Содержание
- 2. AGENDA Interface declaration Interface implementation Built-in .Net interfaces Task1 C# Collections Task 2
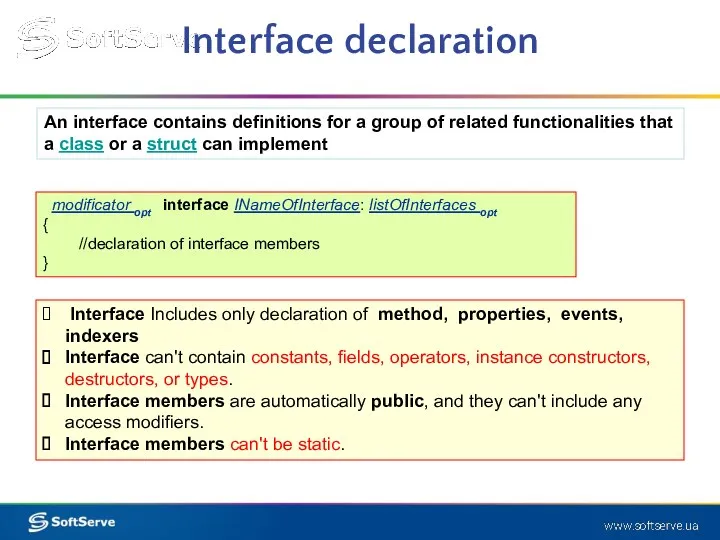
- 3. Interface declaration modificator opt interface INameOfInterface: listOfInterfaces opt { //declaration of interface members } Interface Includes
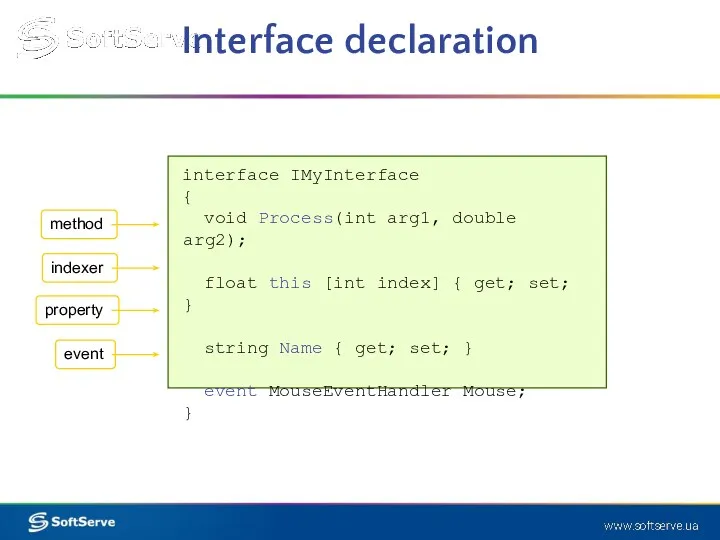
- 4. Interface declaration interface IMyInterface { void Process(int arg1, double arg2); float this [int index] { get;
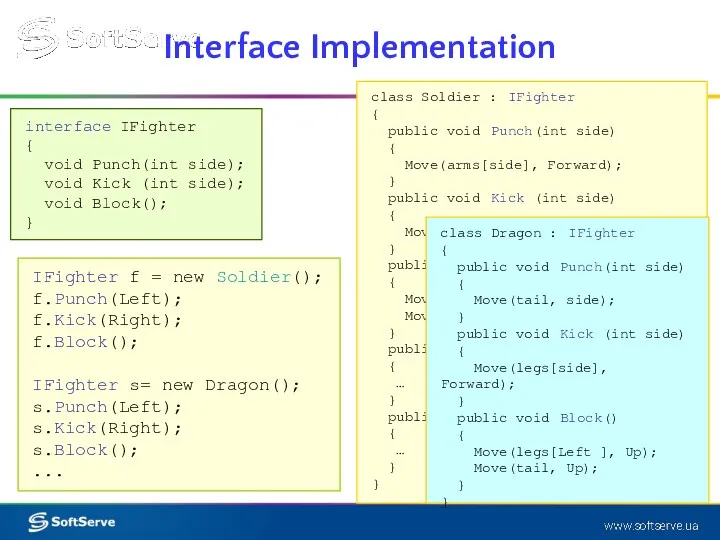
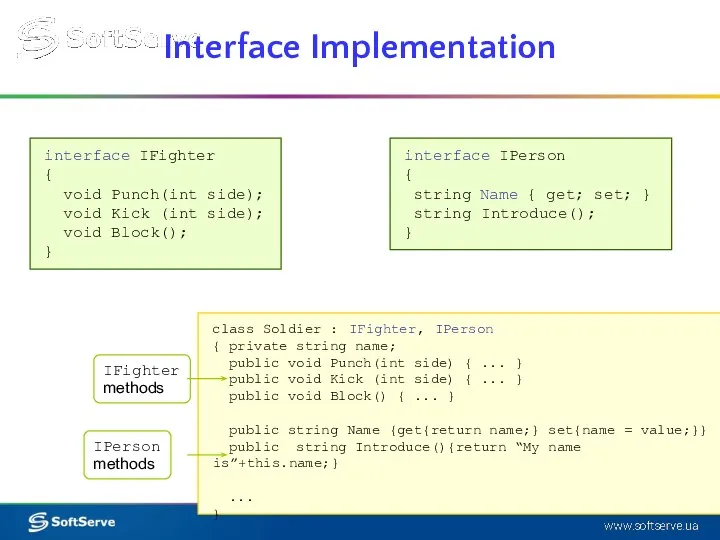
- 5. Interface Implementation interface IFighter { void Punch(int side); void Kick (int side); void Block(); } class
- 6. Any class or struct that implements the interface must implement all its members. By using interfaces,
- 7. interface IPerson { string Name { get; set; } string Introduce(); } interface IFighter { void
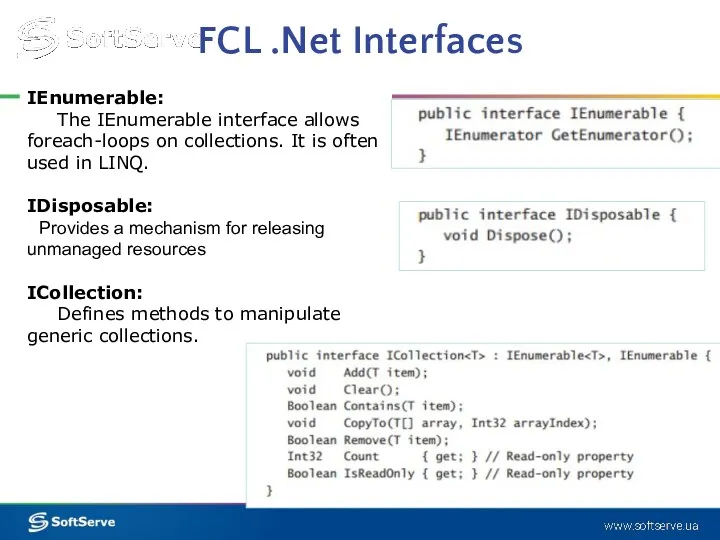
- 8. FCL .Net Interfaces IEnumerable: The IEnumerable interface allows foreach-loops on collections. It is often used in
