Содержание
- 2. Unless otherwise noted, the content of these slides are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0
- 3. Copyright Thanks Thanks to IEEE Computer for permisison to use IEEE Computer magazine articles associated with
- 4. High Level Phases Dawn of Electronic Computing Pre-Internet Communication Research Networks - 1960s - 1970’s The
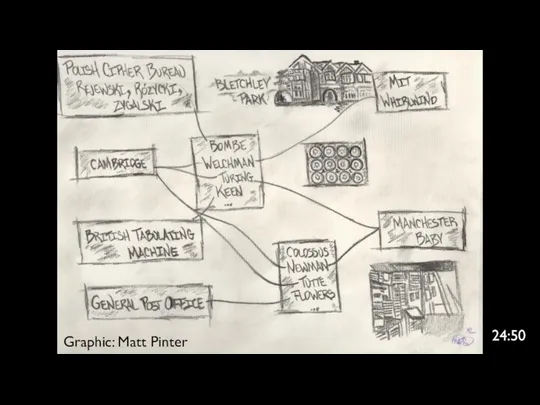
- 5. Alan Turing and Bletchley Park Top secret code breaking effort 10,000 people at the peak (team
- 6. Graphic: Matt Pinter 24:50
- 7. Post-War (1940s) Alumni of the US and UK codebreaking efforts and other started building general purpose
- 8. Post-War (1950s) Math / Science “Won the war” Broad-based investment in maintaining the US/West intellectual lead
- 9. John Forbes Nash Received his Phd. Mathematics at Princeton in 1950 at 22 years old Mathematics
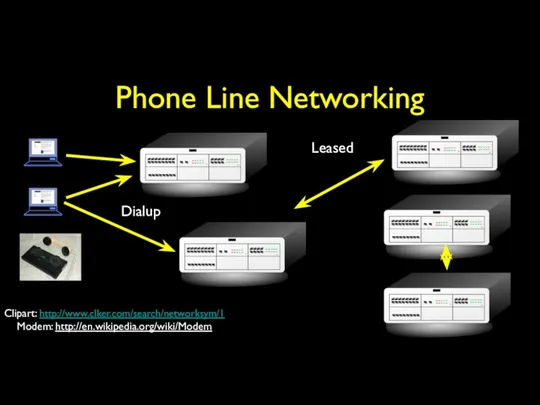
- 10. Phone Line Networking Dialup Leased Clipart: http://www.clker.com/search/networksym/1 Modem: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modem
- 11. Dial-Up Access You were happy to connect to one computer without having to walk across campus
- 12. Data Transfer with Leased Lines You could get a dedicated connection between two points from the
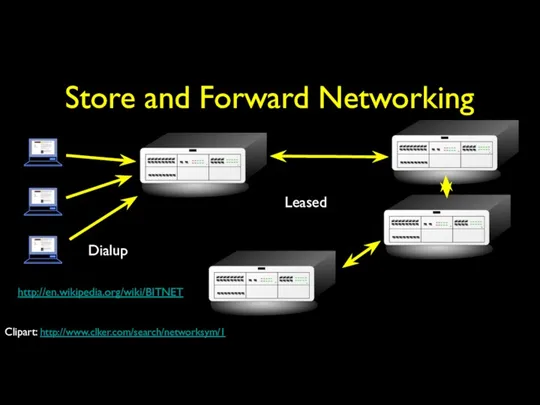
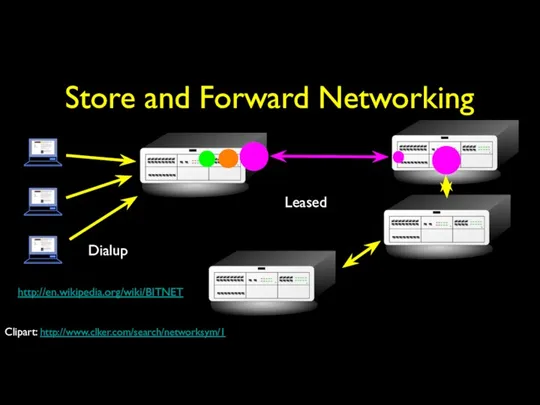
- 13. Store and Forward Networking Dialup Leased http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BITNET Clipart: http://www.clker.com/search/networksym/1
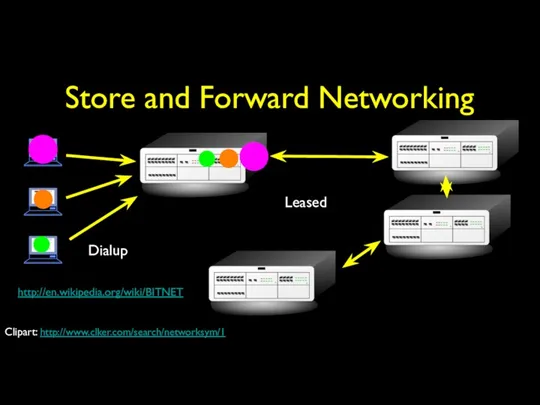
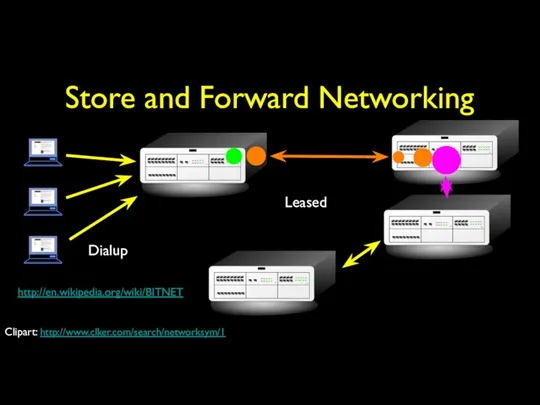
- 14. Store and Forward Networking Dialup Leased http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BITNET Clipart: http://www.clker.com/search/networksym/1
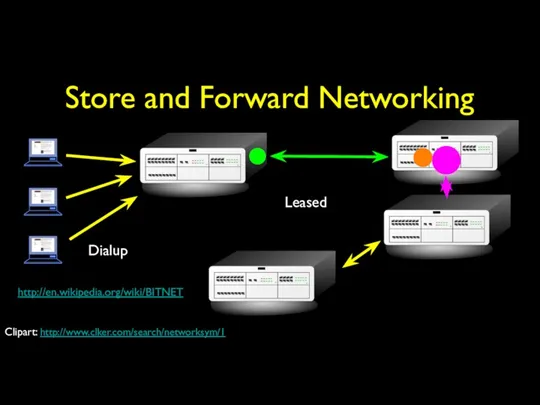
