Содержание
- 2. Lecture Schedule Week 1: Introduction to Operating Systems, Computer System Structures, Operating System Structures Week 2
- 3. Course Schedule Week 6 - Storage Management Midterm exam, Memory Management Week 7 - Storage Management
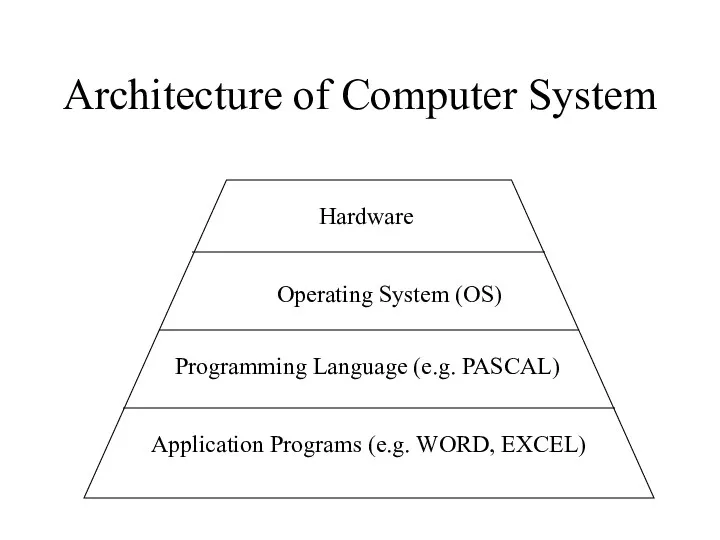
- 4. Architecture of Computer System
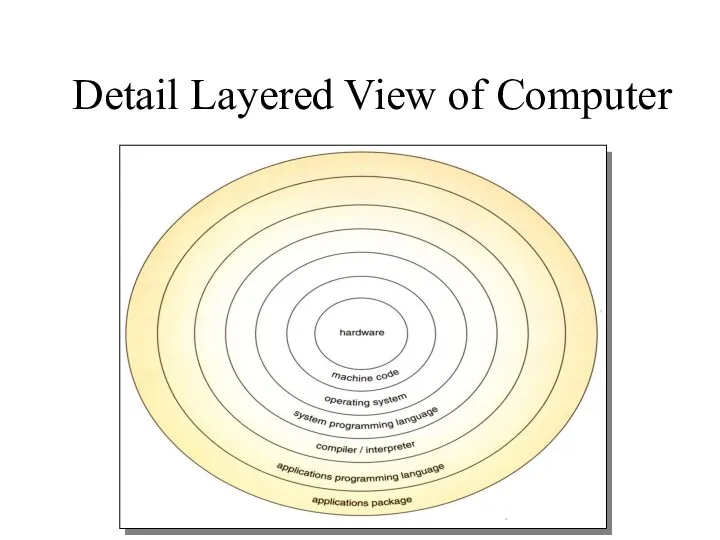
- 5. Detail Layered View of Computer
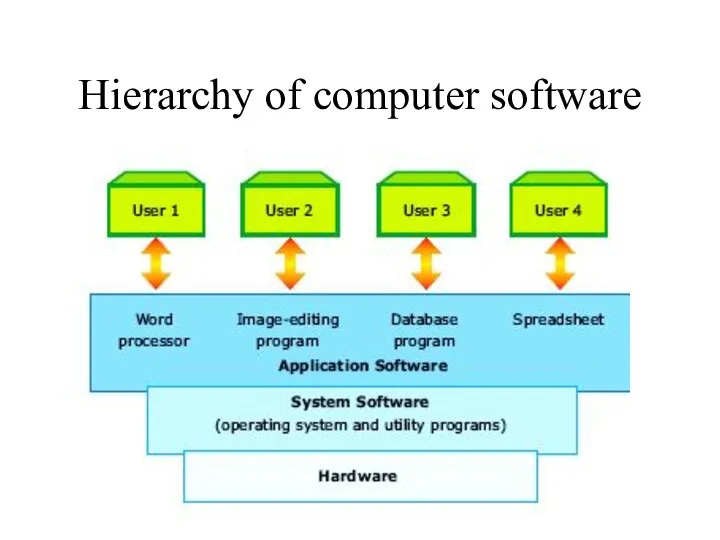
- 6. System Software- Performs essential operation tasks Operating system Utility programs Application Software - Performs specific tasks
- 7. 3 type of programs user / application programs programs used by the users to perform a
- 8. Hierarchy of computer software
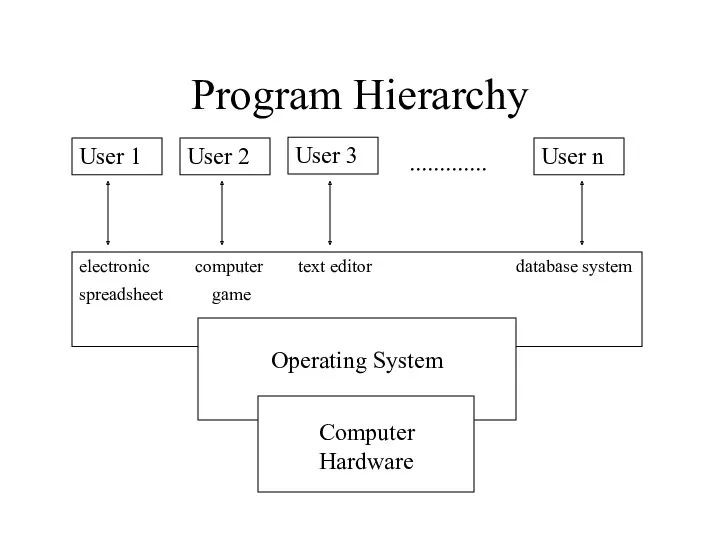
- 9. Program Hierarchy User 1 User 2 User 3 User n ............. electronic computer text editor database
- 10. Operating System a collection of programs which control the resources of a computer system written in
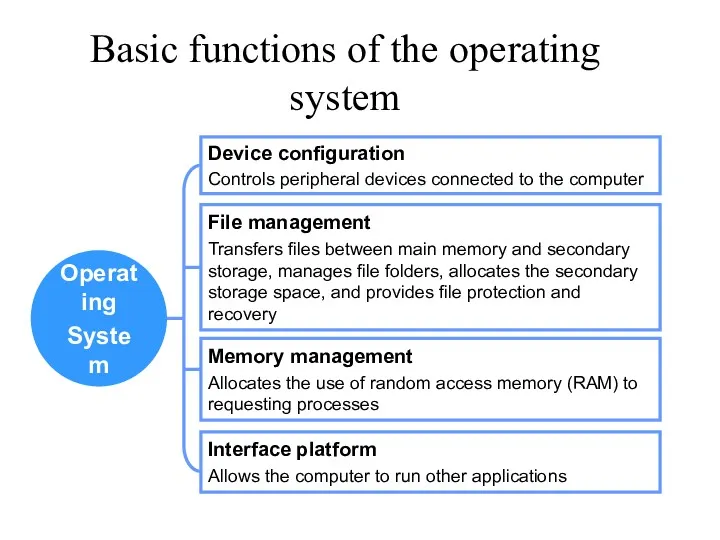
- 11. Operating System Device configuration Controls peripheral devices connected to the computer File management Transfers files between