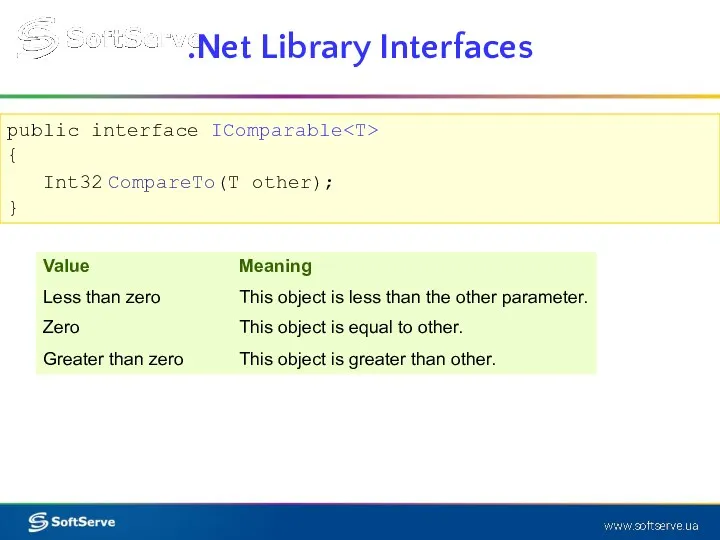
- 9. .Net Library Interfaces public interface IComparable { Int32 CompareTo(T other); }
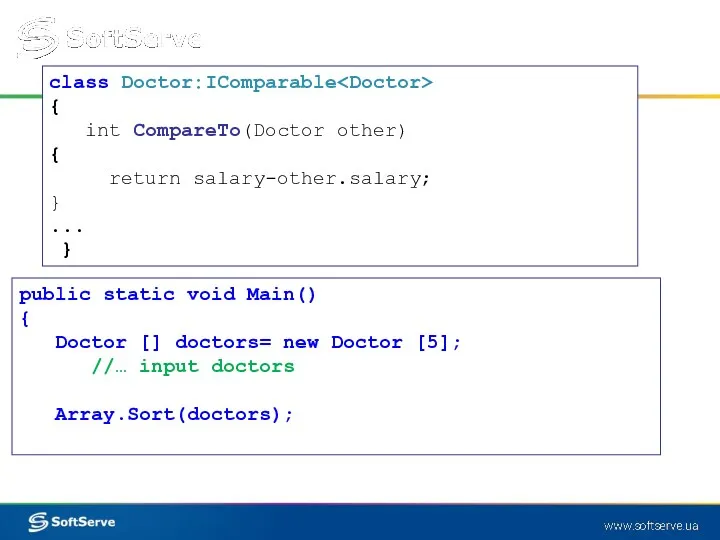
- 10. class Doctor:IComparable { int CompareTo(Doctor other) { return salary-other.salary; } ... } public static void Main()
- 11. Task 5-1. Develop interface IFlyable with method Fly(). Create two classes Bird (with fields: name and
- 12. C# Collections .NET framework provides specialized classes for data storage and retrieval. There are two distinct
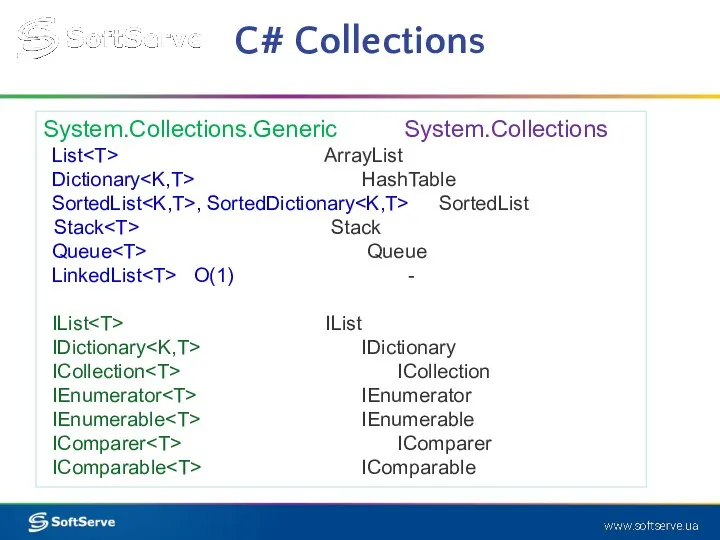
- 13. C# Collections System.Collections.Generic System.Collections List ArrayList Dictionary HashTable SortedList , SortedDictionary SortedList Stack Stack Queue Queue
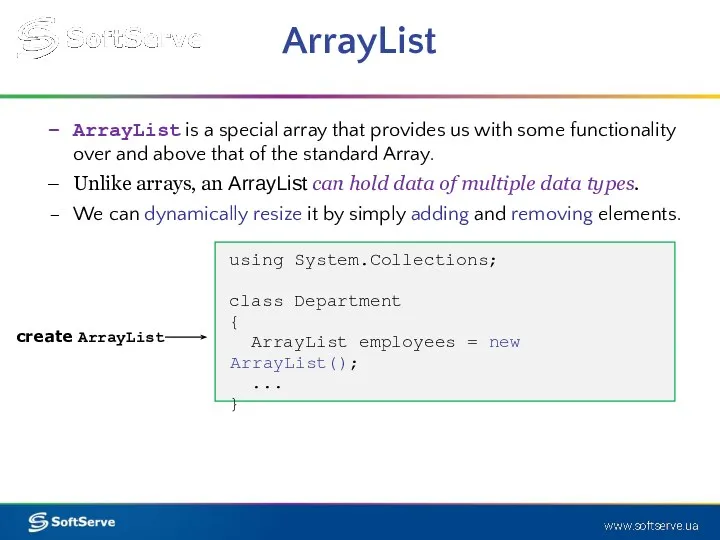
- 14. ArrayList ArrayList is a special array that provides us with some functionality over and above that
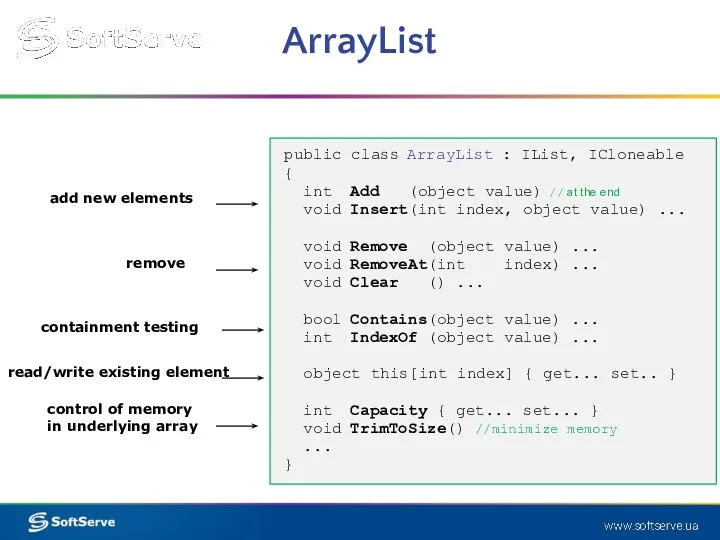
