Содержание
- 2. Intro 24.07.2015 –Internal – 0 1 2 3 Introduction Questions Terms Simplification
- 3. Agenda 24.07.2015 –Internal – 0 1 2 3 Basic design principles Design example Multilayered architecture Architect
- 4. Why we need Architects? 24.07.2015 –Internal – I know Java and SQL, why I need Architect
- 5. Why we need Architects? Short Answer. 24.07.2015 –Internal – I know Java and SQL, why I
- 6. Different architectures 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 7. Outer Function requirements 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 8. Outer quality attributes 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 9. Our internal functional requirements 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 10. Our internal quality requirements 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 11. Design Guidlines 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 12. Resources 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 13. Personal pain experience 24.07.2015 –Internal –
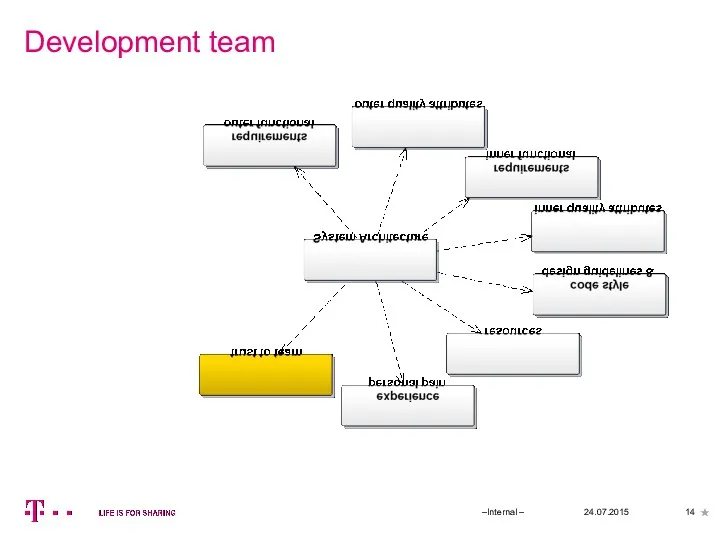
