Содержание
- 2. AGENDA Java OOPs Concepts Encapsulation Inheritance Abstract classes Composition Reference types
- 3. Java OOPs Concepts Object Any entity that has state and behavior is known as an object.
- 4. Java OOPs Concepts Inheritance When one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of parent object
- 5. Encapsulation Encapsulation in Java is a mechanism of wrapping the data (variables) and code acting on
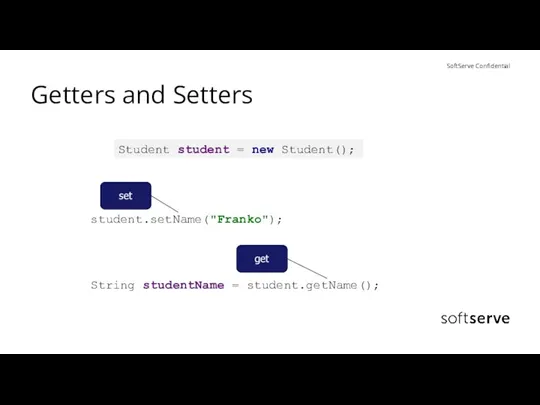
- 6. Getters and Setters get Student student = new Student(); student.setName("Franko"); String studentName = student.getName(); set
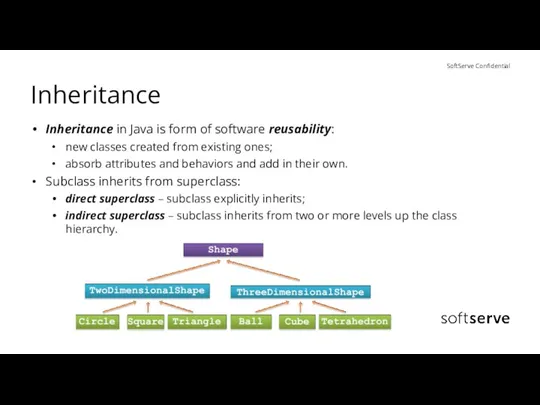
- 7. Inheritance Inheritance in Java is form of software reusability: new classes created from existing ones; absorb
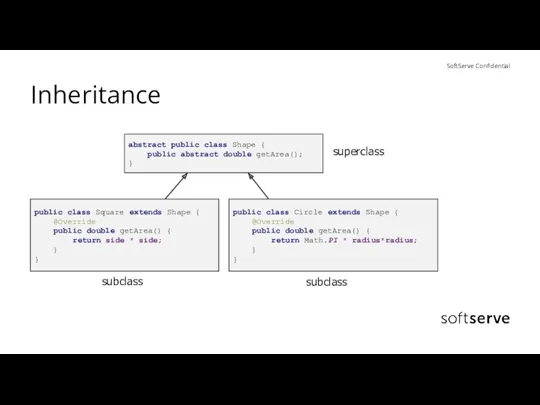
- 8. Inheritance
- 9. Inheritance Example To inherit the properties and methods of a class you use the extends keyword.