- 15. Store and Forward Networking Dialup Leased http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BITNET Clipart: http://www.clker.com/search/networksym/1
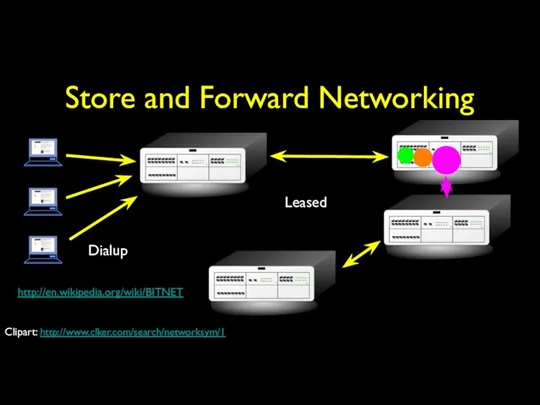
- 16. Store and Forward Networking Dialup Leased http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BITNET Clipart: http://www.clker.com/search/networksym/1
- 17. Store and Forward Networking Dialup Leased http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BITNET Clipart: http://www.clker.com/search/networksym/1
- 18. Store and Forward Networking Dialup Leased http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BITNET Clipart: http://www.clker.com/search/networksym/1
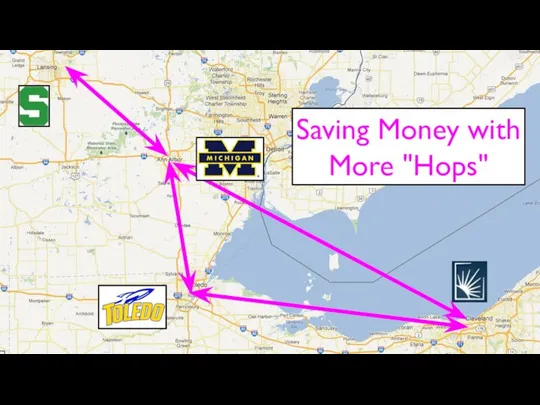
- 19. Saving Money with More "Hops"
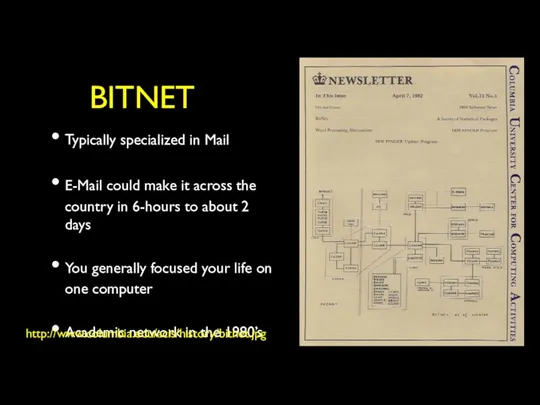
- 20. Store and Forward Networking Typically specialized in Mail E-Mail could make it across the country in
- 21. BITNET Typically specialized in Mail E-Mail could make it across the country in 6-hours to about
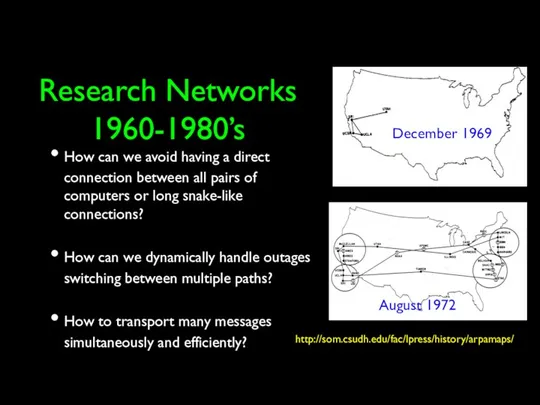
- 22. Research Networks 1960-1980’s How can we avoid having a direct connection between all pairs of computers
- 23. Efficient Message Transmission: Packet Switching Challenge: in a simple approach, like store-and-forward, large messages block small
- 24. Packet Switching - Postcards Hello there, have a nice day. Hello ther (1, csev, daphne) e,
- 25. e, have a (2, csev, daphne) nice day. (3, csev, daphne) Packet Switching - Postcards Hello
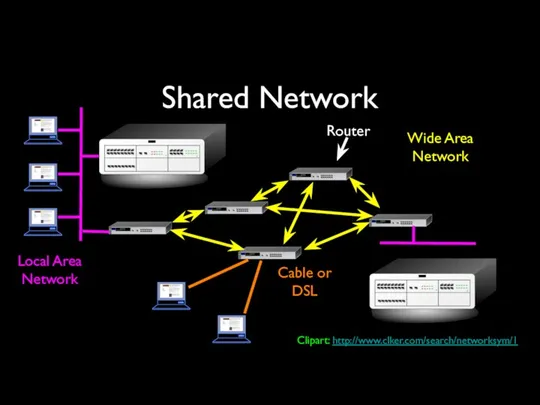
- 26. Shared Network Local Area Network Wide Area Network Cable or DSL Router Clipart: http://www.clker.com/search/networksym/1
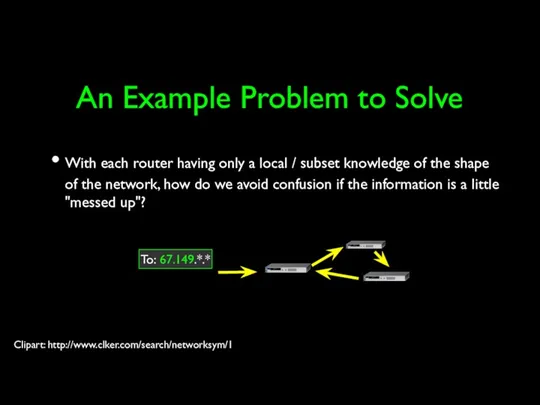
- 27. An Example Problem to Solve With each router having only a local / subset knowledge of
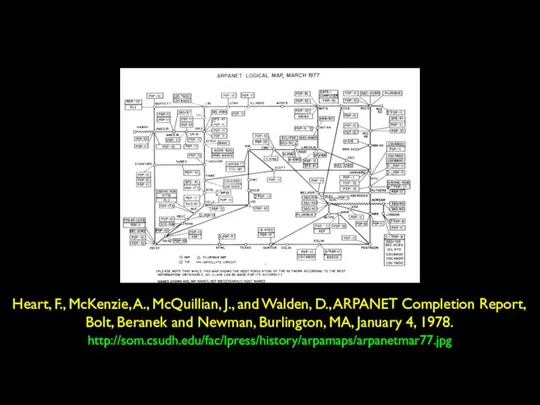
