Содержание
- 2. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Major Topics Decision support systems
- 3. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Decision Support Systems Decision support
- 4. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Decision Support Systems Decision support
- 5. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Decision Support System Users Decision
- 6. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Decision Making Under Risk Decisions
- 7. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Decision-Making Style Decision-making styles of
- 8. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Analytic Decision Making Relies on
- 9. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Analytic Decision Making Use mathematics
- 10. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Heuristic Decision Making A heuristic
- 11. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Analytic and Heuristic Decision Making
- 12. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Intelligence, Choice, and Design The
- 13. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Intelligence Phase The intelligence phase
- 14. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Intelligence Phase A DSS can
- 15. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Choice Phase In the choice
- 16. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Design Phase In the design
- 17. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Design Phase A DSS can
- 18. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Semistructured Decisions Structured decisions are
- 19. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Dimensions of Semistructured Decisions Three
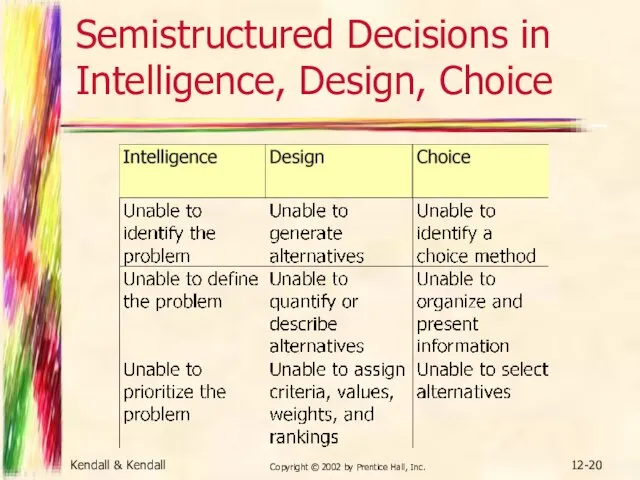
- 20. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Semistructured Decisions in Intelligence, Design,
- 21. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Decision Support System A decision
- 22. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Decision Support System Methods Weighing
- 23. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Weighing Method The weighing method
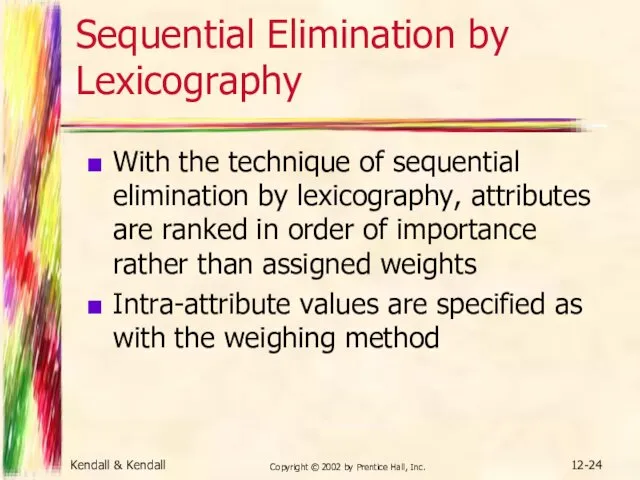
- 24. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Sequential Elimination by Lexicography With
- 25. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Sequential Elimination by Conjunctive Constraints
- 26. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Goal Programming The goal-programming model
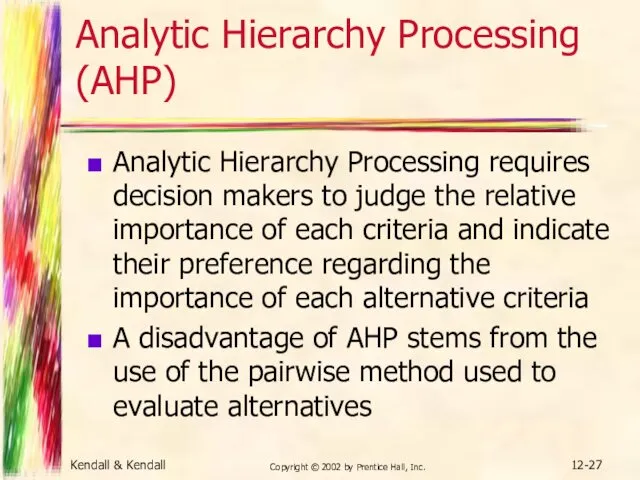
- 27. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Analytic Hierarchy Processing (AHP) Analytic
- 28. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Advantage of Analytic Hierarchy Processing
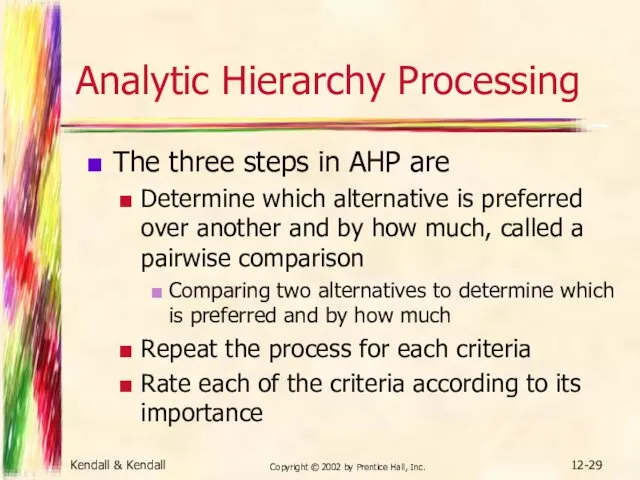
- 29. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Analytic Hierarchy Processing The three
- 30. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Expert Systems Expert systems are
