Содержание
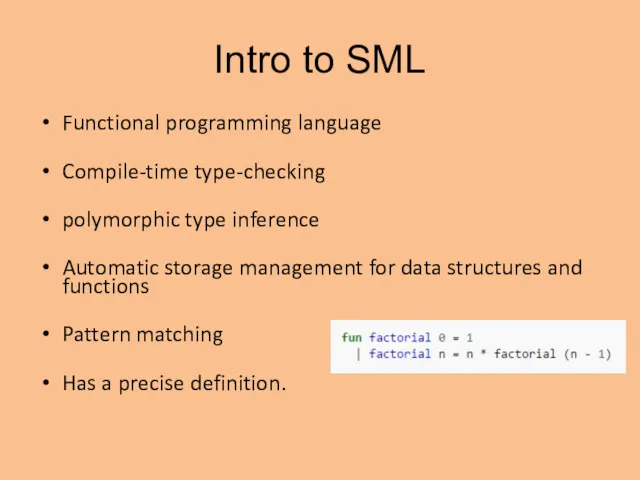
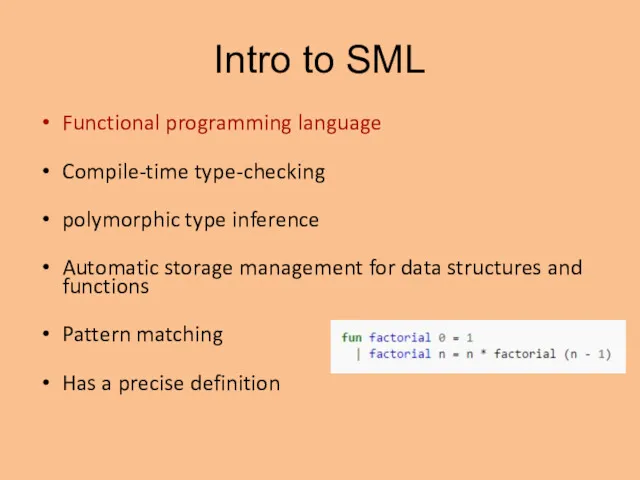
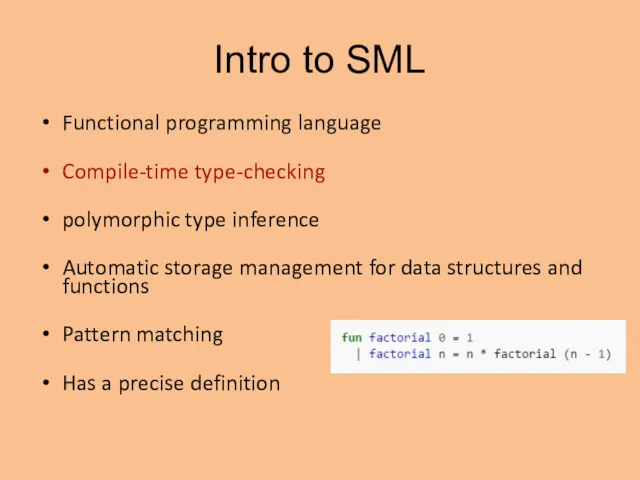
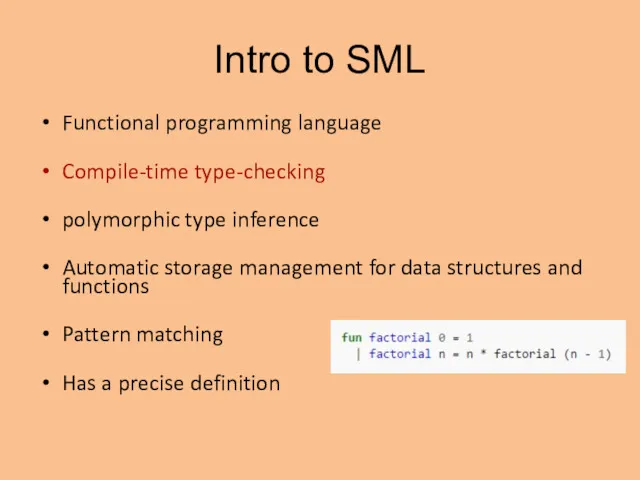
- 2. Intro to SML Functional programming language Compile-time type-checking polymorphic type inference Automatic storage management for data
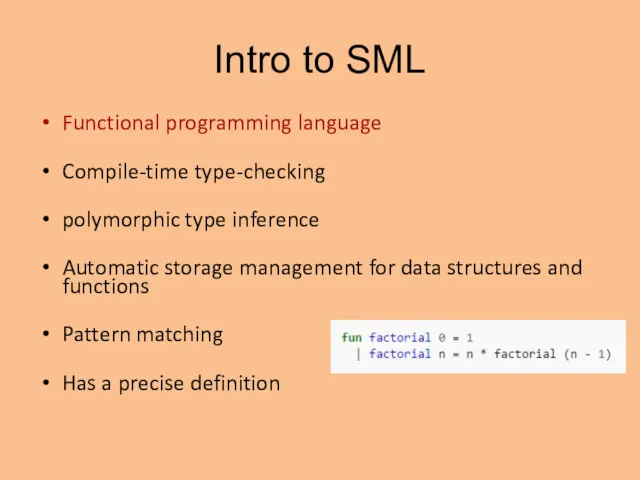
- 3. Intro to SML Functional programming language Compile-time type-checking polymorphic type inference Automatic storage management for data
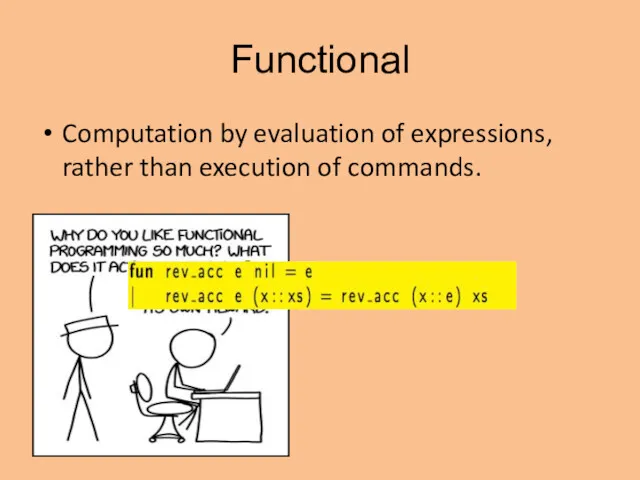
- 4. Functional Computation by evaluation of expressions, rather than execution of commands.
- 5. Syntax val foo = fn : int * int -> int foo :: int -> int
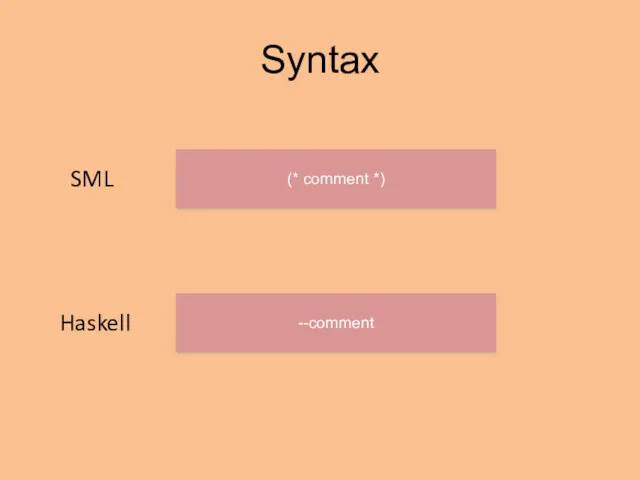
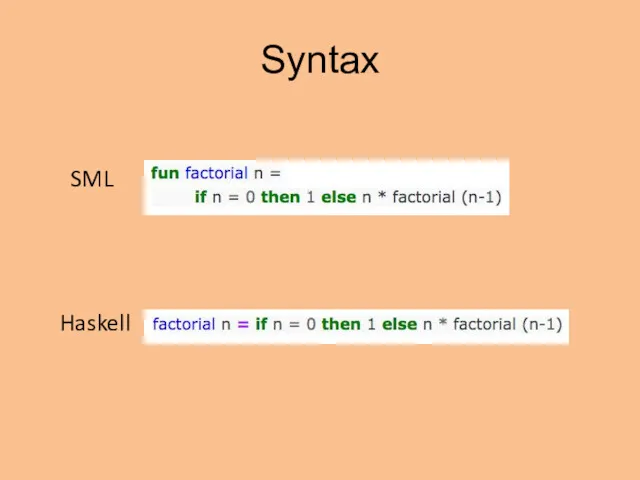
- 6. Syntax (* comment *) --comment SML Haskell
- 7. Syntax SML Haskell
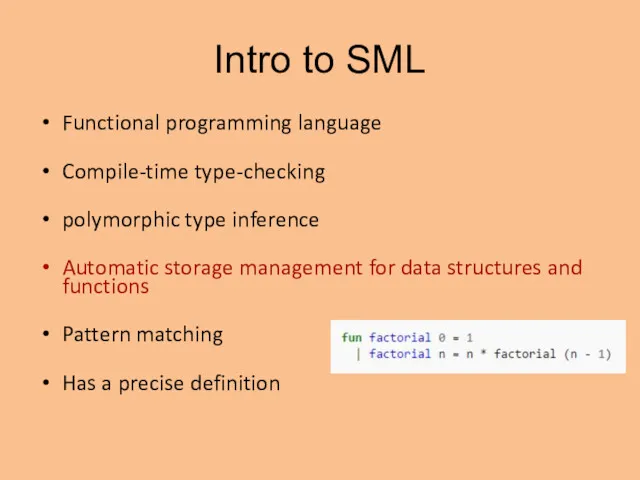
- 8. Intro to SML Functional programming language Compile-time type-checking polymorphic type inference Automatic storage management for data
- 9. Intro to SML Functional programming language Compile-time type-checking polymorphic type inference Automatic storage management for data
