Содержание
- 2. INSITE Data Manager Export and import data Create and store new datasets Copy, move, or rename
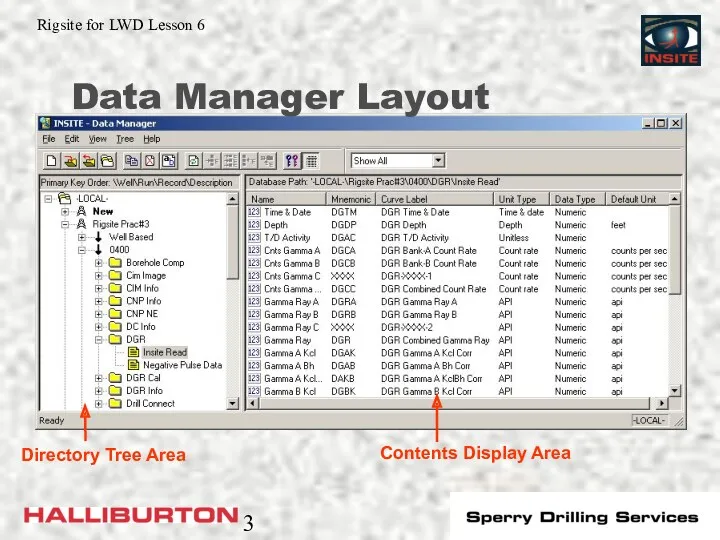
- 3. Data Manager Layout
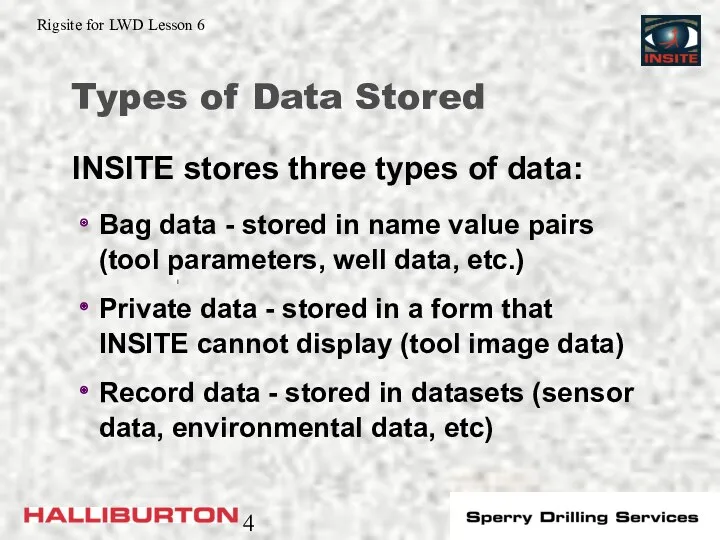
- 4. Types of Data Stored Bag data - stored in name value pairs (tool parameters, well data,
- 5. Record Data Storage A dataset is a collection of associated information stored in the INSITE database
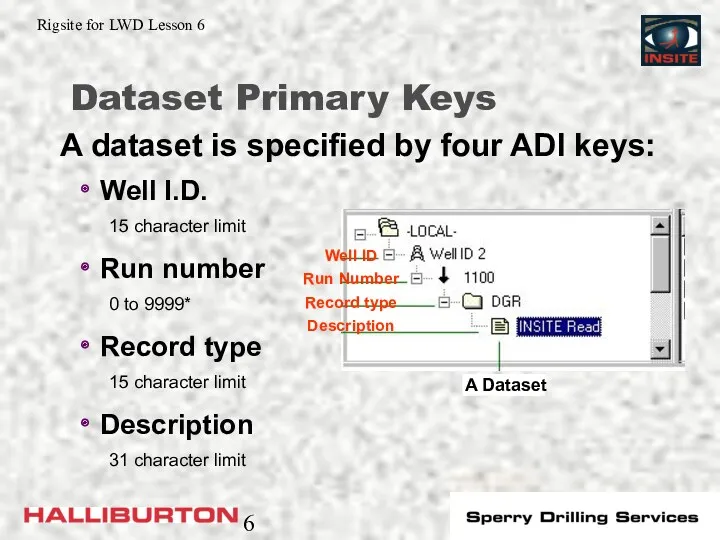
- 6. Well I.D. 15 character limit Run number 0 to 9999* Record type 15 character limit Description
- 7. Primary Key Order Are not a hierarchy; they can be rearranged in any order Are generally
- 8. Run Number Key Number of the MWD run (the run when the data was collected 100,
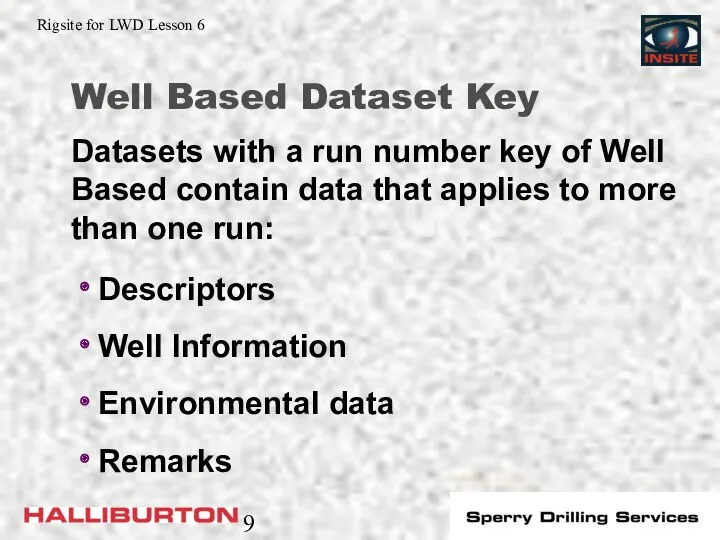
- 9. Well Based Dataset Key Descriptors Well Information Environmental data Remarks Datasets with a run number key
