Содержание
- 2. Purpose Review of computer systems. Evolution of computer systems. Architecture and components of computer systems. Using
- 3. Vocabulary ИКТ – 16. ____________ – tools Информатика – 17. ____________ - emergence Стандартизация – 18.
- 4. Vocabulary Database - база данных Software - программного обеспечения Hardware - аппаратные средства Storage of data
- 5. Vocabulary Data entry - ввод данных Binary numbering system - бинарная система нумерации Decimal numbering system
- 6. Answer my questions What is definition of ICT ? What is main purposes of ICT ?
- 7. System A system is a set of elements or components that interact to accomplish goals.
- 8. Review of computer systems 1) Computer system is defined as the combination of hardware, software, user
- 9. A Computer .... • takes input • processes it according to stored instructions • produces results
- 10. A Computer ....
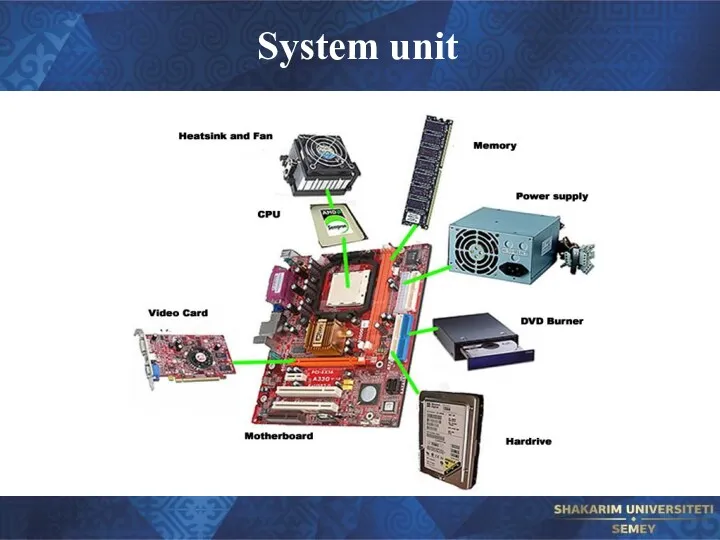
- 11. System unit
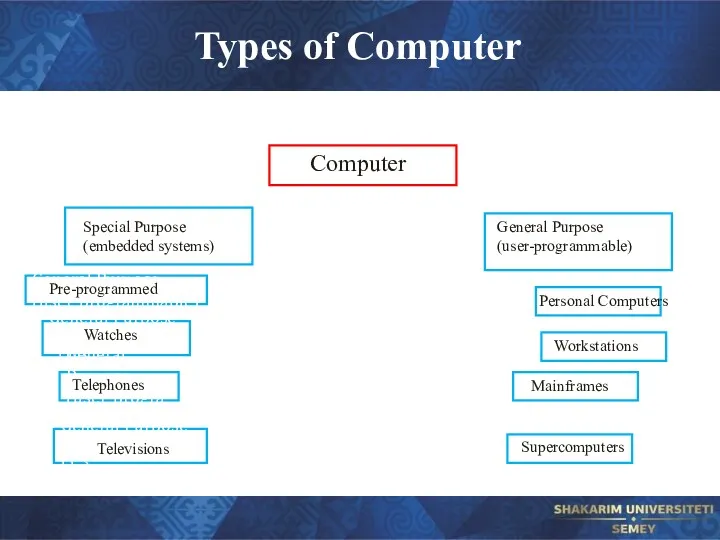
