Содержание
- 2. Chapter 1: A Business Marketing Perspective Business Marketing Management: B2B Michael D. Hutt & Thomas W.
- 3. By the end of this chapter you will understand: The dynamic nature of the business marketing
- 4. Business Marketing Perspectives “Business Marketing” or “Industrial Marketing” are used interchangeably 50% of all business school
- 5. Business Markets Are markets for products and services from local to international Bought by: Businesses Government
- 6. What Are Business Products? Used to manufacture other products Become part of another product Aid in
- 7. Business to Business (B2B) Marketing is Huge Business marketers serve the largest markets of all. Dollar
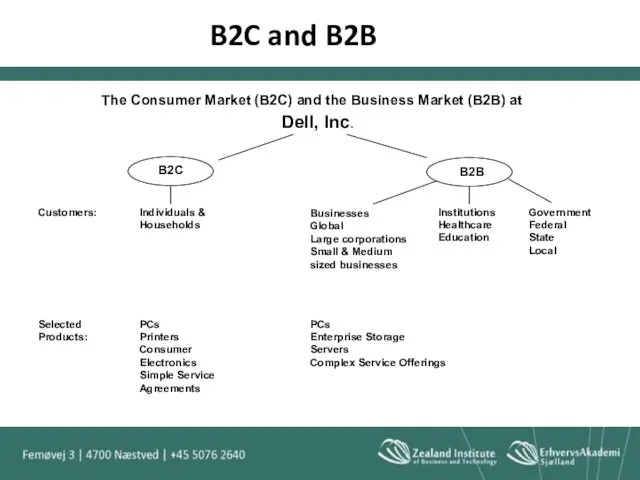
- 8. The Consumer Market (B2C) and the Business Market (B2B) at Dell, Inc. B2C and B2B
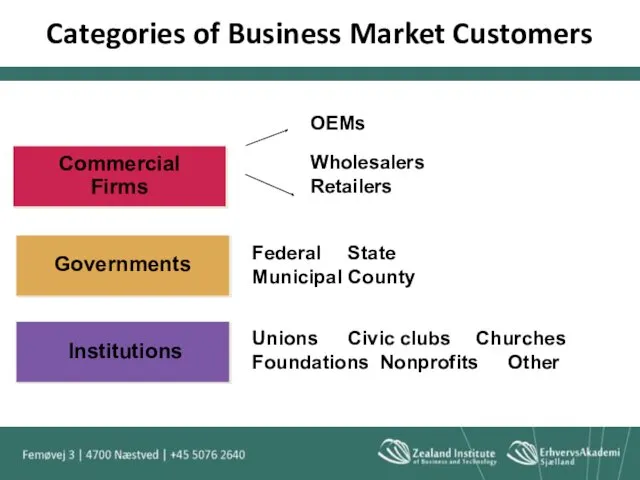
- 9. Categories of Business Market Customers
- 10. Business Marketers vs. Consumer-Goods Marketers Similarly: Both marketers benefit by employing a market orientation, i.e.: They
- 11. Market-Driven Firms Demonstrate… A set of values and beliefs that places customers’ interests first An ability
- 12. Market-Driven Firms Market sensing capability: A company’s ability to sense change and to anticipate customer responses
- 13. Market-Driven Companies View their customer as an asset, thus: Marketing expenditures, once considered expenses, are now
- 14. Develop and nurture customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities by: Identifying, Initiating, Developing, and Maintaining profitable customer
- 15. Professional Marketing Managers Employ Customer Relations Management (CRM) tools for: Identifying and categorizing customer segments Determining
- 16. Professional Marketers: Focus on Profitability Understand forces that affect profitability Align resource allocation to revenues and
- 17. Market-Driven Companies Deliver Value Propositions Create programs that include products, services, ideas and solutions to problems
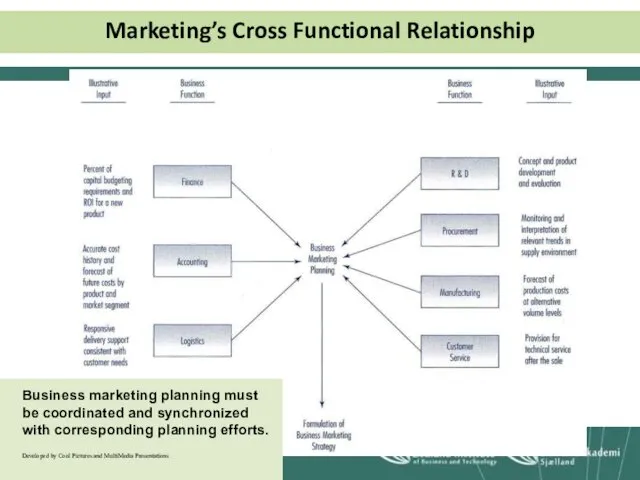
- 18. Marketing’s Cross-Functional Relationships Professional business marketers act as an integrator between various functional areas within the
- 19. Marketing’s Cross Functional Relationship Business marketing planning must be coordinated and synchronized with corresponding planning efforts.