- 12. Other function of Operating System best use of the computer resources provide a background for user’s
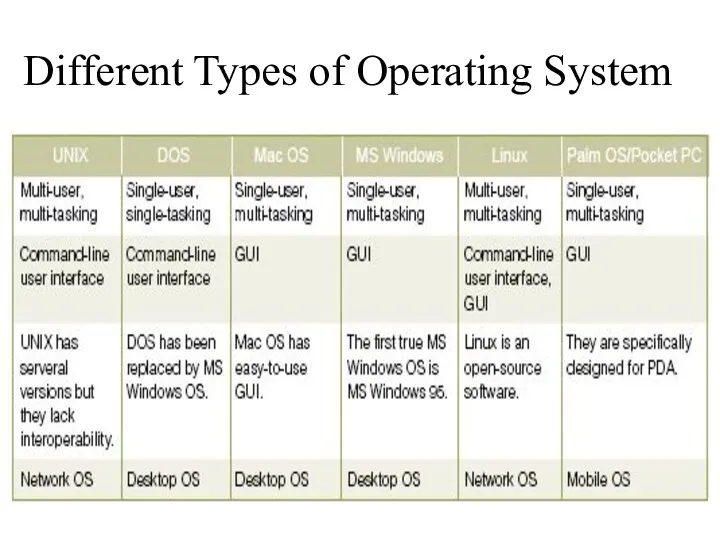
- 13. Common Operating Systems and Their Differences Network Operating System UNIX / Linux / MS Windows2000 Server
- 14. Examples Common operating systems WINDOW used in IBM compatible microcomputers UNIX multi-user, multi-tasking OS used in
- 15. DOS interface
- 16. GUI
- 17. Different Types of Operating System
- 18. Disk Operating System (DOS) a part of operating system to control disk operation 2 parts small
- 19. SMALL SYSTEM AREA in DOS 3 parts boot/boot record i.e. a short program for loading DOS
- 20. Good Operating System efficient time spent to execute its programs should be short small in size
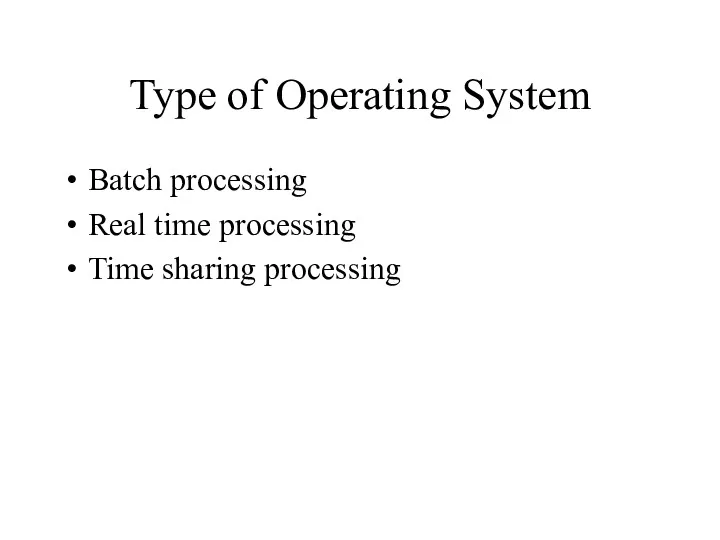
- 21. Type of Operating System Batch processing Real time processing Time sharing processing
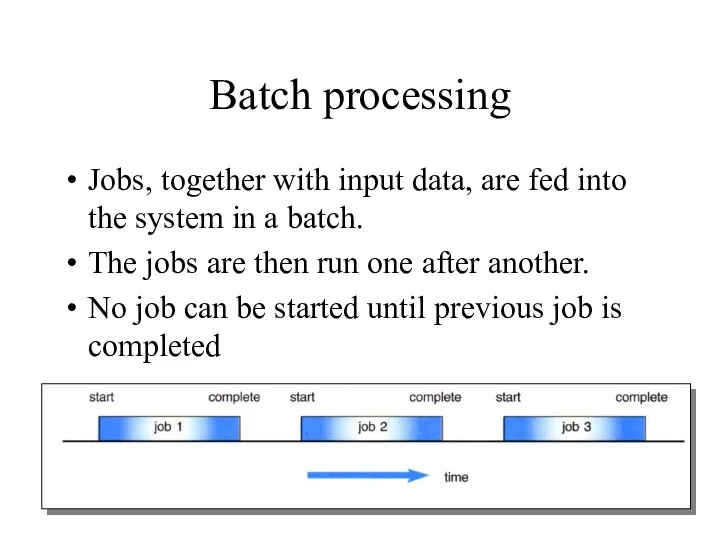
- 22. Batch processing Jobs, together with input data, are fed into the system in a batch. The
- 23. Real time processing immediate response is needed. For example anti-missile defense system airplane landing control system
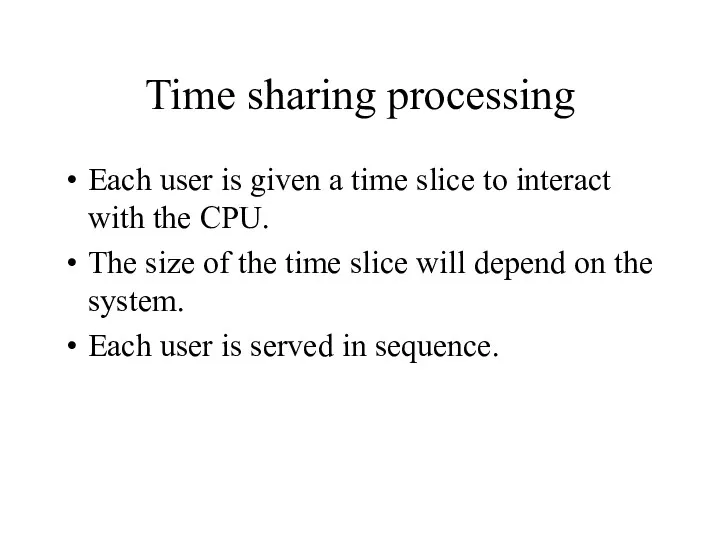
