Содержание
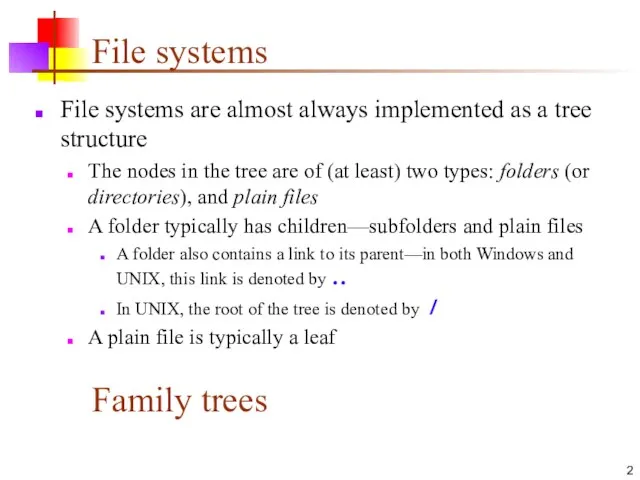
- 2. File systems File systems are almost always implemented as a tree structure The nodes in the
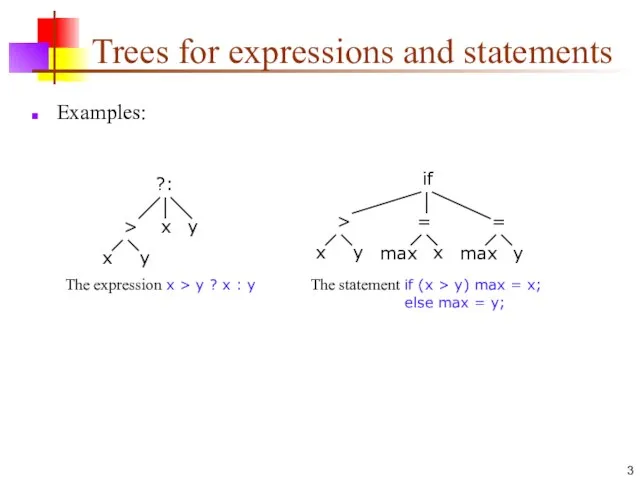
- 3. Trees for expressions and statements Examples:
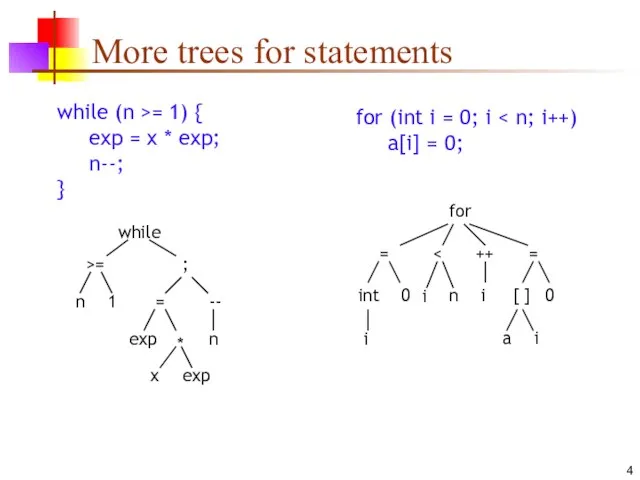
- 4. More trees for statements while (n >= 1) { exp = x * exp; n--; }
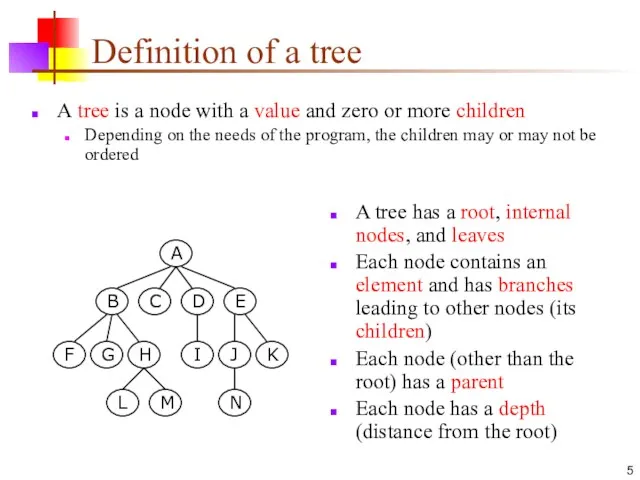
- 5. Definition of a tree A tree is a node with a value and zero or more
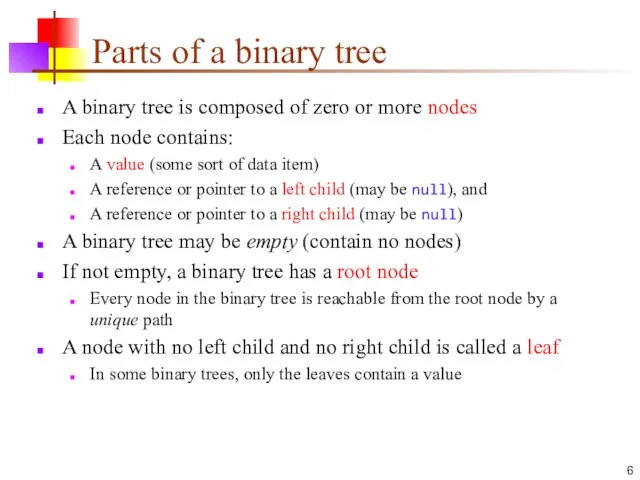
- 6. Parts of a binary tree A binary tree is composed of zero or more nodes Each
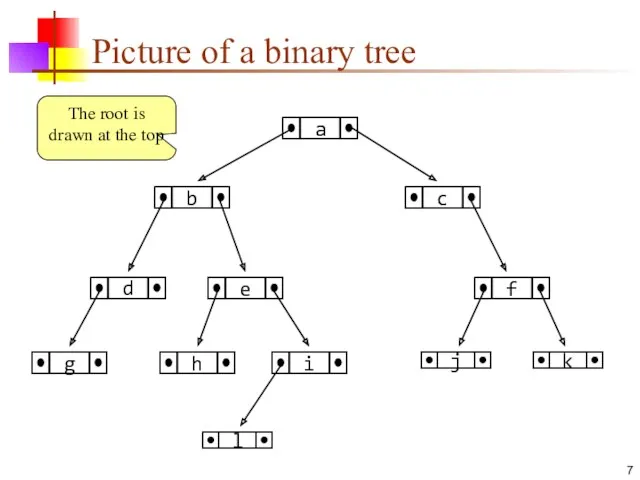
- 7. Picture of a binary tree The root is drawn at the top
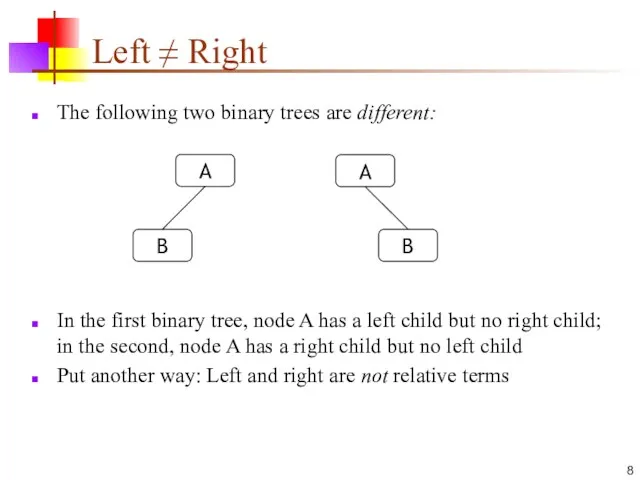
- 8. Left ≠ Right The following two binary trees are different: In the first binary tree, node
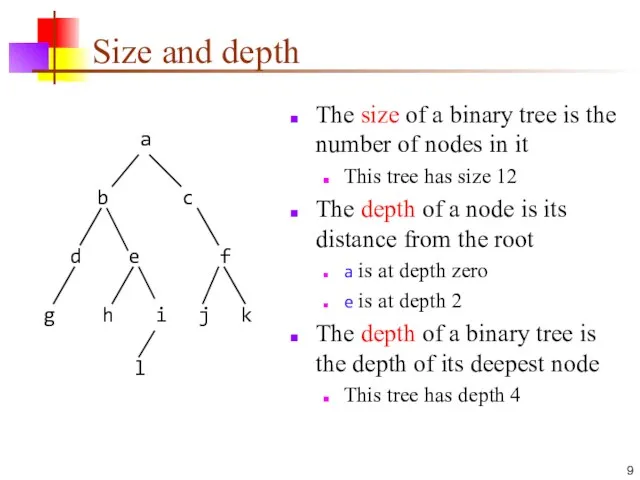
- 9. Size and depth The size of a binary tree is the number of nodes in it
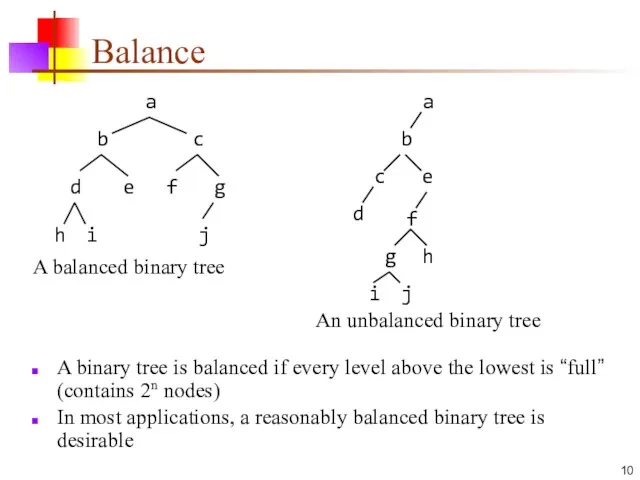
- 10. Balance A binary tree is balanced if every level above the lowest is “full” (contains 2n
- 11. Breadth-first Traversing a tree in breadth-first order means that after visiting a node X, all of