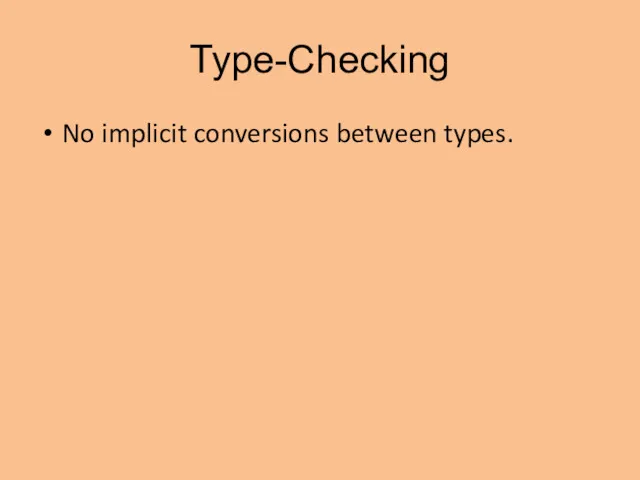
- 10. Type-Checking No implicit conversions between types. Example: Real(3) + 3.14 ACCEPTED 3 + 3.14 REJECTED
- 11. Intro to SML Functional programming language Compile-time type-checking polymorphic type inference Automatic storage management for data
- 12. Intro to SML Functional programming language Compile-time type-checking polymorphic type inference Automatic storage management for data
- 13. Intro to SML Destructive update val vacc = fn : Cat -> Cat signature ARRAY =
- 14. Intro to SML Destructive update signature ARRAY = sig type 'a array (An 'a array is
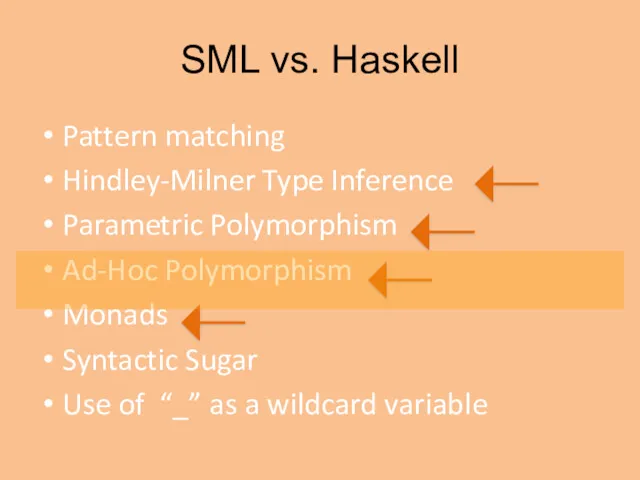
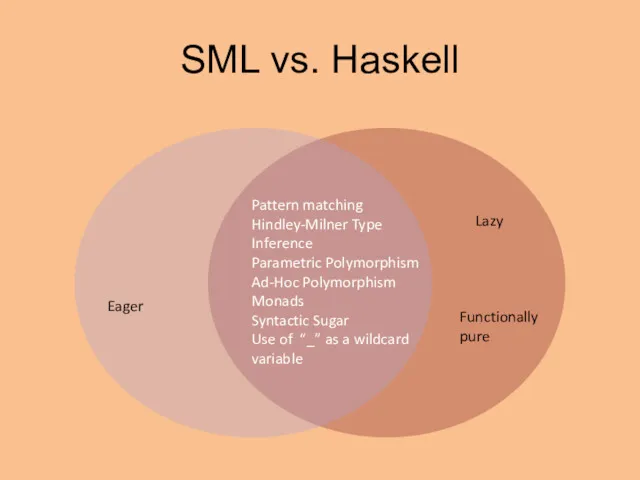
- 15. SML vs. Haskell Pattern matching Hindley-Milner Type Inference Parametric Polymorphism Ad-Hoc Polymorphism Monads Syntactic Sugar Use
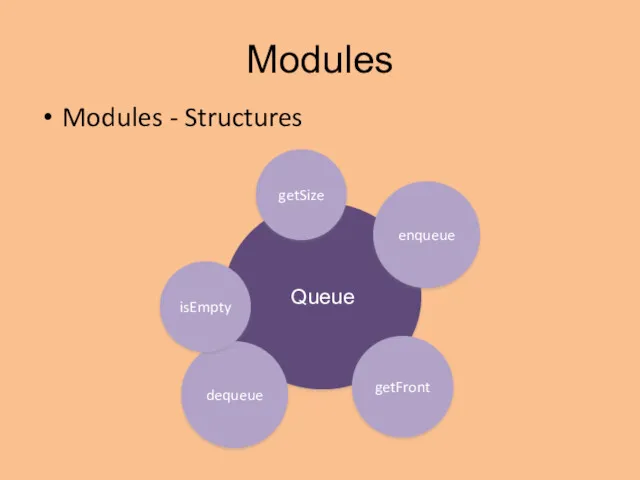
- 16. Modules Modules - Structures Queue enqueue dequeue isEmpty getSize getFront
- 17. Intro to SML Modules - Functors functor PQUEUE(type Item val > : Item * Item ->
