Содержание
- 2. OUTLINE OF TALK 1. Course Syllabus 2. What is software project management 3. Software Project Manager
- 3. SYLLABUS: Learning outcomes A basic knowledge of software project management principles Choose an appropriate project development
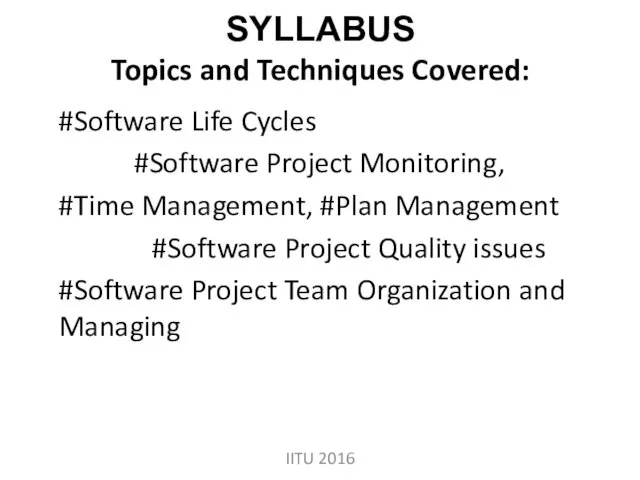
- 4. SYLLABUS Topics and Techniques Covered: #Software Life Cycles #Software Project Monitoring, #Time Management, #Plan Management #Software
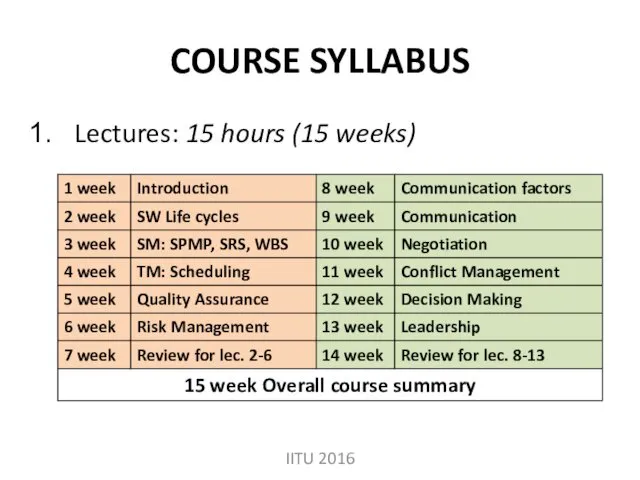
- 5. COURSE SYLLABUS Lectures: 15 hours (15 weeks) IITU 2016
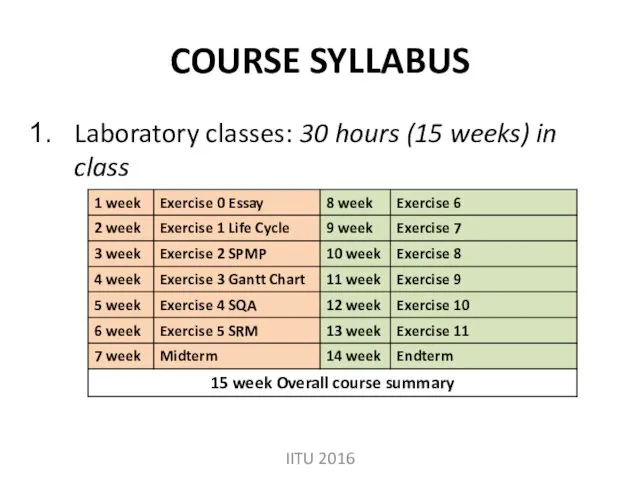
- 6. COURSE SYLLABUS Laboratory classes: 30 hours (15 weeks) in class IITU 2016
- 7. COURSE SYLLABUS: References Authors: Walker Royce Published: Addison - Wesley Year: 1998 ISBN: 0-201-30958-0 IITU 2016
- 8. COURSE SYLLABUS : References Authors: Frank Tsui, Orlando Karam Published: Jones & Bartlett Learning Year: 2013
- 9. COURSE SYLLABUS: References Authors: Carol L. Hoover, Mel Rosso-Llopart, Gil Taran Published: Pearson Education, Inc. Year:
