Содержание
- 2. Жоспар:
- 3. Plan:
- 4. “Paskal Machine” (1642) The first inventor of mechanical counting machines was the brilliant Frenchman Blaise Pascal.
- 5. Механикалық есептеу машиналарының алғашқы өнертапқышы француздық Блэс Паскаль болды. Паскаль салық төлеушінің ұлы компьютердің құрылысын ойластырып,
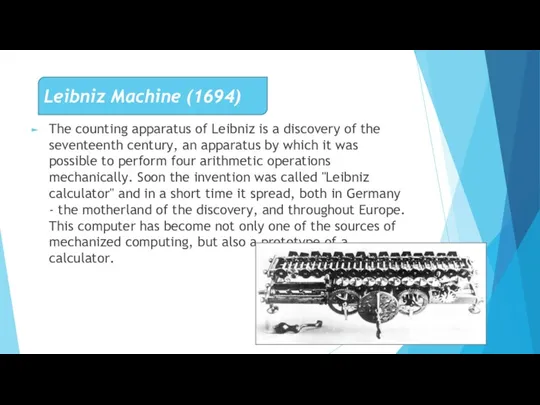
- 6. Лейбництің есептеуіш аппараты XVII ғасырдың ашылуы болып табылады, оның көмегімен төрт арифметикалық амалдарды механикалық түрде орындау
- 7. The counting apparatus of Leibniz is a discovery of the seventeenth century, an apparatus by which
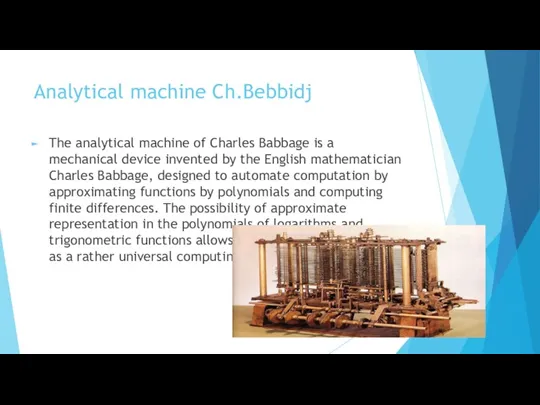
- 8. Analytical machine Ch.Bebbidj The analytical machine of Charles Babbage is a mechanical device invented by the
- 9. Ч.Баббэдждің аналитикалық машинасы Чарльз Баббэдждің аналитикалық машинасы - полиномдық функцияларды жақындату және соңғы айырмашылықтарды есептеу арқылы
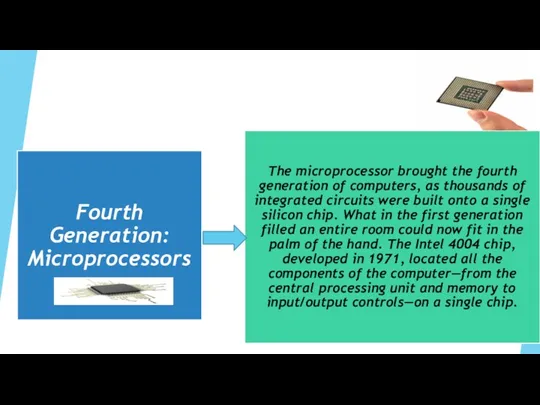
- 10. «Марк-I» (1944) Құрастырушы – Говард Айкен (1900-1973) АҚШ-тағы алғашқы автоматты компьютер: ұзындығы 17 м, салмағы 5
- 11. «Mark-1» (1944) Mark-I (1944) Designer Howard Aiken (1900-1973) The first automatic computer in the USA: length
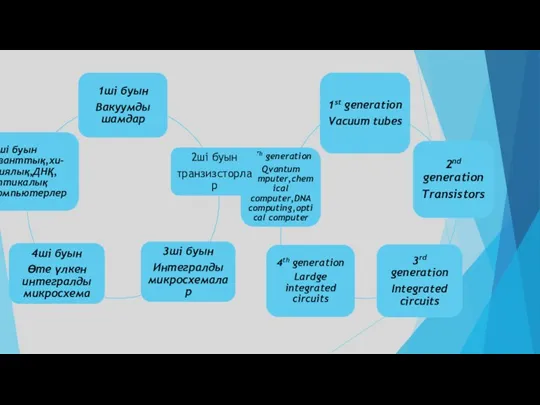
- 13. The first generation systems The first computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for
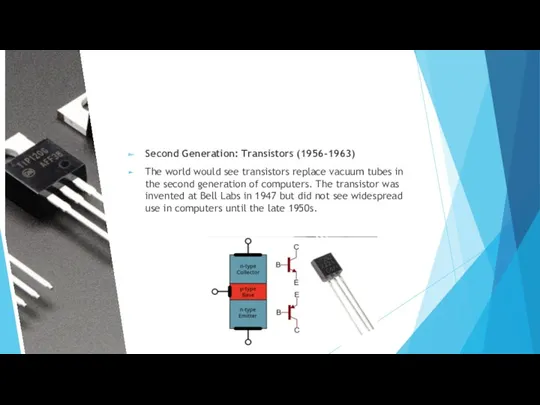
- 14. Second Generation: Transistors (1956-1963) The world would see transistors replace vacuum tubes in the second generation
- 15. Third Generation: Integrated Circuits (1964-1971) The development of the integrated circuit was the hallmark of the
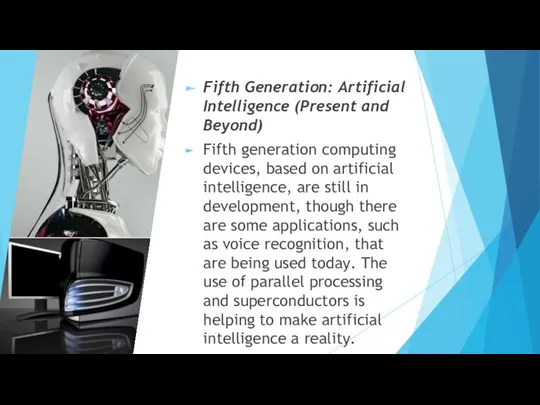
- 17. Fifth Generation: Artificial Intelligence (Present and Beyond) Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence, are
- 18. Importance of computer in our life
- 20. Скачать презентацию











 Система информации и информационное обеспечение управления в органах внутренних дел. Тема №5
Система информации и информационное обеспечение управления в органах внутренних дел. Тема №5 Мониторингтік бағдарламалар реализациясы
Мониторингтік бағдарламалар реализациясы Какая бывает информация 2 класс
Какая бывает информация 2 класс Поняття про мову розмітки, гіпертекстовий документ та його елементи
Поняття про мову розмітки, гіпертекстовий документ та його елементи Презентация к уроку по теме Алгоритмы. Способы описания алгоритмов 4 класс УМК Плаксин М.А.
