Содержание
- 2. Agenda Interface declaration Interface implementation Built-in .Net interfaces Task 5.1 Collections in C# ArrayList & List
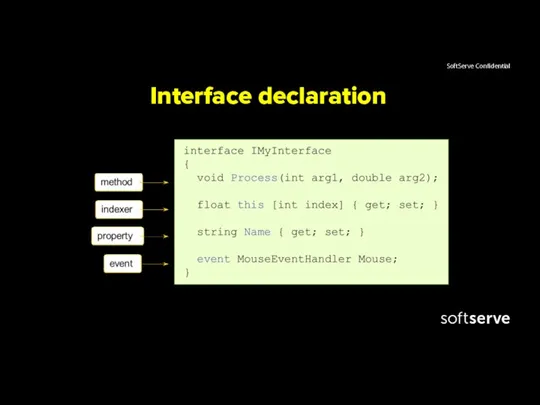
- 3. Interface declaration An interface contains definitions for a group of related functionalities that a class or
- 4. Interface declaration
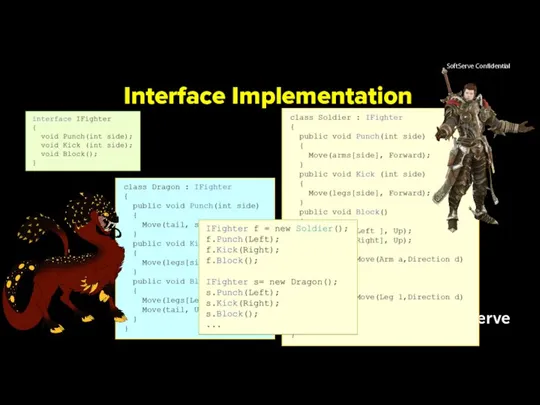
- 5. Interface Implementation
- 6. Interface Implementation Any class or struct that implements the interface must implement all its members. By
- 7. Interface Implementation
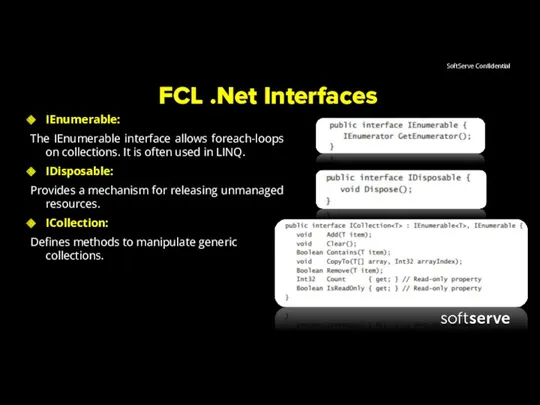
- 8. FCL .Net Interfaces IEnumerable: The IEnumerable interface allows foreach-loops on collections. It is often used in
- 9. .Net Library Interfaces class Doctor:IComparable { int CompareTo(Doctor other) { return salary-other.salary; } ... } public
- 10. Task 5.1 Develop interface IFlyable with method Fly(). Create two classes Bird (with fields: name and
- 11. C# Collections. Generic collections
- 12. C# Collections .NET framework provides specialized classes for data storage and retrieval. There are two distinct
- 13. C# Collections System.Collections.Generic System.Collections List ArrayList Dictionary HashTable SortedList , SortedDictionary SortedList Stack Stack Queue Queue
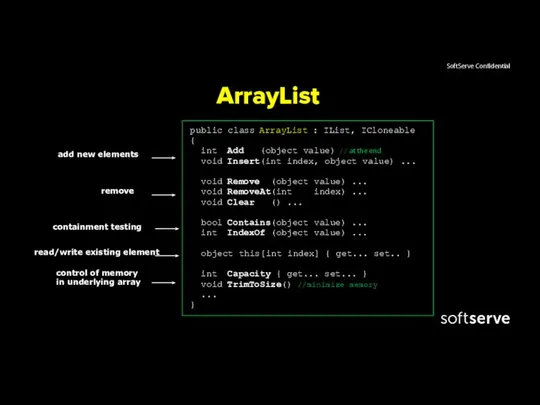
- 14. ArrayList ArrayList is a special array that provides us with some functionality over and above that
- 15. ArrayList public class ArrayList : IList, ICloneable { int Add (object value) // at the end
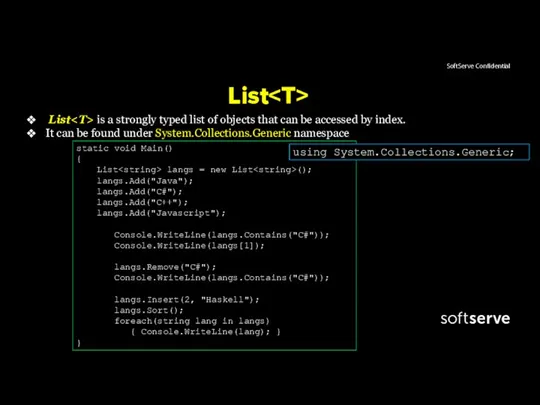
- 16. List List is a strongly typed list of objects that can be accessed by index. It
- 17. List&ArrayList example
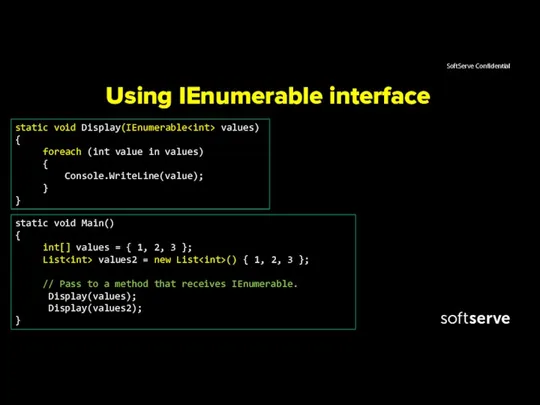
- 18. Using IEnumerable interface static void Display(IEnumerable values) { foreach (int value in values) { Console.WriteLine(value); }
- 19. Dictionary A Dictionary, also called an associative array, is a collection of unique keys and a
- 20. Dictionary Dictionary where we map domain names to their country names: Retrieve values by their keys
- 21. Dictionary example
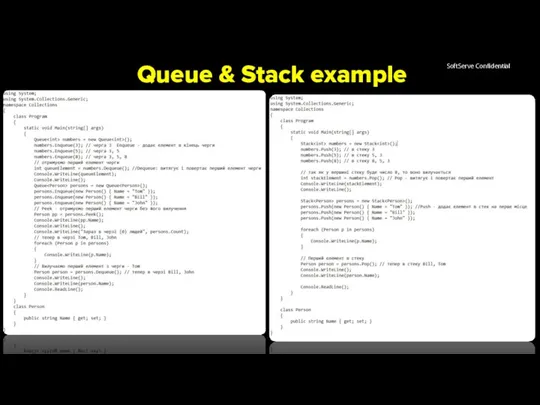
- 22. Queue A Queue is a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data structure. The first element added to the queue
- 23. Stack A stack is a Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) data structure. The last element added to the queue
- 24. Queue & Stack example
- 25. Task 5.2 Develop interface IFlyable with method Fly(). Create two classes Bird (with fields: name and
- 27. Скачать презентацию

















 Растровая и векторная графика
Растровая и векторная графика Как подготовить эффективную презентацию
