Содержание
- 2. Objectives Understand how computers represent data. Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and
- 3. Objectives List the components found on the computer’s motherboard and explain their role in the computer
- 4. Objectives List the various types of memory found in a computer system and explain the purpose
- 5. How Computers Represent Data Binary numbers Only 0s and 1s Bit Smallest piece of data a
- 6. How Computers Represent Data Data storage is in bytes Kilobyte (KB)—one thousand bytes Megabyte (MB)—one million
- 7. (101)2= 5 (1001)2= 9 (11011)2= 27 20 = 1 , 21= 2, 22= 4, 8, 16,
- 8. How Computers Represent Data Characters Letters, numbers, and symbols—converted into numbers the computer understands Character code
- 9. Introducing the System Unit System unit Case that contains the major hardware components of a computer
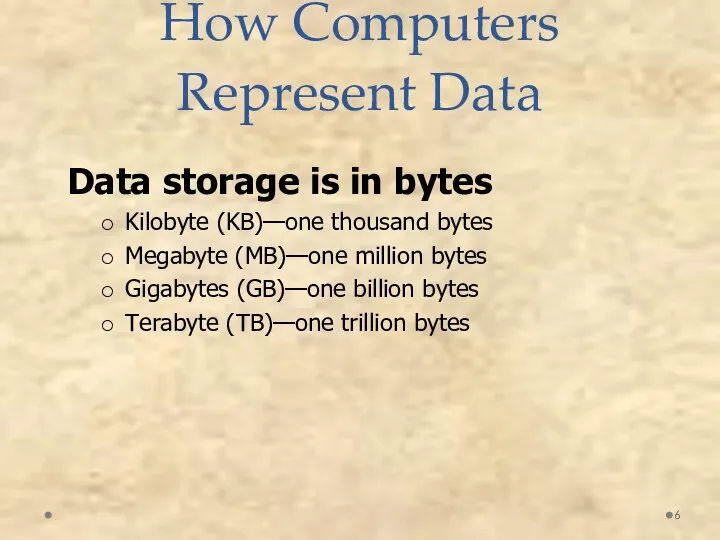
- 10. Motherboard CPU Power supply Cooling fan Internal speaker Drive bays Expansion slots System unit main components
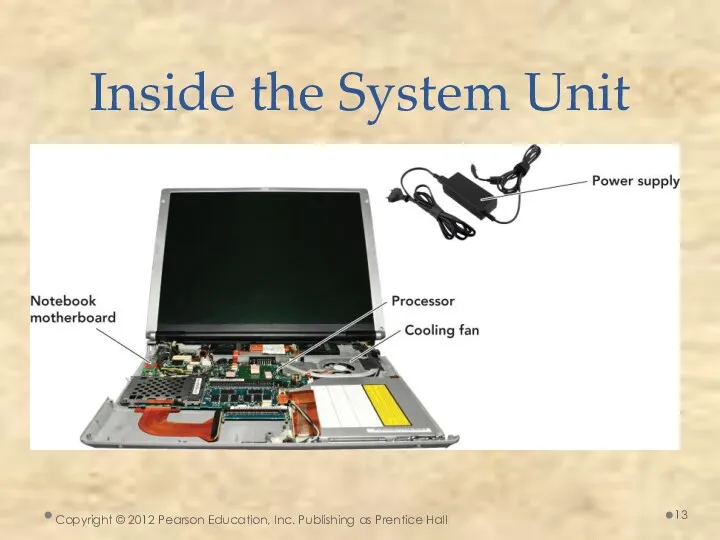
- 11. Inside the System Unit
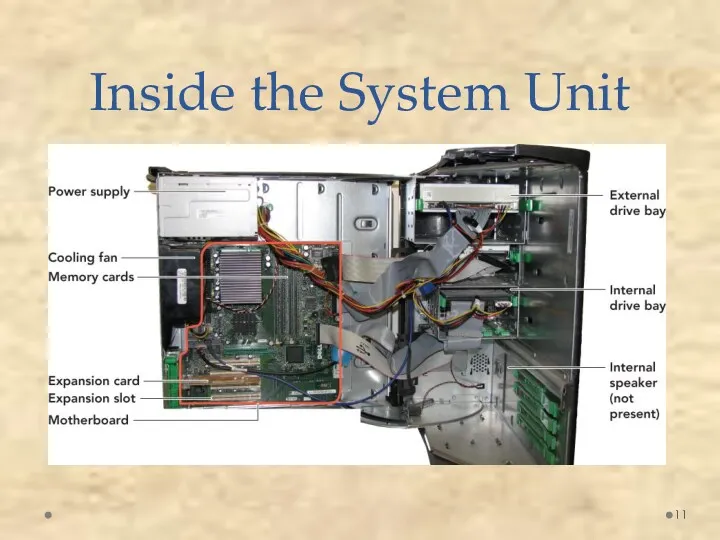
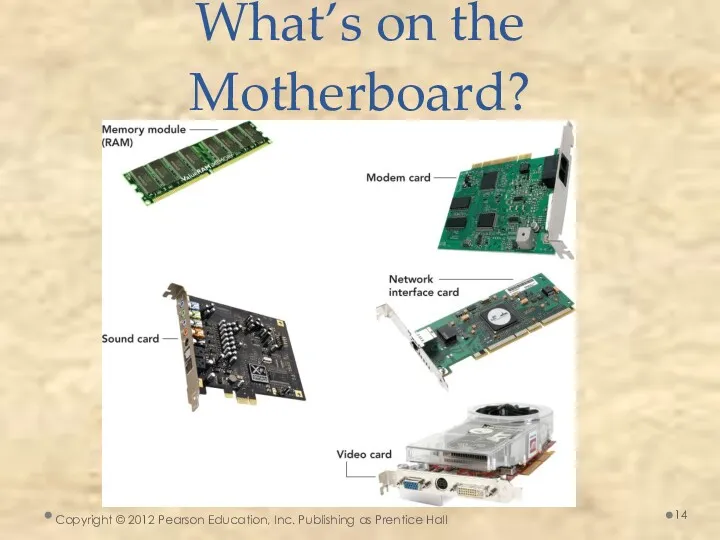
- 12. Expansion Cards Adds functions Provides new connections for peripheral devices Common types: Sound Modem Video (VGA)
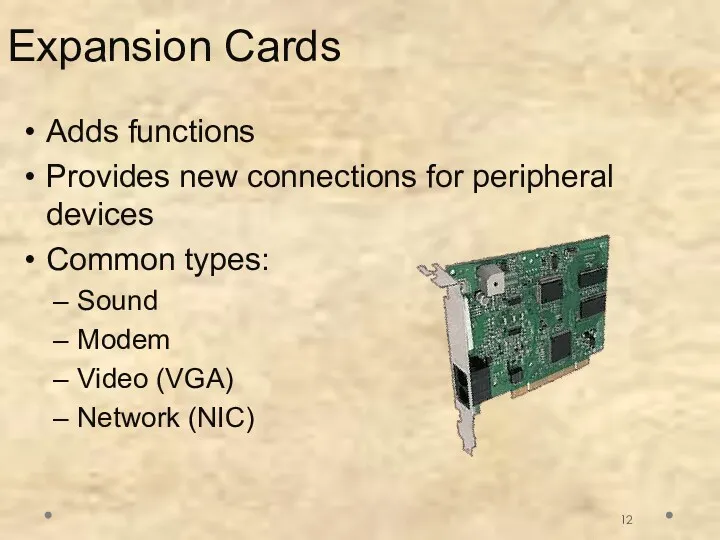
- 13. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Inside the System Unit
- 14. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall What’s on the Motherboard?