- 12. Types of Computer Computer General Purpose (user-programmable) Special Purpose (embedded systems) General Purpose (user-programmable) General Purpose
- 13. Review of computer systems Hardware: Computer Equipment Software: Computer Programs Databases: An organized collections of facts
- 14. Information can be presented in various forms: in the form of symbolic or writing for example:
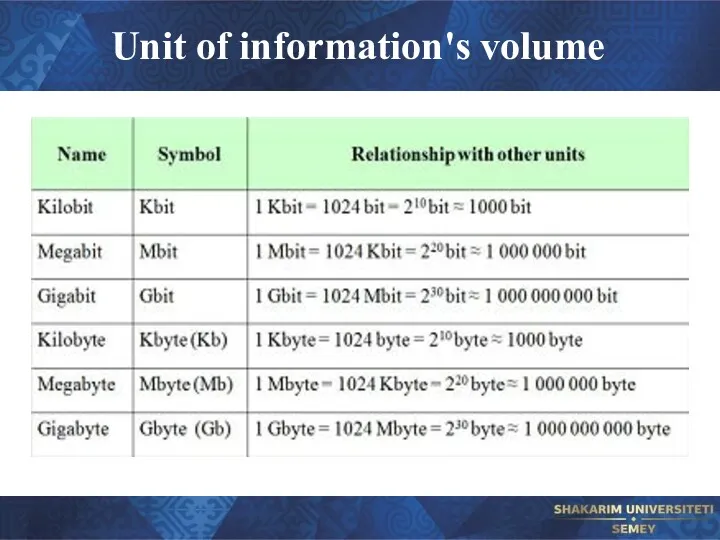
- 15. Unit of information's volume
- 16. Encryption the information Code - a set of symbols to represent information. Encoding - is a
- 17. Bits and Bytes Bit - is the smallest unit of information's volume measurement and denoted by
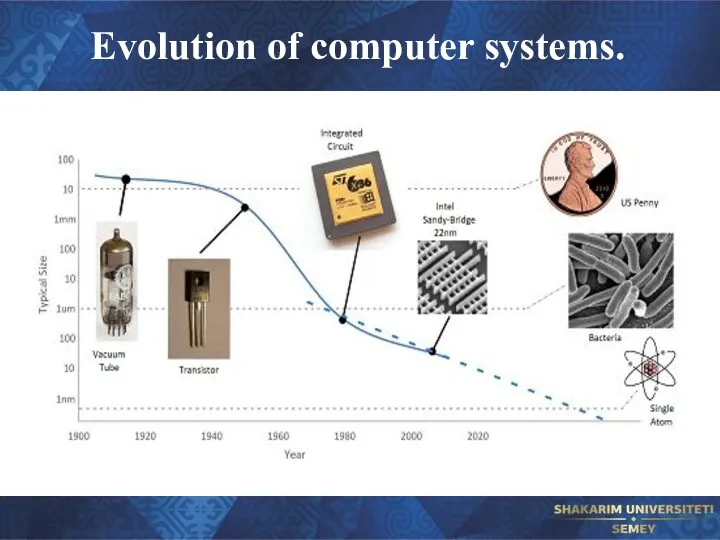
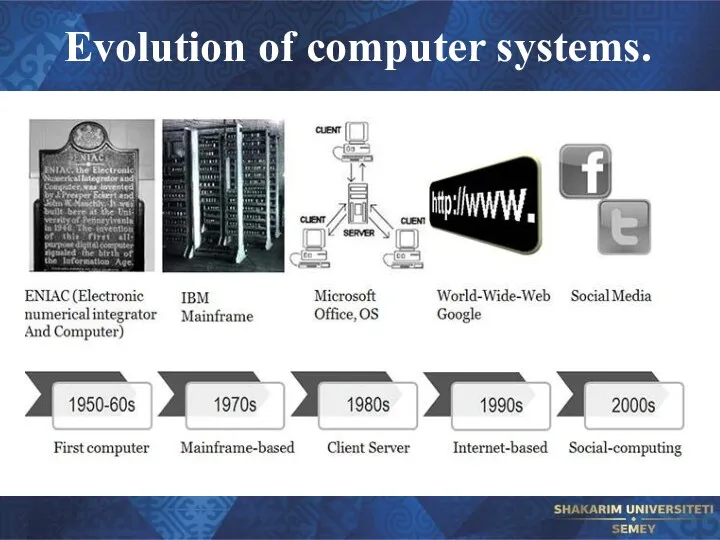
- 18. Evolution of computer systems.
- 19. Evolution of computer systems.
- 20. Evolution of computer systems. Charles Babbage (1791-1871) designed the first automatic computing engine. He invented computers
- 21. Evolution of computer systems.
