Содержание
- 2. Agenda Computer Programming Compilation vs. Interpretation History of Java Main Features of Java JDK History of
- 3. Computer Programming Compilation vs. Interpretation IT Recruiter Course 2015
- 4. Computer Programming Programming – process that leads from an original formulation of a computing problem to
- 5. Computer Programming Creating a sequence of instructions to enable the computer to do something IT Recruiter
- 6. Computer Programming Algorithm The algorithm is often only represented in human-parseable form and reasoned about using
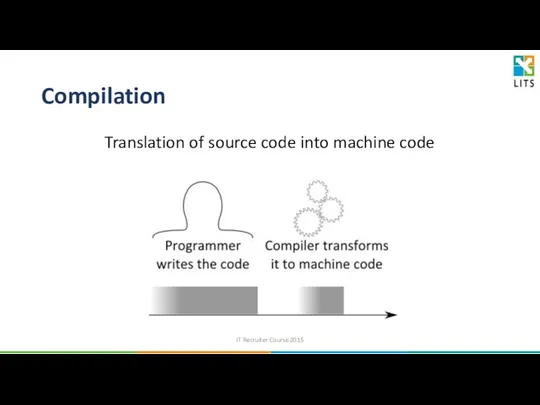
- 7. Compilation Translation of source code into machine code IT Recruiter Course 2015
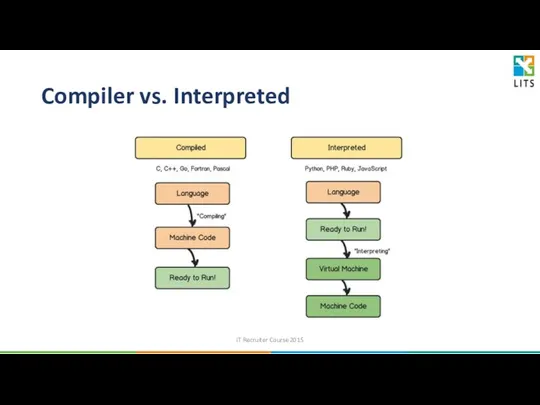
- 8. Compiled Language A compiled language is one where the program, once compiled, is expressed in the
- 9. Interpreted Language An interpreted language is one where the instructions are not directly executed by the
- 10. Compiler vs. Interpreted IT Recruiter Course 2015
- 11. Compiler Language Pros: Faster performance by directly using the native code of the target machine Opportunity
- 12. Interpreted Language Pros: Easier to implement No need to run a compilation stage, i.e. can execute
- 13. Why is This Important to Recruiter? Programming language is just a tool, but usually Ukrainian developers
- 14. Java History of Java. Main Features of Java. JDK. History of Releases. IT Recruiter Course 2015
- 15. History of Java Java language was originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems, which is
- 16. Main Features There were 5 primary goals in the creation of the Java language. It should:
- 17. Simple, Object-oriented and Familiar Java can be programmed without extensive programmer training. The needs of distributed,
- 18. Robust & Secure Java provides extensive compile-time checking, followed by a second level of run-time checking.