- 28. http://som.csudh.edu/fac/lpress/history/arpamaps/arpanetmar77.jpg Heart, F., McKenzie, A., McQuillian, J., and Walden, D., ARPANET Completion Report, Bolt, Beranek and
- 29. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
- 30. Supercomputers... As science needed faster and faster computers, more universities asked for their own Multimillion dollar
- 31. NCSA - Innovation We now “assume” the Internet and the Web - it was not so
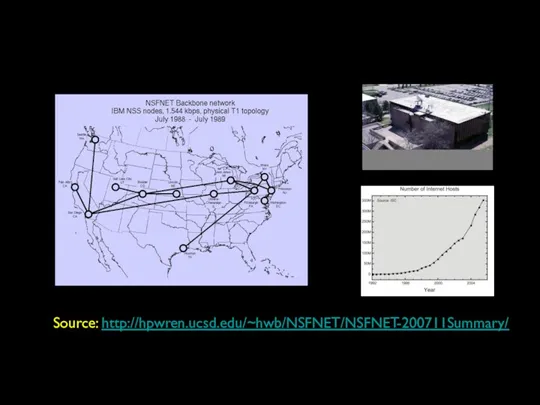
- 32. NSF Net NSFNet was funded by the National Science Foundation Standardized on TCP/IP The first national
- 33. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign University of Michigan
- 34. NSF Net NSFNet was funded by the National Science Foundation Standardized on TCP/IP The first national
- 35. Michigan's State-Wide Network [1] http://www.zakon.org/robert/internet/timeline/ In 1969, Merit was one of the earliest network projects that
- 36. NSFNet @ University of Michigan University of Michigan did not get a Supercomputer Center Proposed a
- 37. Source: http://hpwren.ucsd.edu/~hwb/NSFNET/NSFNET-200711Summary/
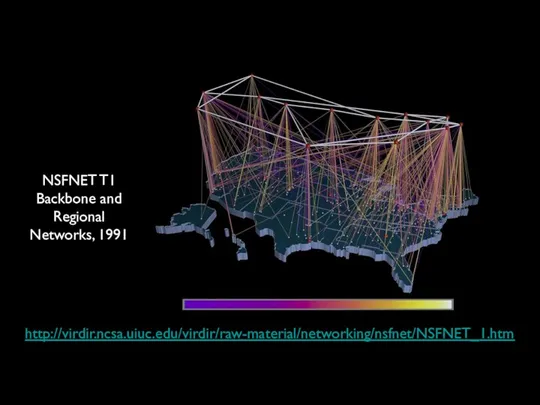
- 38. http://virdir.ncsa.uiuc.edu/virdir/raw-material/networking/nsfnet/NSFNET_1.htm NSFNET T1 Backbone and Regional Networks, 1991
- 39. NSF Net Advocacy Initially aimed at research universities Cleveland FreeNet and similar efforts provided indirect Internet
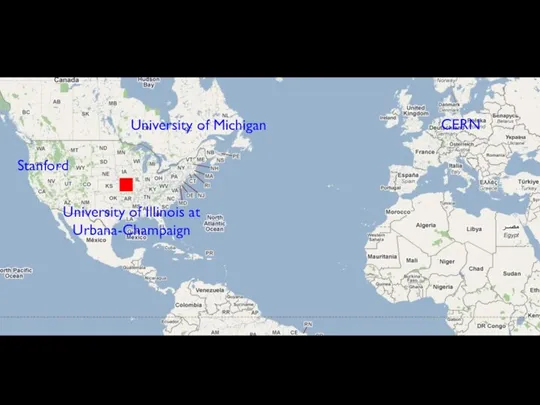
- 40. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign University of Michigan CERN
- 41. CERN - High-Energy (physics) Brilliant physicists from all over the world Work on long, highly detailed
- 43. Visits to CERN! http://club-softball.web.cern.ch/club-softball/Canettes/ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f90ysF9BenI
- 45. The Beginning of the Web: CERN The Internet was infrastructure - the web gave the Internet
