Содержание
- 2. Marketing research taxonomy Marketing essentials 2014/2015 MARKETING RESEARCH EXPLORATORY RESEARCH DESIGN Gathers preliminary information that will
- 3. Problem identification Marketing research fields of employment Marketing essentials 2014/2015 Market share and potential Problem solution
- 4. Research types comparison Marketing Essentials 2014/2015
- 5. Research designs classified by time Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Pretest Posttest Snapshot Longitudinal research Panel research
- 6. Kinds of informations in marketing research Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 INTERNAL INFORMATONS Retrieved inside the company, no
- 7. Information sources in marketing research Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 PRIMARY INFORMATIONS INTERNAL Company employees Company R&D department
- 8. Measurements in marketing research Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Interval scale Possesses assignment, order and distance properties. It
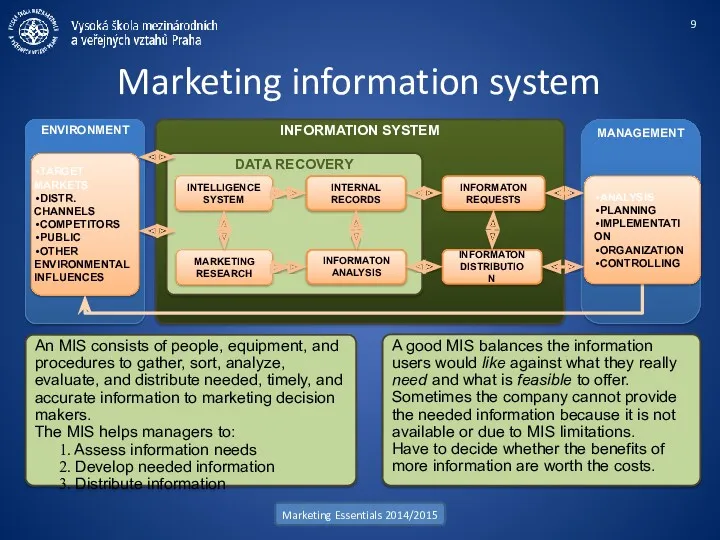
- 9. INFORMATION SYSTEM Marketing information system Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 DATA RECOVERY INTERNAL RECORDS INTELLIGENCE SYSTEM MARKETING RESEARCH
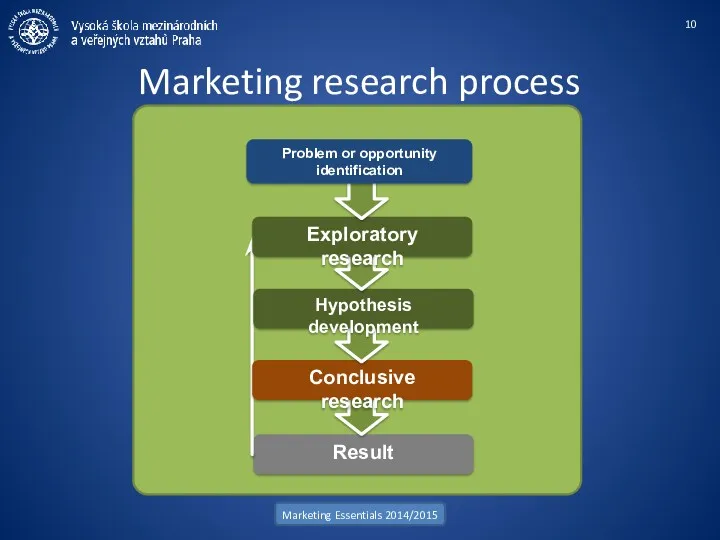
