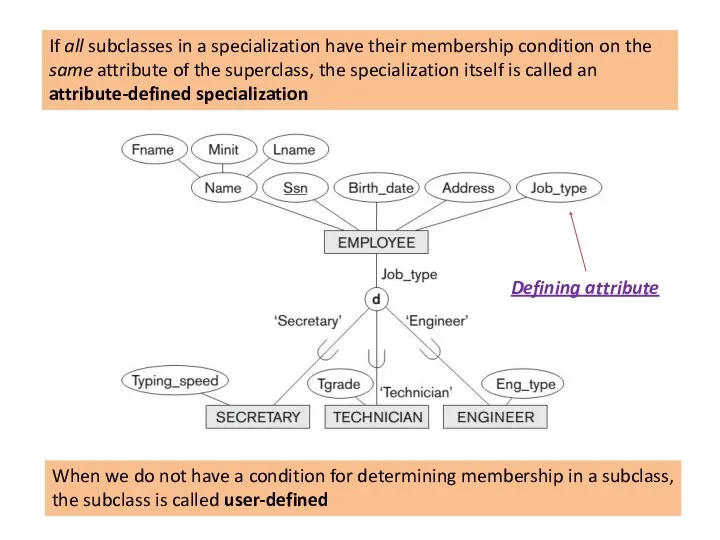
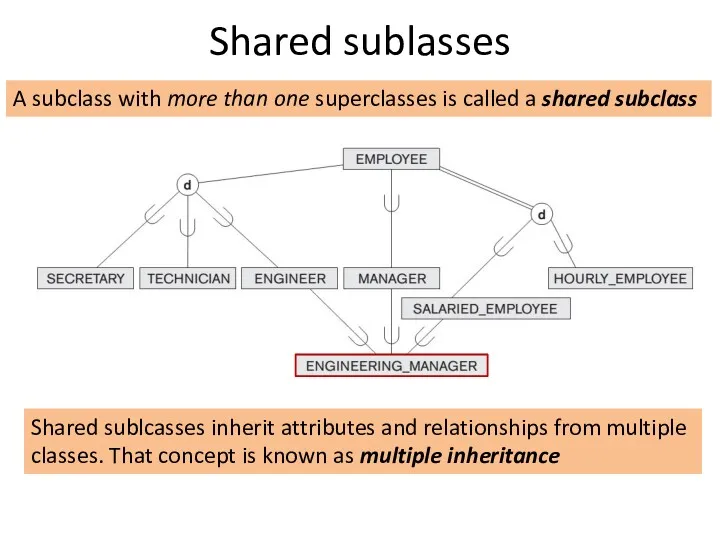
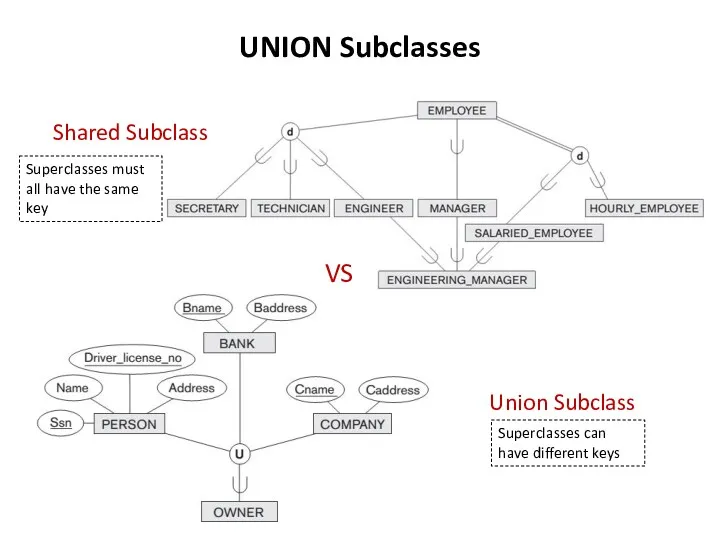
UNION Subclasses
ENGINEERING_MANAGER is a subclass of each of the three superclasses
ENGINEER, MANAGER, and SALARIED_EMPLOYEE, so an entity that is a member of ENGINEERING_MANAGER must exist in all three.
This represents the constraint that an engineering manager must be an ENGINEER, a MANAGER, and a SALARIED_EMPLOYEE simultaneously;
that is, ENGINEERING_MANAGER is a subset of the intersection of the three classes (sets of entities).
