Содержание
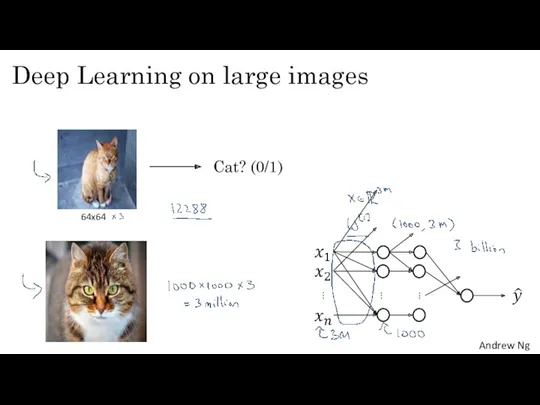
- 2. Deep Learning on large images Cat? (0/1) 64x64
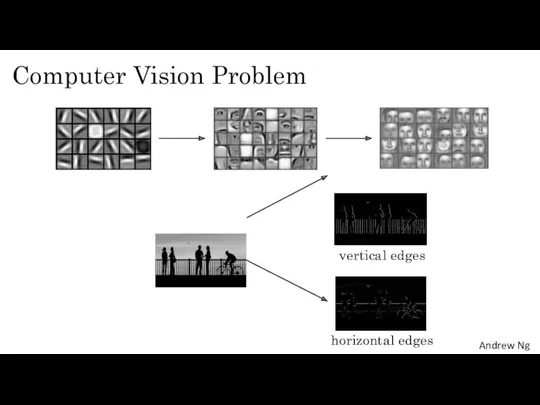
- 3. Computer Vision Problem vertical edges horizontal edges
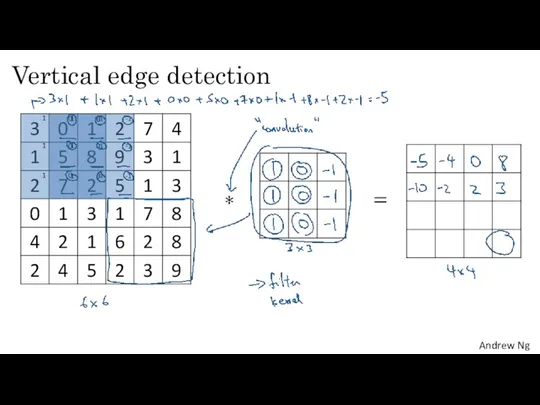
- 4. Vertical edge detection 1 1 1 -1 -1 -1 0 0 0 1 1 1 -1
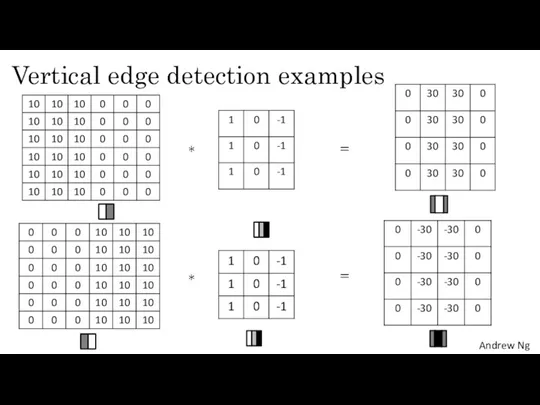
- 5. Vertical edge detection examples
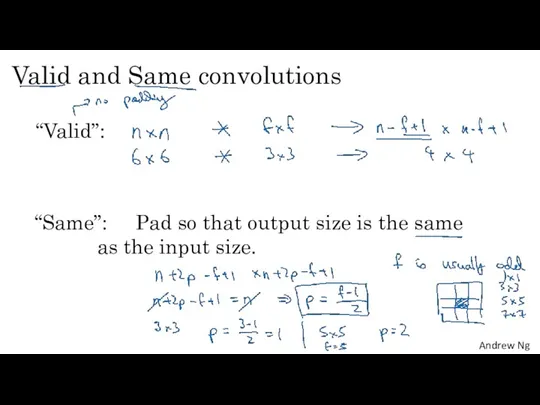
- 6. Valid and Same convolutions “Valid”: “Same”: Pad so that output size is the same as the
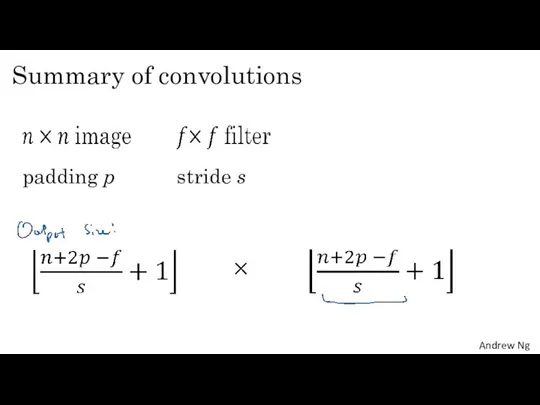
- 7. Summary of convolutions padding p stride s
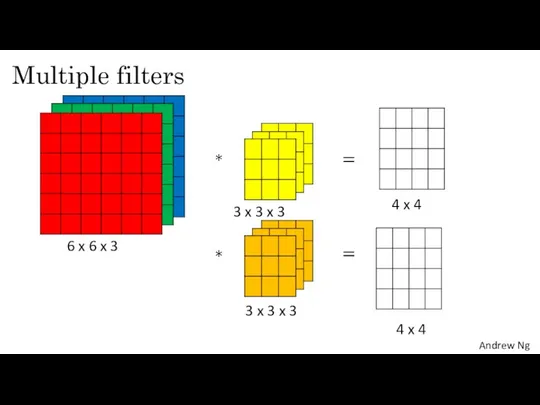
- 8. Multiple filters 6 x 6 x 3 4 x 4 3 x 3 x 3 3
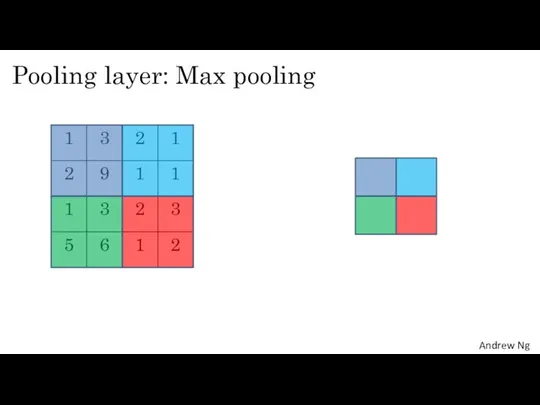
- 9. Pooling layer: Max pooling
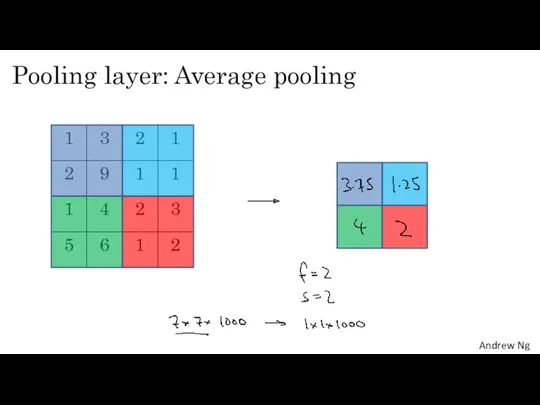
- 10. Pooling layer: Average pooling
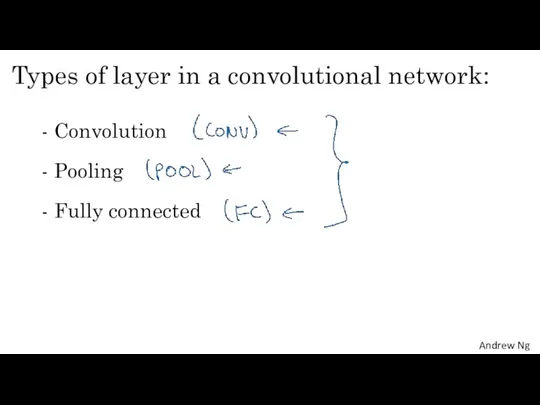
- 11. Types of layer in a convolutional network: - Convolution - Pooling - Fully connected
- 12. Outline Classic networks: LeNet-5 ResNet Inception AlexNet VGG
