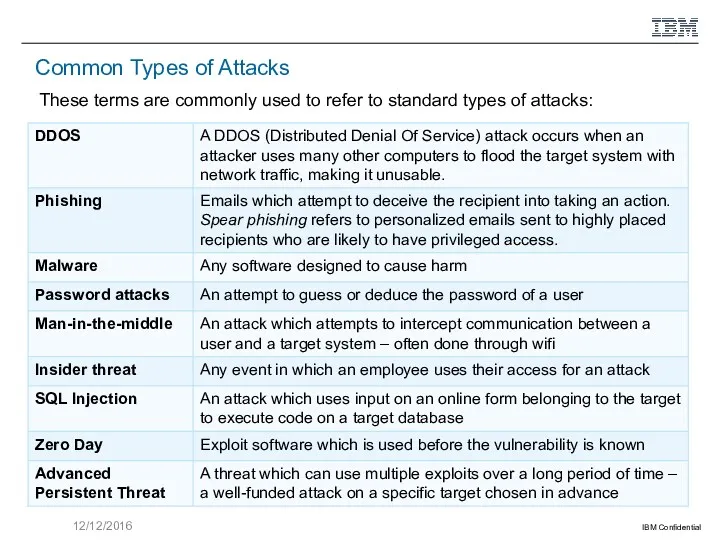
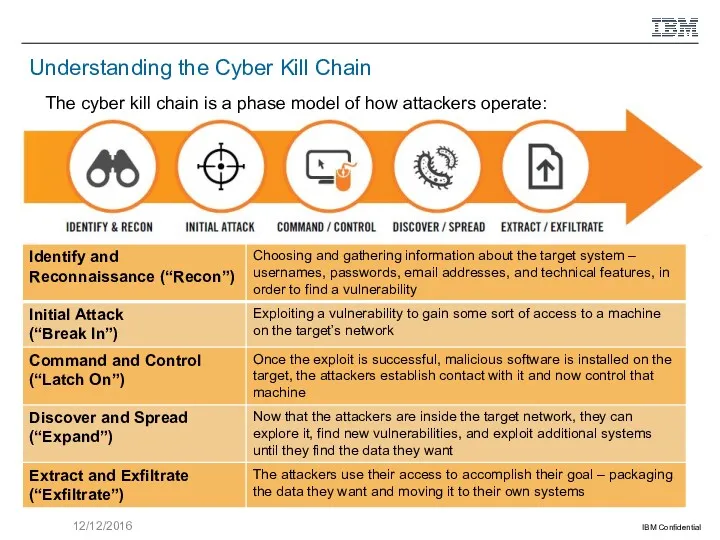
Basic Security Concepts
Some security terms which we will be using throughout
this course
12/12/2016
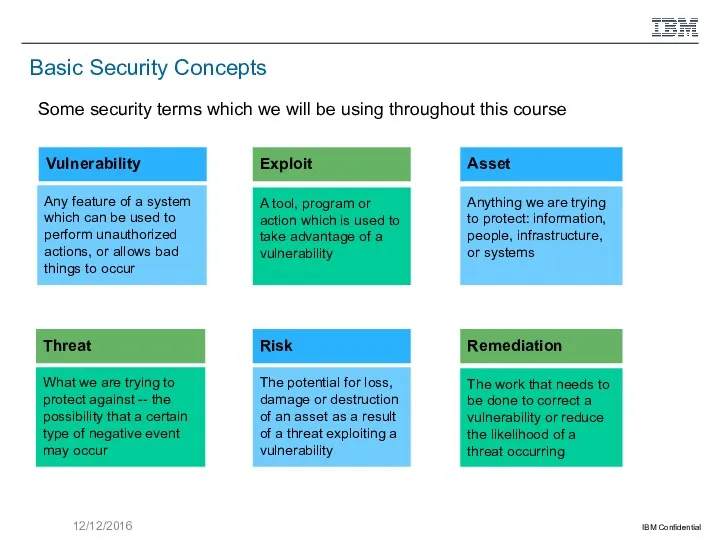
Vulnerability
Any feature of a system which can be used to perform unauthorized actions, or allows bad things to occur
Exploit
A tool, program or action which is used to take advantage of a vulnerability
Remediation
The work that needs to be done to correct a vulnerability or reduce the likelihood of a threat occurring
Asset
Anything we are trying to protect: information,
people, infrastructure, or systems
Threat
What we are trying to protect against -- the possibility that a certain type of negative event may occur
Risk
The potential for loss, damage or destruction of an asset as a result of a threat exploiting a vulnerability


 Project Planning and Configuration. Siemens
Project Planning and Configuration. Siemens Web Application Penetration Testing
Web Application Penetration Testing Проектирование АСУ. Комплекс подсистем технической подготовки производства
Проектирование АСУ. Комплекс подсистем технической подготовки производства Типы данных
Типы данных СММП: вбудовані системи
СММП: вбудовані системи Колизей. 3D - прототипирование
Колизей. 3D - прототипирование Терминал охранника. Проект
Терминал охранника. Проект Информационно-аналитические системы как основа интегрированной системы управления экономическим развитием Санкт-Петербурга
Информационно-аналитические системы как основа интегрированной системы управления экономическим развитием Санкт-Петербурга How did we make the biggest game on Defold in 1 year
How did we make the biggest game on Defold in 1 year Файлы и файловая система. (8 класс)
Файлы и файловая система. (8 класс) Решение логических задач
Решение логических задач Линейные программы
Линейные программы Презентация Подключение к Интернету
Презентация Подключение к Интернету Алгоритмы со структурой выбор
Алгоритмы со структурой выбор Структуры и алгоритмы обработки данных
Структуры и алгоритмы обработки данных Программное обеспечение компьютера
Программное обеспечение компьютера Работа с файлами в Си-шарп
Работа с файлами в Си-шарп Laravel
Laravel Итоги петровских преобразований. Урок по истории России в 10 класс. Интегрированный урок история + информатика
Итоги петровских преобразований. Урок по истории России в 10 класс. Интегрированный урок история + информатика Конспект урока по теме Компьютерные сети
Конспект урока по теме Компьютерные сети Прикладное программирование. Основы языка С++
Прикладное программирование. Основы языка С++ Концепція необмеженого паралелізму. Лекція №7
Концепція необмеженого паралелізму. Лекція №7 Excel электрондық кестесі. Жұмыс кестесінің беті бойынша орын аыустыру, баған енін, жол биіктігін өзгерту
Excel электрондық кестесі. Жұмыс кестесінің беті бойынша орын аыустыру, баған енін, жол биіктігін өзгерту Программирование на языке Паскаль. Основы
Программирование на языке Паскаль. Основы Программирование. Введение
Программирование. Введение Язык SQL. Создание запросов в СУБД Microsoft Access средствами SQL
Язык SQL. Создание запросов в СУБД Microsoft Access средствами SQL Что такое jQuery
Что такое jQuery Машина Тьюринга. Теория алгоритмов
Машина Тьюринга. Теория алгоритмов