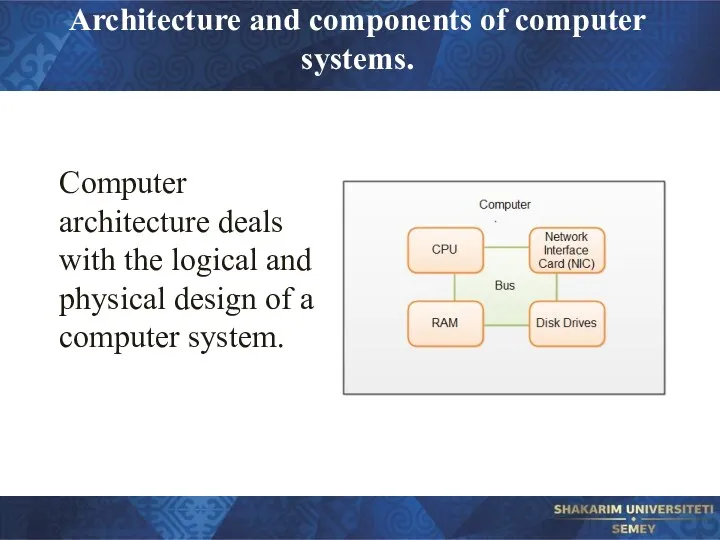
- 22. Architecture and components of computer systems. Computer architecture deals with the logical and physical design of
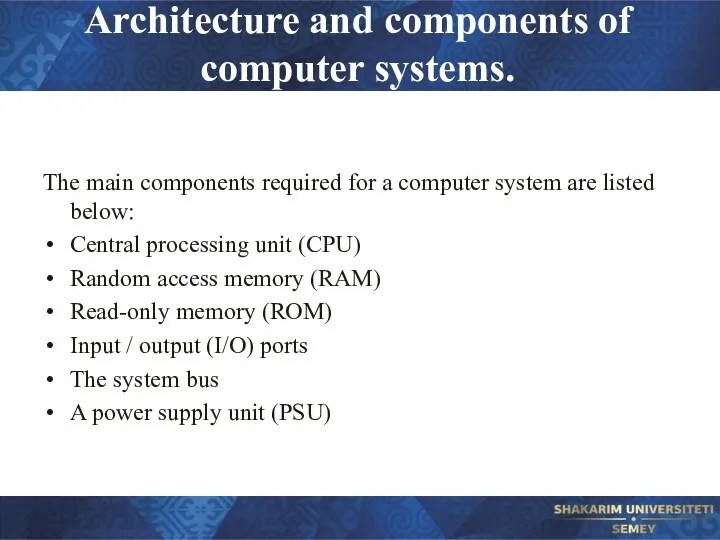
- 23. Architecture and components of computer systems. The main components required for a computer system are listed
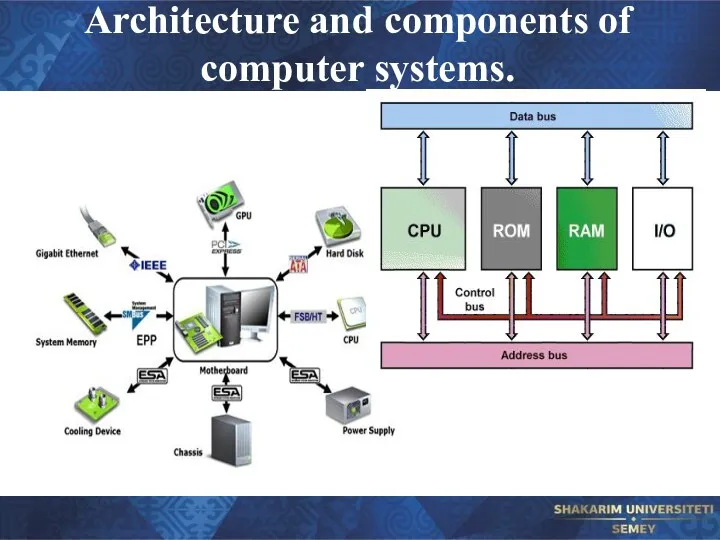
- 24. Architecture and components of computer systems.
- 25. Architecture and components of computer systems.
- 26. Using computer systems. When we are learning When we are working
- 27. Using computer systems.