- 15. ArrayList public class ArrayList : IList, ICloneable { int Add (object value) // at the end
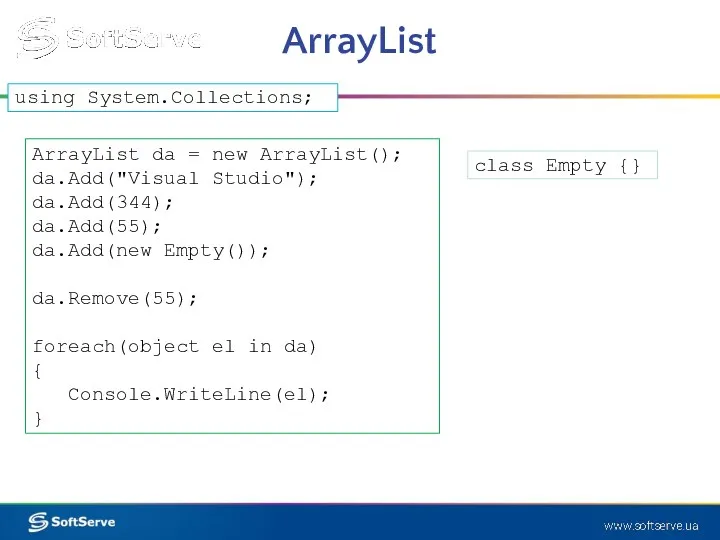
- 16. ArrayList ArrayList da = new ArrayList(); da.Add("Visual Studio"); da.Add(344); da.Add(55); da.Add(new Empty()); da.Remove(55); foreach(object el in
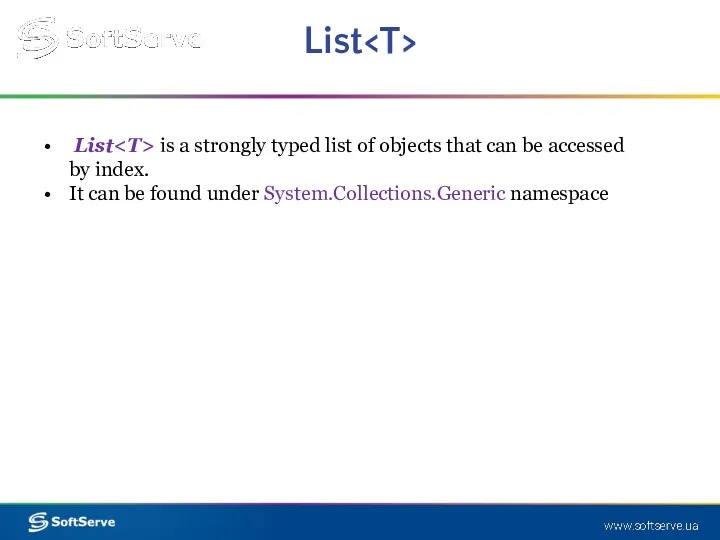
- 17. List List is a strongly typed list of objects that can be accessed by index. It
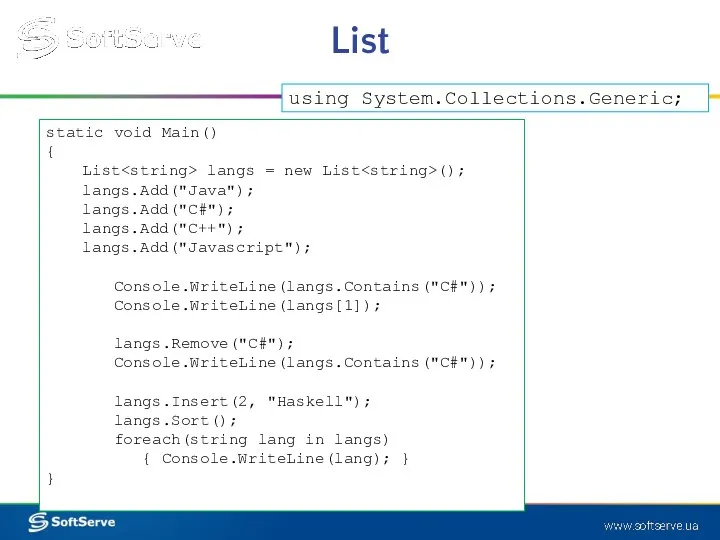
- 18. List static void Main() { List langs = new List (); langs.Add("Java"); langs.Add("C#"); langs.Add("C++"); langs.Add("Javascript"); Console.WriteLine(langs.Contains("C#"));
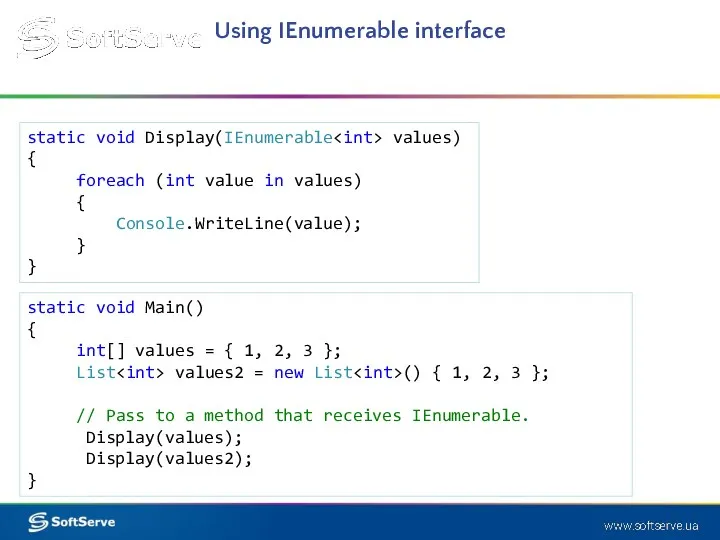
- 19. Using IEnumerable interface static void Display(IEnumerable values) { foreach (int value in values) { Console.WriteLine(value); }
- 20. Dictionary A Dictionary, also called an associative array, is a collection of unique keys and a
- 21. Dictionary Dictionary where we map domain names to their country names: Retrieve values by their keys