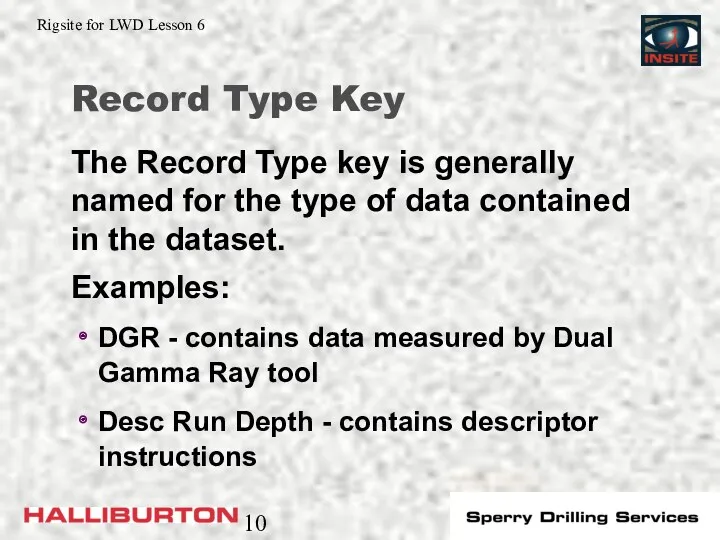
- 10. Record Type Key The Record Type key is generally named for the type of data contained
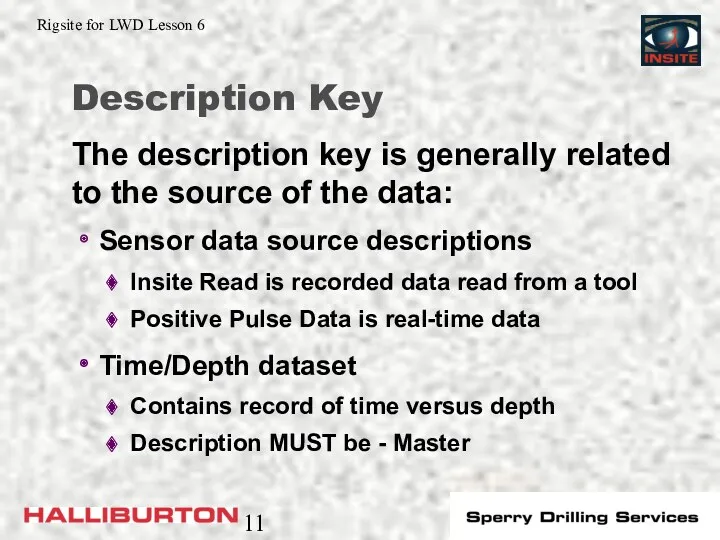
- 11. Description Key Sensor data source descriptions Insite Read is recorded data read from a tool Positive
- 12. Dataset Review Data Manager Dataset 4 Keys
- 13. Dataset Contents Record data Alphanumeric data presented as a table Rows in the table are called
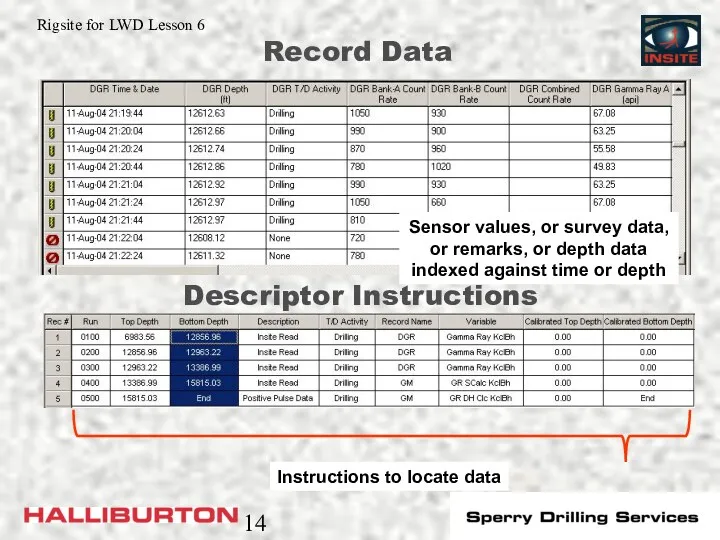
- 14. Record Data Sensor values, or survey data, or remarks, or depth data indexed against time or
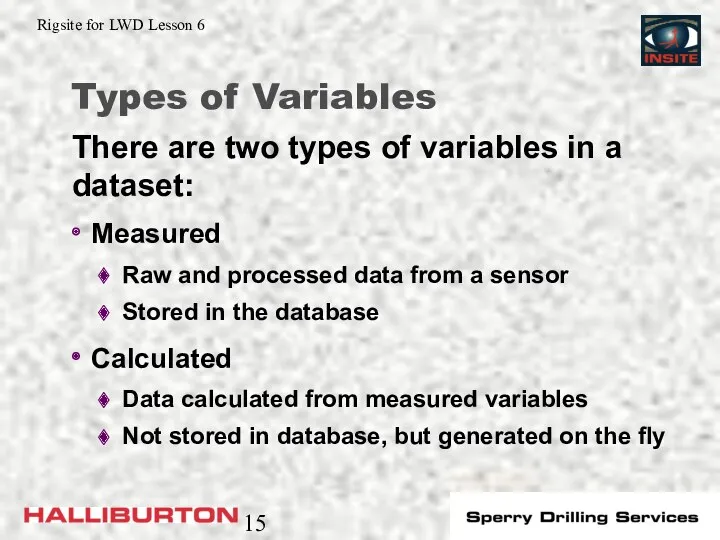
- 15. Types of Variables Measured Raw and processed data from a sensor Stored in the database Calculated
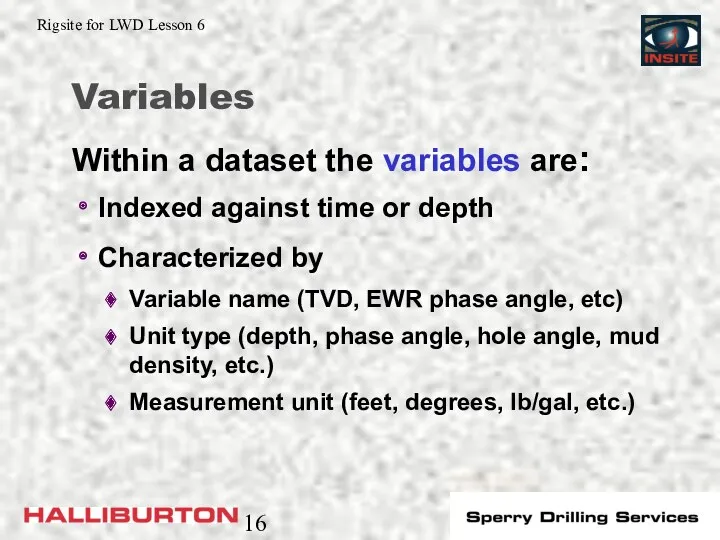
- 16. Variables Indexed against time or depth Characterized by Variable name (TVD, EWR phase angle, etc) Unit