- 46. http://info.cern.ch/images/NextEditorBW.gif
- 47. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign University of Michigan CERN Stanford
- 48. The First Web Server in America The first web server in America was at the Stanford
- 49. 1993: Gopher is Dominant Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Meeting March 29-April 2, 1993 - Columbus,
- 50. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sYNUcFMCIzw What industry was thinking in 1993... 0:30
- 51. 0:30
- 52. Steve Jobs and the World-Wide-Web? For several years the primary web browser and web server were
- 53. 12:23
- 54. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign University of Michigan CERN Stanford
- 55. The Explosive Growth of the Web The web was invented in the early 1990’s Growing in
- 56. Joseph Hardin, UM Mosaic - Netscape - Mozilla - Firefox Mosaic was the first “consumer” web
- 57. 1994: Year of the Web Netscape Founded - April 4, 1994 WWW Conf: May 25-26-27 1994,
- 58. Netscape, JavaScript and FireFox As Microsoft worked to suffocate Netscape:: JavaScript was invented to compete with
- 59. Did Microsoft Save the World-Wide Web? Netscape wanted to make the web browser, web server, and
- 60. World-Wide-Web Consortium The W3C was formed in October 1994 (www.w3c.org) Led by Tim Berners-Lee who moved
- 61. When You Can Assume the Web Internet: TCI Show 08 http://www.vimeo.com/4275919 1:22 December 11-14, 1995 http://www.w3.org/Conferences/WWW4/
- 62. Some Great Books How the Web was Born: The Story of the World Wide Web, James
- 63. Larry Smarr wanted to make supercomputers available to physicists Unversity of Michigan sneaked in 1.54Mb/sec instead
- 64. The Web Land Rush... In the late 1990’s there were many fortunes to be made -
- 65. The Modern Internet In the late 1990’s in the boom there was a great deal of