- 18. SML vs. Haskell Pattern matching Hindley-Milner Type Inference Parametric Polymorphism Ad-Hoc Polymorphism Monads Syntactic Sugar Use
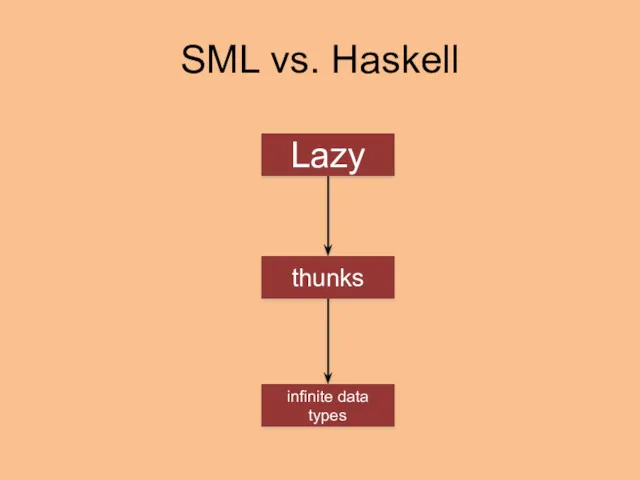
- 19. SML vs. Haskell Lazy infinite data types thunks
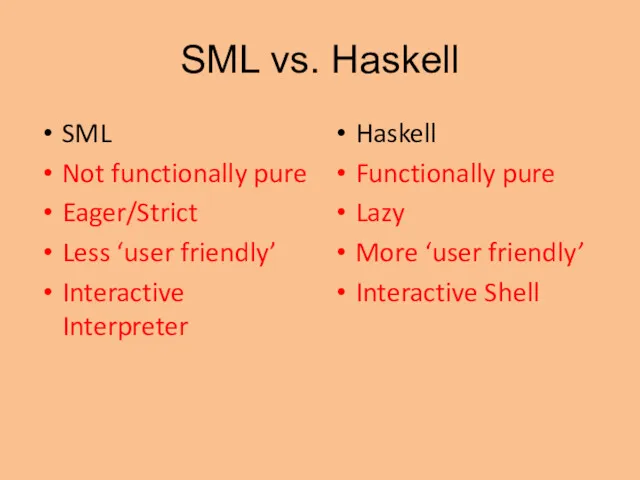
- 20. SML vs. Haskell SML Not functionally pure Eager/Strict Less ‘user friendly’ Interactive Interpreter Haskell Functionally pure
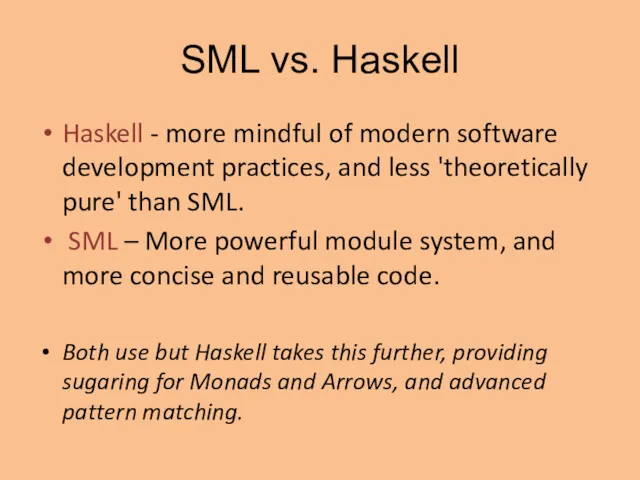
- 21. SML vs. Haskell Haskell - more mindful of modern software development practices, and less 'theoretically pure'
- 22. Thank You!
- 23. Infinite Lists Unique to Haskell: inf = 1 : map (+1) inf [1,2,3,4,5,…] ones = 1
- 25. Скачать презентацию






 Безопасность при использовании современных гаджетов
Безопасность при использовании современных гаджетов Виртуальная реальность как социокультурное явление информационного общества
Виртуальная реальность как социокультурное явление информационного общества Imagine Cup. Мастер-класс по C# от MSP
Imagine Cup. Мастер-класс по C# от MSP Конспект урока по информатике и ИКТ Чувственное познание мира 6 класс