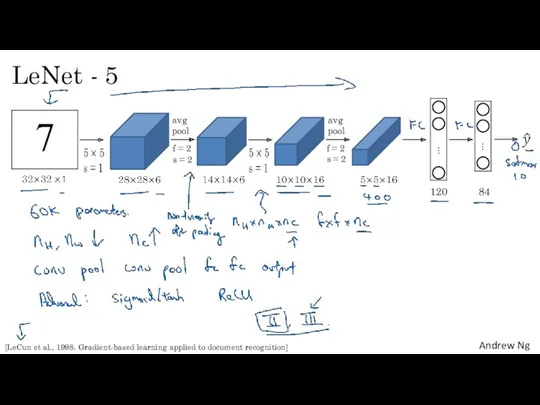
- 13. LeNet - 5 120 84 f = 2 s = 2 avg pool avg pool f
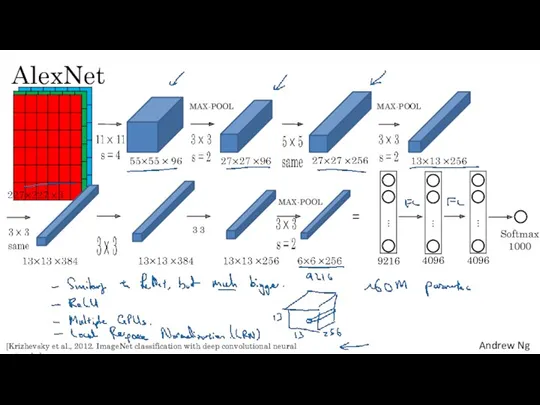
- 14. AlexNet = 9216 4096 4096 MAX-POOL MAX-POOL 3 3 MAX-POOL Softmax 1000 [Krizhevsky et al., 2012.
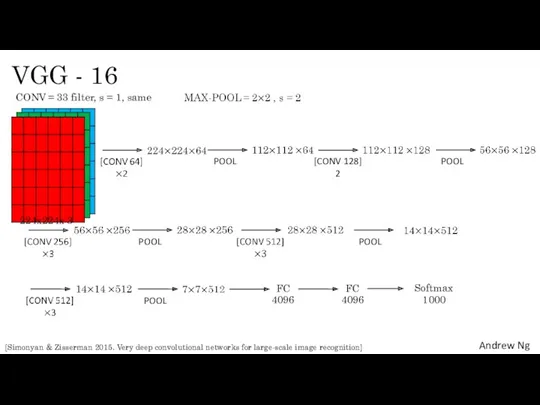
- 15. VGG - 16 224x224x 3 CONV = 33 filter, s = 1, same POOL [CONV 128]
- 16. Inception network [Szegedy et al., 2014, Going Deeper with Convolutions]
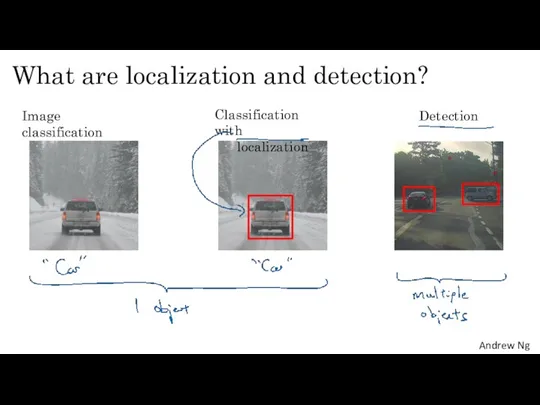
- 17. What are localization and detection? Image classification Classification with localization Detection
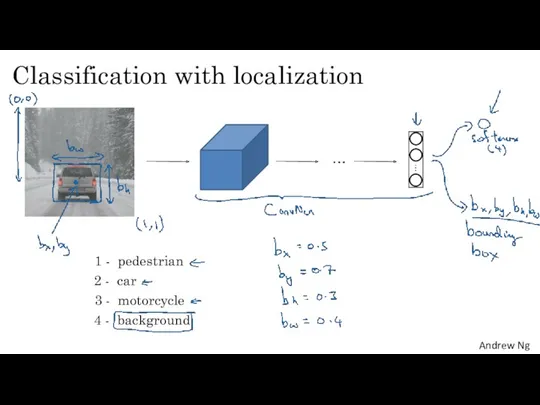
- 18. Classification with localization 1 - pedestrian 2 - car 3 - motorcycle 4 - background
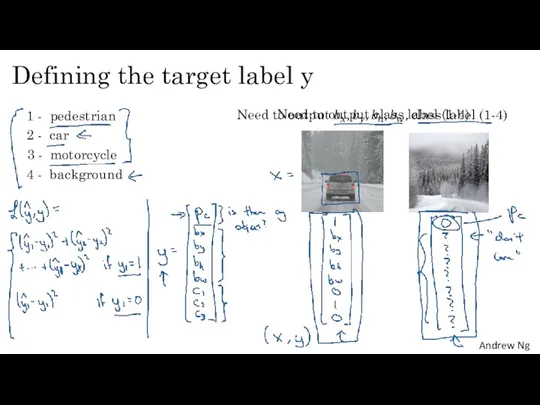
- 19. Defining the target label y 1 - pedestrian 2 - car 3 - motorcycle 4 -
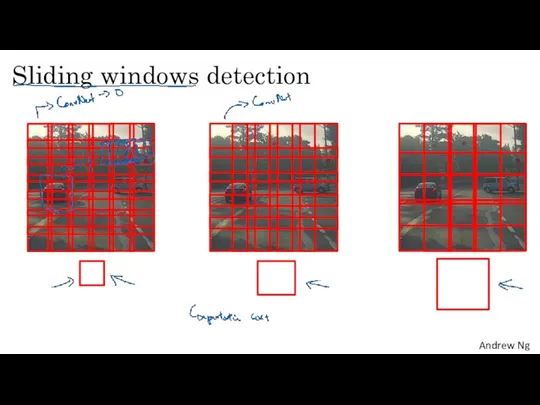
- 20. Sliding windows detection
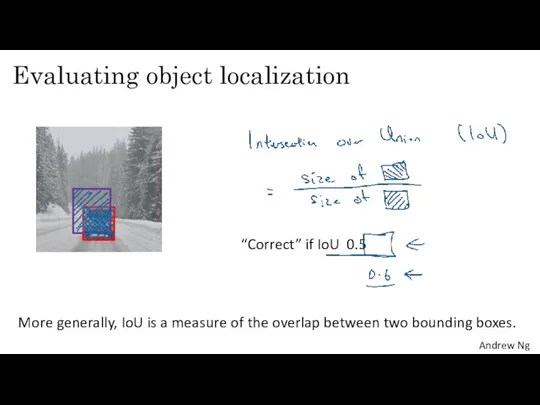
- 21. Evaluating object localization “Correct” if IoU 0.5 More generally, IoU is a measure of the overlap