- 12. Tree traversals A binary tree is defined recursively: it consists of a root, a left subtree,
- 13. Preorder traversal In preorder, the root is visited first If each node is visited before both
- 14. Inorder traversal In inorder, the root is visited in the middle If each node is visited
- 15. Postorder traversal In postorder, the root is visited last If each node is visited after its
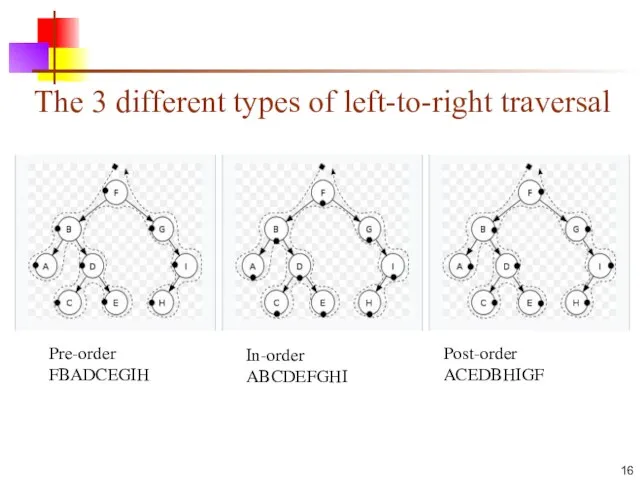
- 16. The 3 different types of left-to-right traversal Pre-order FBADCEGIH In-order ABCDEFGHI Post-order ACEDBHIGF
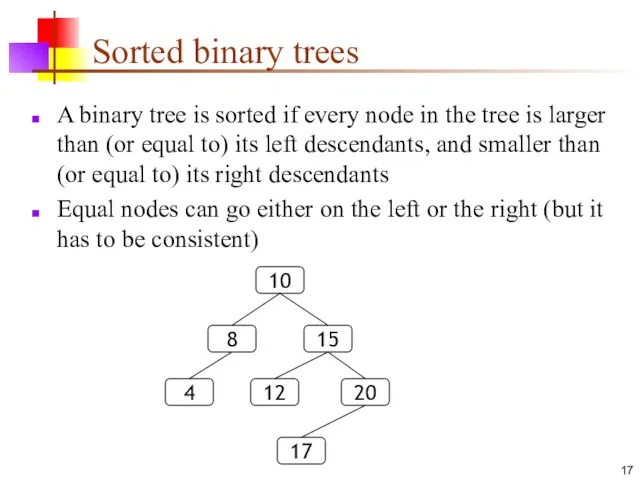
- 17. Sorted binary trees A binary tree is sorted if every node in the tree is larger
- 19. Скачать презентацию





 Позиционные системы счисления
Позиционные системы счисления Локальные сети. Параметры сетей и их стандарты
Локальные сети. Параметры сетей и их стандарты Сбор и подготовка данных
Сбор и подготовка данных Современные накопители информации, используемые в вычислительной технике
Современные накопители информации, используемые в вычислительной технике Использование технологии веб-квест как средство развития познавательных и творческих способностей учащихся