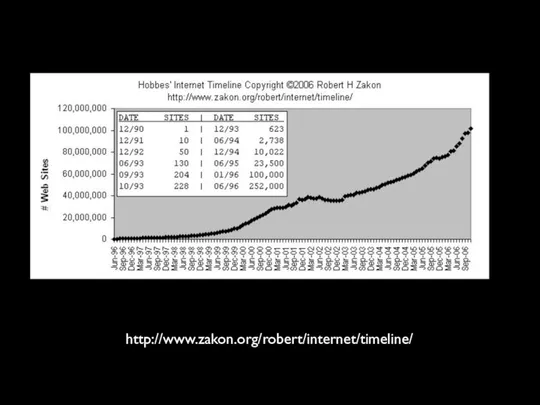
- 66. http://www.zakon.org/robert/internet/timeline/
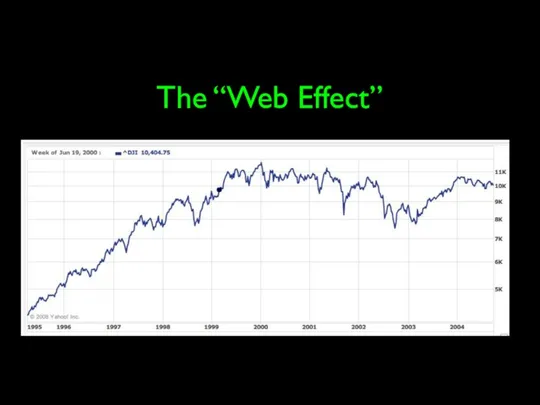
- 67. The “Web Effect”
- 68. A History of Open Source .... http://www.vimeo.com/7307422 http://www.vimeo.com/3800796 http://www.vimeo.com/6215179
- 69. Other Resources Hobbes Internet Timeline http://www.zakon.org/robert/internet/timeline/ A Brief History of the Internet. Barry M. Leiner, et
- 70. Additional Source Information TuringBombeBletchleyPark: Sarah Hartwell, Wikimedia Commons, http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/23/TuringBombeBletchleyPark.jpg. CC: BY-SA, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en SSEM Manchester museum: Parrot
- 72. Скачать презентацию

















![Michigan's State-Wide Network [1] http://www.zakon.org/robert/internet/timeline/ In 1969, Merit was one](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/318110/slide-34.jpg)



























 Государственный кадастровый учет изменений и регистрация права на объекты недвижимости в электронном виде самим заказчиком
Государственный кадастровый учет изменений и регистрация права на объекты недвижимости в электронном виде самим заказчиком Абстрактные классы и интерфейсы. Лекция 34
Абстрактные классы и интерфейсы. Лекция 34 Компьютерное зрение
Компьютерное зрение Копирайтинг. Группа ВК, страница в Instagram,
Копирайтинг. Группа ВК, страница в Instagram, Четыре основных принципа объектно-ориентированного программирования
Четыре основных принципа объектно-ориентированного программирования Интегрированный урок - исследование Моделирование биоритмов человека
Интегрированный урок - исследование Моделирование биоритмов человека Візуальний конструктор iot-рішень. Fractal
Візуальний конструктор iot-рішень. Fractal Задача о пути торможения автомобиля