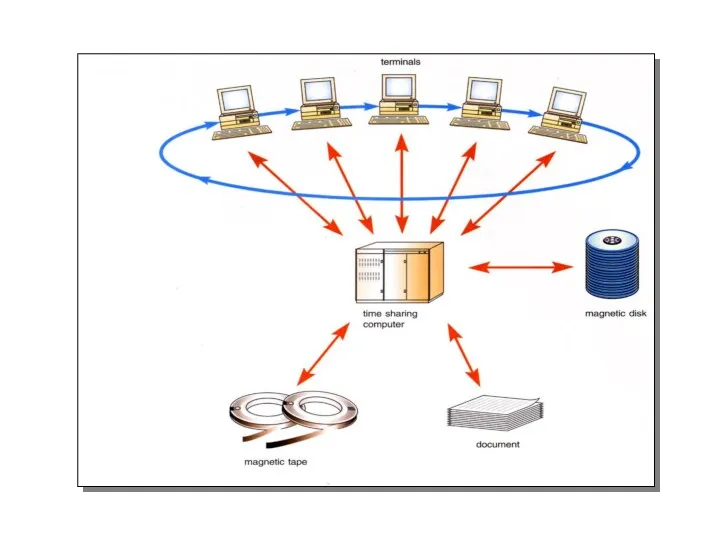
- 24. Time sharing processing Each user is given a time slice to interact with the CPU. The
- 26. Special Features of OS multi-tasking multi-programming parallel processing buffering spooling
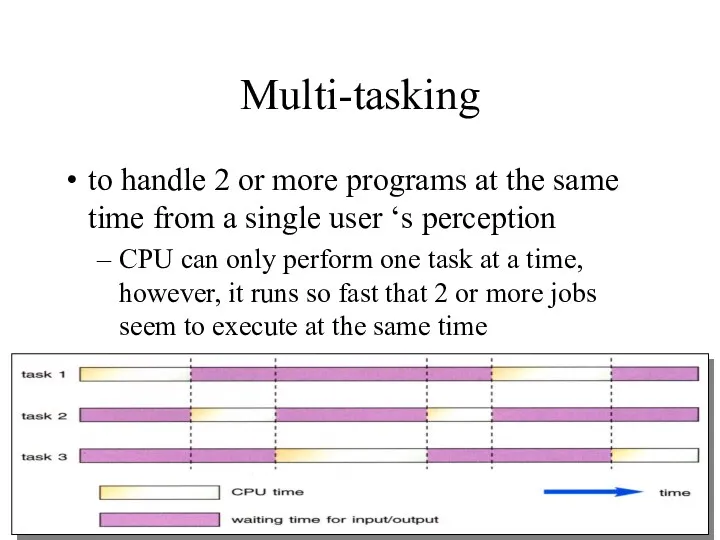
- 27. Multi-tasking to handle 2 or more programs at the same time from a single user ‘s
- 28. Multi-programming 2 or more programs store in the main memory at the same time when one
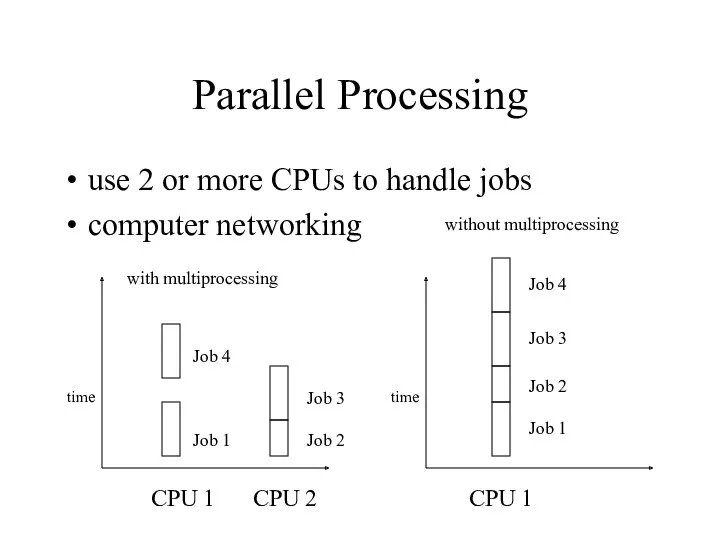
- 29. Parallel Processing use 2 or more CPUs to handle jobs computer networking Job 1 Job 2
- 30. Buffering a temporary storage area (buffers) to read data from input device or send data to
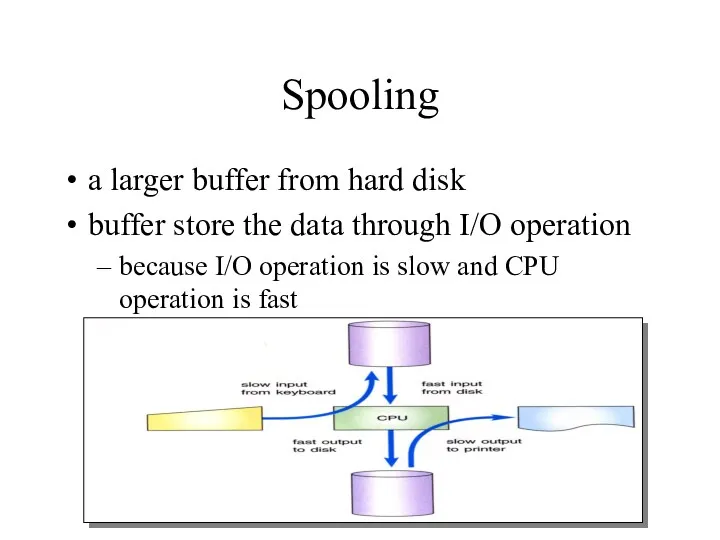
- 31. Spooling a larger buffer from hard disk buffer store the data through I/O operation because I/O
- 33. Скачать презентацию
















 Компьютерная графика. Векторная и растровая графика
Компьютерная графика. Векторная и растровая графика Аудит сайта
Аудит сайта Сутність технології COM
Сутність технології COM Как создать свой сайт
Как создать свой сайт Условный оператор в Паскале. 9 класс
Условный оператор в Паскале. 9 класс Как образуются понятия