- 10. Marketing research process Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Result Conclusive research Hypothesis development Exploratory research Problem or opportunity
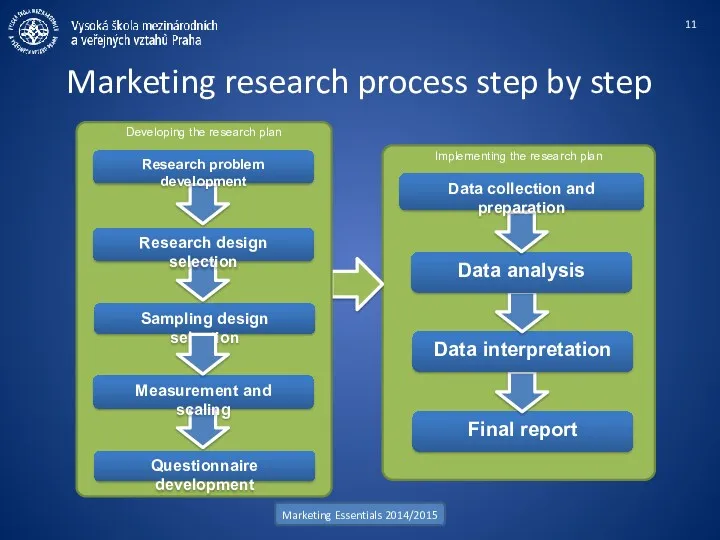
- 11. Implementing the research plan Marketing research process step by step Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Developing the research
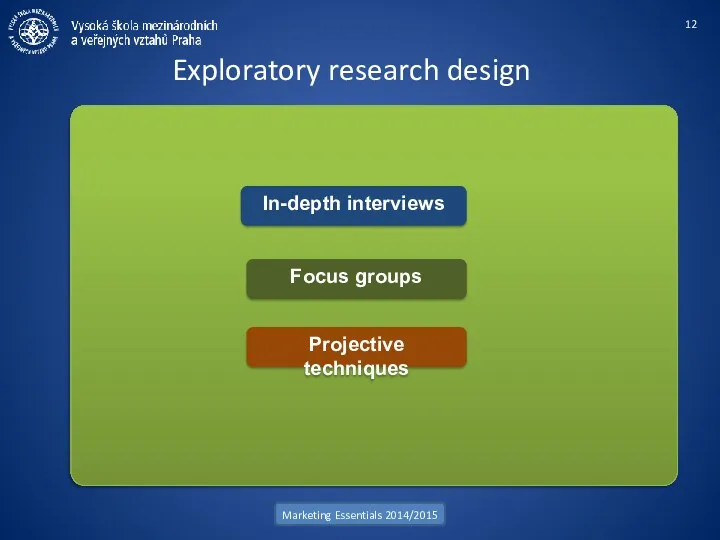
- 12. Exploratory research design Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Projective techniques Focus groups In-depth interviews
- 13. Developing the Research Plan Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Includes: Determining the exact information needed. Developing a plan
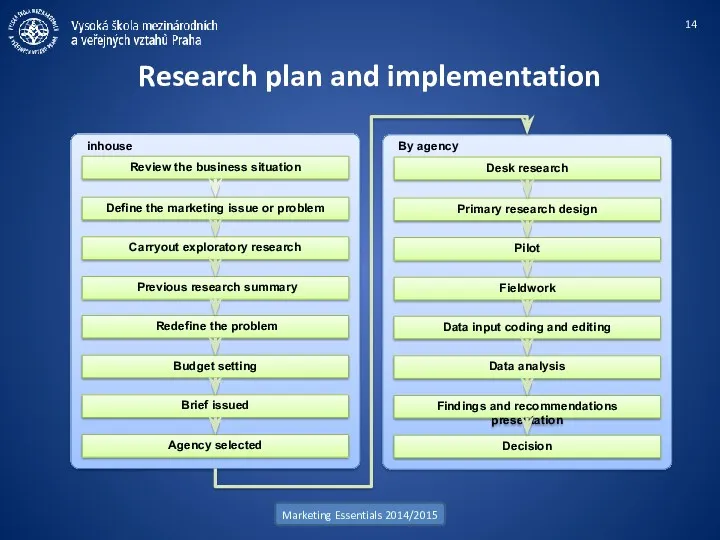
- 14. inhouse Research plan and implementation Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Previous research summary Carryout exploratory research Define the
- 15. Review the business situation Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 We start the process with a review of the
- 16. Defining the issues or problem Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Problems can generally be solved in many ways.
- 17. Carry out exploratory research Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 This stage is designed to clarify the research problem.