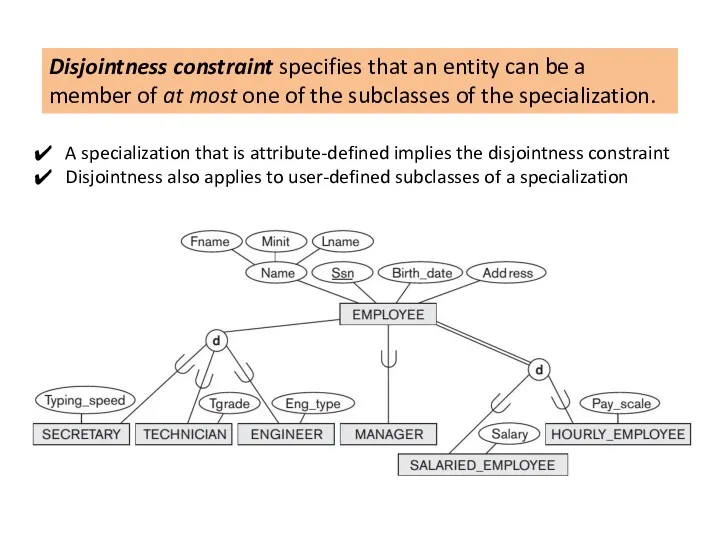
Shared subclass such as ENGINEERING_MANAGER inherits all the attributes of its superclasses SALARIED_EMPLOYEE, ENGINEER, and MANAGER
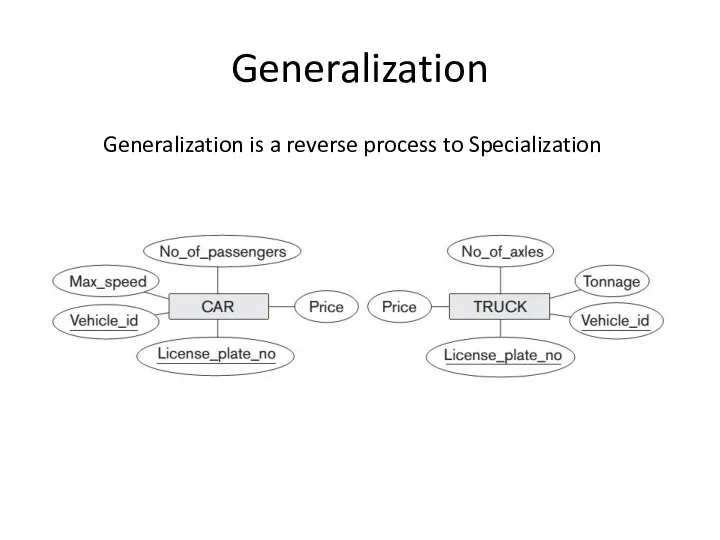
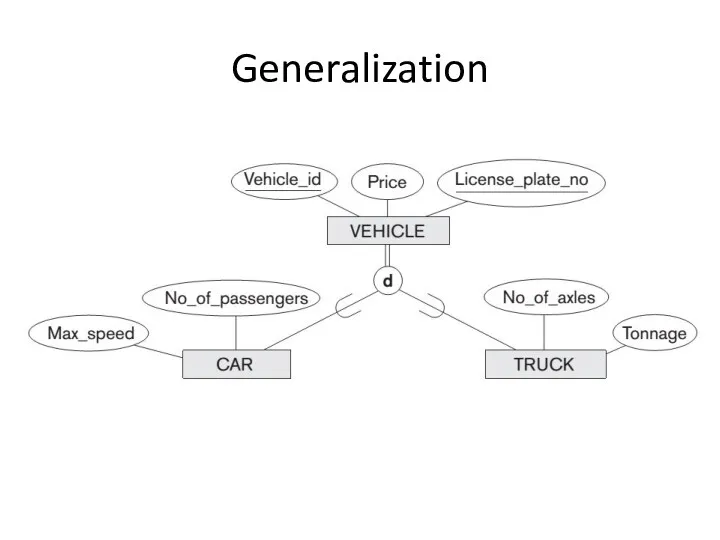
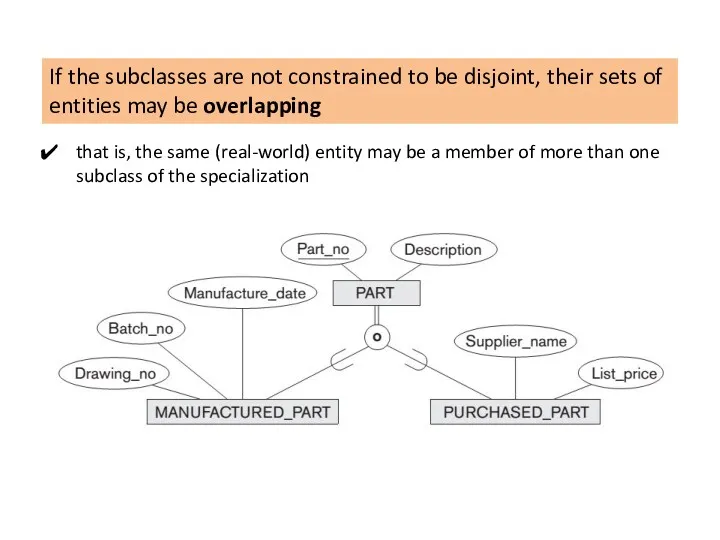
Union subclass is a subset of the union of its superclasses.
