Содержание
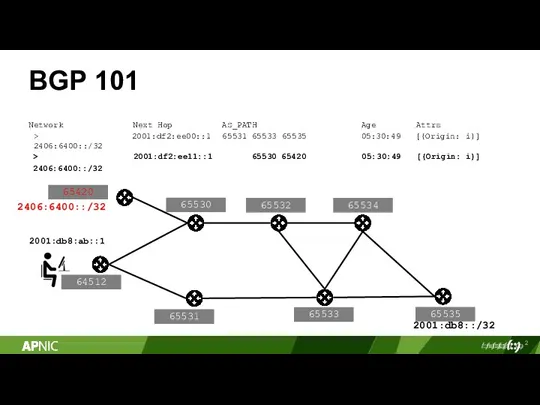
- 2. 2 BGP 101 2001:db8::/32 Network Next Hop AS_PATH Age Attrs 65530 65533 64512 65535 2001:db8:ab::1 65532
- 3. Current Practice Filtering limited to the edges facing the customer Filters on peering and transit sessions
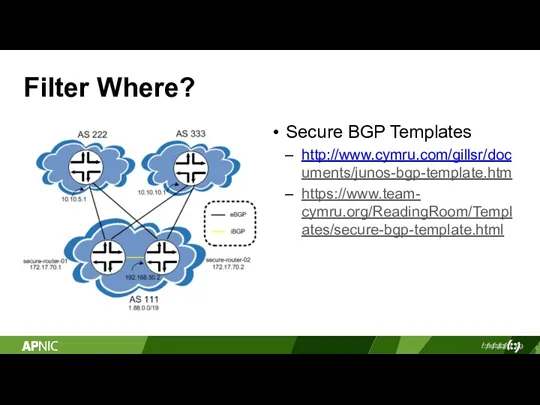
- 4. Filter Where? Secure BGP Templates http://www.cymru.com/gillsr/doc uments/junos-bgp-template.htm https://www.team- cymru.org/ReadingRoom/Templ ates/secure-bgp-template.html
- 5. IP Address & AS Number Digital Certificate RPKI Resource Public Key Infrastructure
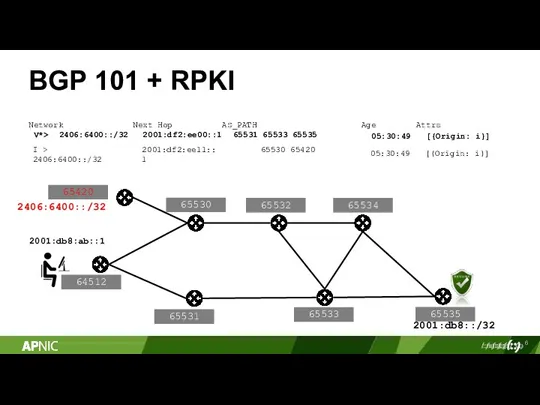
- 6. 6 BGP 101 + RPKI 2001:db8::/32 Network Next Hop AS_PATH Age 05:30:49 05:30:49 Attrs [{Origin: i}]
- 7. PKI In Other Application HTTPS Web Address as RESOURCE Hierarchical Trust Model CA as the root
- 8. What About RPKI?