- 28. Detecting Voltage Levels Why not 10 levels? Would be unreliable Not enough difference between states On/Off
- 29. Bits, Bytes, and so on A bit is one 0 or 1 Short for “binary digit”
- 30. The Binary Numbering System A computer’s internal storage techniques are different from the way people represent
- 31. Binary Representation of Numeric and Textual Information Binary numbering system Base-2 Built from ones and zeros
- 32. Input of Data Resources Data entry Editing Machine readable Source documents Formal record of a transaction
- 33. Process Data into Information Calculate Compare Sort Classify Summarize The quality of the data must be
- 34. Output of Information Transmit information to users Display; paper; audio Storage of data Data are retained
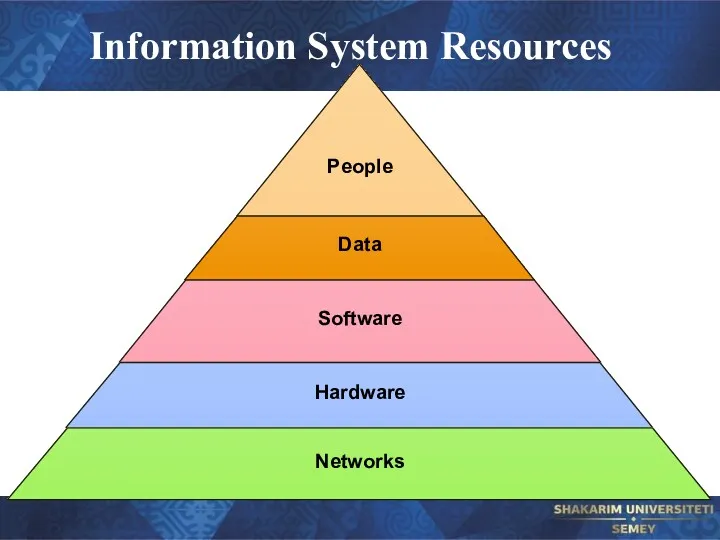
- 35. Information System Resources People Data Software Hardware Networks
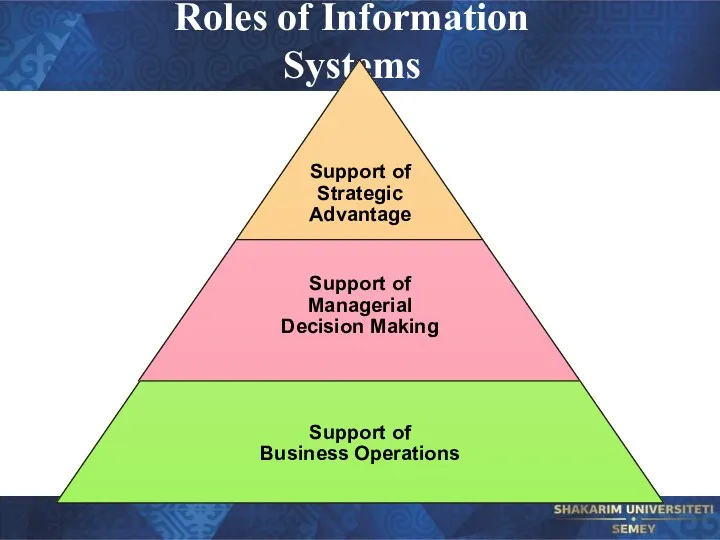
- 36. Roles of Information Systems
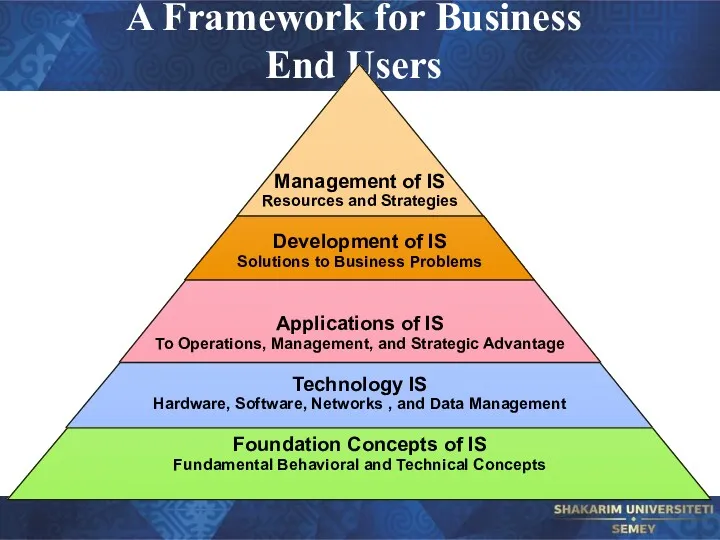
- 37. A Framework for Business End Users
- 38. Q&A. Have you any questions ???
