Содержание
- 2. Head of NIA Global Center and e-Government Academy, NIA Executive Director of Information Architecture Division, Smart
- 3. Contents
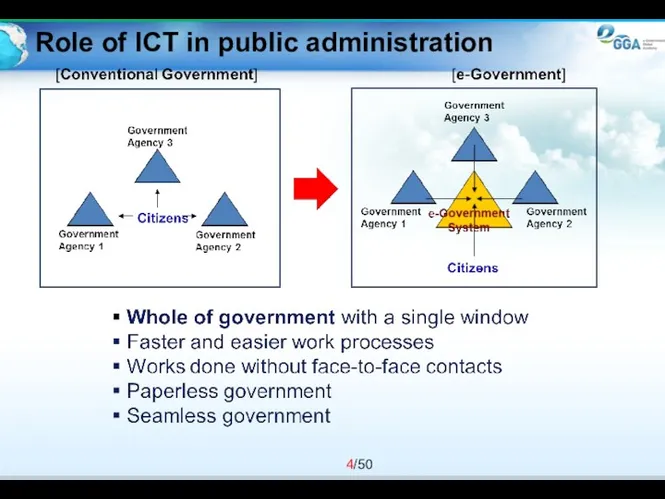
- 4. Role of ICT in public administration
- 5. Public administration before e-Government Many different forms and repetitive tasks
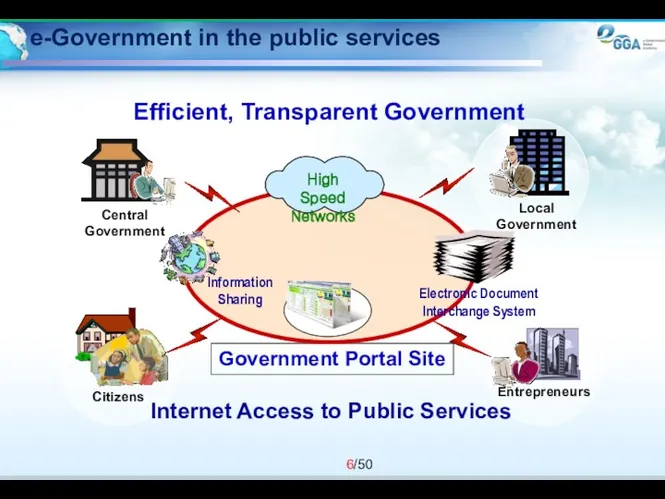
- 6. e-Government in the public services
- 7. Connected Society for the Happiness Connect people to communicate from neighborhood to global community Road Telephone
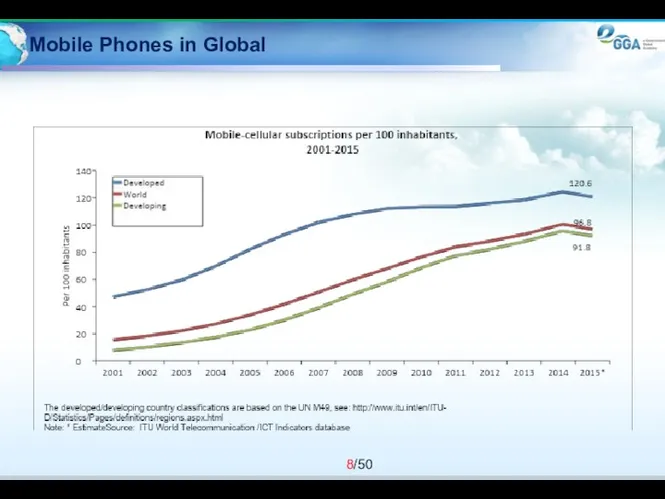
- 8. Mobile Phones in Global
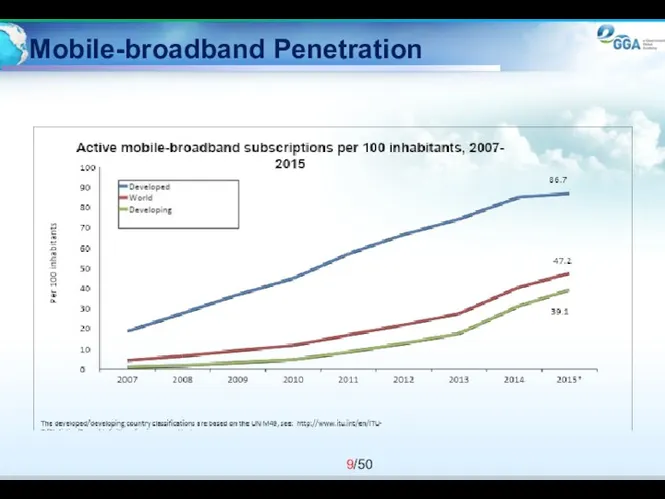
- 9. Mobile-broadband Penetration