Hence, an entity that is a member of OWNER must exist in only one of the superclasses. This represents the constraint that an OWNER may be a COMPANY, a BANK, or a PERSON.
Union subclass such as OWNER entity inherits the attributes of a COMPANY, a PERSON, or a BANK, depending on the superclass to which the entity belongs.



 Пространственная информация и ее представление в ГИС
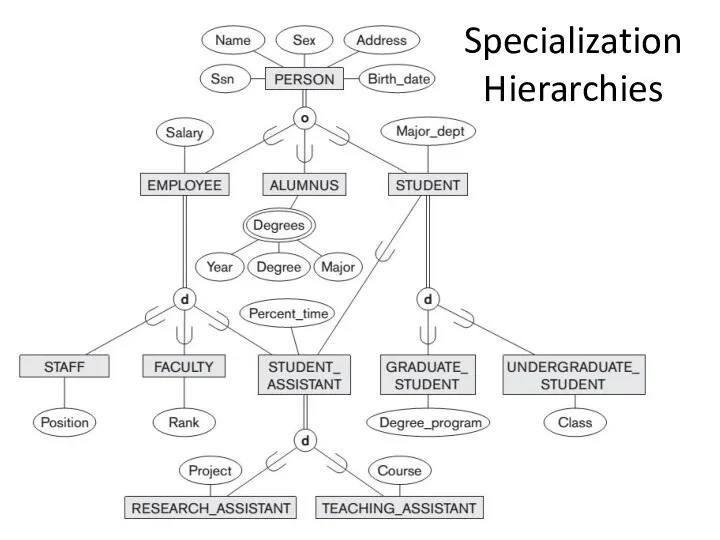
Пространственная информация и ее представление в ГИС Единицы измерения количества информации
Единицы измерения количества информации Методические основы анализа и проектирования ПО
Методические основы анализа и проектирования ПО Примитивы синхронизации. Типы синхронизирующих примитивов
Примитивы синхронизации. Типы синхронизирующих примитивов Выбор данных с использованием команды SELECT языка SQL
Выбор данных с использованием команды SELECT языка SQL Графические редакторы Технология обработки цифровой информации
Графические редакторы Технология обработки цифровой информации Состав системного блока компьютера
Состав системного блока компьютера Вопросы модернизации ЛКС в г. Санкт-Петербурге с применением технологии PON
Вопросы модернизации ЛКС в г. Санкт-Петербурге с применением технологии PON Электромагнитное излучение и его влияние на здоровье человека
Электромагнитное излучение и его влияние на здоровье человека Есептеуіш техниканың даму тарихы
Есептеуіш техниканың даму тарихы Путешествие в страну информатики
Путешествие в страну информатики Мобильные приложения для обучения
Мобильные приложения для обучения Электронные таблицы
Электронные таблицы Презентация к уроку информатики и ИКТ
Презентация к уроку информатики и ИКТ Центры обработки данных (ЦОД)
Центры обработки данных (ЦОД) Концепции системы 1С:Предприятия
Концепции системы 1С:Предприятия Cascading Style Sheet (CSS)
Cascading Style Sheet (CSS) Информационный урок Безопасность в сети интернет
Информационный урок Безопасность в сети интернет Безопасные сайты для детей
Безопасные сайты для детей Презентация к уроку на тему Архиваторы
Презентация к уроку на тему Архиваторы Форматирование символов. MS WORD 1
Форматирование символов. MS WORD 1 Информация. Двоичное кодирование информации
Информация. Двоичное кодирование информации Презентация Представление числовой информации с помощью систем счисления
Презентация Представление числовой информации с помощью систем счисления Развитие творческой активности и умственной самостоятельности школьников
Развитие творческой активности и умственной самостоятельности школьников Основы вычислительных сетей. Модель OSI
Основы вычислительных сетей. Модель OSI Тестирование информационной системы
Тестирование информационной системы Основы языка Pascal. Графика
Основы языка Pascal. Графика Проект Компьютер и здоровье школьников
Проект Компьютер и здоровье школьников