- 20. Business Market Characteristics Business marketing and consumer-goods marketing are different Even though both markets share: Common
- 21. Nature of their markets Market demand Buyer behavior Buyer-seller relationship Environmental influences (competition, political, legal) and
- 22. Business Market Demand Characteristics Derived demand Fluctuating demand Stimulating demand Price sensitivity / demand elasticity
- 23. Derived Demand The demand for business products is called derived demand because the demand for industrial
- 24. Fluctuating Demand Because demand is derived, an increase or decrease in consumer demand can create a
- 25. Stimulating Demand Sometimes, business marketers need to stimulate demand for consumer goods which either incorporate their
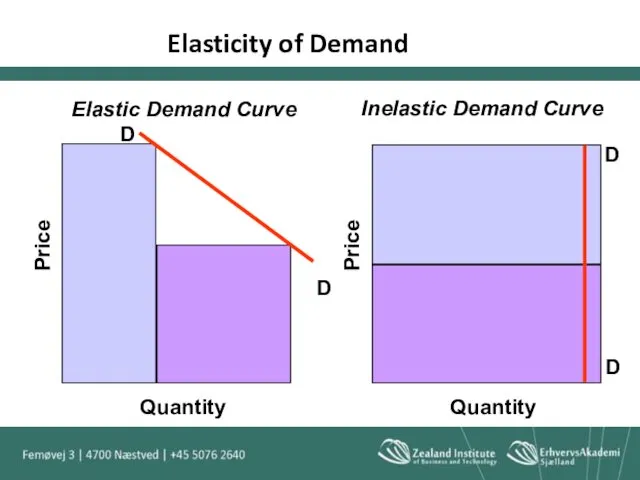
- 26. Inelastic Demand Inelastic demand is demand without regard to price. An increase or decrease in the
- 27. Elasticity of Demand
- 28. Marketers must have a global perspective: They need to look beyond U.S. borders The demand for
- 29. Consumer Product or Business Product? Mentioned earlier, the intended use determines whether or not a product
- 30. Some consumer products become industrial products J.M. Smucker Company sells their jellies and jams to ultimate
- 31. Relationship Marketing All marketing activities directed toward establishing, developing, and maintaining successful exchanges with customers
- 32. Relationship Marketing – con’t Building one-to-one relationships with customers is the heart of business marketing Figure
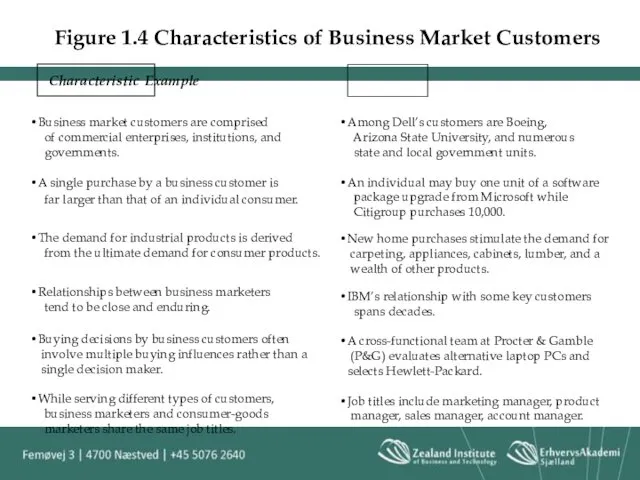
- 33. Figure 1.4 Characteristics of Business Market Customers Characteristic Example Business market customers are comprised of commercial
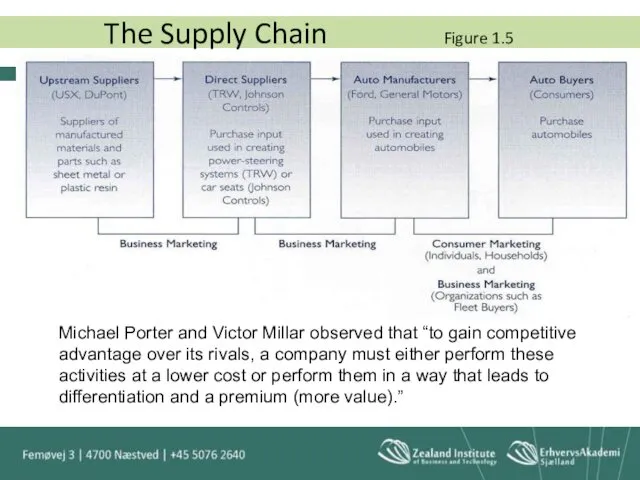
- 34. The Supply Chain Business Marketing is an important influence in the supply chain. When reviewing Figure
- 35. Michael Porter and Victor Millar observed that “to gain competitive advantage over its rivals, a company