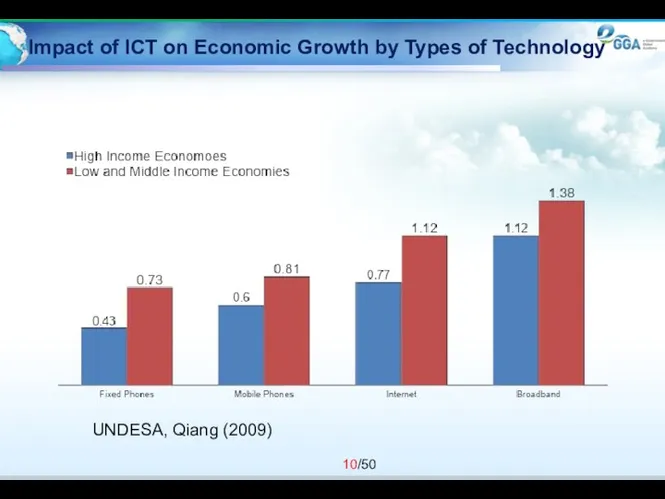
- 10. Impact of ICT on Economic Growth by Types of Technology UNDESA, Qiang (2009)
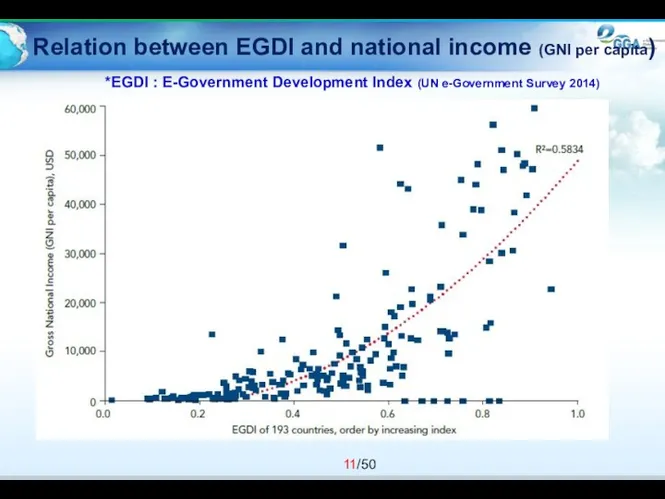
- 11. Relation between EGDI and national income (GNI per capita) *EGDI : E-Government Development Index (UN e-Government
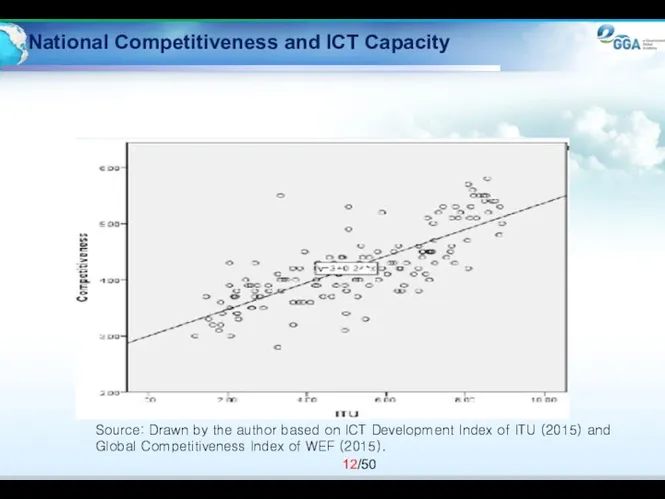
- 12. National Competitiveness and ICT Capacity Source: Drawn by the author based on ICT Development Index of
- 13. Contents
- 14. “e-Government is defined as utilizing the Internet and world-wide-web for delivering government information and services to
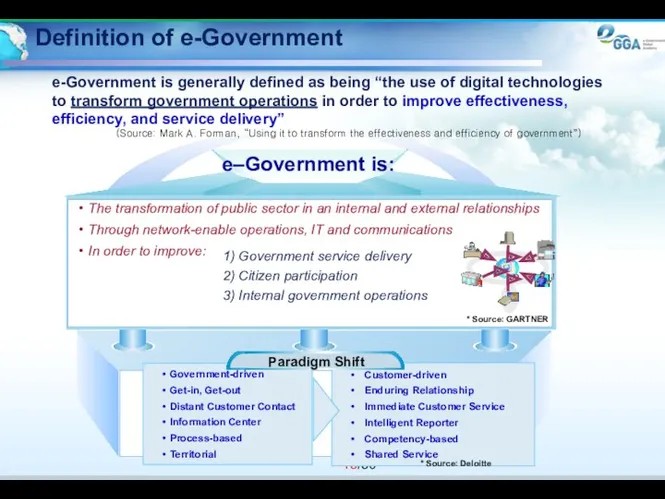
- 15. Definition of e-Government e-Government is generally defined as being “the use of digital technologies to transform
