Содержание
- 2. The Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL) describes computational linguistics as the scientific study of language from
- 3. Why say “Computational Linguistics (CL)” versus “Natural Language Processing” (NLP)? Computational Linguistics The science of computers
- 4. Human languages: are highly ambiguous at all levels are complex , with recursive structures and reference
- 5. Computational linguistic students study subjects such as : semantic computational semantics syntax models in cognitive science
- 6. Phonetics studies the sounds of a language [t] and [d] differ in voice onset time English
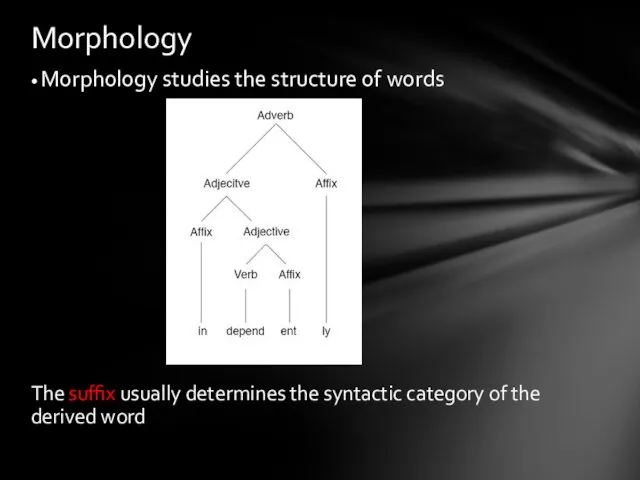
- 7. • Morphology studies the structure of words The suffix usually determines the syntactic category of the
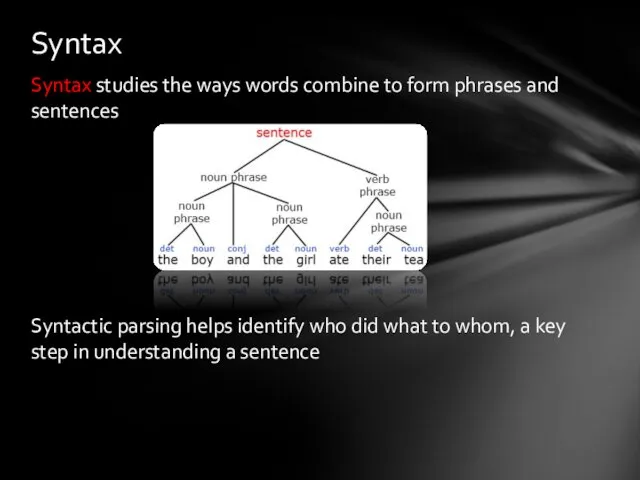
- 8. Syntax studies the ways words combine to form phrases and sentences Syntactic parsing helps identify who
- 9. Semantics studies the meaning of words, phrases and sentences E.g., I ate the oysters in/for an
- 10. Input: a sentence (usually text) f in the source language Output: a sentence e in the
- 11. Language understanding is complicated The necessary knowledge is enormous Most stages of the process involve ambiguity
- 13. Скачать презентацию




![Phonetics studies the sounds of a language [t] and [d]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/3868/slide-5.jpg)



 Моя семья английский язык.
Моя семья английский язык. Жолдама хат
Жолдама хат Велика літера у власних назвах
Велика літера у власних назвах Сингапур системасы буенча ачык дәрес
Сингапур системасы буенча ачык дәрес Презентация Игротека
Презентация Игротека Tabu i eufemizacja a treści aksjologiczne
Tabu i eufemizacja a treści aksjologiczne Конструкции с глаголами Tardar, Soler, Llevar. Глагол Doler
Конструкции с глаголами Tardar, Soler, Llevar. Глагол Doler итоговый урок английского языка во 2 классе
итоговый урок английского языка во 2 классе Засоби милозвучності мови. 10 класс
Засоби милозвучності мови. 10 класс Презентация к уроку английского языка Pets в 4 классе по УМК Никитенко
Презентация к уроку английского языка Pets в 4 классе по УМК Никитенко Қазақ тілі
Қазақ тілі Словарь языка русских жестов
Словарь языка русских жестов Рентгеновское излучение. Виды рентгеновских трубок
Рентгеновское излучение. Виды рентгеновских трубок Музыкально-информационная презентация по английскому языку Robert Burns.His life and creative work
Музыкально-информационная презентация по английскому языку Robert Burns.His life and creative work Reiseprogramm
Reiseprogramm Презентация Здоровьесберегающие технологии на уроках английского языка в начальной школе
Презентация Здоровьесберегающие технологии на уроках английского языка в начальной школе Глагол. Тема № 3
Глагол. Тема № 3 презентация на английском с озвучкой по теме Tunguetwisters
презентация на английском с озвучкой по теме Tunguetwisters Н.В. Левченко Презентация к уроку испанского языка в 8 классе по теме ЗОЖ
Н.В. Левченко Презентация к уроку испанского языка в 8 классе по теме ЗОЖ Difficulties of translation
Difficulties of translation Теоретические основы лингвострановедения
Теоретические основы лингвострановедения Presure present tation
Presure present tation Презентация 2 класс Закрепление лексики на тему Цвета
Презентация 2 класс Закрепление лексики на тему Цвета Презентация к уроку Окружающая среда
Презентация к уроку Окружающая среда Веселая игра Радуга. Учим английский интересно и весело!
Веселая игра Радуга. Учим английский интересно и весело! Современный учитель иностранного языка. Преподавание в рамках ФГОС.
Современный учитель иностранного языка. Преподавание в рамках ФГОС. Искусственно созданные языки мира
Искусственно созданные языки мира Підготовка назви статті, анотації, графічної презентації, нотаток та ключових слів, написання назви
Підготовка назви статті, анотації, графічної презентації, нотаток та ключових слів, написання назви