- 17. Unit Set All data stored in English units Converts to other units on-the-fly for display Active
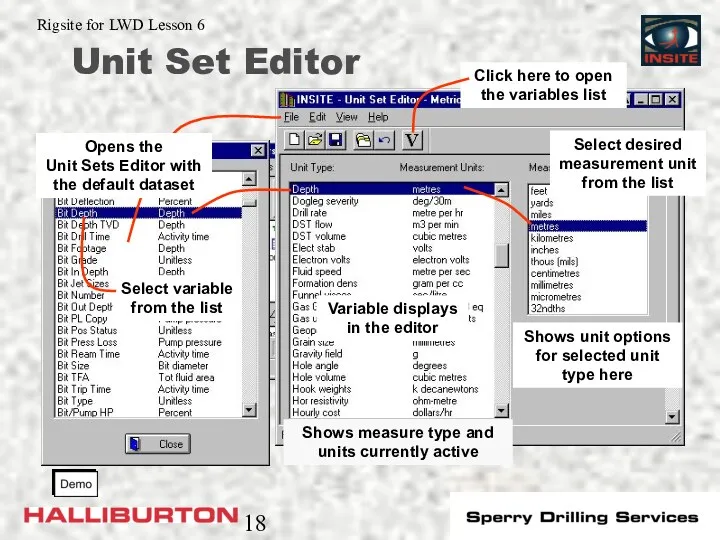
- 18. Unit Set Editor Select desired measurement unit from the list
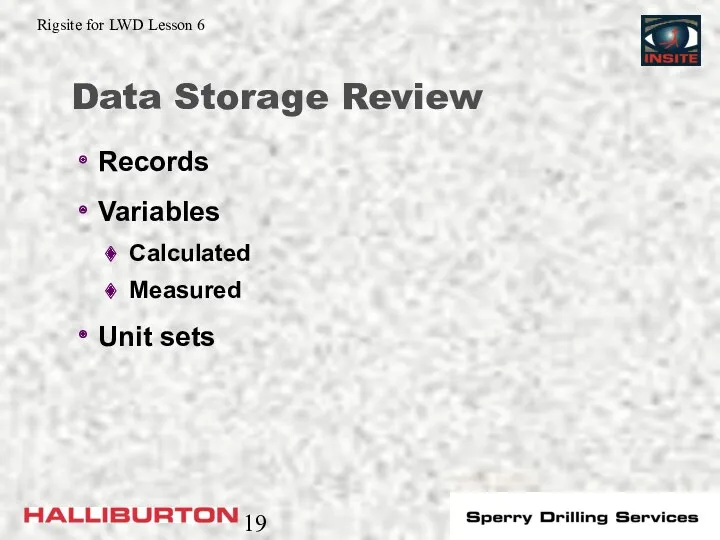
- 19. Data Storage Review Records Variables Calculated Measured Unit sets
- 20. ADI Files An ADI file can only be read by INSITE ADI files can be any
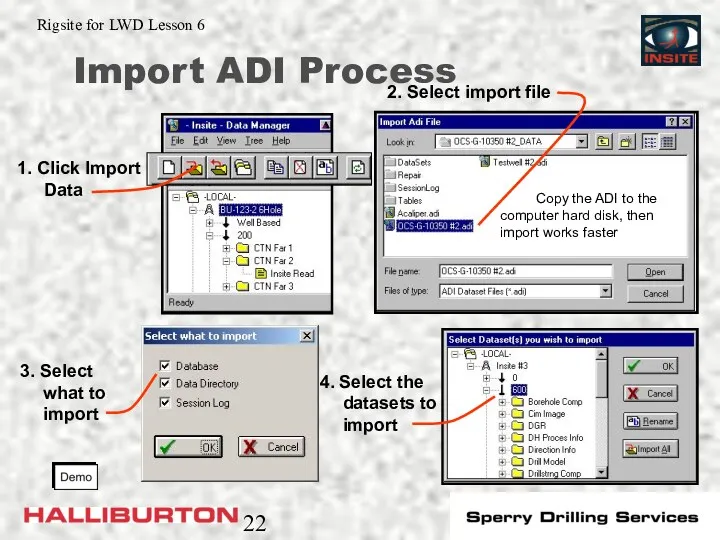
- 21. Importing ADI Files Entire file or selected datasets Datasets with the same 4 keys overwrite Data
- 22. Import ADI Process 3. Select what to import
- 23. Exporting ADI Files Backup INSITE datasets Transfer a dataset to another computer Send a dataset to
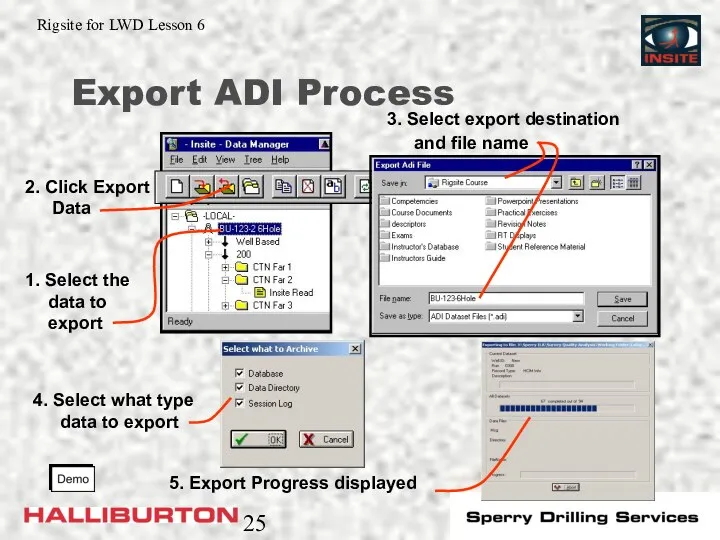
- 24. Export ADI Files Entire well Single run Single record type Single dataset ADI file can include
- 25. Export ADI Process