- 18. Previous research summary Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 As part of this process, previously carried out research should
- 19. Internal research Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Internal research will involve the use of the MIS and the
- 20. Gathering Secondary Data Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Information that already exists somewhere: Internal databases Commercial data services
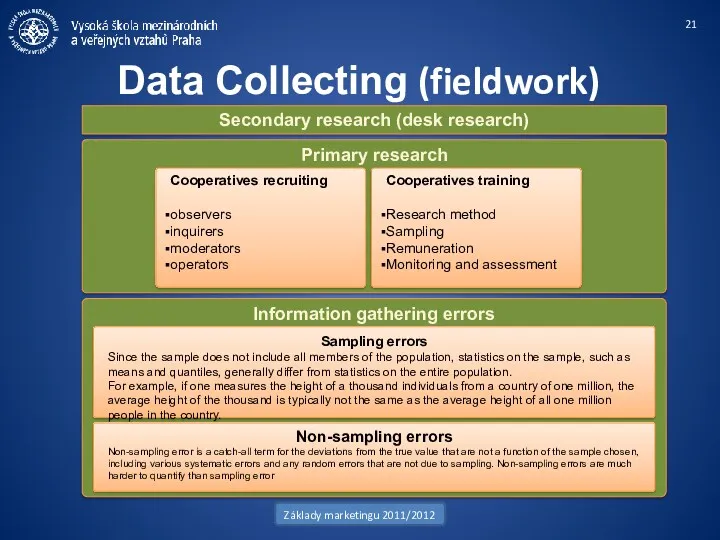
- 21. Primary research Information gathering errors Data Collecting (fieldwork) Základy marketingu 2011/2012 Sampling errors Since the sample
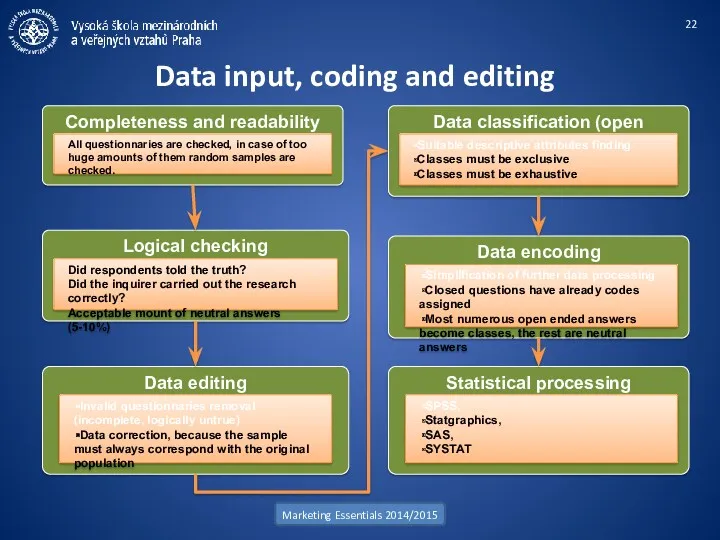
- 22. Completeness and readability check Data input, coding and editing Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 All questionnaries are checked,
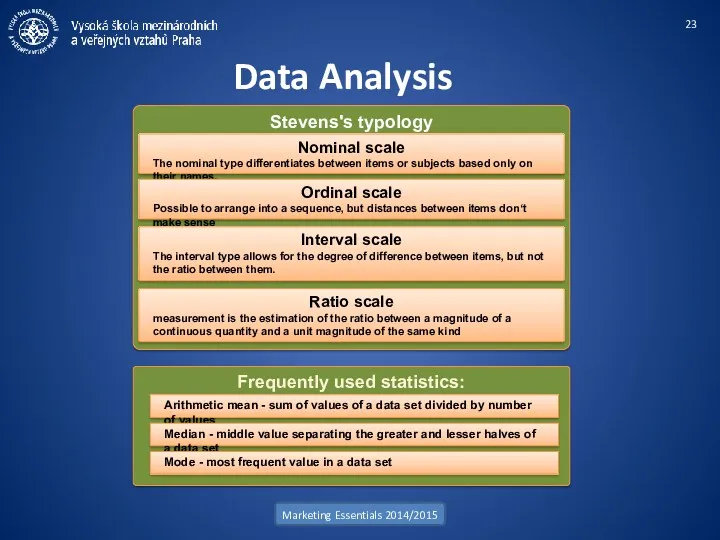
- 23. Stevens's typology Data Analysis Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Nominal scale The nominal type differentiates between items or
- 24. Findings and recommendations presentation Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Don’t confuse presenting data with presenting your evaluation findings
- 25. List brokers – Suppliers of lists of contacts for marketing purposes. They may include names and