- 36. Supply Chain Management This is a technique of linking a manufacturer’s operation with suppliers, key intermediaries
- 37. Managing Relationships in the Supply Chain As important as it is to gain customers, it is
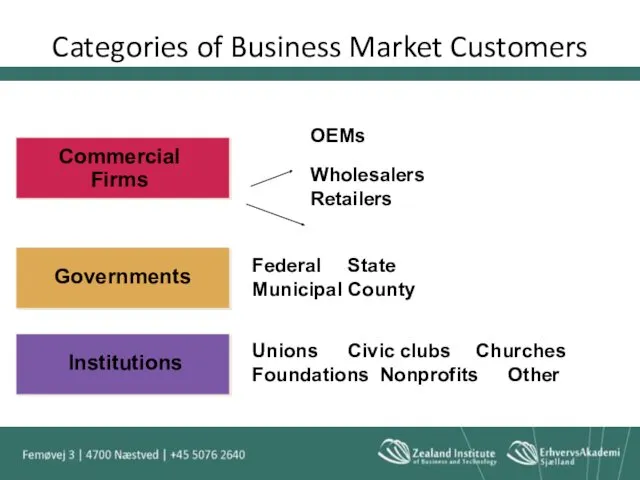
- 38. Categories of Business Market Customers
- 39. Business Market Customer Commercial Enterprises Three categories of Commercial Customers: Users OEMs Dealers and distributors
- 40. Users Users purchase industrial products or services to produce other goods or services that are, in
- 41. Producers Profit oriented companies Produce products - OEM’s and Subcontractors 3M in USA
- 42. OEMs Original Equipment Manufacturers Individuals and organizations that buy business goods and incorporate them into the
- 43. Governments Municipal, State and Federal Government Generally use the bidding approach to purchase goods and services
- 44. Institutions This is the nonprofit segment of the market that does not seek to achieve normal
- 45. Classify industrial goods by asking the following: How does the good or service enter the production
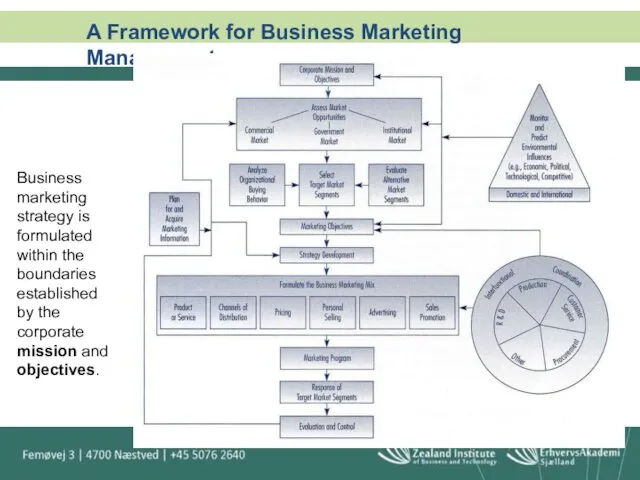
- 46. A Framework for Business Marketing Management Business marketing strategy is formulated within the boundaries established by
- 48. Скачать презентацию





































 Модели тренинга. Модель дома
Модели тренинга. Модель дома Линейка корма TASTY
Линейка корма TASTY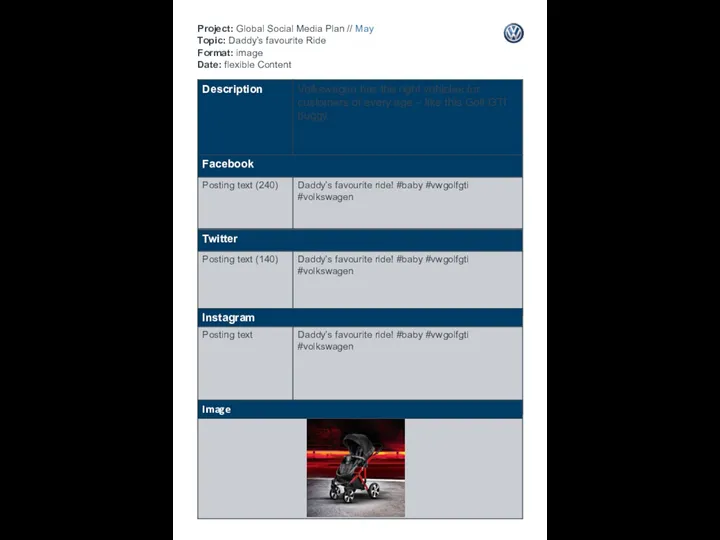 Project: Global Social Media Plan // May Topic: Daddy’s favourite Ride Format: image Date: flexible Content
Project: Global Social Media Plan // May Topic: Daddy’s favourite Ride Format: image Date: flexible Content Оценка эффективности маркетинговой деятельности
Оценка эффективности маркетинговой деятельности Витрины. Магазины Флоенция, Милан 9-13 января
Витрины. Магазины Флоенция, Милан 9-13 января Методики творчества. Теория решения изобретательских задач. (Лекция 9)