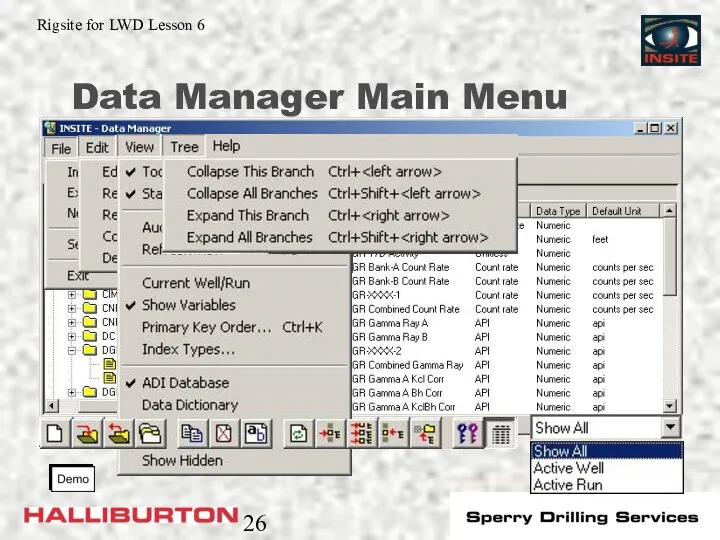
- 26. Data Manager Main Menu
- 27. Dataset Editors Remarks editor General data editor Survey editor Time/Depth editor Descriptor editor Several different dataset
- 28. When to Edit a Dataset Creating a new dataset There are confirmed invalid data Transmission errors
- 29. Before Editing Datasets Correct data is confirmed by other means Do not edit a dataset until:
- 30. Opening Dataset Editors Creating a new dataset automatically opens the editor for that type of dataset
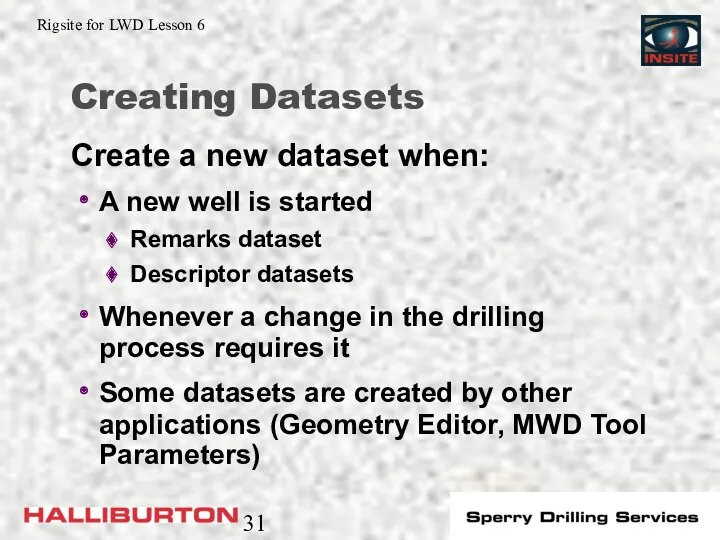
- 31. Creating Datasets A new well is started Remarks dataset Descriptor datasets Whenever a change in the
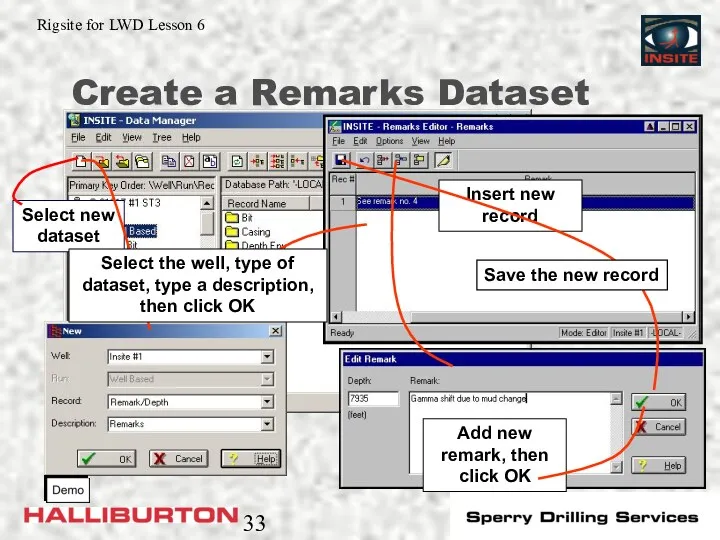
- 32. Remarks Dataset Associates remarks with either time or depth Has a run number of well based
- 33. Create a Remarks Dataset Insert new record Select the well, type of dataset, type a description,