- 15. Motherboard Circuit board that contains the electrical circuitry for the computer The majority of parts found
- 16. What’s on the Motherboard? Central processing unit (CPU) Integrated circuit chip that processes electronic signals Also
- 17. What’s on the Motherboard? CPU (con’t.) Is usually covered by a heat sink A heat-dissipating component
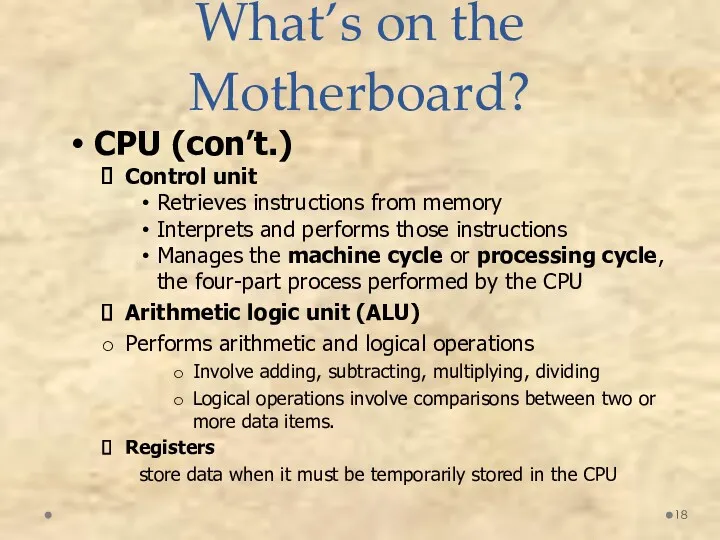
- 18. What’s on the Motherboard? CPU (con’t.) Control unit Retrieves instructions from memory Interprets and performs those
- 19. Machine cycle The computer can only do one thing at a time. Each action must be
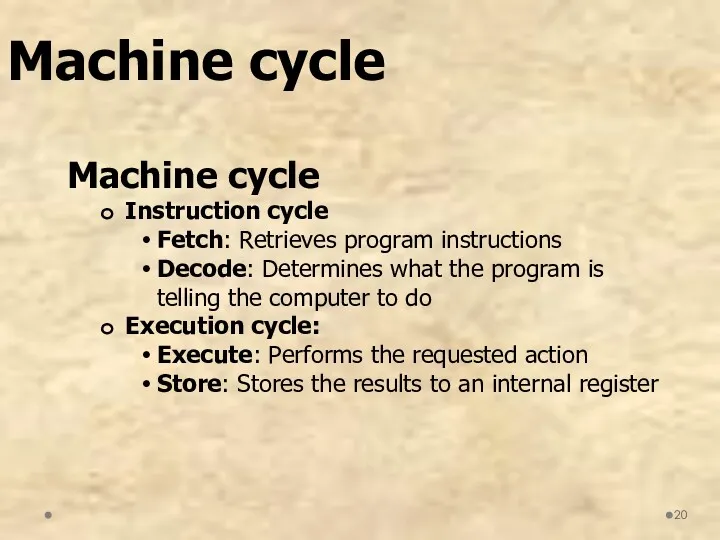
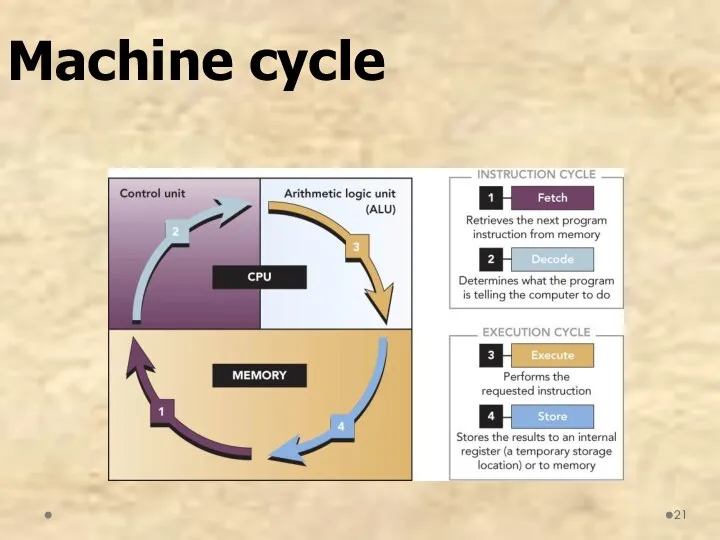
- 20. Machine cycle Instruction cycle Fetch: Retrieves program instructions Decode: Determines what the program is telling the
- 21. Machine cycle
- 22. For example, to add the numbers 5 and 6 and show the answer on the screen
- 23. Number of existing transistors Data bus width and word size Clock speed Operations per microprocessor cycle
- 24. Data bus Group of parallel wires that connect the CPU’s internal components Width measured in bits
