Содержание
- 2. How to run software on a computer? What is a machine code? Instructions Assembly Language Little
- 3. CPU - “brain with a mouth” to eat instructions from memory and produces output out of
- 4. A program, like Firefox.exe (.exe is a Windows convention) Firefox.exe is just a file -- can
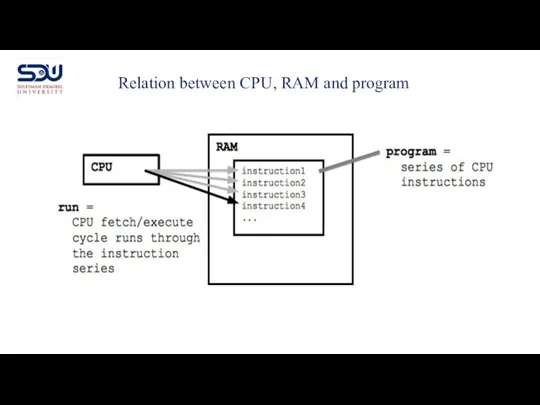
- 5. Relation between CPU, RAM and program
- 6. The language of the machine code is hardwired into the design of the CPU it is
- 7. CPU is capable of performing simple instructions if you load them into RAM. For example, addition/subtraction
- 8. CPU has list of defined instructions, such as: add values store values copy values increment value
- 9. CPU understands only electrical signals, such as: (10110000 01100001) But to be understandable to programmers, assembly
- 10. The Little Man Computer (LMC) is an instructional model of a computer. The LMC is generally
- 11. Little Man Computer xx is the cell number in the memory compartment.
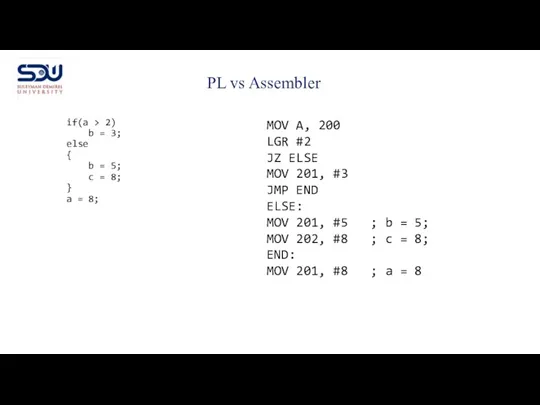
- 12. PL vs Assembler if(a > 2) b = 3; else { b = 5; c =
- 13. PL are translated into machine code PL were created to make developing software simple Programming Languages
- 14. Why there are many PLs? People take ideas from different languages and combine them into a
- 15. Java - used in web applications, software systems, where software needs security, and frequent changes C++
- 16. This table has imaginary numbers. But this numbers shows some intuition PL comparison
- 17. Programmers write code in a “high” level programming language whereas CPU understands very simple “low” level
- 18. Imperative - The focus is on what steps the computer should take rather than what the
- 19. What starts Firefox? Operating System Set of supervisory programs, run when computer first starts Administration behind
- 20. Functions: Program execution Memory management Multitasking Disk access and file systems Networking Security Modern operating systems:
- 21. There are three main families of operating systems: Linux Fedora, Ubuntu, RedHat, Suse mostly free mostly
- 22. Android IOS Windows Phone Ubuntu Touch OS BlackBerry OS Mobile operating systems
- 23. Android developed by Google free to manufacturers to create applications, pay only 20$ and immediately publish
- 24. Ubuntu touch OS: couldn’t find money for publishing main idea: one OS on mobile phone and
- 26. Скачать презентацию





















 Использование сервисов Prezi, Powtoon, Google Slides, Quizizz на занятиях по дисциплине Плавание с методикой преподавания
Использование сервисов Prezi, Powtoon, Google Slides, Quizizz на занятиях по дисциплине Плавание с методикой преподавания Польза и вред интернета
Польза и вред интернета Компьютерные игры как жизнь
Компьютерные игры как жизнь Информационные технологии в юридической деятельности
Информационные технологии в юридической деятельности Построение и анализ алгоритмов. Динамическое программирование. (Лекция 3)
Построение и анализ алгоритмов. Динамическое программирование. (Лекция 3) Процедуры и функции ТР (Подпрограммы)
Процедуры и функции ТР (Подпрограммы) YМ website. User manual
YМ website. User manual Основы веб-разработки: ReactJS
Основы веб-разработки: ReactJS Инструмент морф. ЗD модели
Инструмент морф. ЗD модели Максимальный элемент массива. Обработка массивов
Максимальный элемент массива. Обработка массивов Разработка внешнего вида презентации
Разработка внешнего вида презентации Java.SE.07 Multithreading
Java.SE.07 Multithreading Игровая презентация СВОЯ ИГРА на тему Компьютер как средство обработки информации
Игровая презентация СВОЯ ИГРА на тему Компьютер как средство обработки информации Работа с СУБД SQLite
Работа с СУБД SQLite HTML-VR: программируемые 3D кнопки-гиперссылки и 3Dpx объекты
HTML-VR: программируемые 3D кнопки-гиперссылки и 3Dpx объекты Засоби компютерної графіки
Засоби компютерної графіки Своя игра
Своя игра Two pointers method
Two pointers method Ввод - вывод. Символьные потоки
Ввод - вывод. Символьные потоки Программирование на языке Python. Базовый уровень. Модуль 2. Строки и списки. Списки (занятие 1)
Программирование на языке Python. Базовый уровень. Модуль 2. Строки и списки. Списки (занятие 1) Работа поисковых систем
Работа поисковых систем Модульность ОС. Совместимость ОС
Модульность ОС. Совместимость ОС Системы, модели, графы. Построение информационной модели в виде графа. 8 класс
Системы, модели, графы. Построение информационной модели в виде графа. 8 класс Алгоритмы с ветвлениями
Алгоритмы с ветвлениями Программирование на языке Python
Программирование на языке Python Представление числовой информации с помощью систем счисления
Представление числовой информации с помощью систем счисления Основы логики. Логические операции
Основы логики. Логические операции Циклические алгоритмы. Цикл с параметром
Циклические алгоритмы. Цикл с параметром