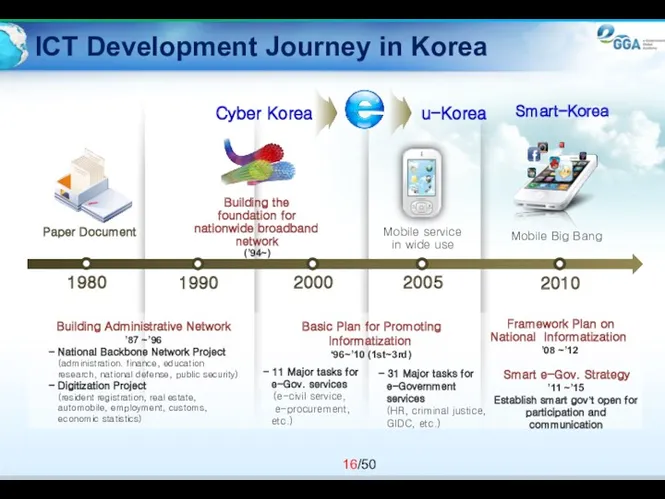
- 16. ICT Development Journey in Korea Basic Plan for Promoting Informatization ‘96~’10 (1st~3rd) Building the foundation for
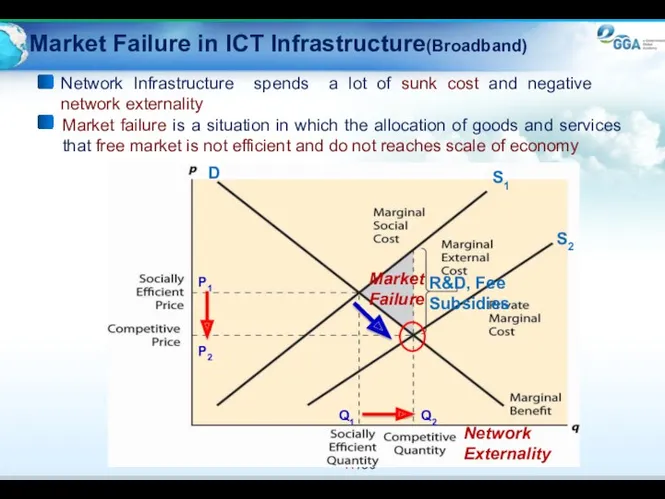
- 17. Market Failure in ICT Infrastructure(Broadband) Market failure is a situation in which the allocation of goods
- 18. Market Failure and the Role of Government Reasons for Market failure Positive and negative externalities Short-term
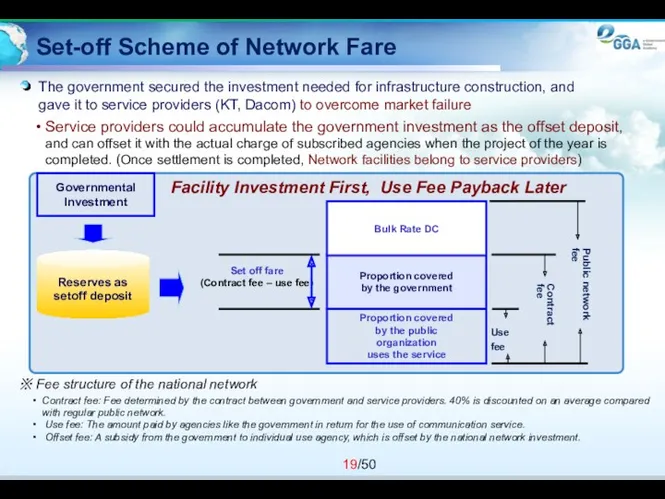
- 19. Set-off Scheme of Network Fare ※ Fee structure of the national network Contract fee: Fee determined
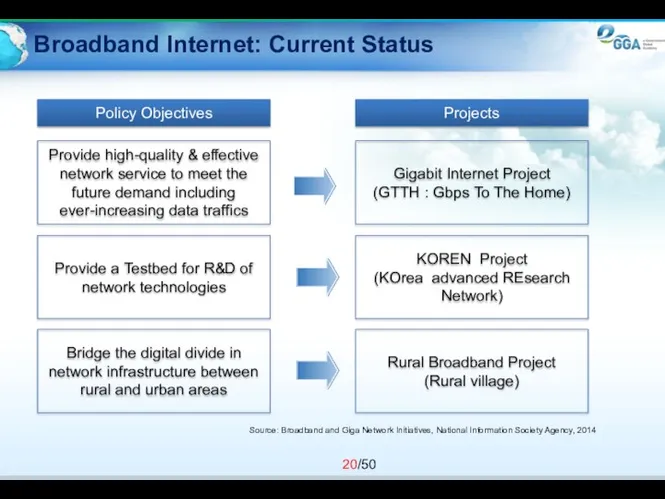