- 22. Queue A Queue is a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data structure. The first element added to the queue
- 23. Queue Queue msgs = new Queue (); msgs.Enqueue("Message 1"); msgs.Enqueue("Message 2"); msgs.Enqueue("Message 3"); Console.WriteLine(msgs.Dequeue()); Console.WriteLine(msgs.Peek()); Console.WriteLine(msgs.Peek());
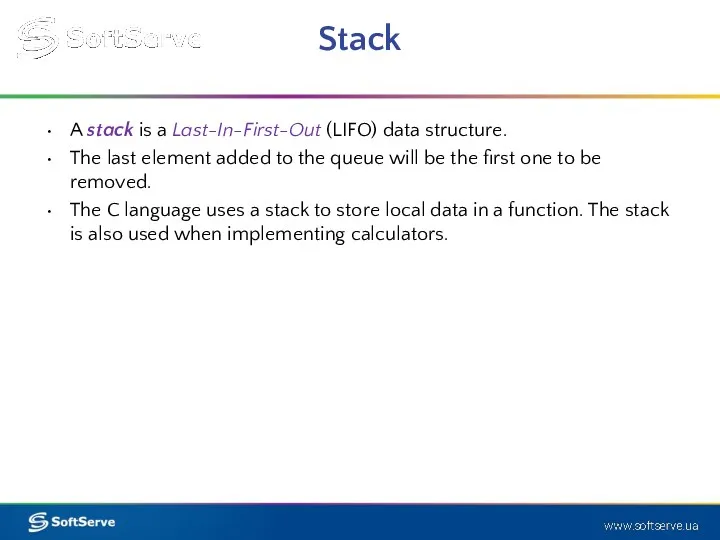
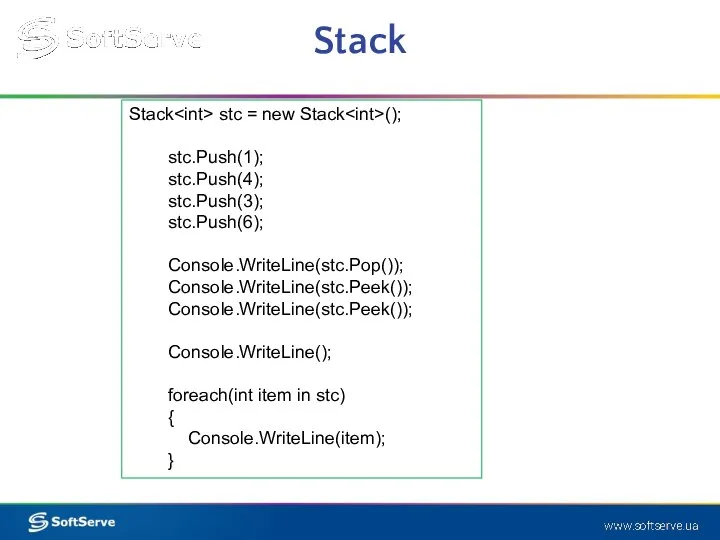
- 24. Stack A stack is a Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) data structure. The last element added to the queue
- 25. Stack Stack stc = new Stack (); stc.Push(1); stc.Push(4); stc.Push(3); stc.Push(6); Console.WriteLine(stc.Pop()); Console.WriteLine(stc.Peek()); Console.WriteLine(stc.Peek()); Console.WriteLine(); foreach(int
- 26. Task 5-2. Collections Declare myColl of 10 integers and fill it from Console. 1) Find and
- 27. Homework 5 1. Create interface IDeveloper with property Tool, methods Create() and Destroy() Create two classes