- 26. Particular Research Services Providers Marketing Essentials 2014/2015
- 27. Quantitative methods Marketing Research Methods Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Observing Questionning Experimenting Qualitative methods In-depth Interview Focus
- 28. Advantages: Observing Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Does not rely on object‘s cooperation Does not influence object observed
- 29. Covert observational research Three Approaches of Observational Research Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Nonstandardized Semi-standardized Standardized Overt observational
- 30. Personal observation Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 observing products in use to detect usage patterns and problems observing
- 31. Trace Analysis Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 credit card records computer cookie records garbology - looking for traces
- 32. Mechanical observation Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 eye-tracking analysis while subjects watch advertisements oculometers - what the subject
- 33. Observation Biases Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Human perception occurs by a complex, unconscious process of abstraction, in
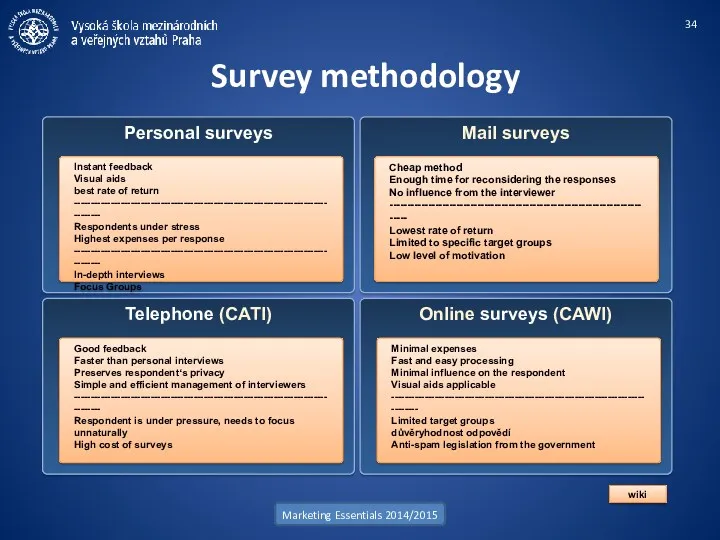
- 34. Survey methodology Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Personal surveys Instant feedback Visual aids best rate of return ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
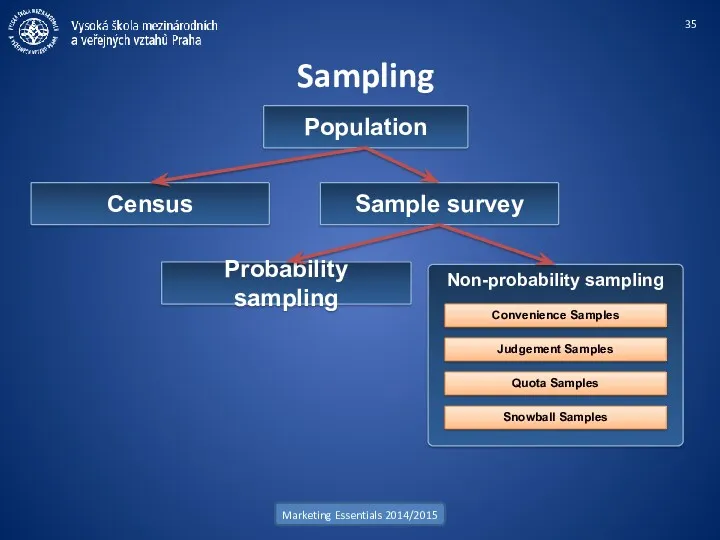
- 35. Sampling Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Population Census Sample survey Probability sampling Non-probability sampling Convenience Samples Judgement Samples
- 36. Quantitative research examples Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Panel survey Omnibus survey Purchase diary panel Brand awareness Brand
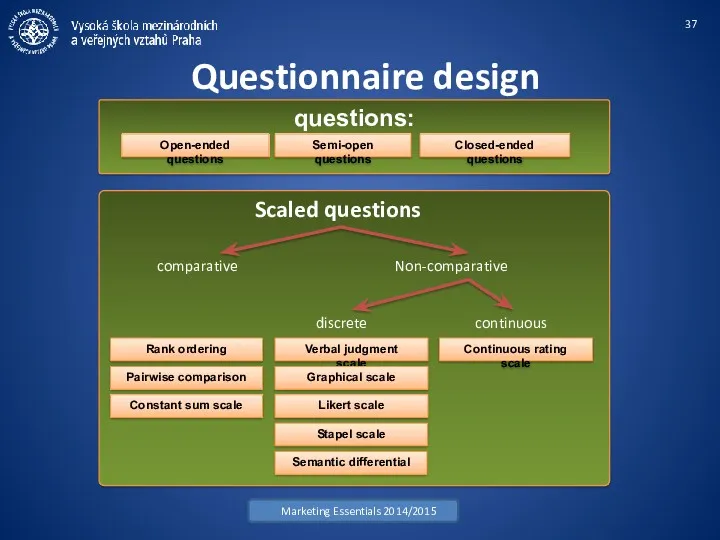
- 37. Questionnaire design Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 questions: Open-ended questions Semi-open questions Closed-ended questions Verbal judgment scale Graphical
- 38. Experimenting Základy marketingu 2011/2012 Internal validity Inferences are said to possess internal validity if a causal
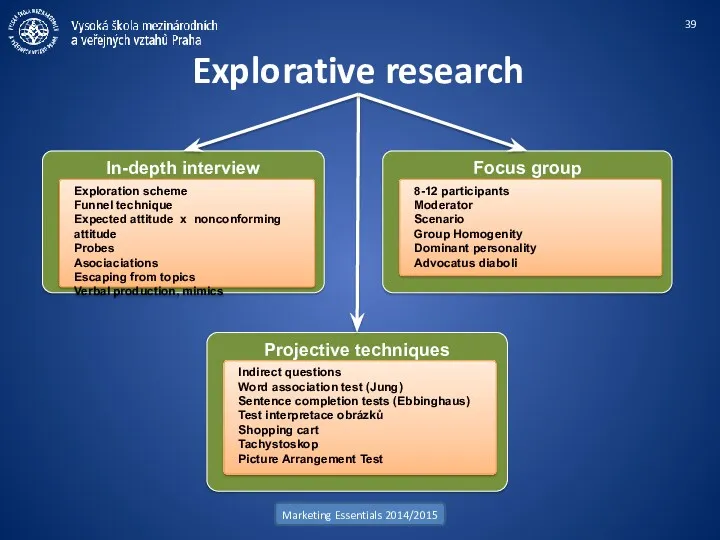
- 39. Explorative research Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 In-depth interview Exploration scheme Funnel technique Expected attitude x nonconforming attitude
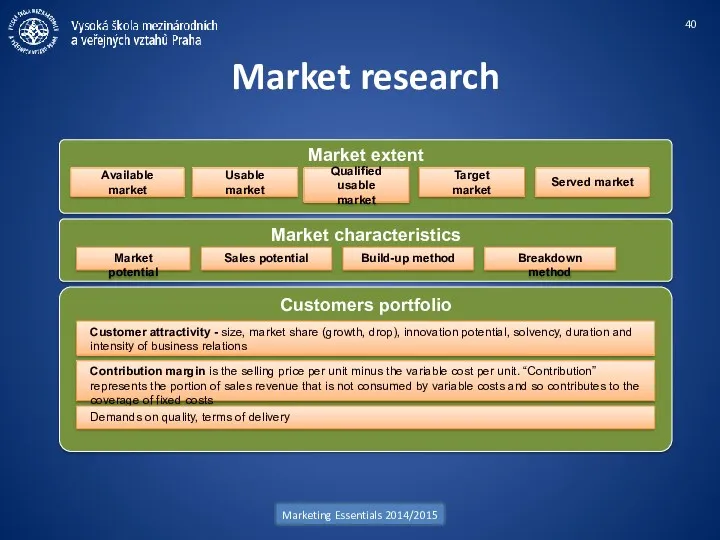
