Слайд 2

LECTURE 9
BASICS OF TIME SERIES FORECASTING
Saidgozi Saydumarov
Sherzodbek Safarov
QM Module Leaders
ssaydumarov@wiut.uz
s.safarov@wiut.uz
Office
hours: by appointment
Room IB 205
EXT: 546
Слайд 3

Lecture outline:
to estimate the change of a value over time and
graph the dynamics of the value
to apply the time series analysis to forecasting a value
to use the two forecasting models:
a) Additive
b) Multiplicative
Слайд 4

Components of time series graph
Trend – the overall pattern of changes
in a specific value over a long period of time (or an overall movement of the time series graph).
Seasonal – regular patterns of variation over one year or less (or repetitive movements of the time series graph).
Irregular – random changes that generally cannot be predicted (or random movements of the time series graph for periods less than a year).
Cyclical – variations above or below the trend line for periods of longer than one year (or cyclical movements of the time series graph for periods of longer than one year)
Слайд 5
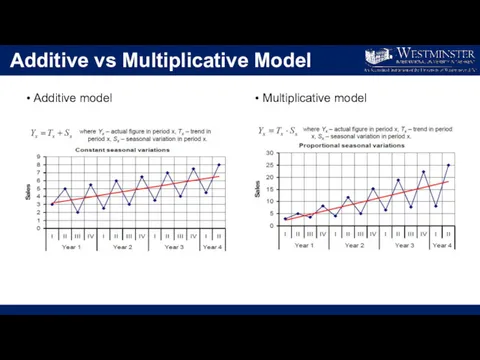
Additive vs Multiplicative Model
Additive model
Multiplicative model
Слайд 6
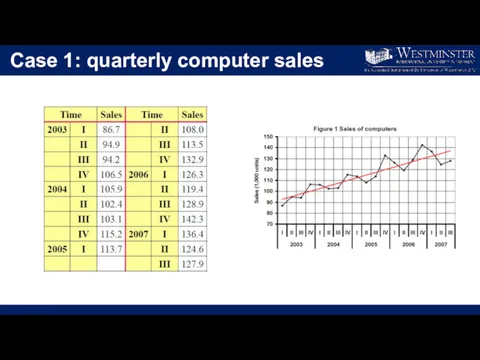
Case 1: quarterly computer sales
Слайд 7
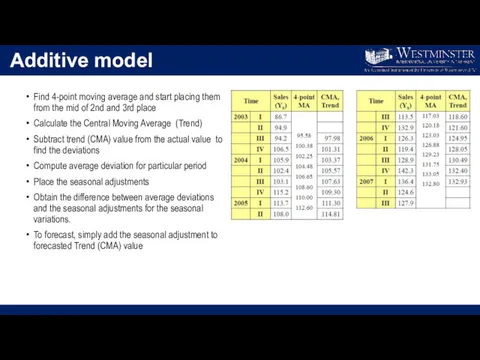
Additive model
Find 4-point moving average and start placing them from the
mid of 2nd and 3rd place
Calculate the Central Moving Average (Trend)
Subtract trend (CMA) value from the actual value to find the deviations
Compute average deviation for particular period
Place the seasonal adjustments
Obtain the difference between average deviations and the seasonal adjustments for the seasonal variations.
To forecast, simply add the seasonal adjustment to forecasted Trend (CMA) value
Слайд 8
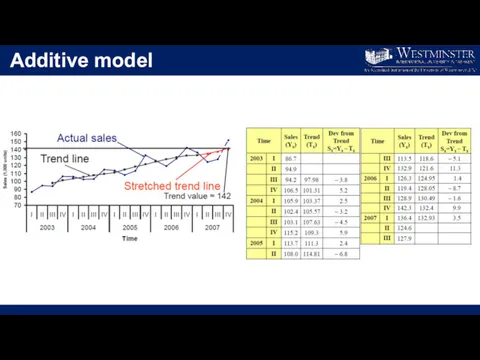
Слайд 9
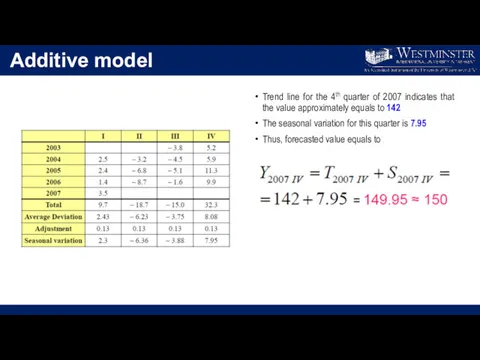
Additive model
Trend line for the 4th quarter of 2007 indicates that
the value approximately equals to 142
The seasonal variation for this quarter is 7.95
Thus, forecasted value equals to
Слайд 10
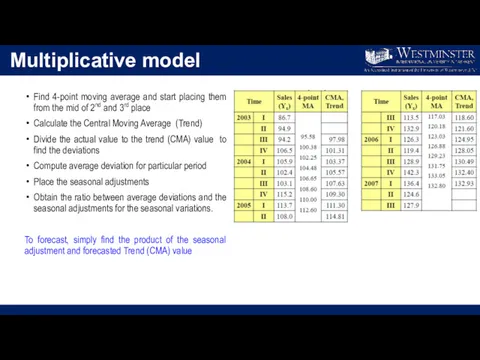
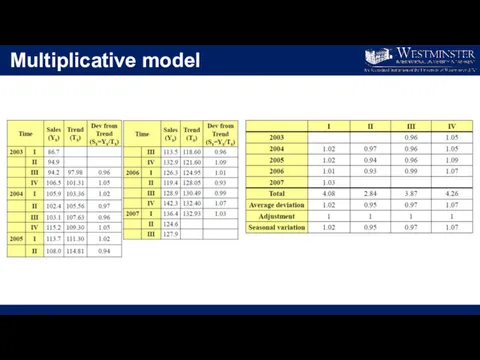
Multiplicative model
Find 4-point moving average and start placing them from the
mid of 2nd and 3rd place
Calculate the Central Moving Average (Trend)
Divide the actual value to the trend (CMA) value to find the deviations
Compute average deviation for particular period
Place the seasonal adjustments
Obtain the ratio between average deviations and the seasonal adjustments for the seasonal variations.
To forecast, simply find the product of the seasonal adjustment and forecasted Trend (CMA) value
Слайд 11
Слайд 12
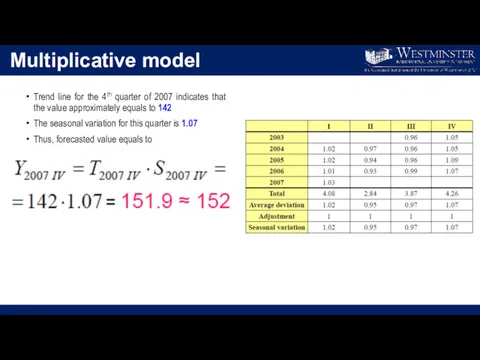
Multiplicative model
Trend line for the 4th quarter of 2007 indicates that
the value approximately equals to 142
The seasonal variation for this quarter is 1.07
Thus, forecasted value equals to
Слайд 13