- 20. Broadband Internet: Current Status
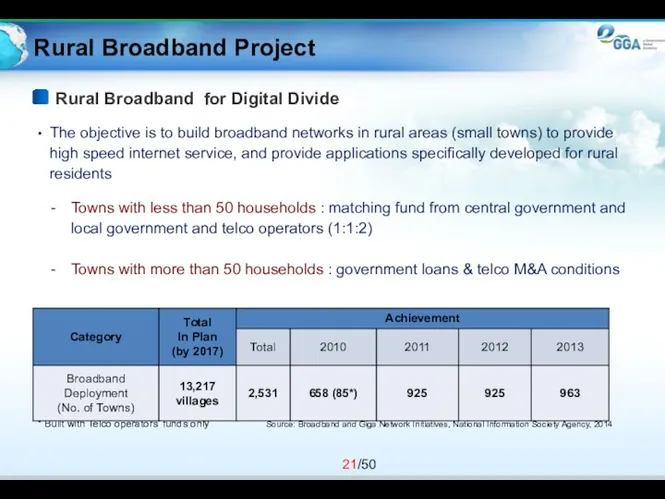
- 21. Rural Broadband Project The objective is to build broadband networks in rural areas (small towns) to
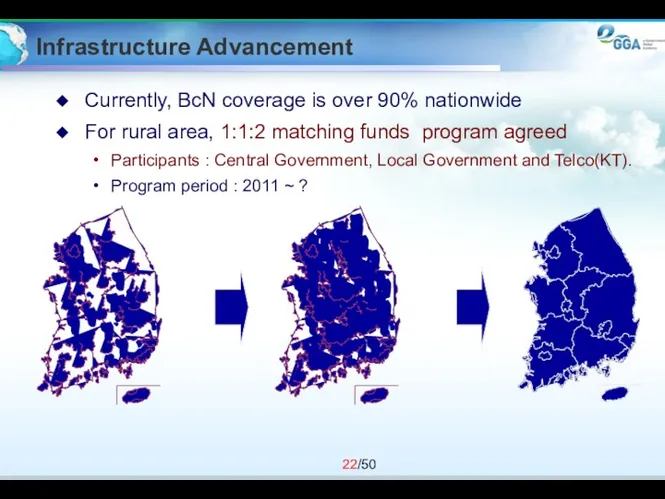
- 22. Infrastructure Advancement Currently, BcN coverage is over 90% nationwide For rural area, 1:1:2 matching funds program
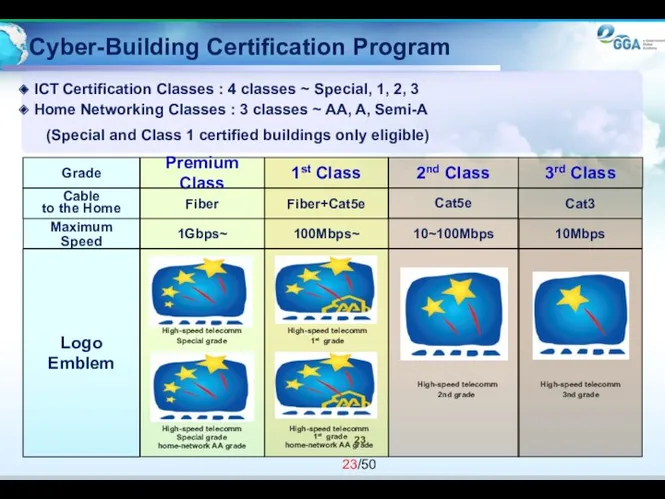
- 23. Cyber-Building Certification Program ICT Certification Classes : 4 classes ~ Special, 1, 2, 3 Home Networking
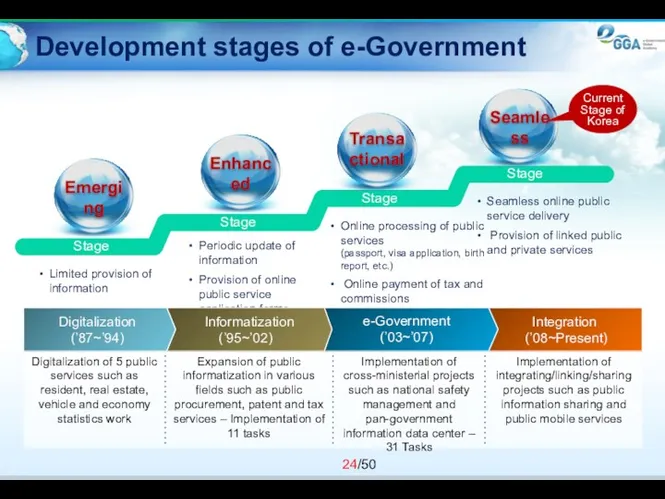
- 24. Development stages of e-Government
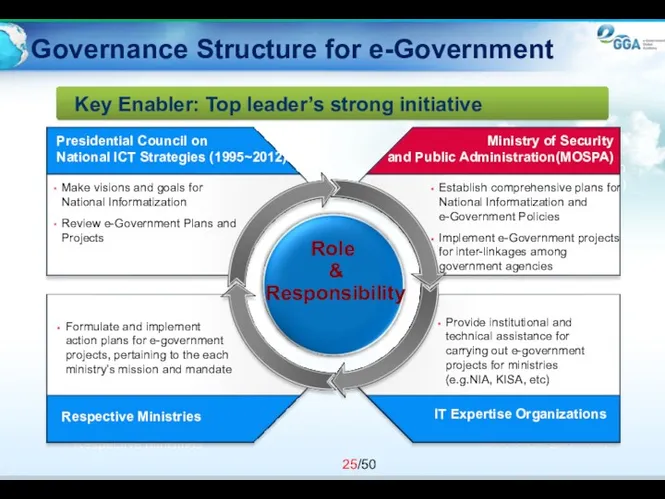
- 25. Governance Structure for e-Government