- 14. Development team 24.07.2015 –Internal –
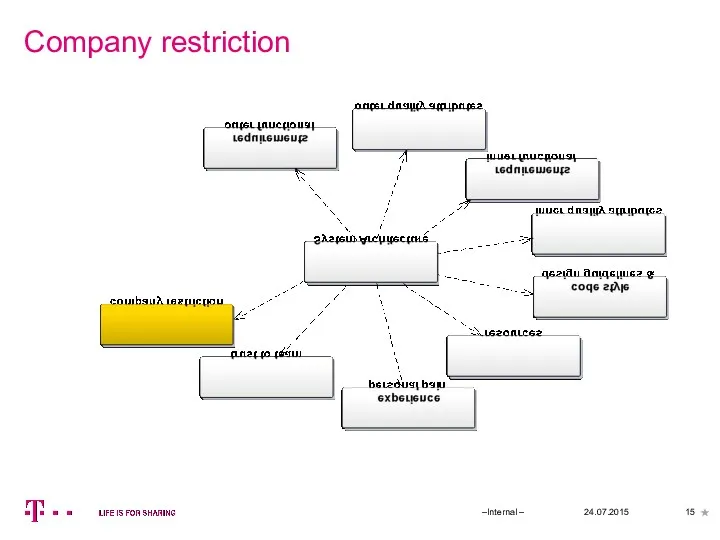
- 15. Company restriction 24.07.2015 –Internal –
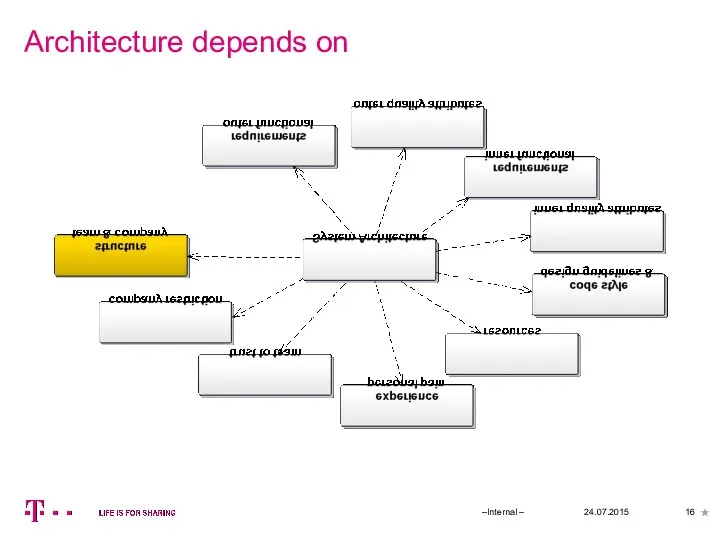
- 16. Architecture depends on 24.07.2015 –Internal –
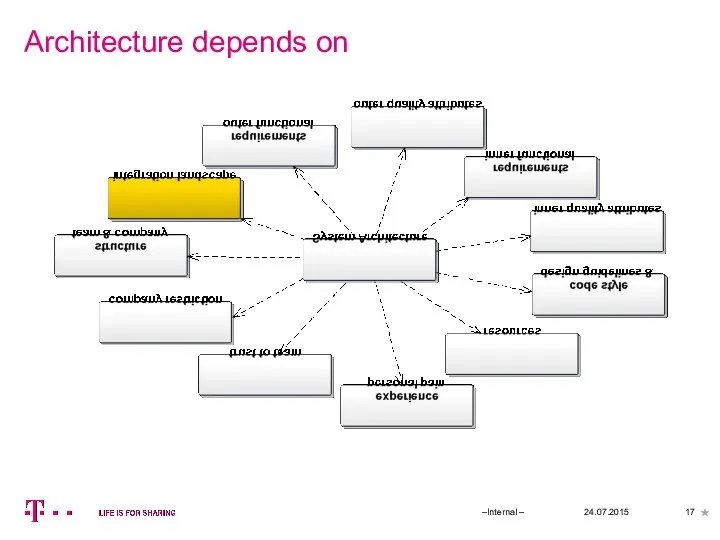
- 17. Architecture depends on 24.07.2015 –Internal –
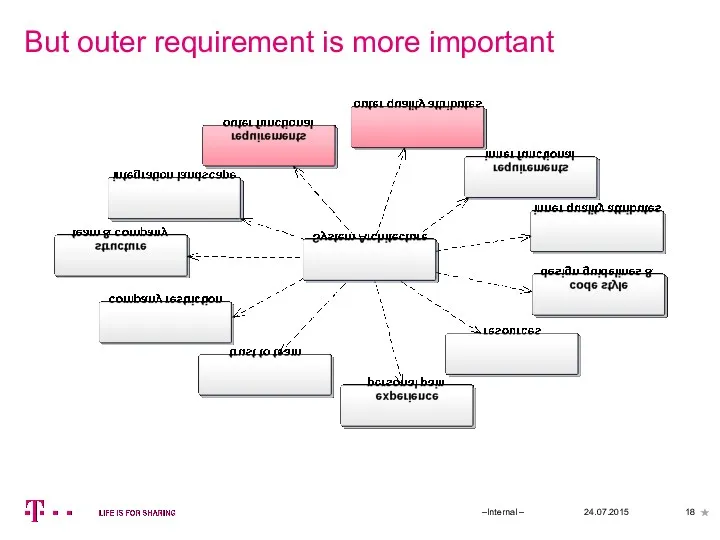
- 18. But outer requirement is more important 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 19. What means good architecture? 24.07.2015 –Internal – Meet requirements Ready for change Ready for scaling and
- 20. ISO 9126 Software quality 24.07.2015 –Internal – Functionality Reliability Usability Efficiency Maintainability Portability Quality attributes
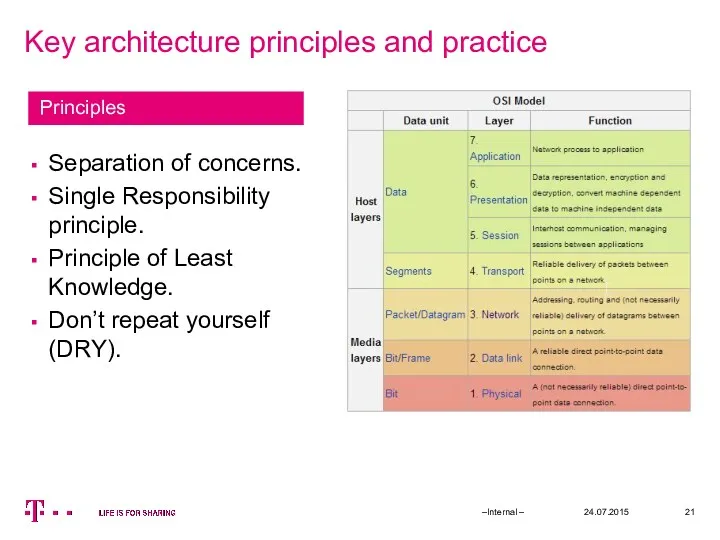
- 21. Key architecture principles and practice 24.07.2015 –Internal – Separation of concerns. Single Responsibility principle. Principle of
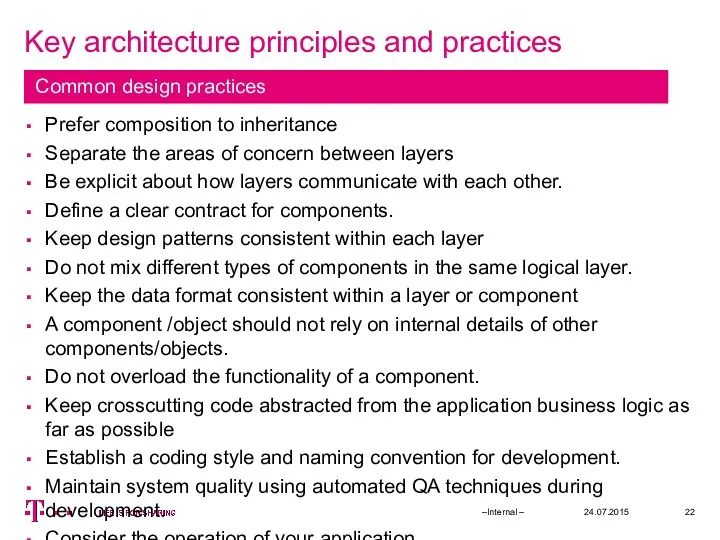
- 22. Key architecture principles and practices 24.07.2015 –Internal – Prefer composition to inheritance Separate the areas of