- 9. The Eco System
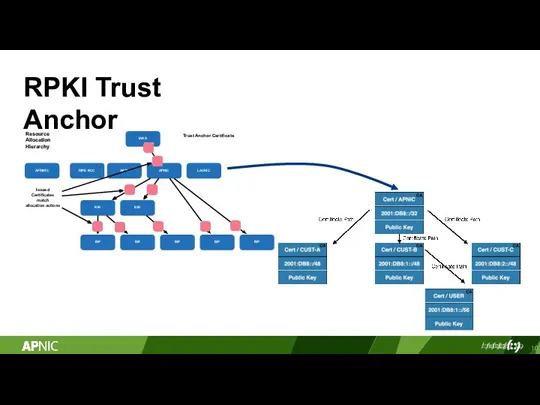
- 10. RPKI Trust Anchor IANA AFRINIC RIPE NCC ARIN APNIC LACNIC NIR NIR ISP ISP ISP ISP
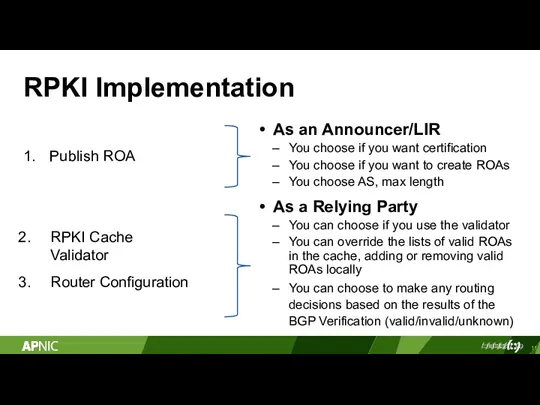
- 11. RPKI Implementation As an Announcer/LIR You choose if you want certification You choose if you want
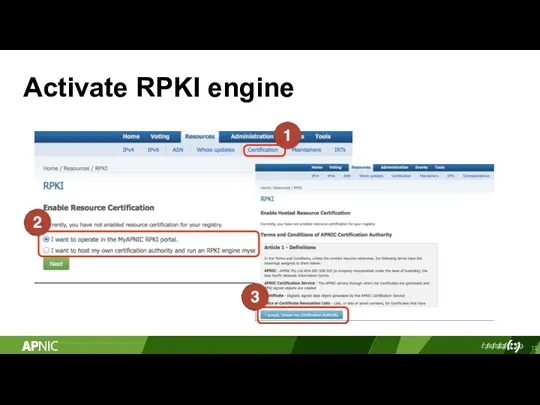
- 12. Activate RPKI engine
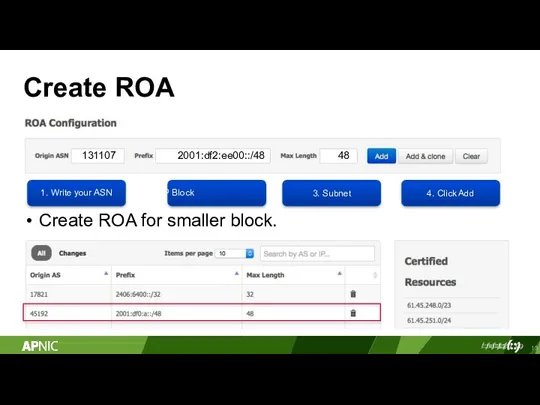
- 13. Create ROA 1. Write your ASN 2. Your IP Block Create ROA for smaller block. 3.
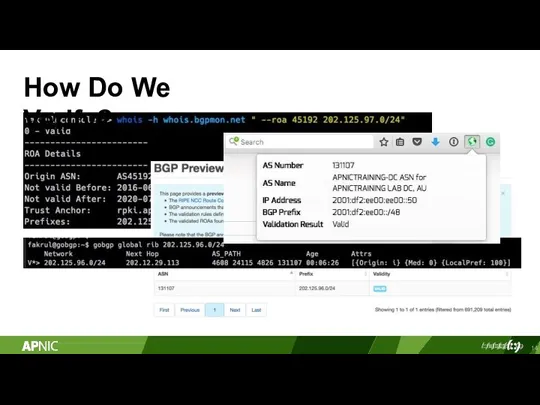
- 14. How Do We Verify?
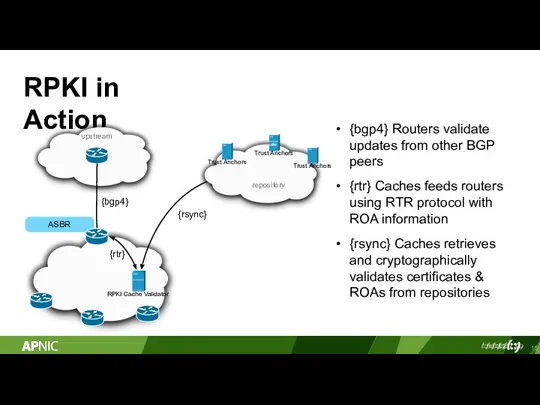
- 15. RPKI in Action {bgp4} Routers validate updates from other BGP peers {rtr} Caches feeds routers using
- 16. RPKI Implementation Issues
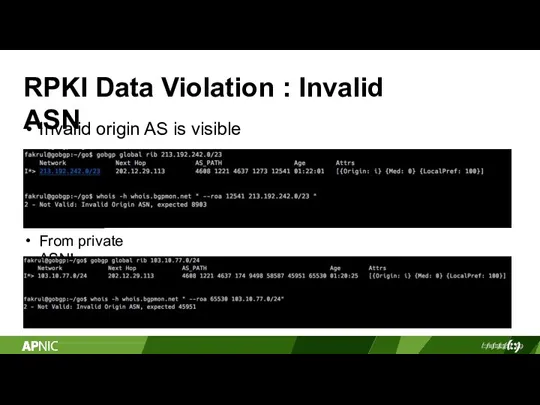
- 17. RPKI Data Violation : Invalid ASN Invalid origin AS is visible From private ASN!