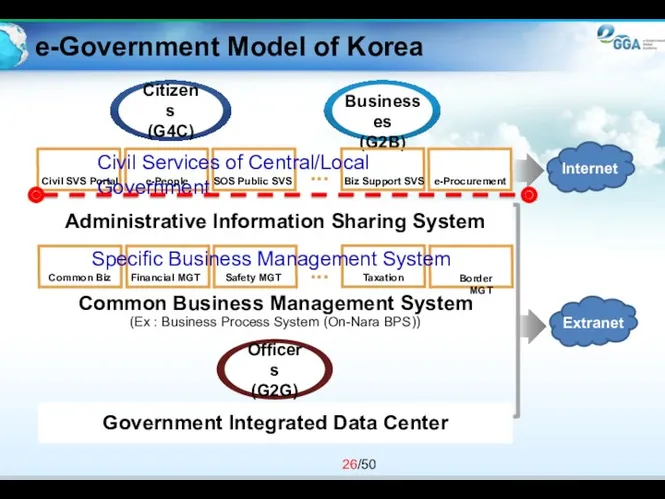
- 26. e-Government Model of Korea
- 27. Contents e-Government Policy in Korea
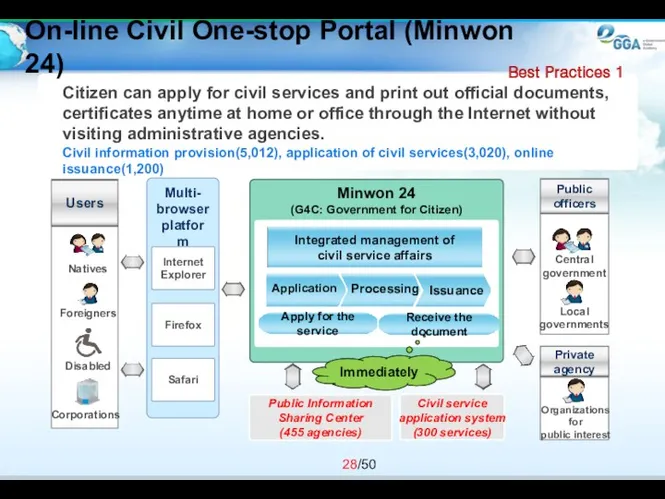
- 28. Citizen can apply for civil services and print out official documents, certificates anytime at home or
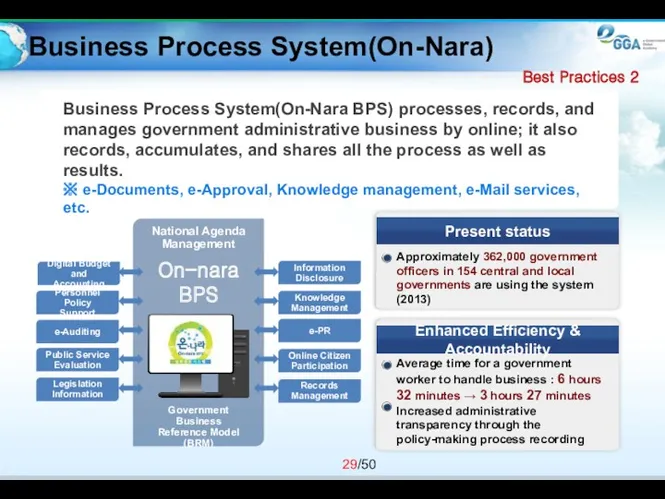
- 29. Business Process System(On-Nara BPS) processes, records, and manages government administrative business by online; it also records,
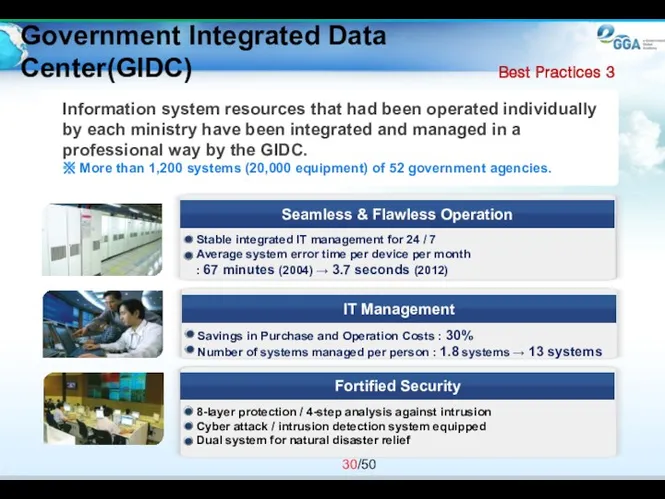
- 30. Information system resources that had been operated individually by each ministry have been integrated and managed
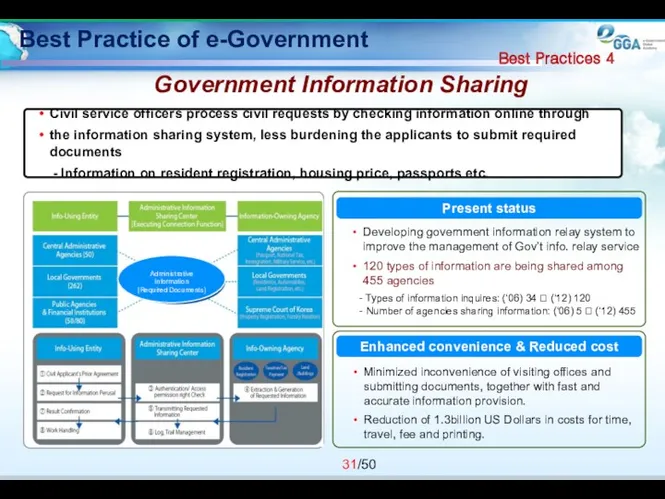