- 29. Скачать презентацию









 Позиционные системы счисления
Позиционные системы счисления Локальные сети. Параметры сетей и их стандарты
Локальные сети. Параметры сетей и их стандарты Сбор и подготовка данных
Сбор и подготовка данных Современные накопители информации, используемые в вычислительной технике
Современные накопители информации, используемые в вычислительной технике Использование технологии веб-квест как средство развития познавательных и творческих способностей учащихся
Использование технологии веб-квест как средство развития познавательных и творческих способностей учащихся Блочные алгоритмы. Блочное шифрование. Сравнение блочных и поточных шифров. Предпосылки создания шифра Фейстеля
Блочные алгоритмы. Блочное шифрование. Сравнение блочных и поточных шифров. Предпосылки создания шифра Фейстеля Параллельное программирование. С++. Thread Support Library. Atomic Operations Library
Параллельное программирование. С++. Thread Support Library. Atomic Operations Library Функции в Excel
Функции в Excel Организация и средства информационных технологий обеспечения управленческой деятельности
Организация и средства информационных технологий обеспечения управленческой деятельности Поиск публикаций и показатели деятельности ученого в Web of Science
Поиск публикаций и показатели деятельности ученого в Web of Science Бездротові мережі
Бездротові мережі Занятие 1. Знакомство с программой Adobe Photoshop
Занятие 1. Знакомство с программой Adobe Photoshop Microsoft Visual Studio — линейка продуктов компании Microsoft
Microsoft Visual Studio — линейка продуктов компании Microsoft Операторы цикла
Операторы цикла Понятие об информации. Представление информации. Информационная деятельность человека.
Понятие об информации. Представление информации. Информационная деятельность человека. Автоматизоване створення запитів у базі даних
Автоматизоване створення запитів у базі даних Архітектура операційних систем
Архітектура операційних систем Windows System Programming
Windows System Programming Личный кабинет
Личный кабинет Мир станочника. Аддитивные технологии и 3D-сканирование
Мир станочника. Аддитивные технологии и 3D-сканирование Методы и средства защиты программ от компьютерных вирусов
Методы и средства защиты программ от компьютерных вирусов 46_Yaroslavskaya_Sasha
46_Yaroslavskaya_Sasha Локальные и глобальные сети ЭВМ. Защита информации в сетях. (Тема 6)
Локальные и глобальные сети ЭВМ. Защита информации в сетях. (Тема 6) Godseeker. Игра
Godseeker. Игра Рабочий стол. Управление компьютером с помощью мыши
Рабочий стол. Управление компьютером с помощью мыши Проектирование изделий из листового металла в NX
Проектирование изделий из листового металла в NX Эти люди изменили мир
Эти люди изменили мир Электронные ресурсы для детей и юношества в общедоступных библиотеках: создание и использование
Электронные ресурсы для детей и юношества в общедоступных библиотеках: создание и использование