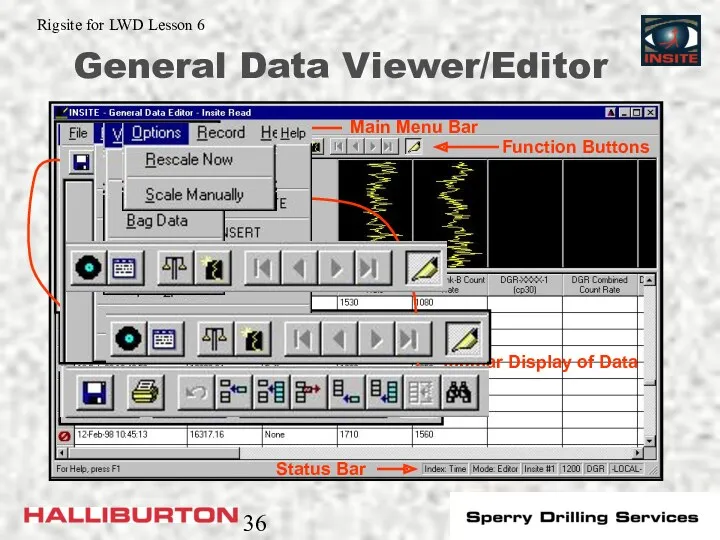
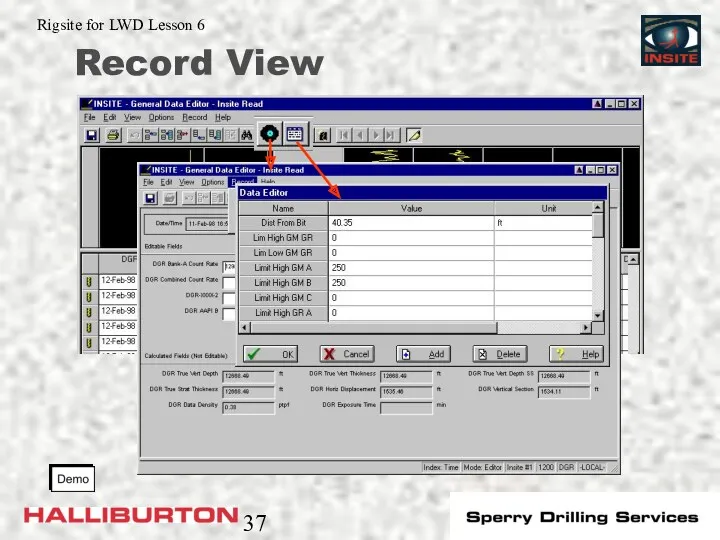
- 34. General Data Viewer/Editor Used for sensor datasets (DGR, EWR, MWD Surf Pres, etc) Three different views
- 35. Caution Do not leave an active data set open in the editor for more than 30
- 36. General Data Viewer/Editor
- 37. Record View
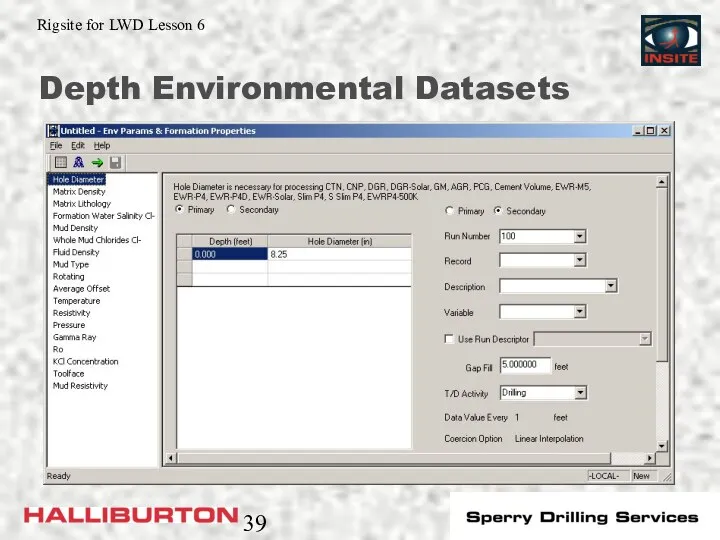
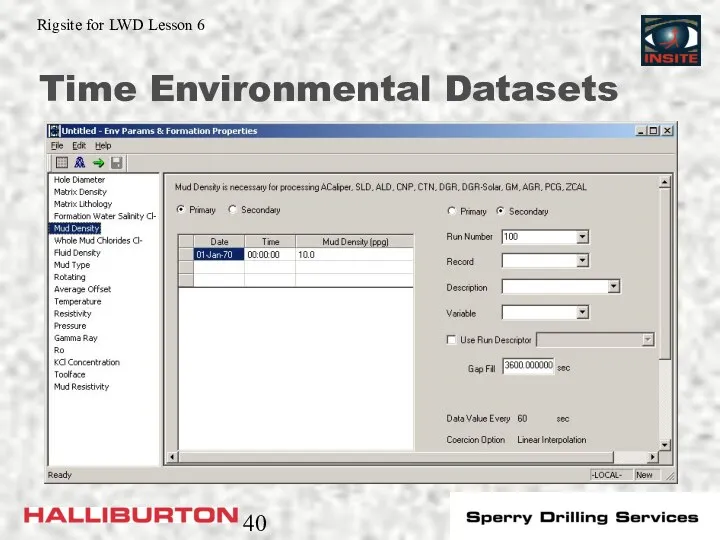
- 38. Environmental Datasets The environmental datasets contain information on the downhole environment: Depth Env Time Env Edited
- 39. Depth Environmental Datasets
- 40. Time Environmental Datasets
- 41. Environmental Datasets Located in the Well Based Run Selecting in Data Manager opens Editor
- 42. Editor and Dataset Review Dataset Editors Creating datasets Remarks editor General data editor Layout Displays Menu
- 43. End of Lesson 6
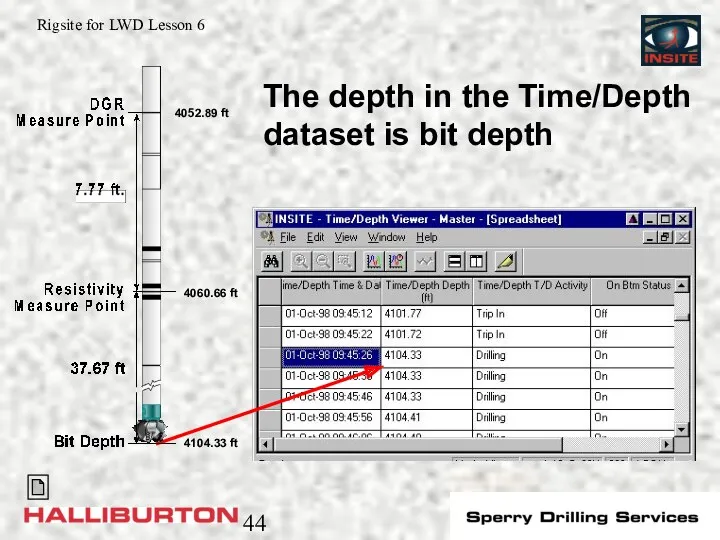