Concluding remarks
Today, you learned
Graphical display of the change of a value
over time
Time series analysis
Two time series models: additive and multiplicative
Forecasting future value with the suitable model












 Алгоритмы
Алгоритмы Глобальные сети
Глобальные сети Путешествие в страну Информатика. 8 класс
Путешествие в страну Информатика. 8 класс CISCO CCIE Program
CISCO CCIE Program Моделирование корреляционных зависимостей
Моделирование корреляционных зависимостей Интернет-зависимость
Интернет-зависимость Настройка коммутаторов Cisco
Настройка коммутаторов Cisco Конвергентные и цифровые технологии
Конвергентные и цифровые технологии Деловая графика в электронных таблицах.
Деловая графика в электронных таблицах. Инженерия программного обеспечения. Введение (модуль 1)
Инженерия программного обеспечения. Введение (модуль 1) Мобильные операционные системы
Мобильные операционные системы Рекомендации психолога
Рекомендации психолога Многоуровневые ИВС и эталонная модель взаимосвязи открытых систем. Занятие 05, 06
Многоуровневые ИВС и эталонная модель взаимосвязи открытых систем. Занятие 05, 06 Компьютерные объекты
Компьютерные объекты История развития компьютерной техники. 8 класс
История развития компьютерной техники. 8 класс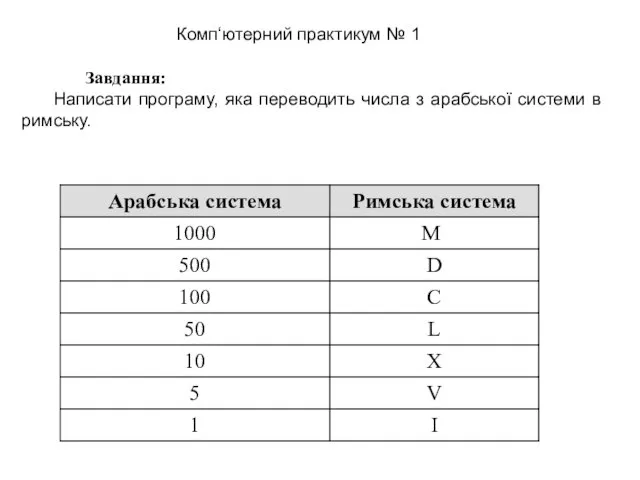 Завдання: Написати програму, яка переводить числа з арабської системи в римську
Завдання: Написати програму, яка переводить числа з арабської системи в римську OSINT(Open Source Intelligency)
OSINT(Open Source Intelligency) Урок по теме Работа со шрифтами. Форматирование текста. 8 класс.
Урок по теме Работа со шрифтами. Форматирование текста. 8 класс. Регистрация в WealTcom
Регистрация в WealTcom Презентация Перевод чисел между системами счисления, основания которых являются степенями числа 2 10 класс
Презентация Перевод чисел между системами счисления, основания которых являются степенями числа 2 10 класс Информационно-логические основы ЭВМ
Информационно-логические основы ЭВМ Тораптық утелиттердің жұмысын оқып үйрену
Тораптық утелиттердің жұмысын оқып үйрену Безопасность при использовании современных гаджетов
Безопасность при использовании современных гаджетов Тестирование мобильных приложений
Тестирование мобильных приложений Текстові і графічні обʼєкти на слайдах. Урок 30
Текстові і графічні обʼєкти на слайдах. Урок 30 Ақпарат. Компьютер. Компьютер құрылғылары,ақпараттық модель
Ақпарат. Компьютер. Компьютер құрылғылары,ақпараттық модель Первый канал
Первый канал Первоначальные сведения о мониторах
Первоначальные сведения о мониторах