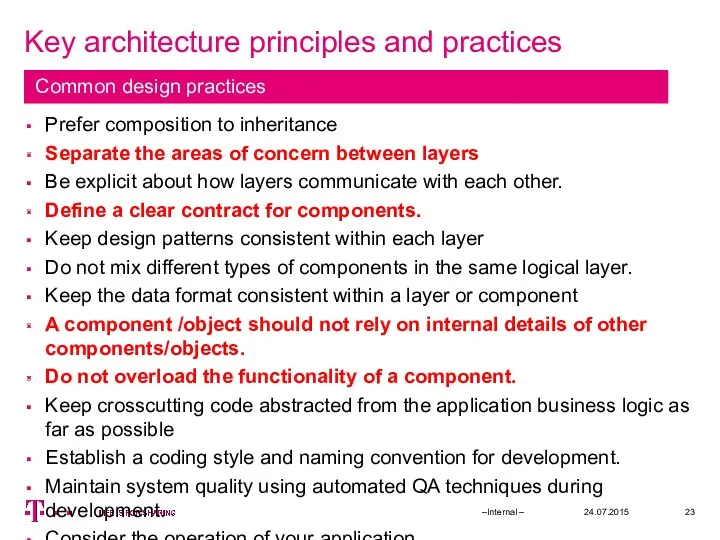
- 23. Key architecture principles and practices 24.07.2015 –Internal – Prefer composition to inheritance Separate the areas of
- 24. Design example
- 25. Design Example: Simple Enterprise Search (SES) 24.07.2015 –Internal – Description: SES is software of search information
- 26. Trying to rewrite requirements 24.07.2015 –Internal – UR01. Users should be able to search accross documents.
- 27. Trying to rewrite requirements 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 28. Looking for Actors 24.07.2015 –Internal –
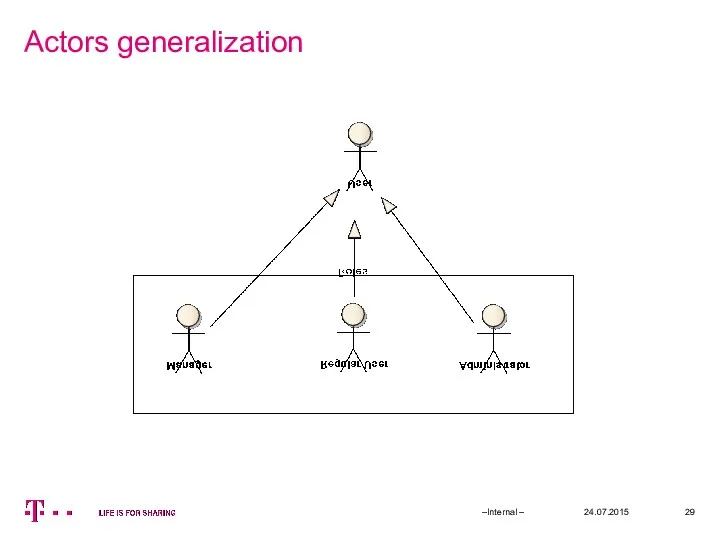
- 29. Actors generalization 24.07.2015 –Internal –
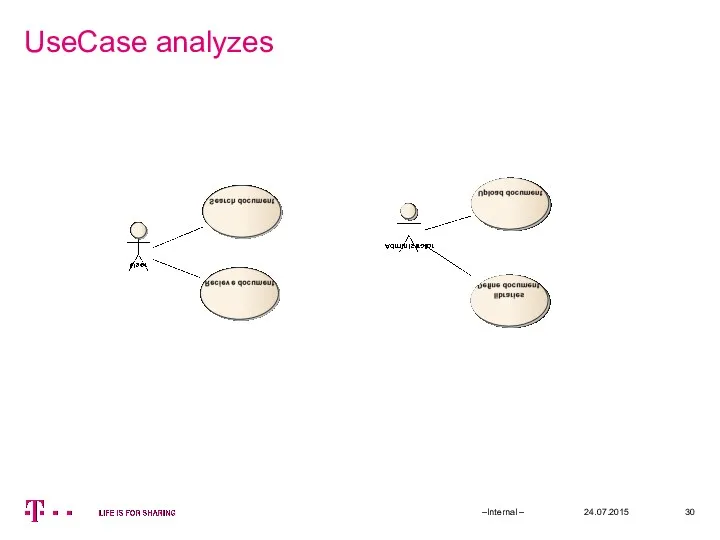
- 30. UseCase analyzes 24.07.2015 –Internal –
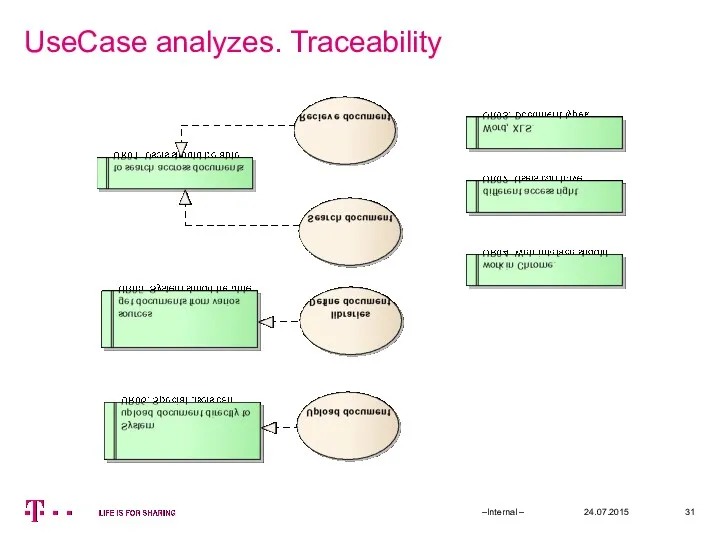
- 31. UseCase analyzes. Traceability 24.07.2015 –Internal –
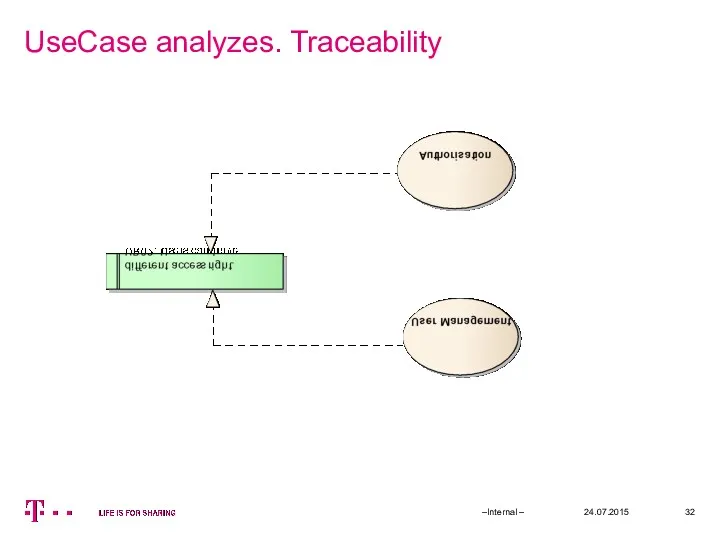
- 32. UseCase analyzes. Traceability 24.07.2015 –Internal –
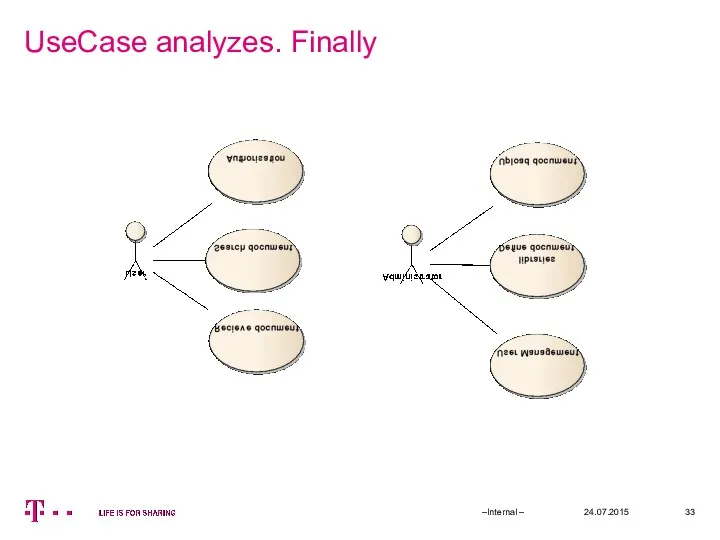
- 33. UseCase analyzes. Finally 24.07.2015 –Internal –