- 40. Скачать презентацию























 SMM для start-up
SMM для start-up Файловый менеджер
Файловый менеджер Команда FevDay. Создание приложения на мобильное устройство
Команда FevDay. Создание приложения на мобильное устройство Эволюция технологий изготовления процессора
Эволюция технологий изготовления процессора Системы счисления
Системы счисления Промышленные ПЛК
Промышленные ПЛК Декоративно-прикладне мистецтво. Підручник
Декоративно-прикладне мистецтво. Підручник ООП 7. Наследование и шаблоны
ООП 7. Наследование и шаблоны Інформаційні процеси та системи
Інформаційні процеси та системи Моделирование бизнес--процессов в управлении и средствами принятии решений графической нотации BPMN
Моделирование бизнес--процессов в управлении и средствами принятии решений графической нотации BPMN Программирование сервера баз данных
Программирование сервера баз данных Программирование на языке Паскаль. §54-61. 10 класс
Программирование на языке Паскаль. §54-61. 10 класс Анализ алгоритмов. (Лекция 16)
Анализ алгоритмов. (Лекция 16) Презентация к уроку Кодирование звуковой информации
Презентация к уроку Кодирование звуковой информации Обзор операций и базовых инструкций языка Си. (Тема 3)
Обзор операций и базовых инструкций языка Си. (Тема 3) Технология Flash в современном интернете
Технология Flash в современном интернете Презентация Ознакомления детей с гжелью
Презентация Ознакомления детей с гжелью Использование электронной доски для развития творческих способностей учащихся начальной школы. Часть 2.
Использование электронной доски для развития творческих способностей учащихся начальной школы. Часть 2. Засоби пошуку інформації в Інтернеті
Засоби пошуку інформації в Інтернеті Технологии построения web-интерфейсов
Технологии построения web-интерфейсов Знецінення як робота з обличчям співрозмовника у соціальних мережах
Знецінення як робота з обличчям співрозмовника у соціальних мережах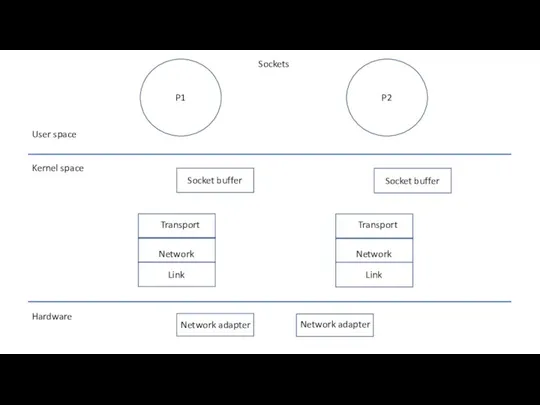 About RAW sockets
About RAW sockets Анализ современных подходов к разработке мобильных приложений на примере приложения: Дневник стрелка
Анализ современных подходов к разработке мобильных приложений на примере приложения: Дневник стрелка Технология проектирования реляционных баз данных. Нормализация и функциональные зависимости
Технология проектирования реляционных баз данных. Нормализация и функциональные зависимости Групповые операции в запросах Access
Групповые операции в запросах Access Проектирование и разработка игрового приложения. Физика и взаимодействие игровых персонажей
Проектирование и разработка игрового приложения. Физика и взаимодействие игровых персонажей Создание альтернативного сайта для ГУО средняя школа №24 г. Гомеля
Создание альтернативного сайта для ГУО средняя школа №24 г. Гомеля Принципи організації розподілених інформаційних систем на основі баз даних та експертних систем в освіті
Принципи організації розподілених інформаційних систем на основі баз даних та експертних систем в освіті