- 10. Inheritance Example public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Rectangle rectangle = new
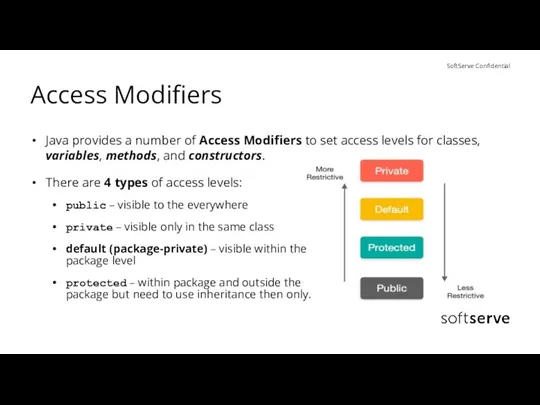
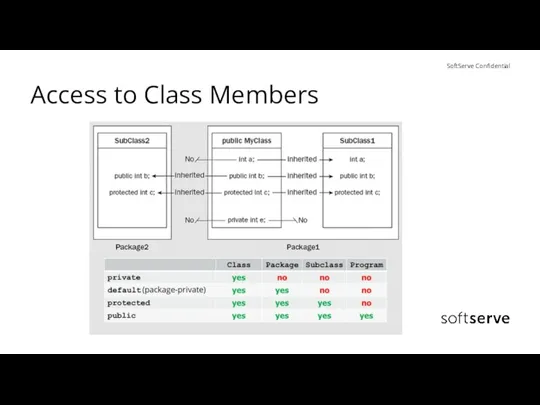
- 11. Access Modifiers Java provides a number of Access Modifiers to set access levels for classes, variables,
- 12. The protected Access Modifier Variables, methods, and constructors, which are declared protected in a superclass can
- 13. Access to Class Members
- 14. Inheritance and Methods Overriding A subclass can modify behavior inherited from a parent class. A subclass
- 15. Abstract Classes A class must be declared abstract when we need to forbid creating instances of
- 16. Abstract Classes public abstract class Figure { /* because this is an abstract method the body
- 17. Abstract Classes public class Rectangle extends Figure { private double length, width; public Rectangle(double length, double
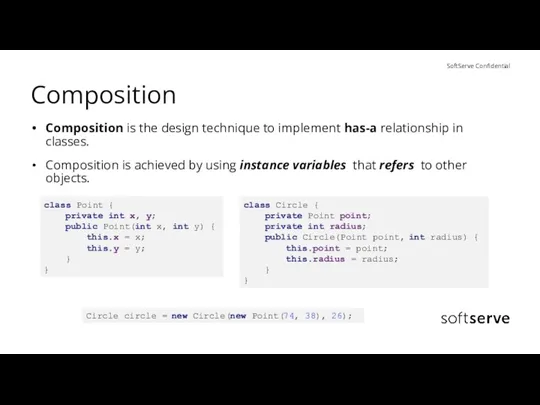
- 18. Composition Composition is the design technique to implement has-a relationship in classes. Composition is achieved by
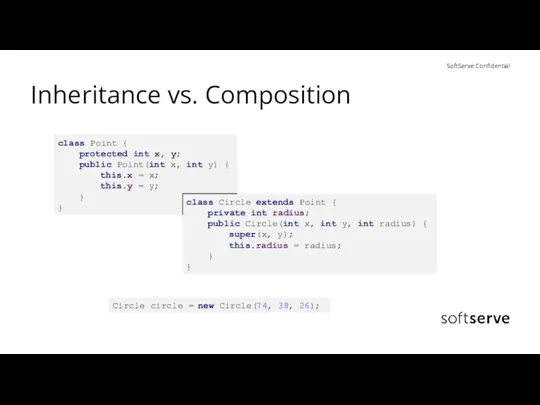
- 19. Inheritance vs. Composition class Point { protected int x, y; public Point(int x, int y) {
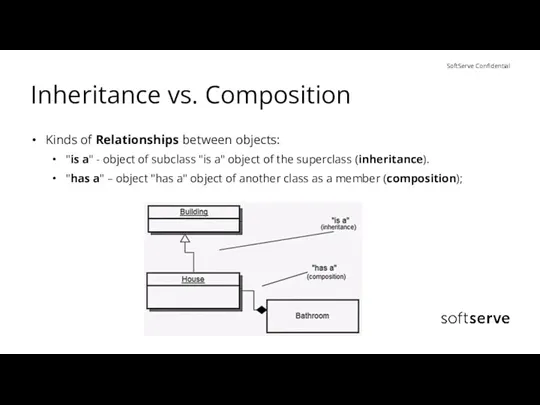
- 20. Inheritance vs. Composition Kinds of Relationships between objects: "is a" - object of subclass "is a"
- 21. Casting Objects Assignment operator. What will be done ? int num = 1; double data =
- 22. Casting Objects Assignment operator. What will be done ? class Aclass { int field1 = 10;
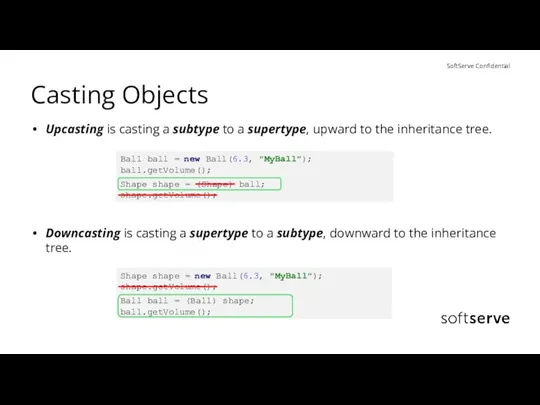
- 23. Casting Objects Upcasting is casting a subtype to a supertype, upward to the inheritance tree. Downcasting
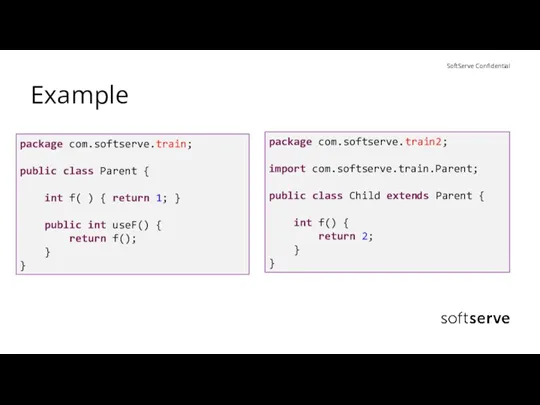
- 24. Example package com.softserve.train; public class Parent { int f( ) { return 1; } public int
- 25. Let's check it package com.samples; import com.softserve.train2.*; public class OOPSamples { public static void main(String... args)
- 26. Keyword super A constructor can call another constructor in its superclass using the keyword super and