- 25. What’s on the Motherboard? System clock Electronic circuit that produces rapid pulses and coordinates the computer’s
- 26. What’s on the Motherboard? System clock (con’t.) Superscalar architecture—enables the CPU to perform more than one
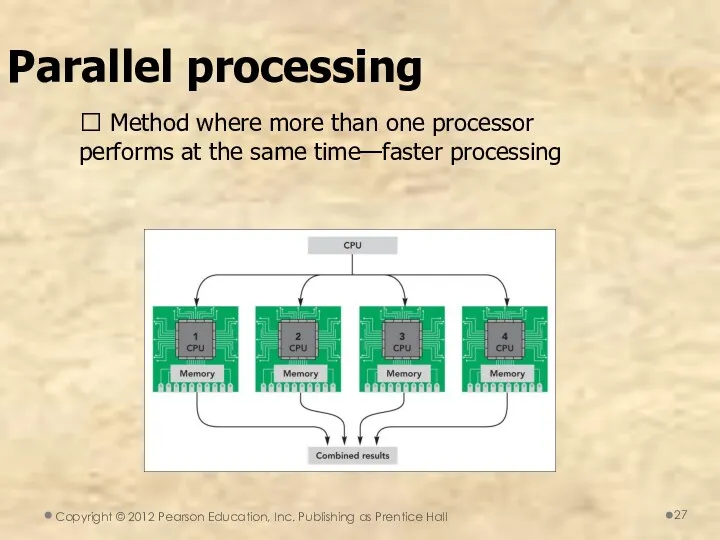
- 27. Parallel processing ? Method where more than one processor performs at the same time—faster processing Copyright
- 28. Instruction pipeline Basic five-stage pipeline machine IF = Instruction Fetch ID = Instruction Decode EX =
- 29. What’s on the Motherboard? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Multi-core processing
- 30. Chipset Set of chips that supply the switching circuitry the CPU requires to move data throughout
- 31. Memory Chips on the motherboard or within the CPU that retain instructions and data Random access
- 32. What’s on the Motherboard? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall RAM (con’t.)
- 33. What’s on the Motherboard? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Memory footprint
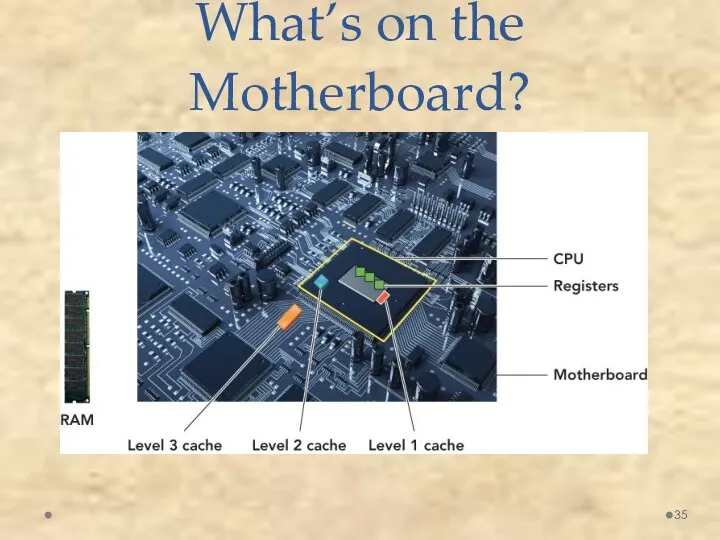
- 34. What’s on the Motherboard? Cache memory Small unit of ultrafast memory built into or near the
- 35. What’s on the Motherboard?