- 31. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Neural Nets Neural nets are
- 32. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- Recommendation Systems Recommendation systems are
- 33. Kendall & Kendall Copyright © 2002 by Prentice Hall, Inc. 12- World Wide Web and Decision
- 35. Скачать презентацию



















 Microsoft OEM Activation (OA) & MDOS Onboarding Training Global Partner Onboarding Team
Microsoft OEM Activation (OA) & MDOS Onboarding Training Global Partner Onboarding Team Разработка игрового приложения в жанре выживания
Разработка игрового приложения в жанре выживания Программирование задач с использованием одномерных массивов
Программирование задач с использованием одномерных массивов Как устроен компьютер
Как устроен компьютер Маруся! Ваш дружелюбный голосовой помощник
Маруся! Ваш дружелюбный голосовой помощник Для чего создан Workbook
Для чего создан Workbook М-файлдар
М-файлдар المحاضرة الثالثة الاسبوع الرابع من الانقطاع الفصل الخامس أدوات جمع المعلومات (1)
المحاضرة الثالثة الاسبوع الرابع من الانقطاع الفصل الخامس أدوات جمع المعلومات (1) Теплотехнические расчеты ограждающих конструкций зданий с применением программного комплекса temper-3d
Теплотехнические расчеты ограждающих конструкций зданий с применением программного комплекса temper-3d Векторный графический редактор Open office.org Draw
Векторный графический редактор Open office.org Draw Сетевое издание РИА Новости
Сетевое издание РИА Новости ВКР: Разработка программного модуля проверки АРМ разработчика в среде Navisworks
ВКР: Разработка программного модуля проверки АРМ разработчика в среде Navisworks Структура ГИС (данные)
Структура ГИС (данные) Язык запросов SQL. Многотабличные запросы
Язык запросов SQL. Многотабличные запросы Формирование изображения на экране монитора
Формирование изображения на экране монитора Электронный документооборот (ЭДО)
Электронный документооборот (ЭДО) Сборка ПК
Сборка ПК Принципи організації розподілених інформаційних систем на основі баз даних та експертних систем в освіті
Принципи організації розподілених інформаційних систем на основі баз даних та експертних систем в освіті Спутниковая связь и ее роль в жизни человека
Спутниковая связь и ее роль в жизни человека Инструкция по использованию Среды дистанционного обучения Мираполис
Инструкция по использованию Среды дистанционного обучения Мираполис Комп'ютерна графіка та робота з нею
Комп'ютерна графіка та робота з нею Двоичное кодирование
Двоичное кодирование Шифр Плейфера. Полибианский квадрат
Шифр Плейфера. Полибианский квадрат Світові тенденції розвитку засобів телекомунікації та їх стан в Україні
Світові тенденції розвитку засобів телекомунікації та їх стан в Україні Презентации по теме Программирование на языке Паскаль
Презентации по теме Программирование на языке Паскаль Динамические данные разветвленной структуры
Динамические данные разветвленной структуры Презентация по теме Понятие как форма мышления 6класс
Презентация по теме Понятие как форма мышления 6класс Корпоративные сети
Корпоративные сети