- 31. Best Practice of e-Government Government Information Sharing Civil service officers process civil requests by checking information
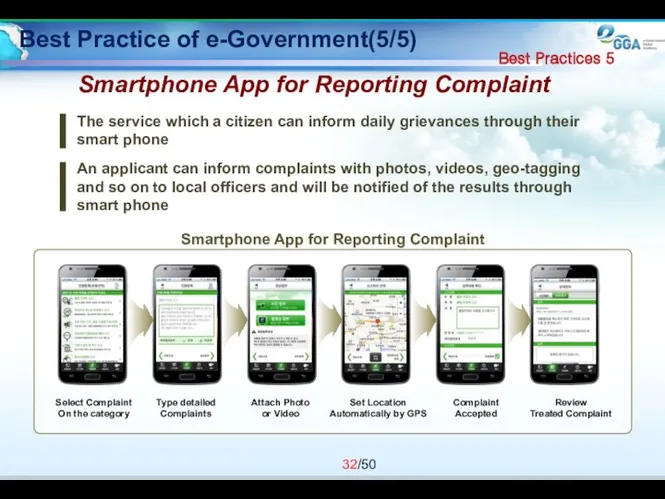
- 32. Best Practice of e-Government(5/5) Smartphone App for Reporting Complaint The service which a citizen can inform
- 33. Key Success Factors
- 34. Key Success Factors
- 35. Key Success Factors
- 36. Key Success Factors
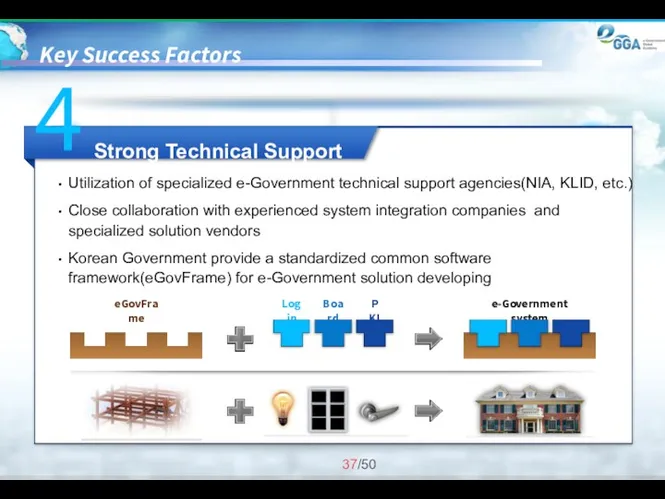
- 37. Key Success Factors
- 38. Contents
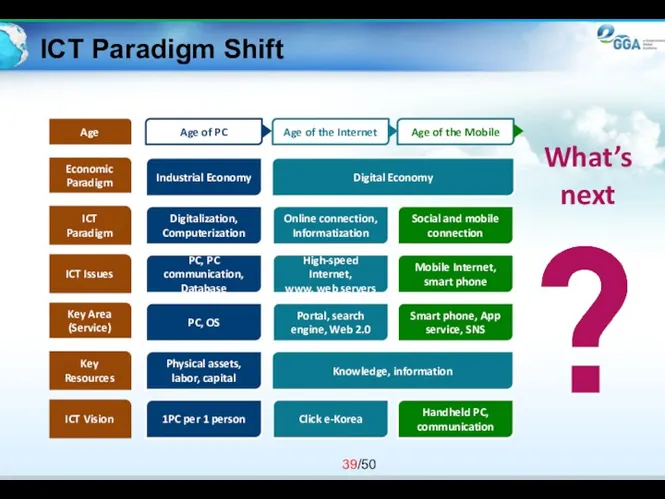
- 39. ICT Paradigm Shift Age of the Mobile Age of the Internet Age of PC Industrial Economy
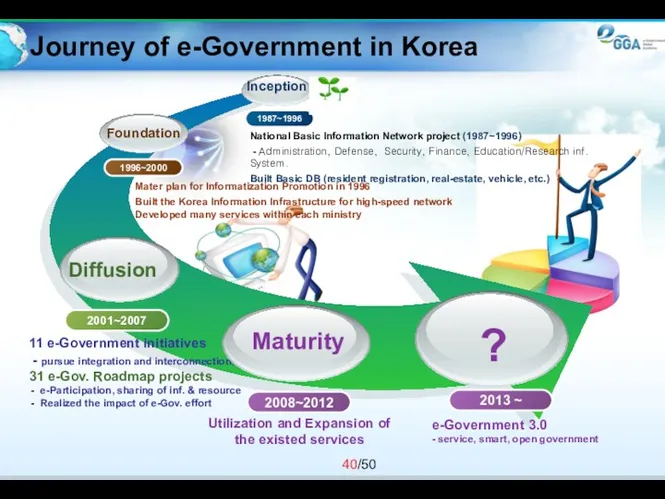
