Слайд 2
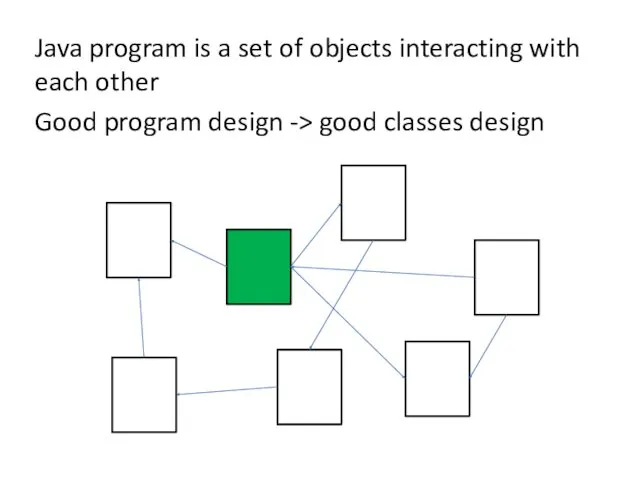
Java program is a set of objects interacting with each other
Good
program design -> good classes design
Слайд 3

SOLID
SOLID is a mnemonic acronym introduced by Robert C. Martin in
the early 2000s which stands for five basic principles of object-oriented programming and design.
Single responsibility
Open-closed
Liskov substitution
Interface segregation
Dependency inversion
Слайд 4

S
Single Responsibility Principle
“An object should have only a single responsibility, and
that responsibility should be entirely encapsulated by the class.”
Слайд 5

O
Open/closed principle
“Software entities (classes, modules, functions, etc.) should be open for
extension, but closed for modification”
Once completed, the implementation of a class could only be modified to correct errors; new or changed features would require that a different class be created
Слайд 6

L
Liskov substitution principle
“objects in a program should be replaceable with instances
of their subtypes without altering the correctness of that program”
In a computer program, if S is a subtype of T, then objects of type T may be replaced with objects of type S (i.e., objects of type S may be substituted for objects of type T) without altering any of the desirable properties of that program (correctness, task performed, etc.)
Слайд 7

I
Interface segregation principle
“many client-specific interfaces are better than one general-purpose interface.”
Once
an interface has become too 'fat' it needs to be split into smaller and more specific interfaces so that any clients of the interface will only know about the methods that relate to them. In a nutshell, no client should be forced to depend on methods it does not use.






 Алгоритмизация и программирование разветвляющихся алгоритмов
Алгоритмизация и программирование разветвляющихся алгоритмов Возможности сетевого программного обеспечения для организации коллективной деятельности в компьютерных сетях
Возможности сетевого программного обеспечения для организации коллективной деятельности в компьютерных сетях Разработка программных модулей
Разработка программных модулей Цикл с параметром в языке Pascal
Цикл с параметром в языке Pascal Компьютер и его части. 2 класс
Компьютер и его части. 2 класс Нормативно-правовые документы и стандарты в области защиты информации и информационной безопасности
Нормативно-правовые документы и стандарты в области защиты информации и информационной безопасности Использование редактора блок-схем при решении математических задач на Паскале
Использование редактора блок-схем при решении математических задач на Паскале Жобалау әдістемесі түсінігі және тарихы
Жобалау әдістемесі түсінігі және тарихы Spatial Data Structures
Spatial Data Structures BW the game
BW the game Киберпреступность
Киберпреступность Брокасса. Инновационная компания на рынке услуг по кассовой технике
Брокасса. Инновационная компания на рынке услуг по кассовой технике Оператор ветвления (условный оператор)
Оператор ветвления (условный оператор) Система автоматического тестирования Яндекс. Контест
Система автоматического тестирования Яндекс. Контест Автоматизированная система снабжения. Фрегат Корпорация Web-Заказ
Автоматизированная система снабжения. Фрегат Корпорация Web-Заказ Сети передачи данных (урок 4)
Сети передачи данных (урок 4) Звуковая информация. Временная дискретизация звука
Звуковая информация. Временная дискретизация звука Основы алгебры логики. Логические основы компьютера
Основы алгебры логики. Логические основы компьютера Программирование на языке Python. Символьные строки
Программирование на языке Python. Символьные строки Русский по четвергам. Интернет-ресурсы
Русский по четвергам. Интернет-ресурсы Программа-тест по Visual Studio
Программа-тест по Visual Studio Основы логики
Основы логики Предмет информатики. Роль информации в жизни людей. Информация и знания
Предмет информатики. Роль информации в жизни людей. Информация и знания Мультиплексирование данных в стандарте MPEG-2
Мультиплексирование данных в стандарте MPEG-2 СКУР Пассажир. Система контроля уровня риска
СКУР Пассажир. Система контроля уровня риска План-конспект урока информатики Решение расчетных задач с помощью электронных таблиц
План-конспект урока информатики Решение расчетных задач с помощью электронных таблиц Продвижение сайтов в поисковых системах
Продвижение сайтов в поисковых системах Лингвистические парадоксы. Удивительный мир научных книг - 2018
Лингвистические парадоксы. Удивительный мир научных книг - 2018