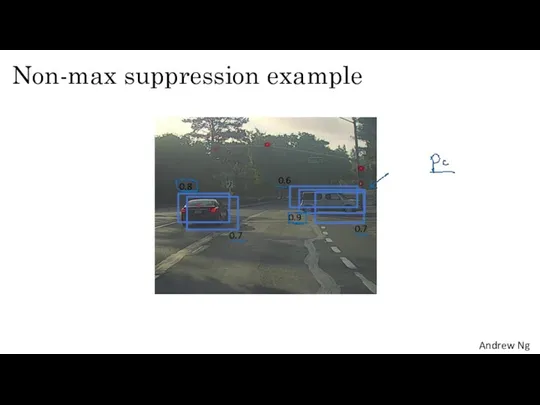
- 22. Non-max suppression example
- 23. Non-max suppression algorithm Discard all boxes with While there are any remaining boxes: Pick the box
- 24. Non-max suppression example 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.9 0.7
- 26. Скачать презентацию

![Inception network [Szegedy et al., 2014, Going Deeper with Convolutions]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/213190/slide-15.jpg)


 Искусственный интеллект (ИИ)
Искусственный интеллект (ИИ) Знакомство с Paint.NET
Знакомство с Paint.NET Принципы организации вычислительных сетей
Принципы организации вычислительных сетей Введение в UML
Введение в UML Информация. Классификация информации
Информация. Классификация информации Алгоритм и его формальное исполнение
Алгоритм и его формальное исполнение Устройство пк
Устройство пк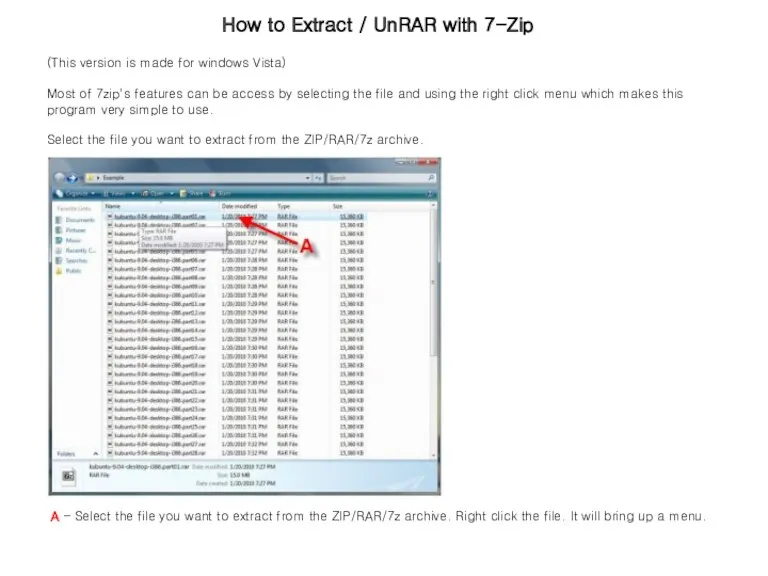 How to extract file with 7-Zip
How to extract file with 7-Zip Эффективное сопровождение образовательного процесса, используя АИС СГО