- 27. Inheritance public class Circle { private double radius; // Constructors public Circle() { this.radius = 1.0;
- 28. Inheritance public class Cylinder extends Circle { private double height; // Constructors public Cylinder() { super();
- 29. Inheritance public Cylinder(double height) { super(); // invoke superclass' constructor Circle() this.height = height; } public
- 30. Inheritance // Getter and Setter // Return the volume of this Cylinder public double getVolume() {
- 31. Inheritance public class ClassA { public int i = 1; public void m1() { System.out.println("ClassA, metod
- 32. Inheritance public class ClassB extends ClassA { public double i = 1.1; public void m1() {
- 33. Inheritance public class ApplAB { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("The Start."); ClassA a =
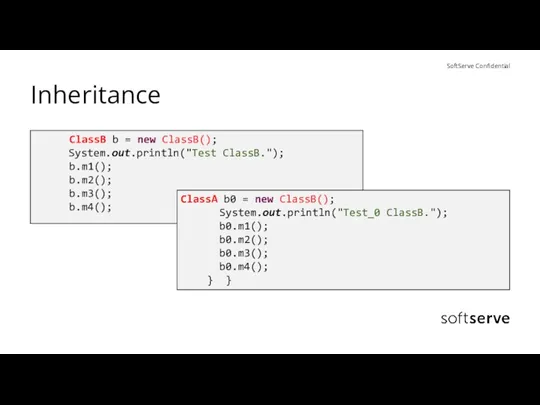
- 34. Inheritance ClassB b = new ClassB(); System.out.println("Test ClassB."); b.m1(); b.m2(); b.m3(); b.m4(); ClassA b0 = new
- 35. Practical tasks 1. Create abstract class Car with model, maxSpeed and yearOfManufacture properties and run() and
- 36. Practical tasks 2. Create three classes: Point with attributes x and y Line which contains two
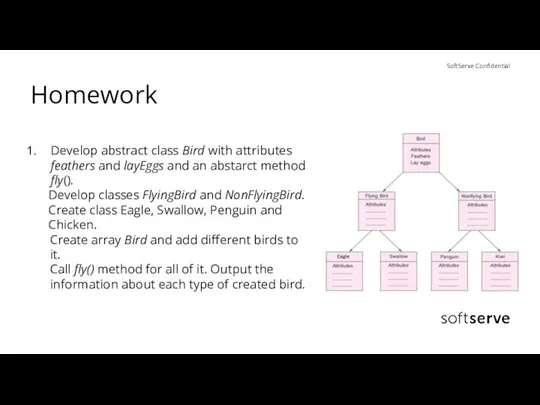
- 37. Homework Develop abstract class Bird with attributes feathers and layEggs and an abstarct method fly(). Develop
- 38. Homework 2. Support we have a class Employee Create a Developer class that extends the Employee
- 40. Скачать презентацию





![Inheritance Example public class Main { public static void main(String[]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/371998/slide-9.jpg)















![Inheritance public class ApplAB { public static void main(String[] args)](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/371998/slide-32.jpg)



 Кодирование текстовой информации. Представление информации в компьютере
Кодирование текстовой информации. Представление информации в компьютере HTML Forms
HTML Forms Технология ATM, Fire Wire. Беспроводные технологии. Лекция №6
Технология ATM, Fire Wire. Беспроводные технологии. Лекция №6 Продвижение ВФСК ГТО в социальных сетях