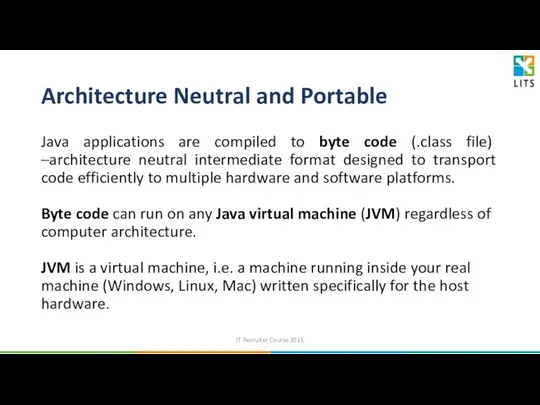
- 19. Architecture Neutral and Portable Java is intended to let application developers “write once, run anywhere”, meaning
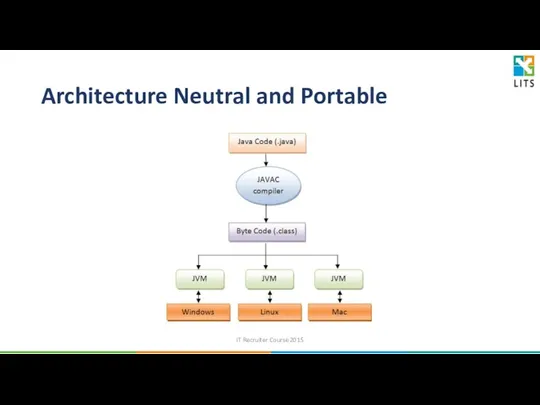
- 20. Architecture Neutral and Portable Java applications are compiled to byte code (.class file) –architecture neutral intermediate
- 21. Architecture Neutral and Portable IT Recruiter Course 2015
- 22. High Performance Java has a lot of optimization techniques: Just-In-Time compilation (the program is stored in
- 23. High Performance Java performance is generally: slower than compiled languages such as C or C++ similar
- 24. Java Development Kit JDK contains tools for developing, debugging, and monitoring Java applications. For instance: javac
- 25. Java Version History JDK Alpha and Beta (1995) JDK 1.0 (January 23, 1996) JDK 1.1 (February
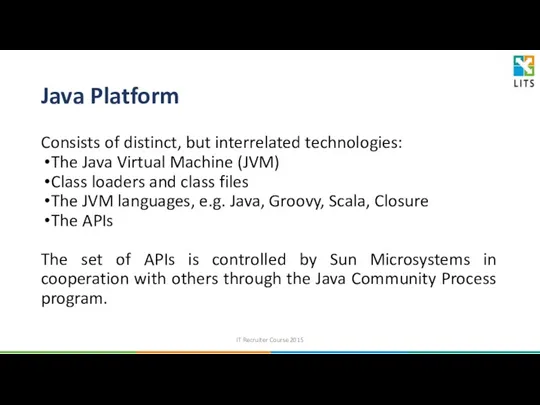
- 26. Java Platform Consists of distinct, but interrelated technologies: The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Class loaders and
- 27. Java Platform Editions Java Card – a technology that allows small Java-based applications to be run
- 28. Java Platform Editions Java SE (Standard Edition) – for general-purpose use on desktop PCs, servers and
- 29. Why is This Important to Recruiter? Java is just an example, but good recruiter needs to:
- 30. Java Technologies Servlet. JSP. JDBC. Hibernate. Swing. Spring Framework. IT Recruiter Course 2015
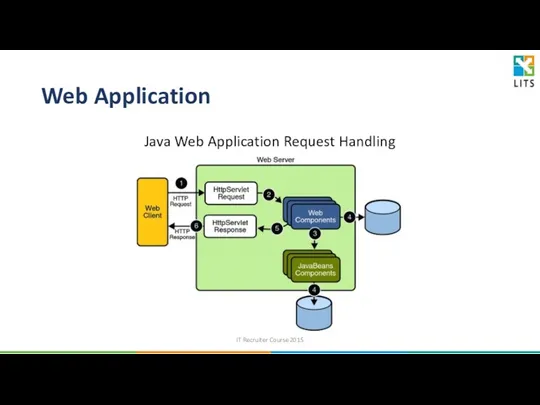
- 31. Web Application Java Web Application Request Handling IT Recruiter Course 2015
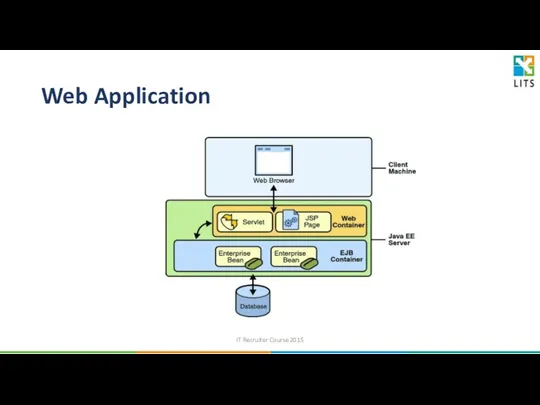
- 32. Web Application IT Recruiter Course 2015
- 33. Servlet Java programming language class used to extend the capabilities of a server by providing dynamic
- 34. Java Server Pages technology that helps to create dynamically generated web pages based on HTML, XML
- 35. Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an API for the Java programming language that defines how a
- 36. Hibernate object-relational mapping (ORM) library for the Java language, providing a framework for mapping an object-oriented
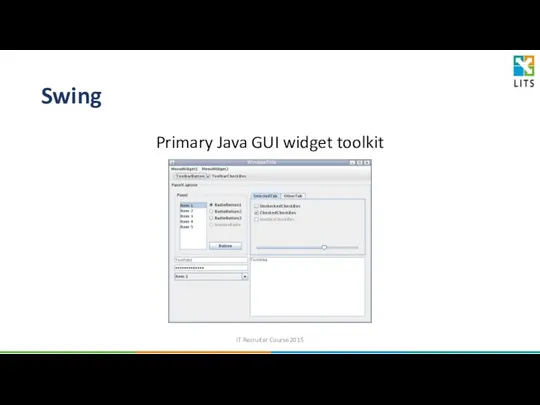
- 37. Swing Primary Java GUI widget toolkit IT Recruiter Course 2015
- 38. Spring Framework is an open-source application framework and inversion of control container for the Java platform
- 39. Why is This Important to Recruiter? Java technology stack is just an example, but good recruiter
- 40. Examples of Java Projects Real anonymized descriptions IT Recruiter Course 2015
- 41. Project #1 Web application with user interface Main technologies: Java 6.x, Javascript JDBC, Hibernate Spring 3.x