Эффективное сопровождение образовательного процесса, используя АИС СГО Оптимальное проектирование на основе решения задачи линейного программирования
Оптимальное проектирование на основе решения задачи линейного программирования Ролевая игра Mass Effect
Ролевая игра Mass Effect Преобразование ER- модели в реляционную
Преобразование ER- модели в реляционную Что такое 3D-моделирование и где оно применяется
Что такое 3D-моделирование и где оно применяется Напрямки та інструменти веб-дизайну
Напрямки та інструменти веб-дизайну Графика в C++
Графика в C++ Принципы переноса ранее разработанных приложенийна смартфон. Лекция 4
Принципы переноса ранее разработанных приложенийна смартфон. Лекция 4 Голосовые мессенджеры
Голосовые мессенджеры Язык РНР Управляющие конструкции
Язык РНР Управляющие конструкции Кодирование звуковой информации
Кодирование звуковой информации Разработка сайта с применением Framework Bootstrap
Разработка сайта с применением Framework Bootstrap Развитие автомобильных телеканалов в 2019 г
Развитие автомобильных телеканалов в 2019 г Компьютерные программные продукты для разработки бизнес-планов (Project Expert, COMFAR, Альт-Инвест, PROPSPIN)
Компьютерные программные продукты для разработки бизнес-планов (Project Expert, COMFAR, Альт-Инвест, PROPSPIN) Analysis and Design of Data Systems. General Definitions of 2NF & 3NF Boyce-Codd Normal Form (Lecture 16)
Analysis and Design of Data Systems. General Definitions of 2NF & 3NF Boyce-Codd Normal Form (Lecture 16) Автоматизированная компьютерная система Умный дом
Автоматизированная компьютерная система Умный дом Кроссворд про школу (с клавиатурой)
Кроссворд про школу (с клавиатурой) Optimizarea activităţii de prestare a serviciilor de transport prin aplicarea modelelor matematice şi sistemelor informatice
Optimizarea activităţii de prestare a serviciilor de transport prin aplicarea modelelor matematice şi sistemelor informatice Моделирование как метод познания. Моделирование и формализация. Информатика. 9 класс
Моделирование как метод познания. Моделирование и формализация. Информатика. 9 класс Введение в программную инженерию. Лекция №1
Введение в программную инженерию. Лекция №1