- 44. 4104.33 ft 4060.66 ft 4052.89 ft The depth in the Time/Depth dataset is bit depth
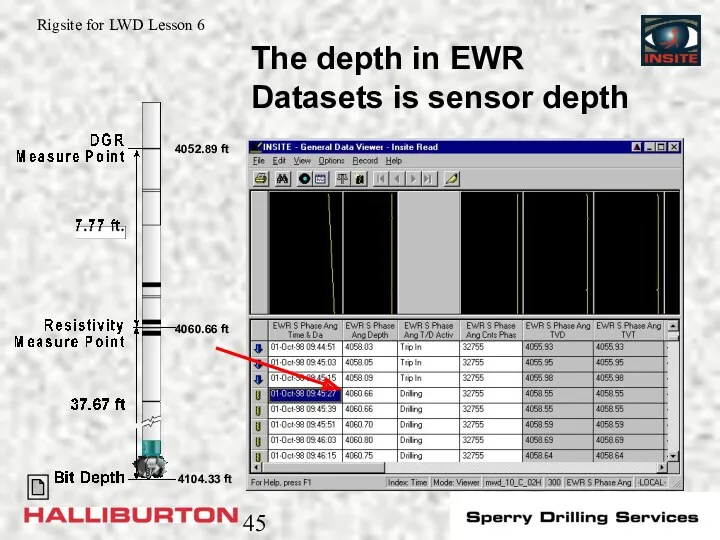
- 45. 4104.33 ft 4060.66 ft 4052.89 ft The depth in EWR Datasets is sensor depth
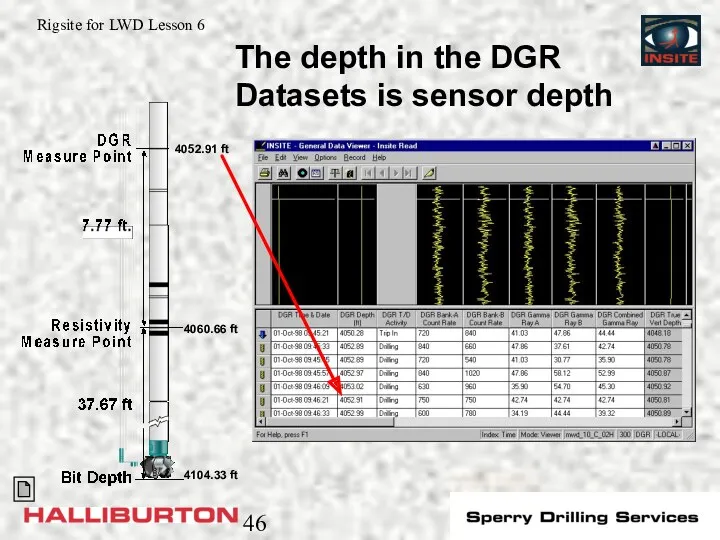
- 46. 4104.33 ft 4060.66 ft 4052.91 ft The depth in the DGR Datasets is sensor depth
- 48. Скачать презентацию






















 Компьютерная графика (Autodesk 3ds max). Создание и работа с примитивами. Управление объектами. (Лекция 2.1)
Компьютерная графика (Autodesk 3ds max). Создание и работа с примитивами. Управление объектами. (Лекция 2.1) СМИ нового формата. Журналисты современной информации
СМИ нового формата. Журналисты современной информации Моделирование и его разновидности
Моделирование и его разновидности Развитие детей с помощью курсов робототехники
Развитие детей с помощью курсов робототехники Пользовательские хуки