Как подготовить эффективную презентацию Сервисы интернета
Сервисы интернета Искусственный интеллект
Искусственный интеллект МегаФон. Услуги CDN в операторском бизнесе
МегаФон. Услуги CDN в операторском бизнесе Основы алгоритмизации и объектно-ориентированного программирования
Основы алгоритмизации и объектно-ориентированного программирования Антивирустар. Компьютерлік вирус
Антивирустар. Компьютерлік вирус Принципы управления, построения и алгоритмы функционирования элементов САУ и СА
Принципы управления, построения и алгоритмы функционирования элементов САУ и СА Uvers - A New Generation Social Network
Uvers - A New Generation Social Network Программирование на языке Python
Программирование на языке Python Функции защиты от перегрузок CPU. Функции защиты от петель в сетях Ethernet с помощью управляемых коммутаторов L2
Функции защиты от перегрузок CPU. Функции защиты от петель в сетях Ethernet с помощью управляемых коммутаторов L2 مبانی کامپیوتر و برنامه سازی
مبانی کامپیوتر و برنامه سازی Решение задач общего машиностроения в программном комплексе
Решение задач общего машиностроения в программном комплексе Многопрофильная командная инженерная олимпиада для школьников 9-11 классов
Многопрофильная командная инженерная олимпиада для школьников 9-11 классов Информатика. Материалы к лекции 5. Пользовательская форма на VBA
Информатика. Материалы к лекции 5. Пользовательская форма на VBA Microsoft тарихы
Microsoft тарихы Java for web. Log4j
Java for web. Log4j Протоколи міждоменної маршрутизації. (Лекція 6)
Протоколи міждоменної маршрутизації. (Лекція 6) Физкультминутка на уроках
Физкультминутка на уроках Инструкция по запуску дистанционных курсов
Инструкция по запуску дистанционных курсов Цикл с параметром (цикл с заданным числом повторений, цикл-ДЛЯ)
Цикл с параметром (цикл с заданным числом повторений, цикл-ДЛЯ) Задачи, которые решает Система управления взаимоотношениями с контактами, клиентами и партнерами
Задачи, которые решает Система управления взаимоотношениями с контактами, клиентами и партнерами Hire-pal. The question is … What needs to change?
Hire-pal. The question is … What needs to change? Перевод целых чисел из десятичной системы счисления в любую другую
Перевод целых чисел из десятичной системы счисления в любую другую Общение в интернете
Общение в интернете Основные этапы развития информационного общества
Основные этапы развития информационного общества Программирование на языке Python. Циклические алгоритмы
Программирование на языке Python. Циклические алгоритмы DA 101 Protecting your Domain Admin Account
DA 101 Protecting your Domain Admin Account