- 42. Project #2 Web application Main technologies: Java 6.x, C++, CORBA Hibernate, JDBC EJB 3 Spring Swing
- 44. Скачать презентацию































 Үлестірілген жүйелер
Үлестірілген жүйелер Теоретическое моделирование перевода
Теоретическое моделирование перевода Программирование на языке Паскаль. Основы
Программирование на языке Паскаль. Основы Использование коммуникационных возможностей официального сайта организации, реализация принципов доступности информации
Использование коммуникационных возможностей официального сайта организации, реализация принципов доступности информации Математическая логика (Булева алгебра)
Математическая логика (Булева алгебра) Логика и алгоритмы
Логика и алгоритмы Гипертекстовые информационные технологии
Гипертекстовые информационные технологии Caching Architectures and Graphics Processing
Caching Architectures and Graphics Processing Data Modeling and Databases Lab 3: Introduction to SQL
Data Modeling and Databases Lab 3: Introduction to SQL Представление числовой информации с помощью систем счисления
Представление числовой информации с помощью систем счисления Типы алгоритмических структур
Типы алгоритмических структур Файл и файловая система. Решение задач
Файл и файловая система. Решение задач Ювелирный магазин 1С:Розница 8
Ювелирный магазин 1С:Розница 8 Моделювання бізнес-процесів лісозаготівлі
Моделювання бізнес-процесів лісозаготівлі Устройство компьютера
Устройство компьютера Организация пространства устройства ввода и вывода
Организация пространства устройства ввода и вывода 1С:Документооборот
1С:Документооборот Компьютерная графика и анимация LOGO. Внеаудиторная работа №9
Компьютерная графика и анимация LOGO. Внеаудиторная работа №9 Информационные технологии обучения математике
Информационные технологии обучения математике Создание веб-сайтов
Создание веб-сайтов Кодирование звуковой информации
Кодирование звуковой информации Хранение информации. Память человека и память человечества. Оперативная и долговременная память. Файлы и папки. (5 класс)
Хранение информации. Память человека и память человечества. Оперативная и долговременная память. Файлы и папки. (5 класс) Overview of apps and web sites for language learning
Overview of apps and web sites for language learning Visual Studio 2008. Overview
Visual Studio 2008. Overview Уровни тестирования программного обеспечения
Уровни тестирования программного обеспечения Новости в Молдове. Новости в мире
Новости в Молдове. Новости в мире Lifebuilding Планирование
Lifebuilding Планирование Аддитивные технологии: 3D-печать
Аддитивные технологии: 3D-печать