Конспект урока по информатике и ИКТ Чувственное познание мира 6 класс О группе Однажды в сказке/ Once Upon A Time
О группе Однажды в сказке/ Once Upon A Time ТБ в кабинете информатики
ТБ в кабинете информатики Анализ программы с подпрограммами
Анализ программы с подпрограммами Программирование на языке Python. §62. Массивы
Программирование на языке Python. §62. Массивы Файлы и файловая система. (8 класс)
Файлы и файловая система. (8 класс) Электронная таблица Microsoft Excel
Электронная таблица Microsoft Excel Достоверность информации в Интернете
Достоверность информации в Интернете Алгоритмические структуры
Алгоритмические структуры Методика программирования сверлильных операций со смещением нуля (07)
Методика программирования сверлильных операций со смещением нуля (07) Операционные системы
Операционные системы Алгоритмы и структуры данных
Алгоритмы и структуры данных Интерфейс. Общие определени.я Интерфейс пользователя. Междупрограммный интерфейс
Интерфейс. Общие определени.я Интерфейс пользователя. Междупрограммный интерфейс Система обліку страхового агентства
Система обліку страхового агентства Общие понятия информатики и кодирования информации. Лекция 1
Общие понятия информатики и кодирования информации. Лекция 1 Создание видеофильма средствами Windows Movie Maker
Создание видеофильма средствами Windows Movie Maker Инженерный дизайн
Инженерный дизайн Ретроспективный взгляд на важную информацию из курсов ST-7PROG1 and ST-7PROG2
Ретроспективный взгляд на важную информацию из курсов ST-7PROG1 and ST-7PROG2 Понятие репозитория проекта, структура проекта
Понятие репозитория проекта, структура проекта Основные методологические аспекты проектирования информационной системы. Методологии проектирования ИС
Основные методологические аспекты проектирования информационной системы. Методологии проектирования ИС Принципи побудови комутаторів та комутаційних середовищ паралельних КС. (Тема 15)
Принципи побудови комутаторів та комутаційних середовищ паралельних КС. (Тема 15) Системы счисления
Системы счисления Фейсбук
Фейсбук Лабораторная 8. Инструментальные средства создания web-серверов
Лабораторная 8. Инструментальные средства создания web-серверов Разработка, создание эффектов и демонстрация презентации
Разработка, создание эффектов и демонстрация презентации