Пользовательские хуки Электронный учебник по информатике
Электронный учебник по информатике Операционные системы. Введение, основные понятия и термины. (Лекция 1)
Операционные системы. Введение, основные понятия и термины. (Лекция 1) Логические элементы компьютера
Логические элементы компьютера Robots
Robots Introduction to informational and communication technologies
Introduction to informational and communication technologies Операционные системы
Операционные системы Викторина по информатике Инфознайка. 6 класс
Викторина по информатике Инфознайка. 6 класс Игра Удивительный мир информатики
Игра Удивительный мир информатики Структура Web приложений
Структура Web приложений Стандартные функции языка CLIPS. Стандартные арифметические функции
Стандартные функции языка CLIPS. Стандартные арифметические функции Игра Самый умный. Информатика
Игра Самый умный. Информатика Информационные процессы и системы в правовой сфере
Информационные процессы и системы в правовой сфере Основы 3D-моделирования машиностроительных объектов
Основы 3D-моделирования машиностроительных объектов Обзор программных продуктов дистрибутива Линукс Юниор
Обзор программных продуктов дистрибутива Линукс Юниор Применение ИКТ на уроках естествознания
Применение ИКТ на уроках естествознания Час кода в России
Час кода в России Subversion
Subversion Проектирование ПО ИС. Лекция 7
Проектирование ПО ИС. Лекция 7 Computer graphics
Computer graphics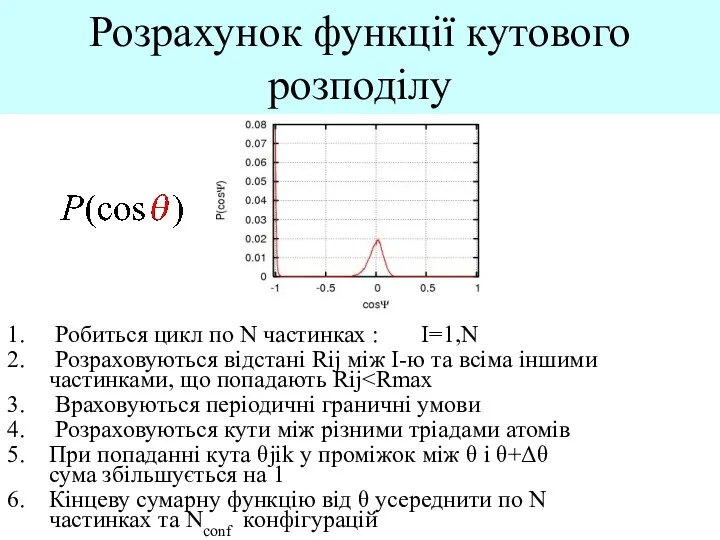 Розрахунок функції кутового розподілу
Розрахунок функції кутового розподілу Изучение графического редактора PAINT
Изучение графического редактора PAINT Презентация Ребусы
Презентация Ребусы Declaring PL/SQL Variables. (Lecture 2)
Declaring PL/SQL Variables. (Lecture 2)