Как образуются понятия Файлы и файловые структуры. Компьютер как унивесальное устройство для работы с информацией
Файлы и файловые структуры. Компьютер как унивесальное устройство для работы с информацией Статистические методы обработки информации
Статистические методы обработки информации Методическая разработка урока информатики по теме Законы алгебры логики в 9 классе
Методическая разработка урока информатики по теме Законы алгебры логики в 9 классе Интернет. Основные понятия и возможности
Интернет. Основные понятия и возможности Технічна експлуатація автоматизованих систем поштового зв’язку
Технічна експлуатація автоматизованих систем поштового зв’язку Измерение информации
Измерение информации Разработка мероприятия по информатике Системы управления базами данных
Разработка мероприятия по информатике Системы управления базами данных Принципы и структура системного анализа. Декомпозиция системы
Принципы и структура системного анализа. Декомпозиция системы КВН
КВН Представление чисел в памяти компьютера. 9 класс
Представление чисел в памяти компьютера. 9 класс Zelio Logic - Communication Extension
Zelio Logic - Communication Extension Презентация к урокуАлгоритм.Свойства алгоритмов
Презентация к урокуАлгоритм.Свойства алгоритмов Новые информационные технологии
Новые информационные технологии Алгоритмы, структуры алгоритмов, структурное программирование
Алгоритмы, структуры алгоритмов, структурное программирование Task 3. Internet. Тренажёр ЕГЭ
Task 3. Internet. Тренажёр ЕГЭ Wi-Fi тechnology
Wi-Fi тechnology Кодирование звуковой информации. Представление информации в компьютере
Кодирование звуковой информации. Представление информации в компьютере Технология создания мультимедийной презентации
Технология создания мультимедийной презентации Планування безпроводових мереж на базі технології Wi-Fi на прикладі Web-відділу компанії Вияр
Планування безпроводових мереж на базі технології Wi-Fi на прикладі Web-відділу компанії Вияр Контекстная реклама в Яндекс-Директ (ЯД*)
Контекстная реклама в Яндекс-Директ (ЯД*) Выполнение работ по одной или нескольким профессиям рабочих, должностям служащих
Выполнение работ по одной или нескольким профессиям рабочих, должностям служащих Сетевые операционные системы. Операционные среды, системы и оболочки
Сетевые операционные системы. Операционные среды, системы и оболочки