- 40. Utilization and Expansion of the existed services Inception Foundation National Basic Information Network project (1987~1996) -
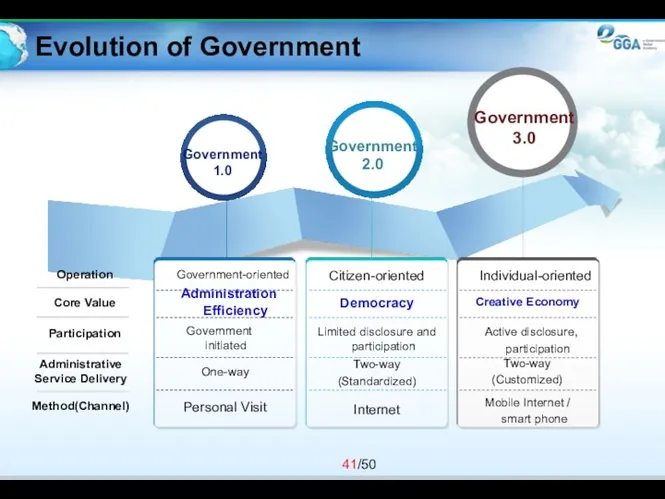
- 41. Evolution of Government Individual-oriented Creative Economy Active disclosure, participation Mobile Internet / smart phone Two-way (Customized)
- 42. Vision and Strategy of Government 3.0 Vision Objective Strategy Value
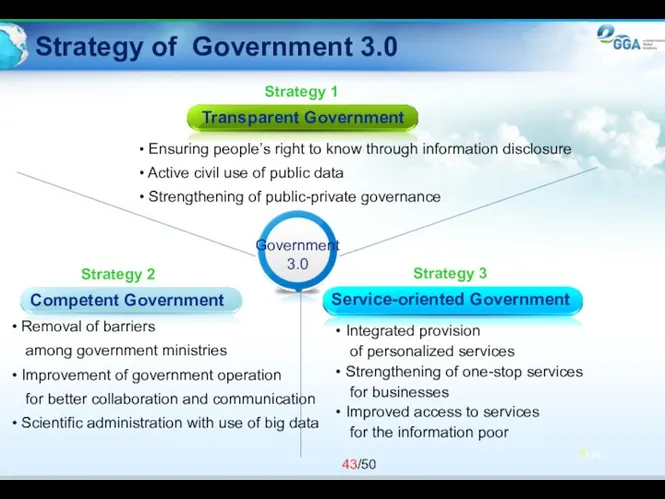
- 43. Strategy of Government 3.0 7/ 19 Strategy 3 Strategy 2 Strategy 1
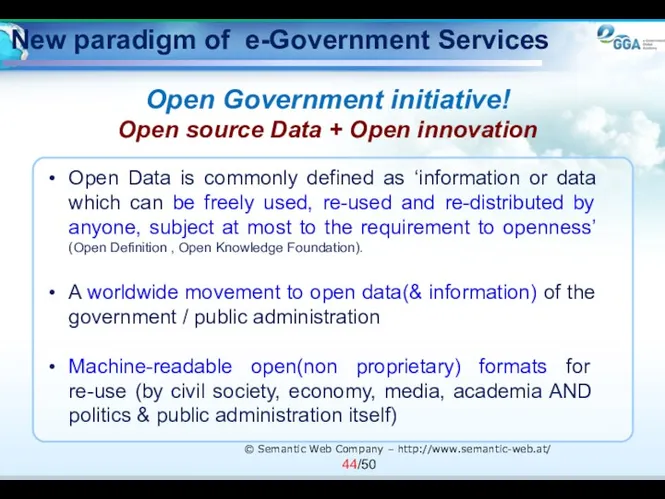
- 44. New paradigm of e-Government Services Open Government initiative! Open source Data + Open innovation © Semantic
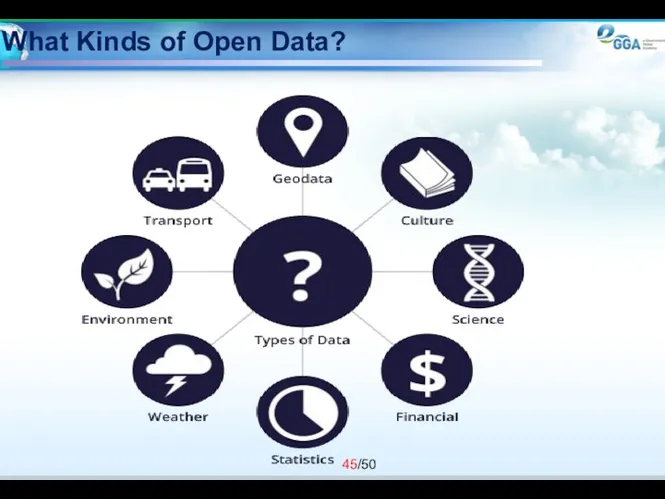
- 45. What Kinds of Open Data?