Методики творчества. Теория решения изобретательских задач. (Лекция 9) Предложение для клиентов Корпорации Адвекс.Недвижимость
Предложение для клиентов Корпорации Адвекс.Недвижимость Новогодние корпоративы на базе отдыха Ратомка
Новогодние корпоративы на базе отдыха Ратомка Выявление спроса на приключенческий туризм
Выявление спроса на приключенческий туризм Интернет-магазины
Интернет-магазины Творческая студия светланы Бросалиной. Свадебный декор
Творческая студия светланы Бросалиной. Свадебный декор Ассортимент лекарственных препаратов
Ассортимент лекарственных препаратов Московская область, Варшавское шоссе, Восточное бутово. Управление коммерческой недвижимости
Московская область, Варшавское шоссе, Восточное бутово. Управление коммерческой недвижимости Бизнес Круг. Агентство маркетинга и бизнес-коммуникаций
Бизнес Круг. Агентство маркетинга и бизнес-коммуникаций Маркетинговые стратегии
Маркетинговые стратегии Люксовые бренды
Люксовые бренды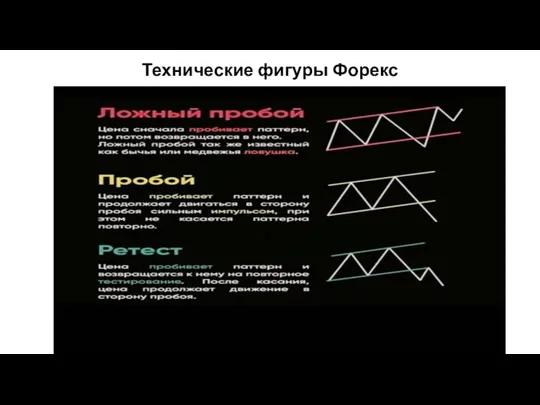 Технические фигуры Форекс
Технические фигуры Форекс Проект 50 идей для новогодних каникул
Проект 50 идей для новогодних каникул Типовые модульные решения для энергосбережения. Диспетчеризация на базе ИВК ЭЛЕКОМ-Информ
Типовые модульные решения для энергосбережения. Диспетчеризация на базе ИВК ЭЛЕКОМ-Информ Овсяные хлопья Ясно солнышко
Овсяные хлопья Ясно солнышко Маркетинг-план компании Atomy. Плодотворное сотрудничество
Маркетинг-план компании Atomy. Плодотворное сотрудничество Oscar Tiye – итальянский обувной бренд
Oscar Tiye – итальянский обувной бренд Акция ИТС для сотрудников
Акция ИТС для сотрудников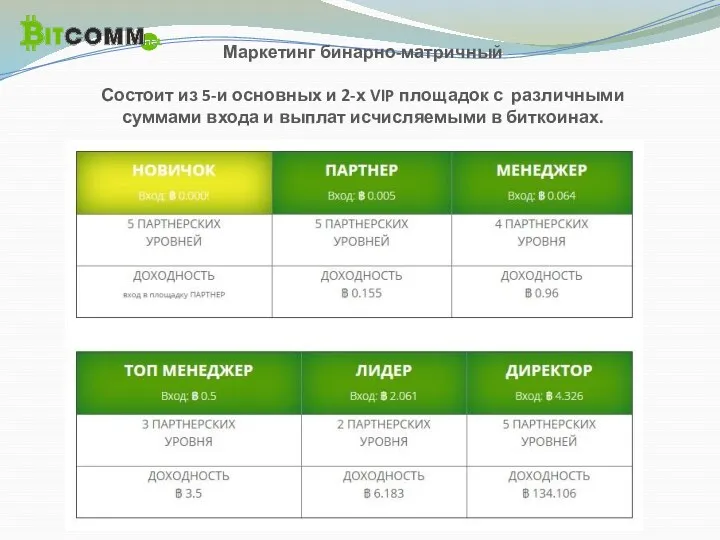 Маркетинг бинарно-матричный
Маркетинг бинарно-матричный Доставка фруктов, овощей и шампиньонов при заказе от 1000 рублей
Доставка фруктов, овощей и шампиньонов при заказе от 1000 рублей Облачная АТС@втосекретарь
Облачная АТС@втосекретарь Развитие коммерческого потенциала
Развитие коммерческого потенциала Introducing. The new world trade center. Brenda
Introducing. The new world trade center. Brenda