Продвижение ВФСК ГТО в социальных сетях Информация
Информация Архітектура, розроблення та експлуатація інформаційних систем корпоративного і національного рівнів
Архітектура, розроблення та експлуатація інформаційних систем корпоративного і національного рівнів Глобальное информационное общество
Глобальное информационное общество Персональный компьютер
Персональный компьютер Презентация. Оперативная память
Презентация. Оперативная память Construct 2. Знакомство c программой Part 2 event sheet & текстовая строка
Construct 2. Знакомство c программой Part 2 event sheet & текстовая строка Запуск и Интерфейс программы AutoCAD-2014
Запуск и Интерфейс программы AutoCAD-2014 Основы логики
Основы логики Инструкция участия в вебинаре в системе веб-коммуникаций на базе IVA R
Инструкция участия в вебинаре в системе веб-коммуникаций на базе IVA R Антивирустық бағдарламалар. Кірме сөздер
Антивирустық бағдарламалар. Кірме сөздер Основы программирования (ОП)
Основы программирования (ОП) Презентации
Презентации Протокол NAT. Характеристики NAT
Протокол NAT. Характеристики NAT Оборудование биометрической системы контроля и управления доступом БиоСКУД Сонда Эксперт
Оборудование биометрической системы контроля и управления доступом БиоСКУД Сонда Эксперт Cyber-Safety
Cyber-Safety Ввод-вывод. (Тема 16)
Ввод-вывод. (Тема 16) ВКР: Разработка прототипа автоматизированного рабочего места диспетчера учебного учреждения
ВКР: Разработка прототипа автоматизированного рабочего места диспетчера учебного учреждения Анимации в презентации
Анимации в презентации Использование современных технологий в обучении музыке
Использование современных технологий в обучении музыке 1_1 Энтропия как мера степени неопределенности
1_1 Энтропия как мера степени неопределенности Информационные модели на графах
Информационные модели на графах Внеклассное мероприятие. Путешествие с Инфознайкой
Внеклассное мероприятие. Путешествие с Инфознайкой Комп’ютерне моделювання процесу дорожнього руху
Комп’ютерне моделювання процесу дорожнього руху Работа с аудиоредактором звуковых файлов Audacity
Работа с аудиоредактором звуковых файлов Audacity