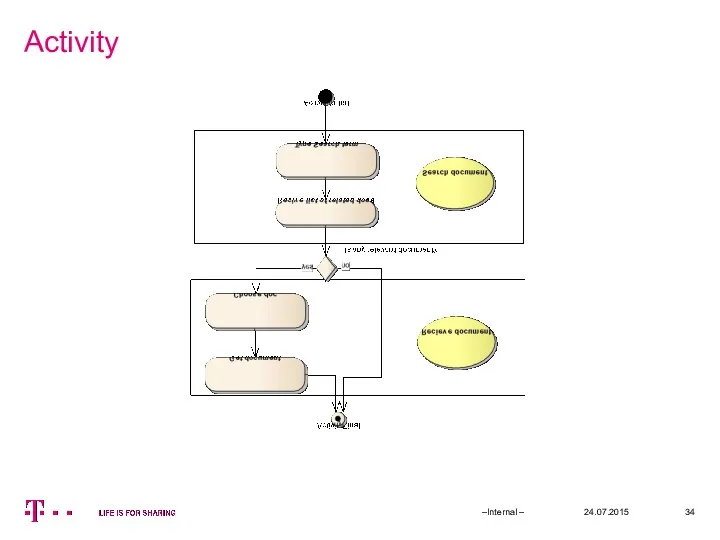
- 34. Activity 24.07.2015 –Internal –
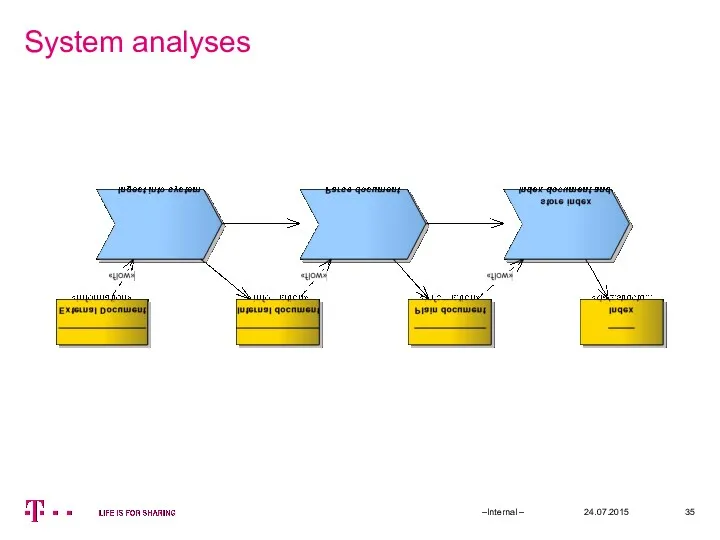
- 35. System analyses 24.07.2015 –Internal –
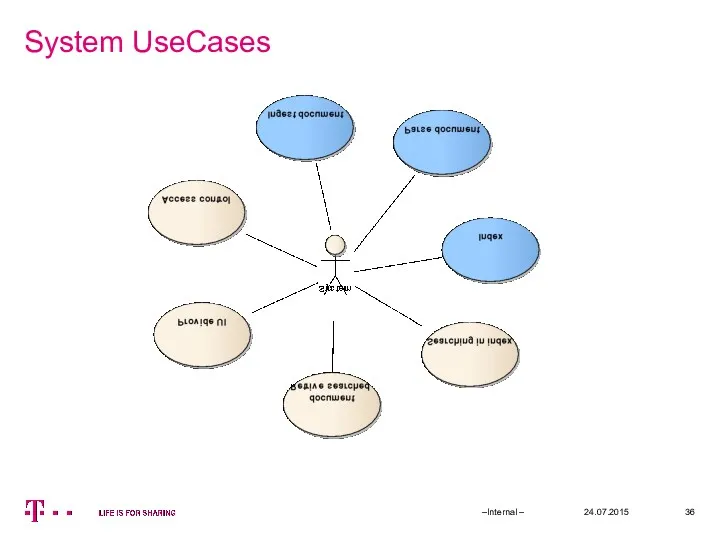
- 36. System UseCases 24.07.2015 –Internal –
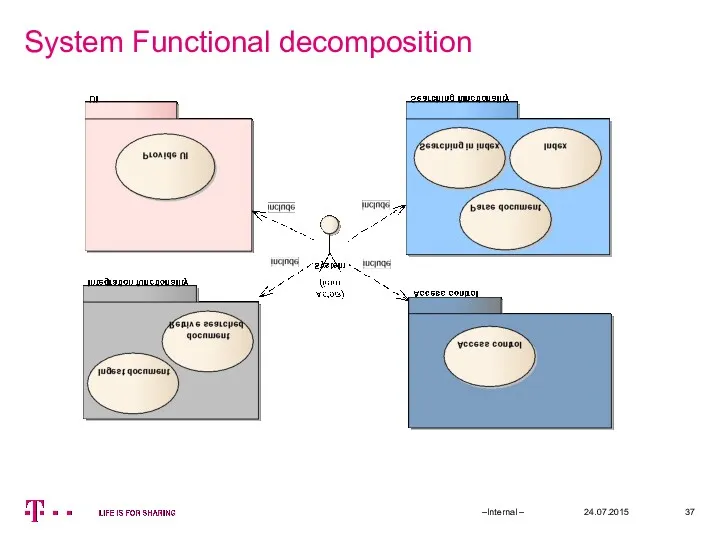
- 37. System Functional decomposition 24.07.2015 –Internal –
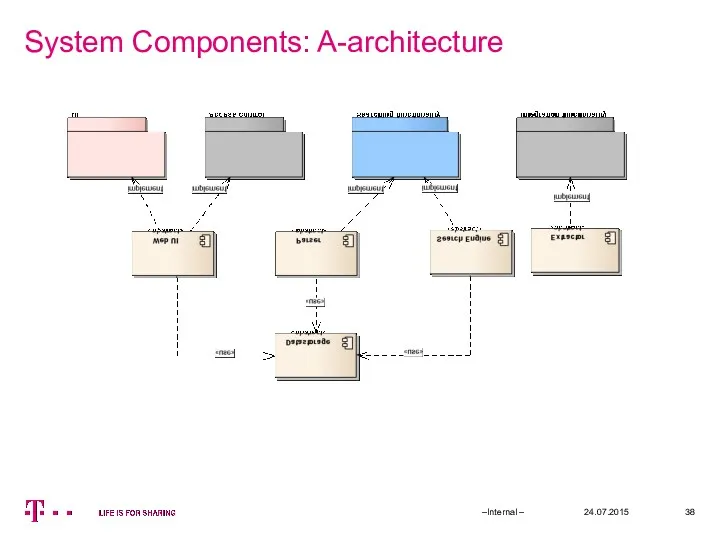
- 38. System Components: A-architecture 24.07.2015 –Internal –
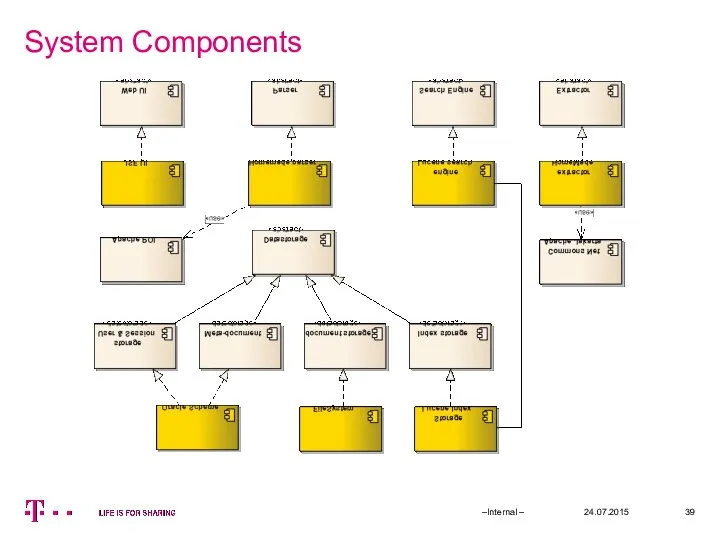
- 39. System Components 24.07.2015 –Internal –
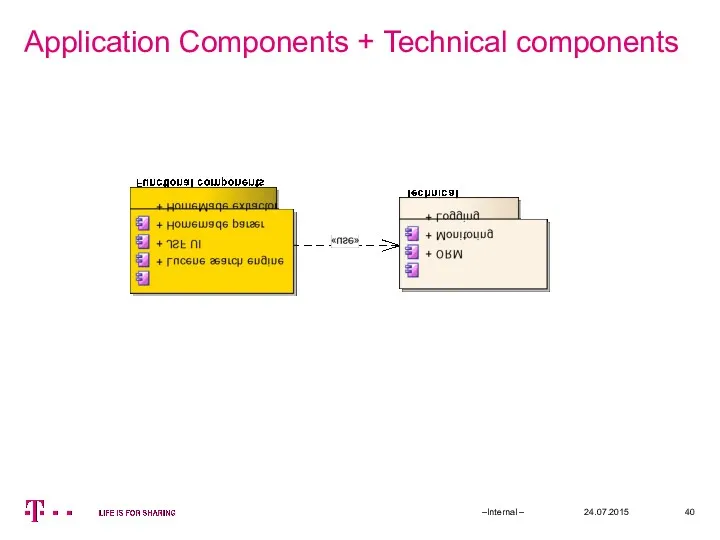
- 40. Application Components + Technical components 24.07.2015 –Internal –
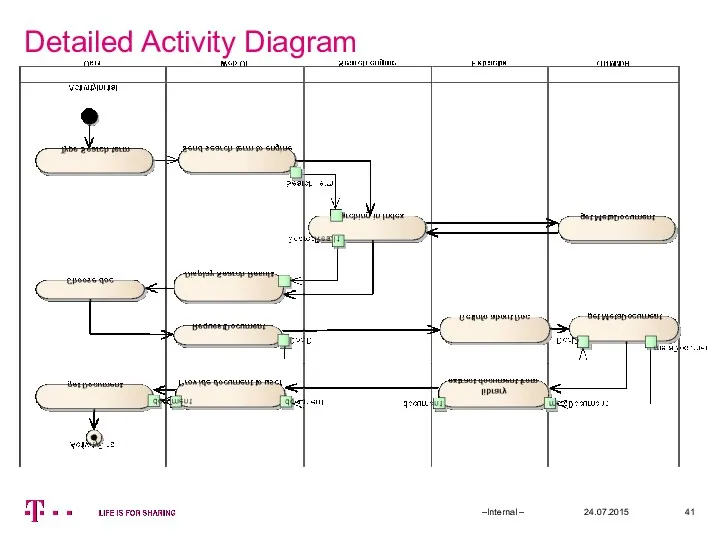
- 41. Detailed Activity Diagram 24.07.2015 –Internal –
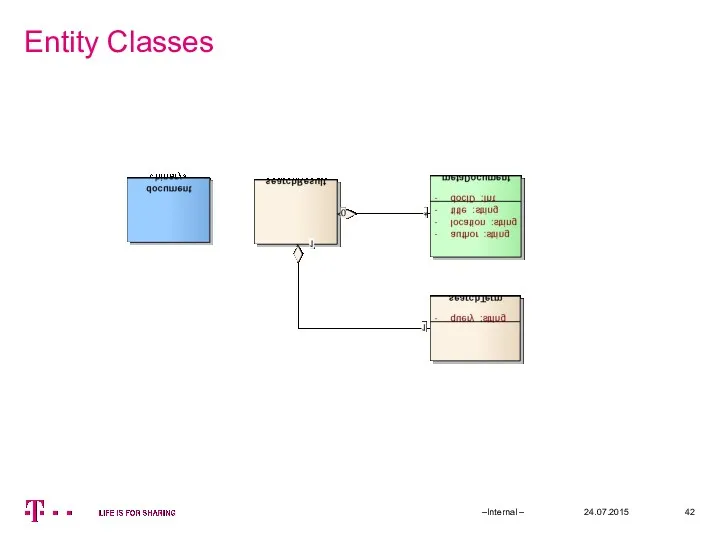
- 42. Entity Classes 24.07.2015 –Internal –
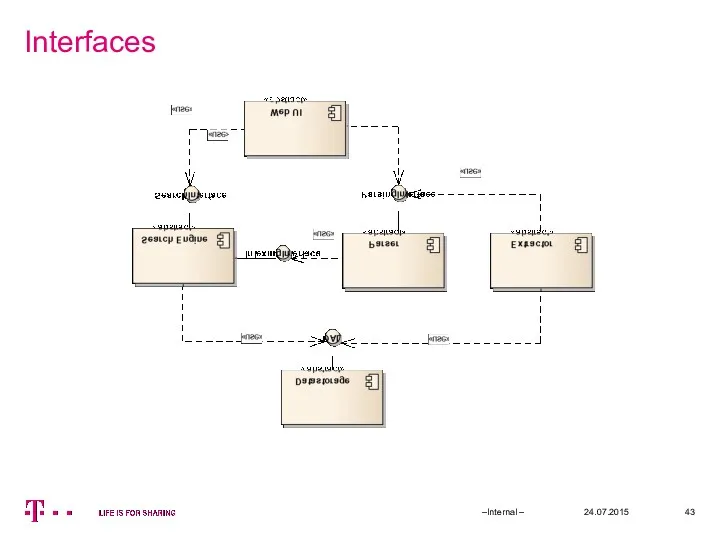
- 43. Interfaces 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 44. Behavior classes 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 45. Questions? 24.07.2015 -Internal Design example ?