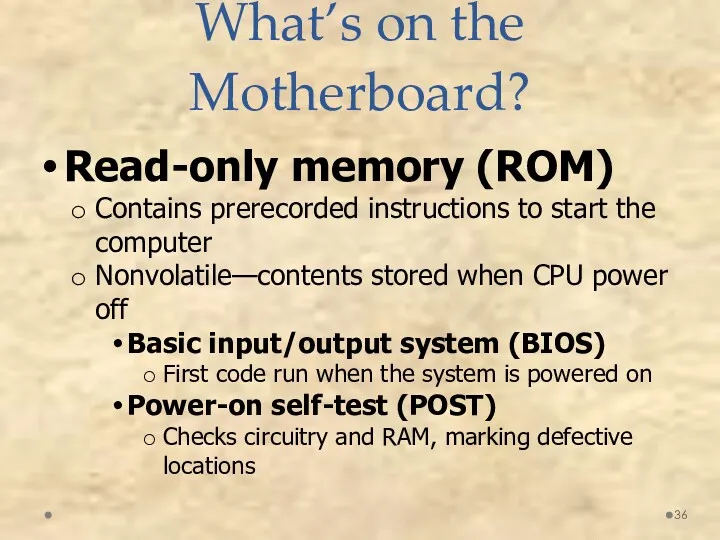
- 36. Read-only memory (ROM) Contains prerecorded instructions to start the computer Nonvolatile—contents stored when CPU power off
- 37. What’s on the Outside of the Box? Front panel Power switch Used to turn the computer
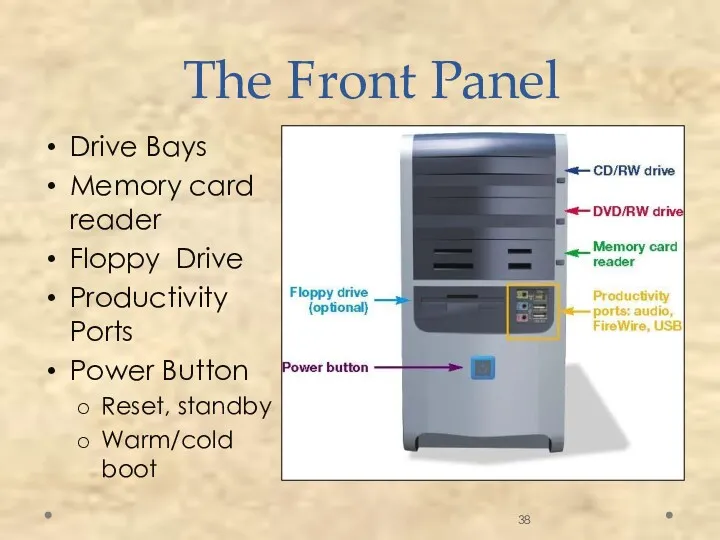
- 38. The Front Panel Drive Bays Memory card reader Floppy Drive Productivity Ports Power Button Reset, standby
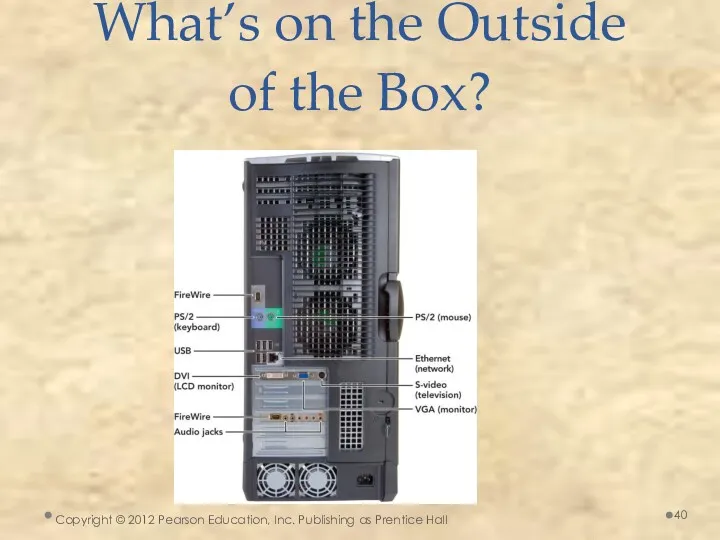
- 39. What’s on the Outside of the Box? Outside a system unit Connector—physical receptacle used to plug
- 40. What’s on the Outside of the Box? Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice
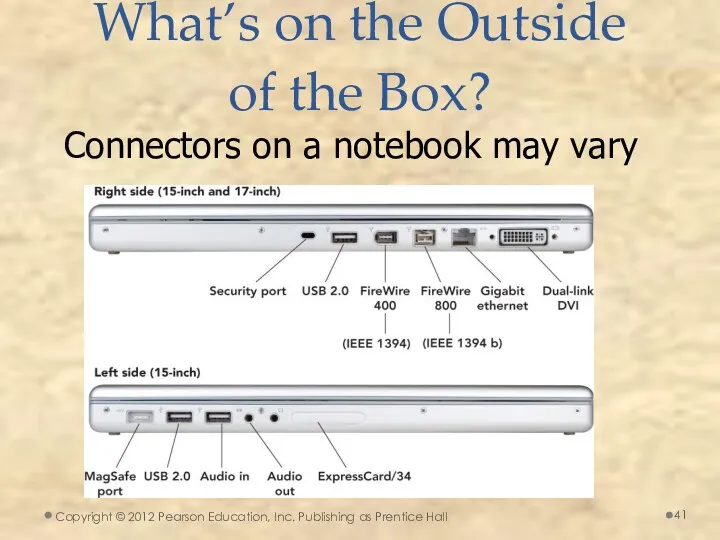
- 41. What’s on the Outside of the Box? Connectors on a notebook may vary Copyright © 2012
- 42. What’s on the Outside of the Box? USB (universal serial bus) ports Connects up to 127
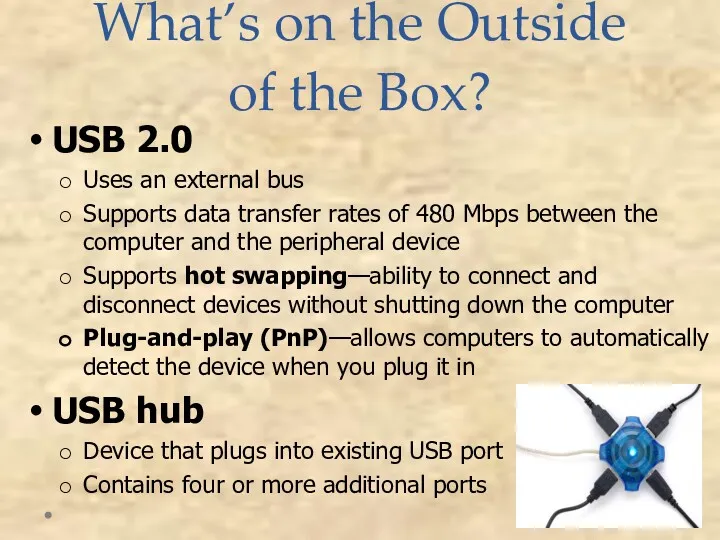
- 43. What’s on the Outside of the Box? USB 2.0 Uses an external bus Supports data transfer
- 44. What’s on the Outside of the Box? Video connectors VGA (video graphics array) port 15-pin male
- 45. What’s on the Outside of the Box? Additional connectors Telephone Network PC card slot PC card
- 46. What’s on the Outside of the Box? Legacy technology Older technology that is being phased out