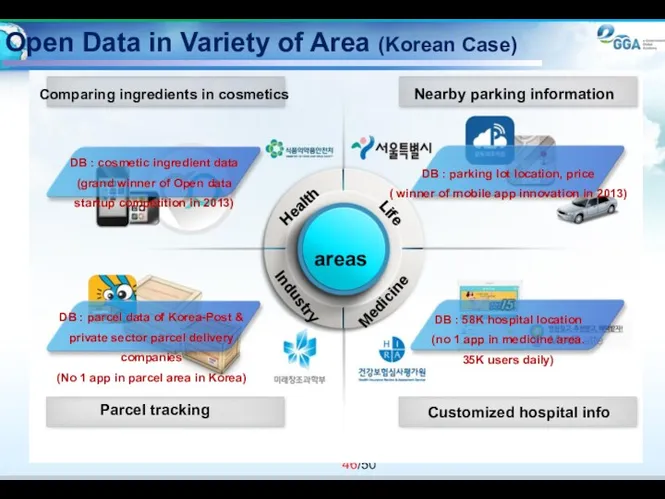
- 46. Open Data in Variety of Area (Korean Case) areas Health Life Medicine Industry Comparing ingredients in
- 47. Contents
- 48. Coming of the Hyper-connected
- 49. Coming of the Hyper-connected Society
- 50. Create new business opportunity by opening public data Create new business opportunity in a creative economy
- 52. Скачать презентацию


















 Базовые категории и понятия информатики
Базовые категории и понятия информатики Информация Свойства информации
Информация Свойства информации Domain valuation result page
Domain valuation result page Возможности личного кабинета студента ЮФУ
Возможности личного кабинета студента ЮФУ Информатизация образовательного процесса
Информатизация образовательного процесса Adobe Photoshop графикалық редакторы
Adobe Photoshop графикалық редакторы Адаптивные модели процесса разработки программного обеспечения. (Лекция 10)
Адаптивные модели процесса разработки программного обеспечения. (Лекция 10) Преобразование информации путем рассуждений
Преобразование информации путем рассуждений Почему люди идут на работу в интернет
Почему люди идут на работу в интернет Интернет-магазин с нуля
Интернет-магазин с нуля Показатели защищенности средств вычислительной техники. Основы информационной безопасности
Показатели защищенности средств вычислительной техники. Основы информационной безопасности Сортировка TimSort
Сортировка TimSort OPENMP
OPENMP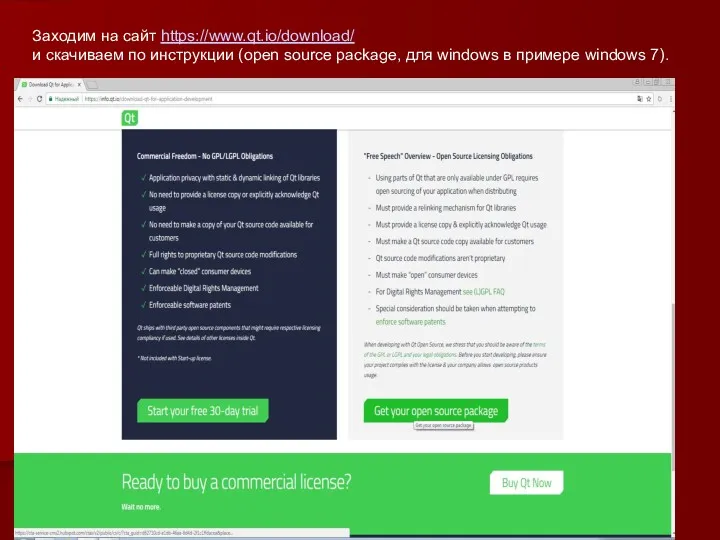 Инструкция по установке QT
Инструкция по установке QT Модель данных. I, II и III нормальные формы
Модель данных. I, II и III нормальные формы Компьютерная графика. Растровая графика
Компьютерная графика. Растровая графика Разработка мобильного приложения Квест по УрФУ в дополненной реальности
Разработка мобильного приложения Квест по УрФУ в дополненной реальности Construct 2. Урок3
Construct 2. Урок3 Информация ПФДО для родителей. Доступное дополнительное образование для детей в Ярославской области
Информация ПФДО для родителей. Доступное дополнительное образование для детей в Ярославской области Локальные сети
Локальные сети Графики и диаграммы
Графики и диаграммы Программное обеспечение пк
Программное обеспечение пк Игра Сетикет. Правила поведения в интернете
Игра Сетикет. Правила поведения в интернете Технология ввода текста. Редактирование текста
Технология ввода текста. Редактирование текста Global Social Media Plan
Global Social Media Plan Компьютерные презентации
Компьютерные презентации Возможности динамических (электронных) таблиц. Лекция
Возможности динамических (электронных) таблиц. Лекция Архітектура комп’ютера та організація комп’ютерних мереж
Архітектура комп’ютера та організація комп’ютерних мереж