- 46. Coffe 10 minutes 18:50
- 47. Multilayer application pattern
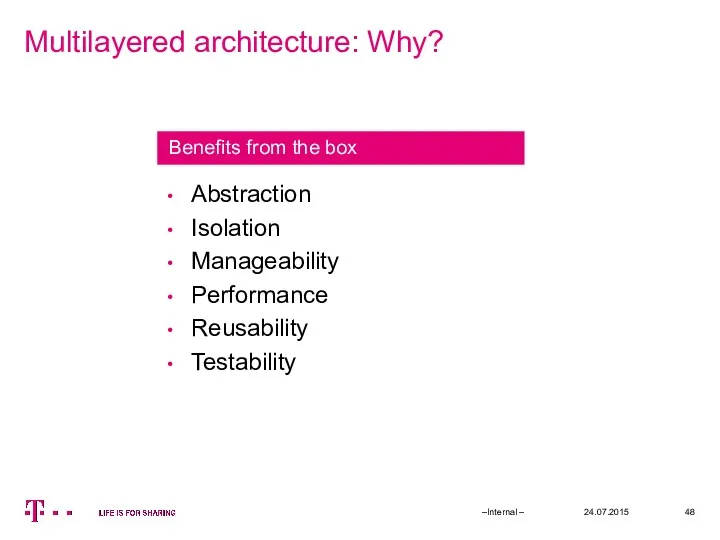
- 48. Multilayered architecture: Why? 24.07.2015 –Internal – Abstraction Isolation Manageability Performance Reusability Testability Benefits from the box
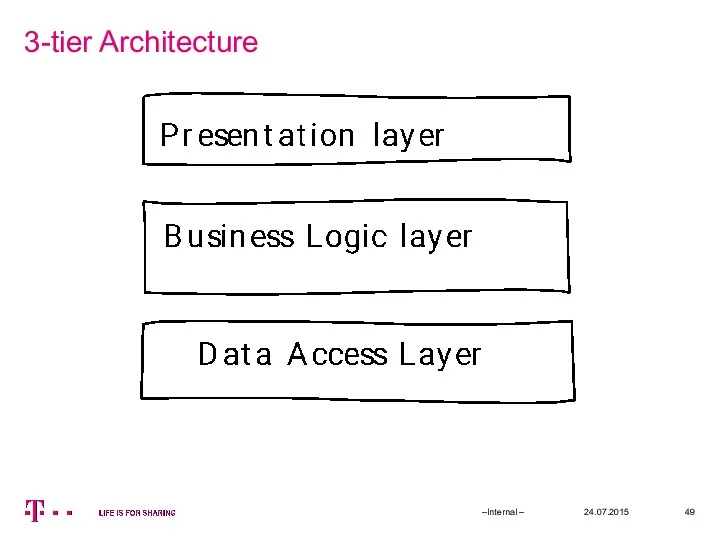
- 49. 3-tier Architecture 24.07.2015 –Internal –
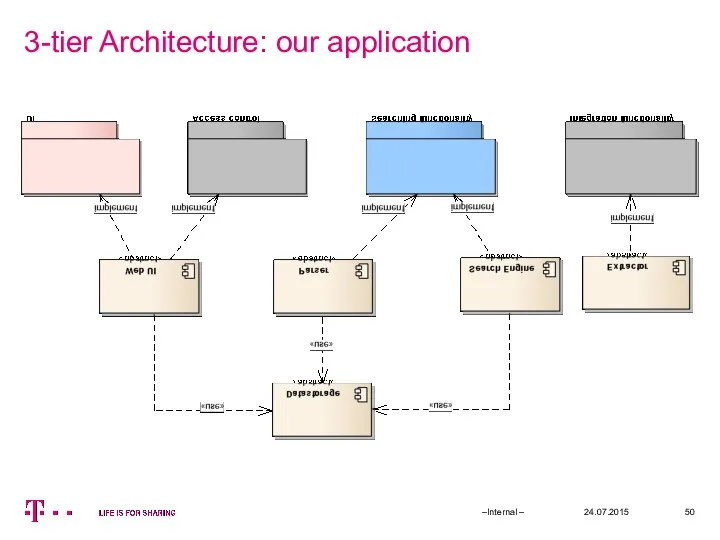
- 50. 3-tier Architecture: our application 24.07.2015 –Internal –
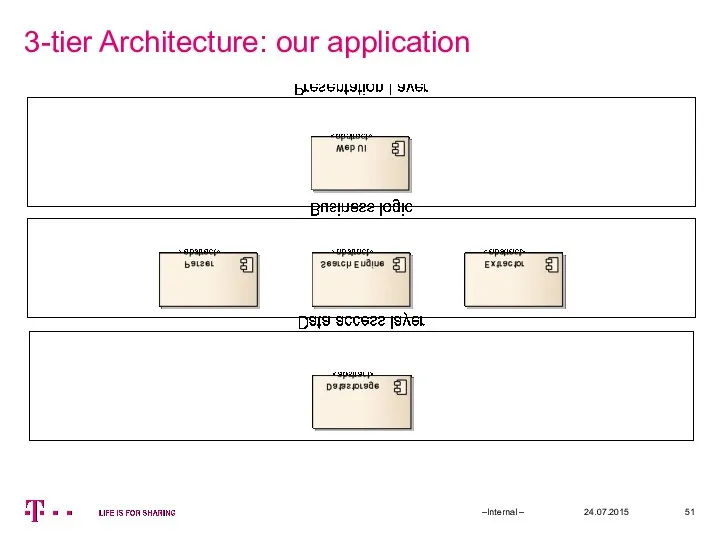
- 51. 3-tier Architecture: our application 24.07.2015 –Internal –
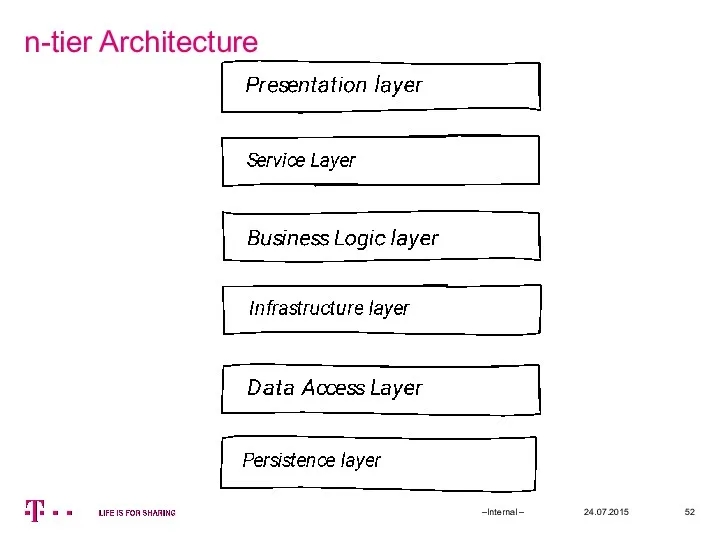
- 52. n-tier Architecture 24.07.2015 –Internal –
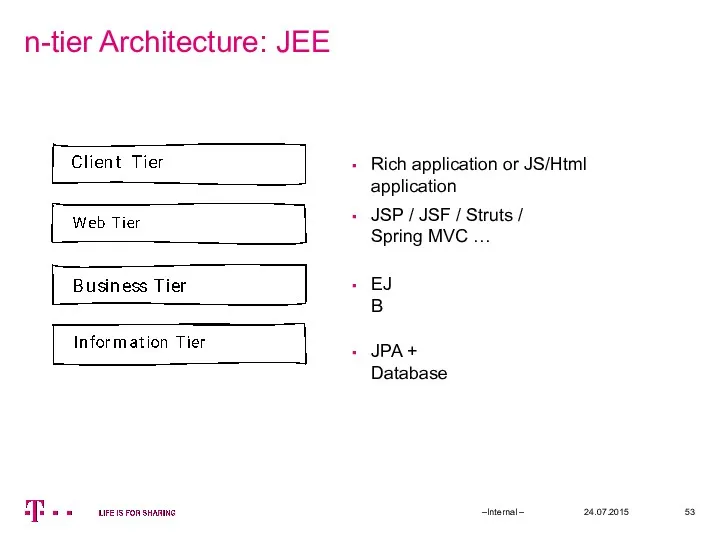
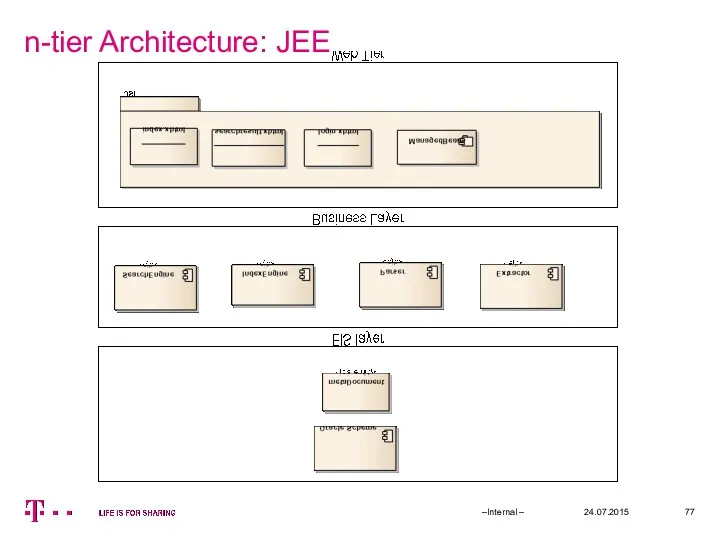
- 53. n-tier Architecture: JEE 24.07.2015 –Internal – Rich application or JS/Html application JSP / JSF / Struts
- 54. n-tier Architecture: JEE 24.07.2015 –Internal –
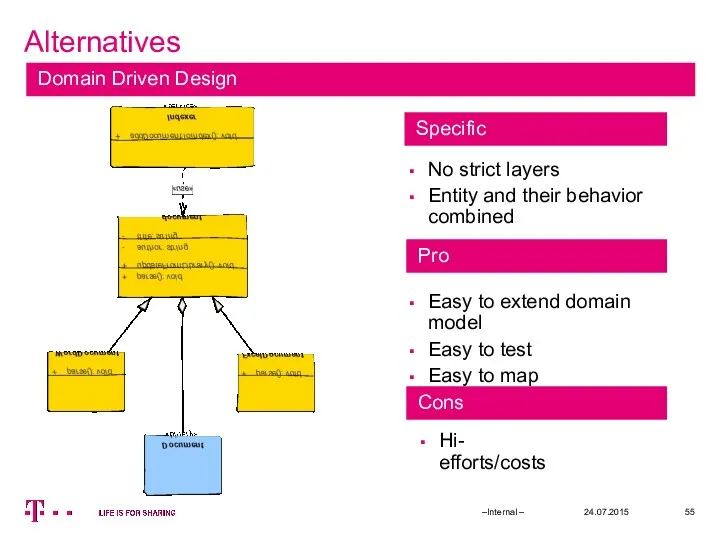
- 55. Alternatives 24.07.2015 –Internal – Domain Driven Design No strict layers Entity and their behavior combined Easy