- 47. Summary Understand how computers represent data. Understand the measurements used to describe data transfer rates and
- 48. Summary List the components found on the computer’s motherboard and explain their role in the computer
- 49. Summary List the various types of memory found in a computer system and explain the purpose
- 51. Скачать презентацию





























 Адресация в сети интернет
Адресация в сети интернет Algebra relacyjna. Wprowadzenie do systemów baz danych
Algebra relacyjna. Wprowadzenie do systemów baz danych Управление аптечной сетью
Управление аптечной сетью PyQt: GUI на Python при помощи Qt
PyQt: GUI на Python при помощи Qt ООП на Delphi – 6: Заставка программы и элемент таймер
ООП на Delphi – 6: Заставка программы и элемент таймер Сортировка массива. Алгоритмы сортировки
Сортировка массива. Алгоритмы сортировки Компьютерные сети
Компьютерные сети Системное и прикладное программное обеспечение
Системное и прикладное программное обеспечение Текстовый процессор OpenOffice.org Writer
Текстовый процессор OpenOffice.org Writer п. 2-4-2 (8 кл. дистант)
п. 2-4-2 (8 кл. дистант) Машина Тьюринга
Машина Тьюринга Технические средства компьютерной графики
Технические средства компьютерной графики Информационные ресурсы общества