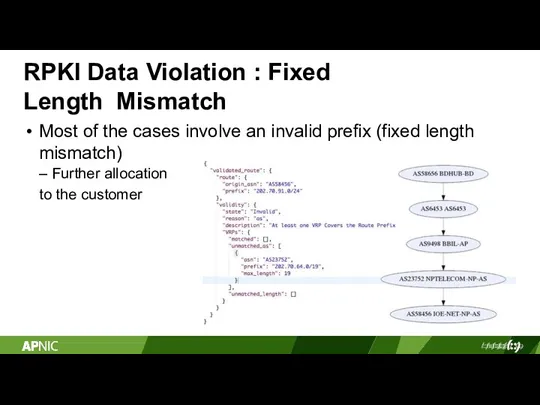
- 18. RPKI Data Violation : Fixed Length Mismatch Most of the cases involve an invalid prefix (fixed
- 19. Fiji Total ASNs delegated by RIR: 8, Visible IPv4 routes: 50, Visible IPv6 routes: 5 http://rpki.apnictraining.net/output/fj.html
- 20. Moving Forward RPKI adoption is growing You are encouraged to create ROA. Experiment, test, play and
- 21. Data Collection GoBGP https://github.com/osrg/gobgp RPKI Dashboard https://github.com/remydb/RPKI-Dashboard RIPE RPKI Statistics https://lirportal.ripe.net/certification/content/static/statistics/world-roas.html RIPE Cache Validator API http://rpki-validator.apnictraining.net:8080/export
- 23. Скачать презентацию









 Управление реляционными базами данных. Языки определения данных и языки манипулирования данными
Управление реляционными базами данных. Языки определения данных и языки манипулирования данными Защита информации
Защита информации Кодирование и обработка звуковой информации. Создание звукового клипа
Кодирование и обработка звуковой информации. Создание звукового клипа Динамические структуры данных. Односвязные и двусвязные списки
Динамические структуры данных. Односвязные и двусвязные списки Опасности в Интернете
Опасности в Интернете Помощники человека при счёте
Помощники человека при счёте Слова с компьютерной начинкой. Блиц-турнир
Слова с компьютерной начинкой. Блиц-турнир Характеристика и типы линий связи
Характеристика и типы линий связи Условный рендеринг
Условный рендеринг Администрирование межсетевых экранов. Лекция 7
Администрирование межсетевых экранов. Лекция 7 Как GC освобождает память
Как GC освобождает память Ресурсы для организации дистанционного обучения (1)
Ресурсы для организации дистанционного обучения (1) Устройство и функционирование информационной системы
Устройство и функционирование информационной системы Технология JSF (Java Server Faces)
Технология JSF (Java Server Faces) Алгоритм работы с фрагментами рисунка: поворот, наклон
Алгоритм работы с фрагментами рисунка: поворот, наклон Административно-правовые формы и методы реализации исполнительной власти
Административно-правовые формы и методы реализации исполнительной власти Основы работы в системе управления базами данных (СУБД) MS Access
Основы работы в системе управления базами данных (СУБД) MS Access Табличный процессор Microsoft Excel 2007
Табличный процессор Microsoft Excel 2007 Технологии программирования
Технологии программирования Язык С. Алгоритмические структуры
Язык С. Алгоритмические структуры SVG: Syntax Sprites Animation
SVG: Syntax Sprites Animation Как продвигать свой бизнес без сложных настроек
Как продвигать свой бизнес без сложных настроек Введение в JavaScript. Лекция 16
Введение в JavaScript. Лекция 16 Язык Python. Виключення
Язык Python. Виключення Мультемедиялық тенологияларды ң оқу үдеріснде пайдалану
Мультемедиялық тенологияларды ң оқу үдеріснде пайдалану Разработка Web-сайтовс использованием языка разметки гипертекста НТМL.
Разработка Web-сайтовс использованием языка разметки гипертекста НТМL. Моделювання технологічних процесів експлуатації засобів електротранспорту
Моделювання технологічних процесів експлуатації засобів електротранспорту Краткая характеристика содержания произведения печати или рукописи - аннотация
Краткая характеристика содержания произведения печати или рукописи - аннотация