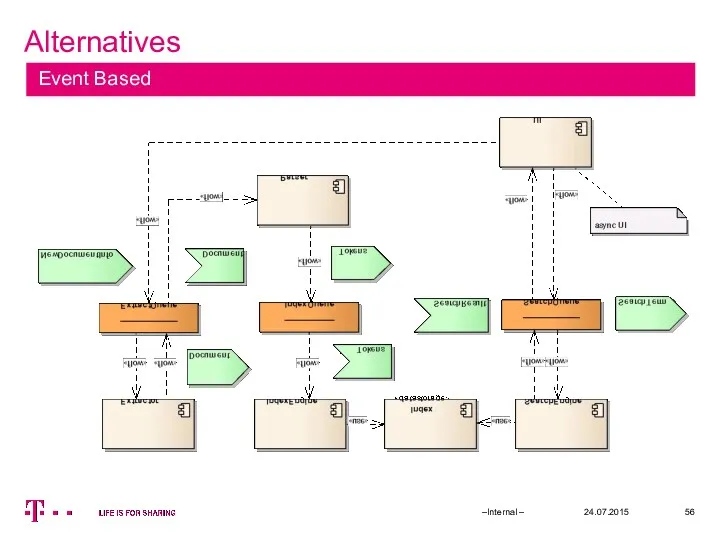
- 56. Alternatives 24.07.2015 –Internal – Event Based
- 57. Important 24.07.2015 –Internal – Please start your enterprise application from n-tiers architecture It is clear and
- 58. Questions? 24.07.2015 -Internal Multilayered architecture
- 59. Coffe 15 minutes xx:xx
- 60. Architect Role in PLC
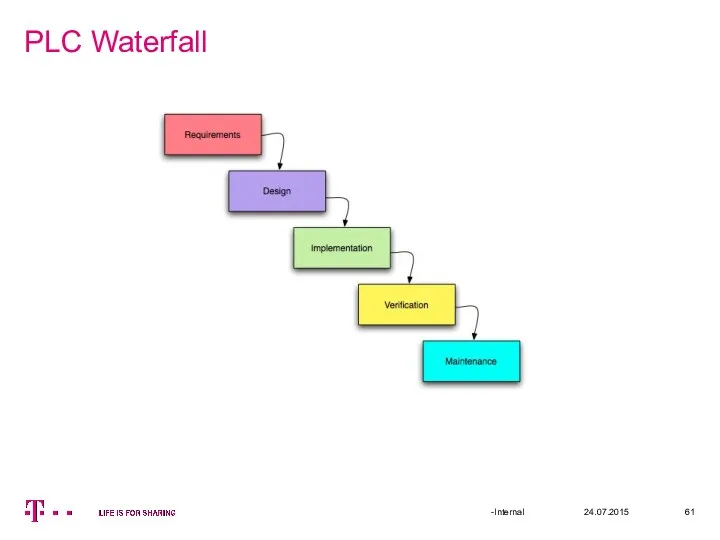
- 61. PLC Waterfall 24.07.2015 -Internal
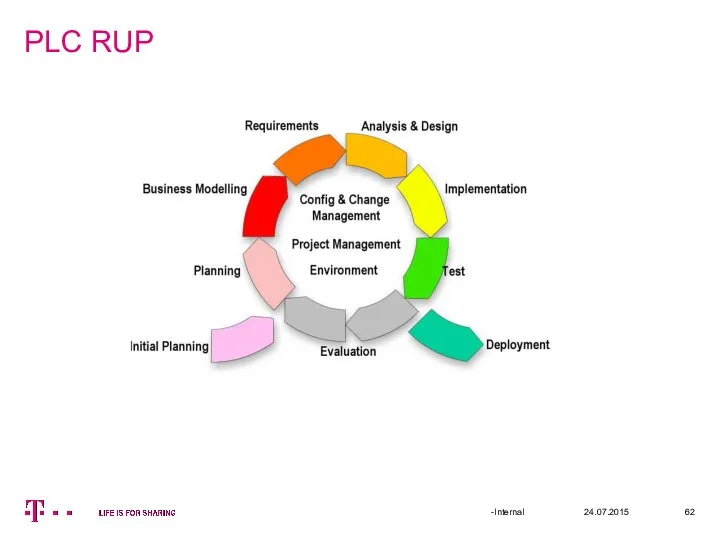
- 62. PLC RUP 24.07.2015 -Internal
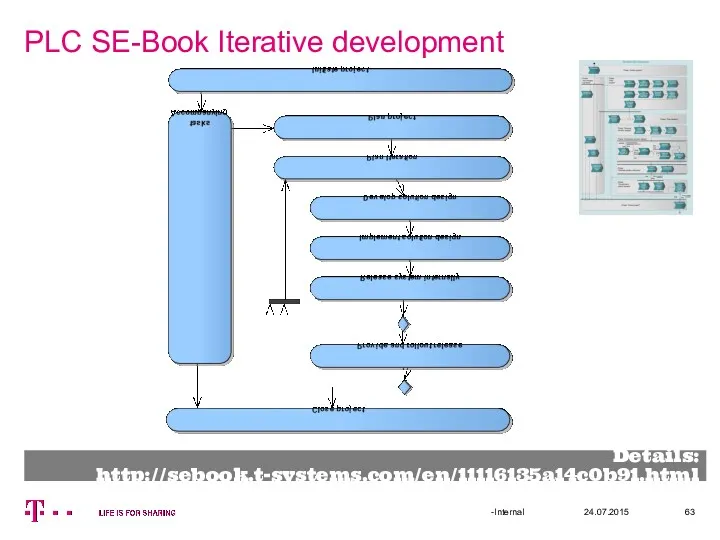
- 63. PLC SE-Book Iterative development 24.07.2015 Details: http://sebook.t-systems.com/en/11116135a14c0b91.html -Internal
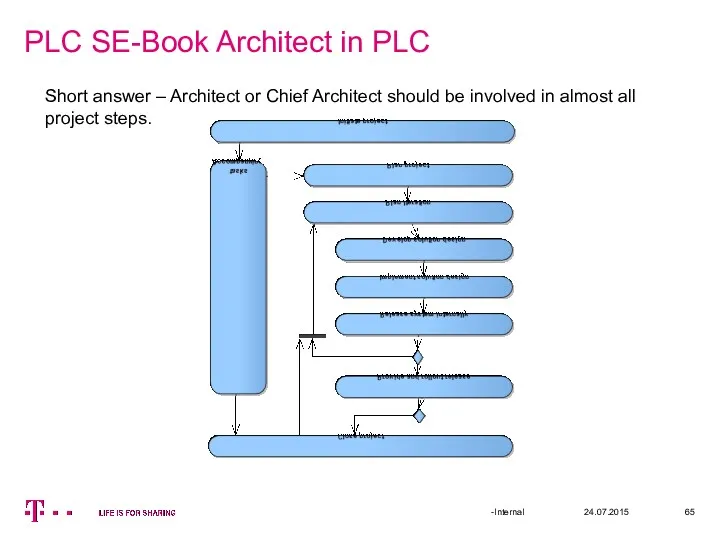
- 64. PLC SE-Book Architect in PLC 24.07.2015 Discussion: In which project steps Architect should be involved? -Internal
- 65. PLC SE-Book Architect in PLC 24.07.2015 -Internal Short answer – Architect or Chief Architect should be
- 66. PLC SE-Book Architect tasks: Plan project 24.07.2015 -Internal WBS - Work Breakdown Structure Provide effort estimation
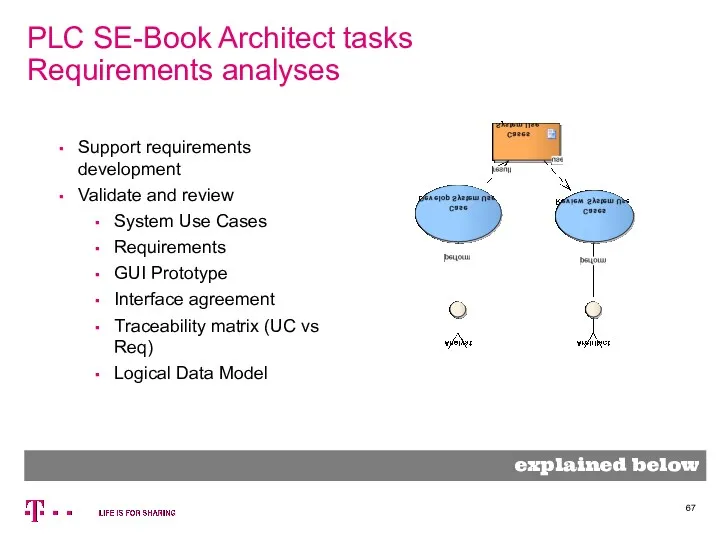