Использование технологии веб-квест как средство развития познавательных и творческих способностей учащихся Блочные алгоритмы. Блочное шифрование. Сравнение блочных и поточных шифров. Предпосылки создания шифра Фейстеля
Блочные алгоритмы. Блочное шифрование. Сравнение блочных и поточных шифров. Предпосылки создания шифра Фейстеля Параллельное программирование. С++. Thread Support Library. Atomic Operations Library
Параллельное программирование. С++. Thread Support Library. Atomic Operations Library Функции в Excel
Функции в Excel Организация и средства информационных технологий обеспечения управленческой деятельности
Организация и средства информационных технологий обеспечения управленческой деятельности Поиск публикаций и показатели деятельности ученого в Web of Science
Поиск публикаций и показатели деятельности ученого в Web of Science Бездротові мережі
Бездротові мережі Занятие 1. Знакомство с программой Adobe Photoshop
Занятие 1. Знакомство с программой Adobe Photoshop Microsoft Visual Studio — линейка продуктов компании Microsoft
Microsoft Visual Studio — линейка продуктов компании Microsoft Операторы цикла
Операторы цикла Понятие об информации. Представление информации. Информационная деятельность человека.
Понятие об информации. Представление информации. Информационная деятельность человека. Автоматизоване створення запитів у базі даних
Автоматизоване створення запитів у базі даних Архітектура операційних систем
Архітектура операційних систем Windows System Programming
Windows System Programming Личный кабинет
Личный кабинет Мир станочника. Аддитивные технологии и 3D-сканирование
Мир станочника. Аддитивные технологии и 3D-сканирование Методы и средства защиты программ от компьютерных вирусов
Методы и средства защиты программ от компьютерных вирусов 46_Yaroslavskaya_Sasha
46_Yaroslavskaya_Sasha Локальные и глобальные сети ЭВМ. Защита информации в сетях. (Тема 6)
Локальные и глобальные сети ЭВМ. Защита информации в сетях. (Тема 6) Godseeker. Игра
Godseeker. Игра Рабочий стол. Управление компьютером с помощью мыши
Рабочий стол. Управление компьютером с помощью мыши Проектирование изделий из листового металла в NX
Проектирование изделий из листового металла в NX Эти люди изменили мир
Эти люди изменили мир Электронные ресурсы для детей и юношества в общедоступных библиотеках: создание и использование
Электронные ресурсы для детей и юношества в общедоступных библиотеках: создание и использование