Задача о пути торможения автомобиля Мессенджеры и приложения как новый вид прессы
Мессенджеры и приложения как новый вид прессы Команды ARP и PING
Команды ARP и PING Устройство персонального компьютера
Устройство персонального компьютера презентация к 1-ому уроку информатики по УМК Матвеевой Человек и информация
презентация к 1-ому уроку информатики по УМК Матвеевой Человек и информация Обработка текстовой информации
Обработка текстовой информации Фирменные шрифты
Фирменные шрифты Конвергентный журналист
Конвергентный журналист Алгоритмический язык Pascal
Алгоритмический язык Pascal Язык запросов SQL. Введение
Язык запросов SQL. Введение Вычислительная система. Аппаратная платформа. ОС и управление аппаратными компонентами компьютера. (Тема 1.1.2)
Вычислительная система. Аппаратная платформа. ОС и управление аппаратными компонентами компьютера. (Тема 1.1.2) Анимированные ребусы
Анимированные ребусы Тема 1. Системы связи. Лекция 2. Сигналы электросвязи
Тема 1. Системы связи. Лекция 2. Сигналы электросвязи Средства антивирусной защиты
Средства антивирусной защиты Безопасность в интернете
Безопасность в интернете Сходство и различие радиотехнических САУ и других автоматических систем
Сходство и различие радиотехнических САУ и других автоматических систем Электронное дидактическое пособие. Золотая осень (для дошкольников)
Электронное дидактическое пособие. Золотая осень (для дошкольников) Работа с электронными таблицами в программе Microsoft Excel
Работа с электронными таблицами в программе Microsoft Excel Стандартны оформления программного кода
Стандартны оформления программного кода Accelerate Azure migrations with Windows Server & SQL Server 2008 and 2008 R2 end of support
Accelerate Azure migrations with Windows Server & SQL Server 2008 and 2008 R2 end of support Windows операциялық жүйесін орнату
Windows операциялық жүйесін орнату