- 67. PLC SE-Book Architect tasks Requirements analyses explained below Support requirements development Validate and review System Use
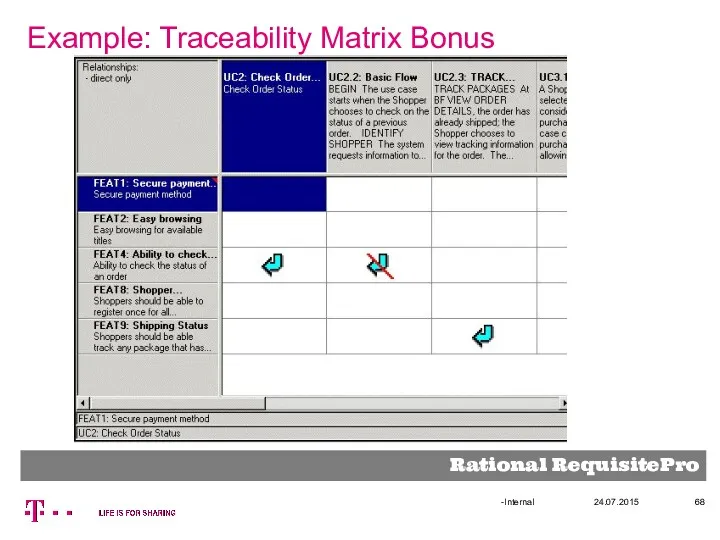
- 68. Example: Traceability Matrix Bonus 24.07.2015 -Internal Rational RequisitePro
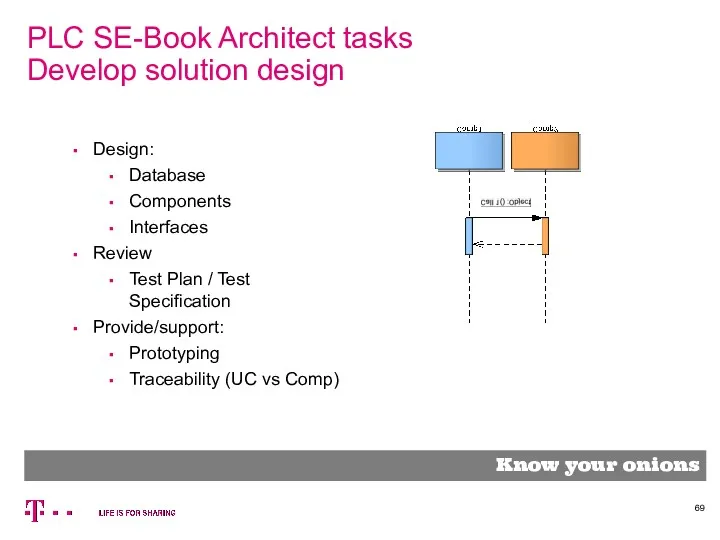
- 69. PLC SE-Book Architect tasks Develop solution design Know your onions Design: Database Components Interfaces Review Test
- 70. PLC SE-Book Architect tasks: Implementation Yes, we can code, at least after worktime Create program Test
- 71. PLC SE-Book Architect tasks: Test We hate QA activities, but we do it. Review test strategy
- 72. PLC SE-Book Architect tasks: Rollout 24.07.2015 -Internal Prepare Transfer to Operation Support Productive Operation
- 73. PLC SE-Book Architect tasks: Close project 24.07.2015 -Internal Determine and Analyze KPIs and Derive Measures
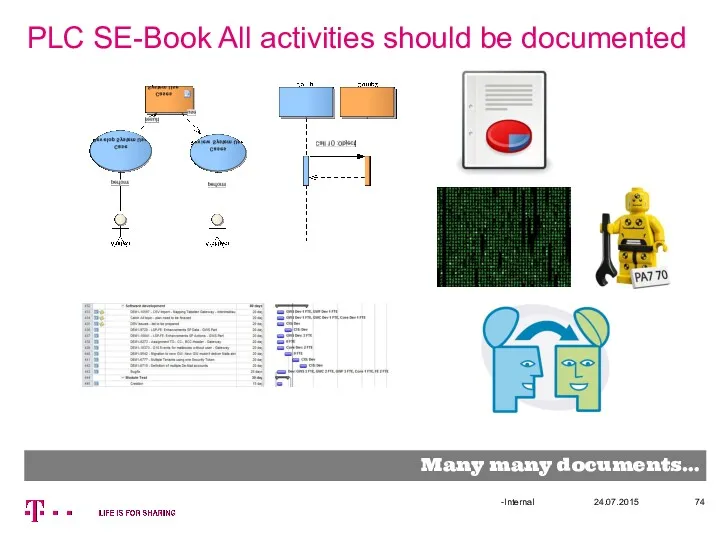
- 74. PLC SE-Book All activities should be documented 24.07.2015 -Internal Many many documents…
- 75. Questions? 24.07.2015 -Internal Architect in PLC ?