- 10. What is the Project? Some dictionary definitions: “A specific plan or design” “A planned undertaking” “A
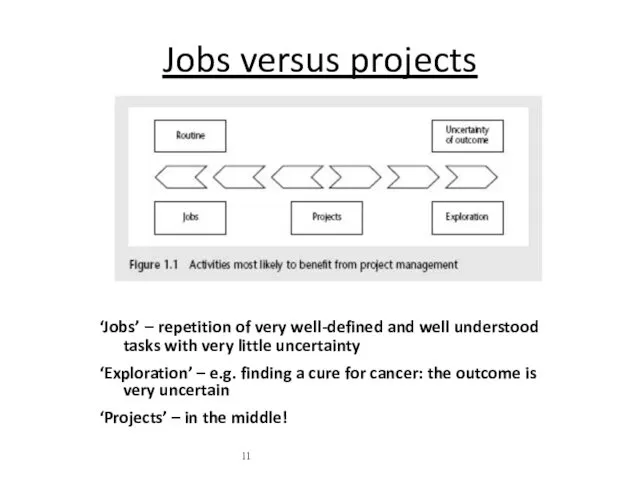
- 11. Jobs versus projects ‘Jobs’ – repetition of very well-defined and well understood tasks with very little
- 12. SOFTWARE ENGINEERING What is software project management? Is it really different from ‘ordinary’ project management? How
- 13. Project’s characteristics A task is more ‘project-like’ if it is: Non-routine Planned Aiming at a specific
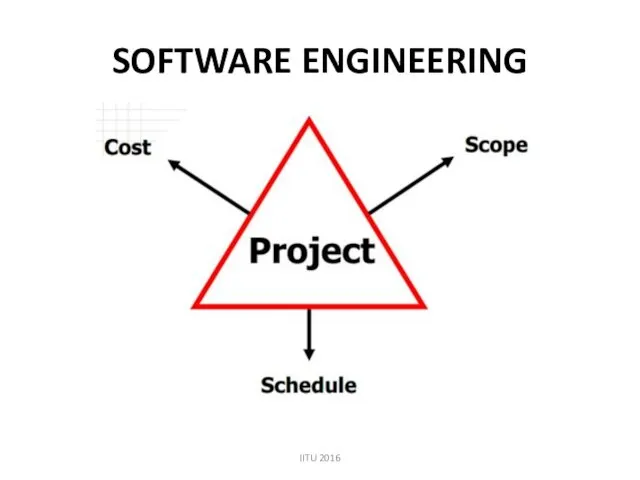
- 14. SOFTWARE ENGINEERING IITU 2016
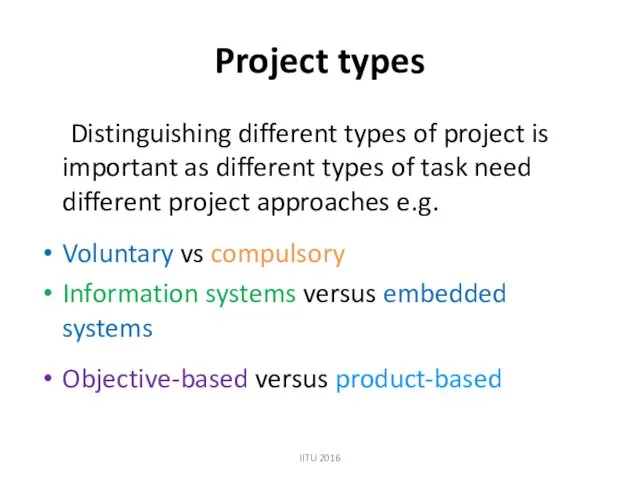
- 15. Project types Distinguishing different types of project is important as different types of task need different
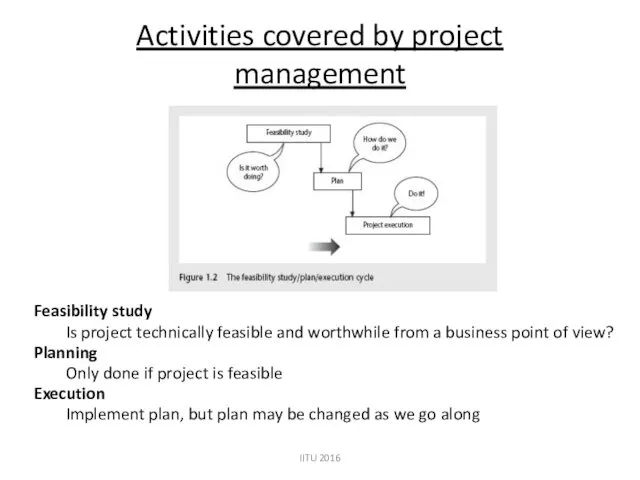
- 16. IITU 2016 Activities covered by project management Feasibility study Is project technically feasible and worthwhile from
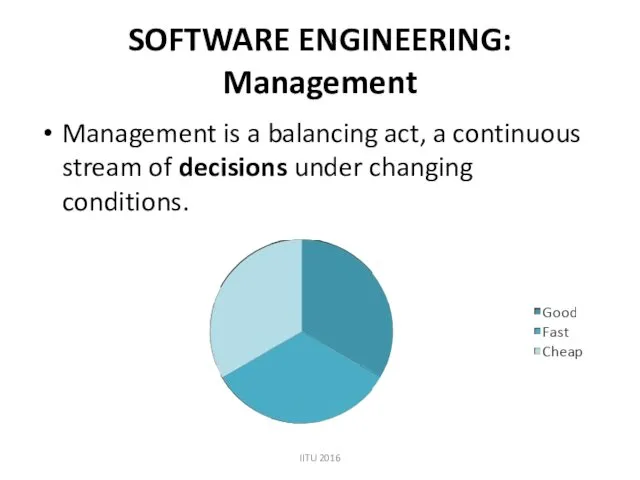
- 17. SOFTWARE ENGINEERING: Management Management is a balancing act, a continuous stream of decisions under changing conditions.