Презентация к уроку по теме Алгоритмы. Способы описания алгоритмов 4 класс УМК Плаксин М.А. Табличные процессоры как средство обработки деловой информации
Табличные процессоры как средство обработки деловой информации Основные проблемы построения сетей
Основные проблемы построения сетей Непозиционные системы счисления
Непозиционные системы счисления Электронные таблицы
Электронные таблицы Оператор перехода Goto. Цикл метки. Язык программирования Pascal
Оператор перехода Goto. Цикл метки. Язык программирования Pascal ЕЦУР: основные проблемы у ОМСУ и их решение
ЕЦУР: основные проблемы у ОМСУ и их решение Інформаційна система оцінювання знань студентів
Інформаційна система оцінювання знань студентів Методики збору даних. (Лекція 6)
Методики збору даних. (Лекція 6)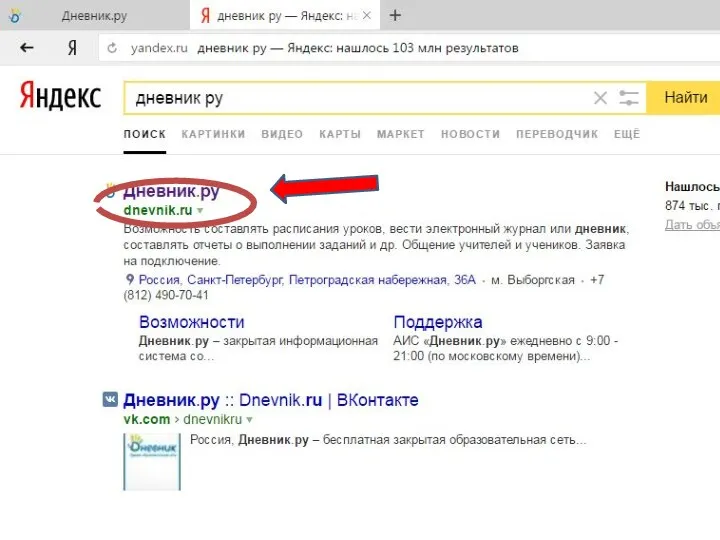 Электронный дневник
Электронный дневник Моделирование в Excel. Старинная задача о лошади
Моделирование в Excel. Старинная задача о лошади Средства массовой информации и их роль в культурной сфере
Средства массовой информации и их роль в культурной сфере Сервисы для интерактивного взаимодействия
Сервисы для интерактивного взаимодействия Діаграма Ганта – що це, як побудувати в Excel
Діаграма Ганта – що це, як побудувати в Excel Сервис контроля за детьми и их ценными вещами Не теряйся
Сервис контроля за детьми и их ценными вещами Не теряйся Тема 4. Занятие 3. Функции
Тема 4. Занятие 3. Функции Программирование на языках высокого уровня
Программирование на языках высокого уровня Типовая схема организации связи цифровой сети МО РФ
Типовая схема организации связи цифровой сети МО РФ Тестирование программного обеспечения
Тестирование программного обеспечения Организация защиты персональных данных в корпорации RHANA
Организация защиты персональных данных в корпорации RHANA Радио, телевидение и Web-камеры в Интернете
Радио, телевидение и Web-камеры в Интернете Анимация и анимационные средства. 2D и 3D анимация. (Лекция 7)
Анимация и анимационные средства. 2D и 3D анимация. (Лекция 7) Операционные системы. Файловые системы. Загрузчики. Виртуальные среды
Операционные системы. Файловые системы. Загрузчики. Виртуальные среды Разработка презентационных материалов предприятия, организации. Заготовки публикаций в Publisher
Разработка презентационных материалов предприятия, организации. Заготовки публикаций в Publisher