- 76. Resume
- 77. n-tier Architecture: JEE 24.07.2015 –Internal –
- 78. Key architecture principles and practices 24.07.2015 –Internal – Prefer composition to inheritance Separate the areas of
- 79. Thank you!
- 80. References
- 81. Sources 24.07.2015 -Internal Architecture itself Rozanski&Woods POSA Fowler EIP GOF
- 82. Sources 24.07.2015 -Internal Architecture practice / PLC aspects CMMI® for Development, Version 1.3 Carr, Marvin et
- 83. Sources 24.07.2015 -Internal SOA / EDA The Growing Role of Events in Enterprise Applications. Five forces.
- 84. Sources 24.07.2015 -Internal Requirements IEEE Recommended Practice for Software Requirements Specifications IEEE Std 830-1998 Requirements management
- 86. Скачать презентацию



























 Оформление списка литературы к научной работе
Оформление списка литературы к научной работе Строим свой сайт
Строим свой сайт Что такое “Платформер”
Что такое “Платформер” Компьютерная графика http://compgraph.tpu.ru/
Компьютерная графика http://compgraph.tpu.ru/ Интеллектуальные информационные системы. Классификация интеллектуальных информационных систем
Интеллектуальные информационные системы. Классификация интеллектуальных информационных систем Файловые системы. Работа с файлами в Windows API. Асинхронный и синхронный файловый ввод-вывод
Файловые системы. Работа с файлами в Windows API. Асинхронный и синхронный файловый ввод-вывод Oracle and/or its affiliates. Resources
Oracle and/or its affiliates. Resources Начальные сведения. Определение и основные понятия. Что могут содержать Web-страницы HTML теги?
Начальные сведения. Определение и основные понятия. Что могут содержать Web-страницы HTML теги? Операторы языка С++. Структура программы. Лекция 2
Операторы языка С++. Структура программы. Лекция 2 NP-складність і NP-повнота. Приклади наближених алгоритмів для NP-повних задач. Лекція 4
NP-складність і NP-повнота. Приклади наближених алгоритмів для NP-повних задач. Лекція 4 Основи Java Script. Масиви
Основи Java Script. Масиви Метод координат. Способы кодирования информации
Метод координат. Способы кодирования информации Архитектура приложений реального времени
Архитектура приложений реального времени Инструкция PackageAssistant. Помощник в настройке смартфонов
Инструкция PackageAssistant. Помощник в настройке смартфонов Автоматизоване створення та публікування веб-сайтів
Автоматизоване створення та публікування веб-сайтів Единый семинар фирмы 1С для бухгалтеров и руководителей
Единый семинар фирмы 1С для бухгалтеров и руководителей Технология хранения, обработки и анализа данных
Технология хранения, обработки и анализа данных Маршрутизация между VLAN
Маршрутизация между VLAN Робота зі ЗМІ
Робота зі ЗМІ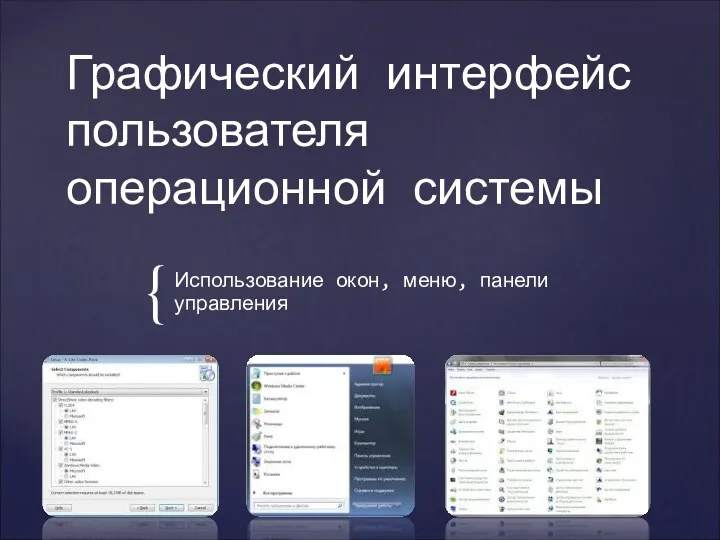 Графический интерфейс пользователя операционной системы
Графический интерфейс пользователя операционной системы Internet
Internet Магнитные носители информации
Магнитные носители информации Школьная библиотека: Копилочка. Инновационные формы профессионального взаимодействия
Школьная библиотека: Копилочка. Инновационные формы профессионального взаимодействия Криптографические средства защиты информации
Криптографические средства защиты информации Создание учебных курсов в системе Moodle
Создание учебных курсов в системе Moodle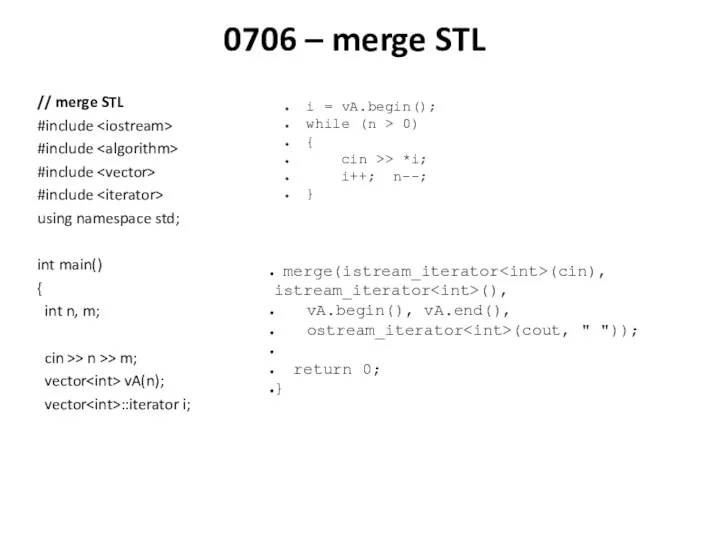 STL алгоритмы
STL алгоритмы Что такое пиксель
Что такое пиксель Интернет: за и против
Интернет: за и против