- 18. SOFTWARE ENGINEERING: Management This involves the following activities: Planning – deciding what is to be done
- 19. SOFTWARE ENGINEERING: Management Monitoring – checking on progress Controlling – taking action to remedy hold-ups Innovating
- 20. MANAGEMENT ROLE Why do we need manager? When we do not need manager? IITU 2016
- 21. SOFTWARE PROJECT MANAGER POSITION Team Leader vs Project Manager IITU 2016 Planning Organizing Staffing Directing Controlling
- 22. SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Principles : Alan Davis (15 most important princip.) Royce Walker (top 10 princ.) Anthony
- 24. Скачать презентацию













 Табличные процессоры
Табличные процессоры Современные тенденции развития информационных технологий и ресурсов
Современные тенденции развития информационных технологий и ресурсов Exceptions. Исключение в Java
Exceptions. Исключение в Java Презентация к уроку Информатики и ИКТ в 9-м классе по теме: Электронные таблицы
Презентация к уроку Информатики и ИКТ в 9-м классе по теме: Электронные таблицы Digital Twin. Занятие 2
Digital Twin. Занятие 2 Коллектив разработчиков. Лидер
Коллектив разработчиков. Лидер Анализ интернет-журнала Wonderzine на жанровое разнообразие
Анализ интернет-журнала Wonderzine на жанровое разнообразие Знакомство с Microsoft Excel
Знакомство с Microsoft Excel Электронные таблицы (часть 3)
Электронные таблицы (часть 3) Запись и хранение данных. Массивы, списки, очереди, стеки, файловый ввод-вывод. Основные понятия о базах данных. (Лекция 3)
Запись и хранение данных. Массивы, списки, очереди, стеки, файловый ввод-вывод. Основные понятия о базах данных. (Лекция 3) N-схема моделирования
N-схема моделирования Интернет-СМИ
Интернет-СМИ Разработка дизайна сайта для продажи автомобилей
Разработка дизайна сайта для продажи автомобилей Кодирование графической информации. Качество растрового изображения
Кодирование графической информации. Качество растрового изображения Архитектура и структура персонального компьютера
Архитектура и структура персонального компьютера Обработка информации и алгоритмы
Обработка информации и алгоритмы Проблемы, связанные с использованием сервиса мой арбитр
Проблемы, связанные с использованием сервиса мой арбитр Информация и информационные процессы. Информационное общество
Информация и информационные процессы. Информационное общество Разработка мобильного приложения к чемпионату мира по футболу 2018
Разработка мобильного приложения к чемпионату мира по футболу 2018 Моделі локалізації об'єктів на зображенні у мережевих комп'ютерних системах аналізу зображень
Моделі локалізації об'єктів на зображенні у мережевих комп'ютерних системах аналізу зображень Метрология. Метрики программного обеспечения
Метрология. Метрики программного обеспечения Устранение неполадок и справочная служба
Устранение неполадок и справочная служба Базы данных и Система управления базами данных (СУБД)
Базы данных и Система управления базами данных (СУБД) Исследование возможности создания электронных документов на основе шаблонов в организации
Исследование возможности создания электронных документов на основе шаблонов в организации Результаты исследований методом контент-анализа (постановка задачи)
Результаты исследований методом контент-анализа (постановка задачи) Uso práctico de la aplicación La Rueda De La Vida
Uso práctico de la aplicación La Rueda De La Vida Основы теории проектирования
Основы теории проектирования Призначення, завдання, функції, класифікація ІОС
Призначення, завдання, функції, класифікація ІОС