Информационные ресурсы общества Оформление документов по вознаграждению (инструкция для агентов)
Оформление документов по вознаграждению (инструкция для агентов) Антивирус орнату
Антивирус орнату Каскадные таблицы стилей (CSS)
Каскадные таблицы стилей (CSS) Расчеты с использование электронных таблиц
Расчеты с использование электронных таблиц Прикладное ПО. Командная строка и командные файлы
Прикладное ПО. Командная строка и командные файлы С программой MS Access
С программой MS Access Интеграция с государственными системами - ЕГАИС, маркировка, онлайн-ККТ
Интеграция с государственными системами - ЕГАИС, маркировка, онлайн-ККТ презентация к уроку Глобальная компьютерная сеть Интернет
презентация к уроку Глобальная компьютерная сеть Интернет Проблемы виртуального общения
Проблемы виртуального общения Презентация к уроку по учету трат_1
Презентация к уроку по учету трат_1 Многомерные массивы
Многомерные массивы Презентация к выступлению
Презентация к выступлению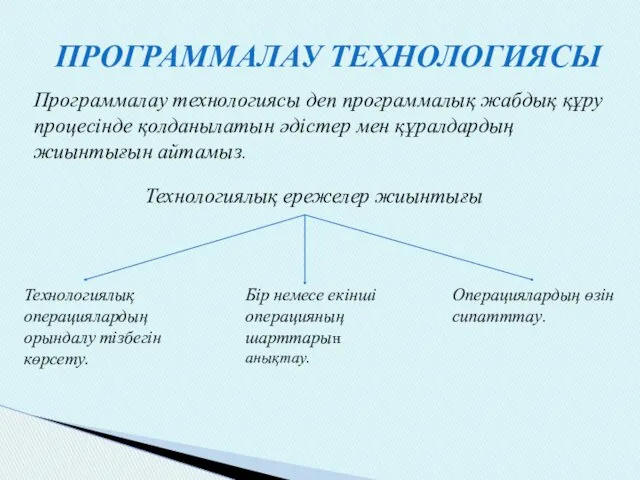 Программалау технологиясы
Программалау технологиясы Телемедицина в современном информационном обществе
Телемедицина в современном информационном обществе Ғаламтормен дұрыс жұмыс жасау – мәдениет
Ғаламтормен дұрыс жұмыс жасау – мәдениет