- 40. Market research Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Market extent Available market Market characteristics Market potential Usable market Qualified
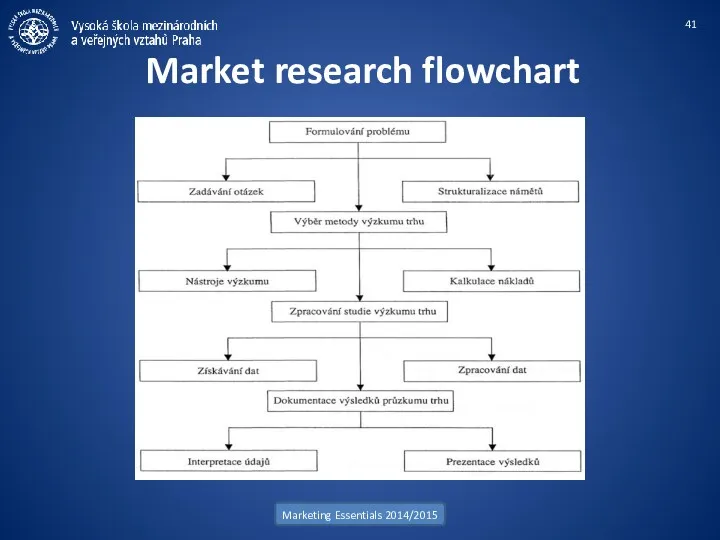
- 41. Market research flowchart Marketing Essentials 2014/2015
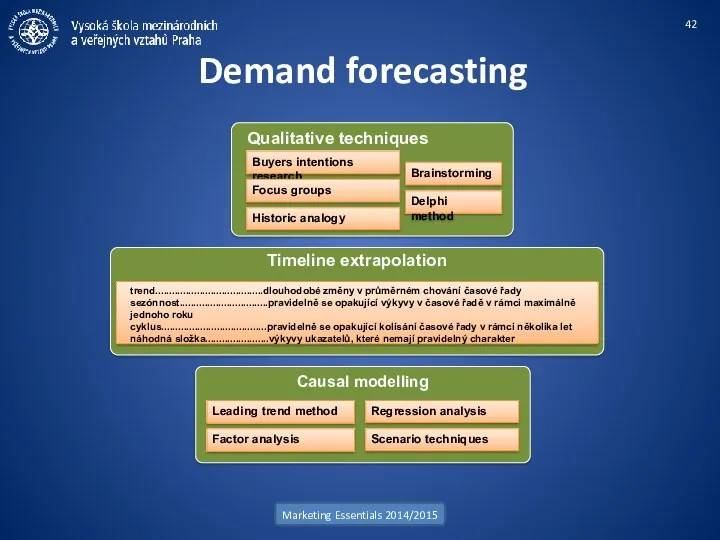
- 42. Demand forecasting Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Qualitative techniques Timeline extrapolation Buyers intentions research Causal modelling Delphi method
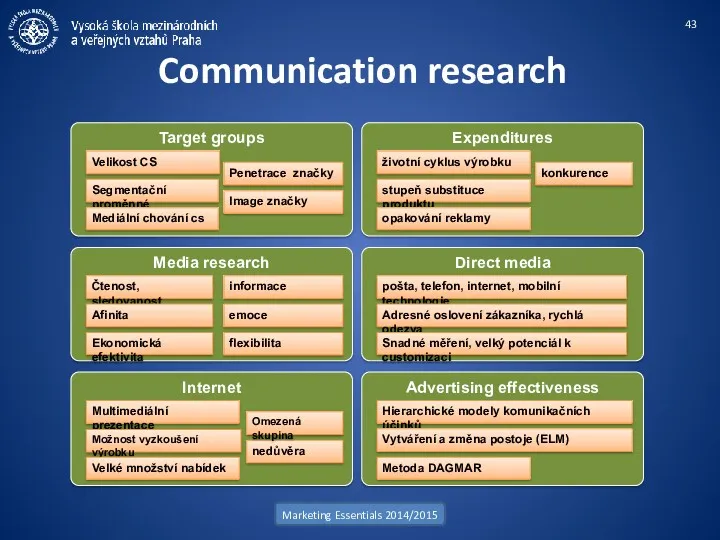
- 43. Communication research Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Target groups Velikost CS Image značky Penetrace značky Segmentační proměnné Mediální
- 44. Communication Research Základy marketingu 2011/2012 Preliminary tests ■ Internal evaluation ■ Communication Effects Post-tests ■ Exposure
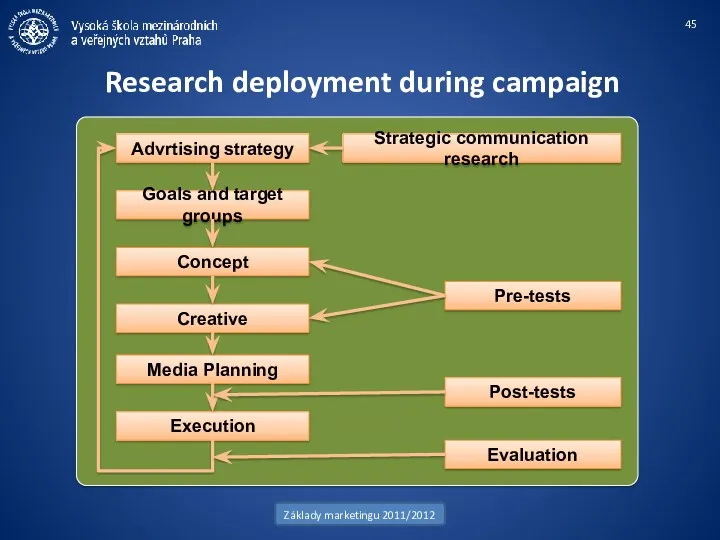
- 45. Research deployment during campaign Základy marketingu 2011/2012 Advrtising strategy Goals and target groups Concept Creative Media
- 46. Strategic communication research Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 product ■ strenghts & weaknesses ■ USP ■ persuasive arguments
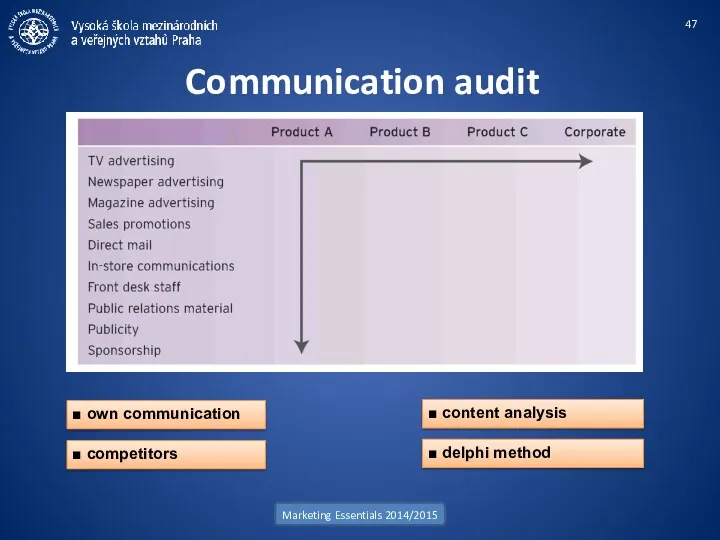
- 47. Communication audit Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 ■ content analysis ■ delphi method ■ own communication ■ competitors
- 48. Campaign pre-testing Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Testing objectives ■ adequate stimuli ■ communication effects estimation ■ frekvency
- 49. Pre-testing limitations Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 ■ subjective evaluation ■ unnatural conditions ■ consumer jury effect ■
- 50. Advertising Campaign Evaluation Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Post testing techniques Exposure : ■ GRP, reach, OTS measured
- 51. Post-testing limitations Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 ■ isolated effect of single ad spot ■ selective memory ■
- 52. Communication campaign evaluation Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Měření TOMA Měření postoje Měření image Měření nákupního záměru Trackingové
- 53. Communication campaign evaluation Marketing Essentials 2014/2015 Questions to ask: • Have you heard of ______ campaign?
- 55. Скачать презентацию


































 Продам
Продам Штрих-кодирование упаковочных листов
Штрих-кодирование упаковочных листов Eye-tracking как инструмент повышения конверсии сайта
Eye-tracking как инструмент повышения конверсии сайта DURACELL Коммерческое предложение для сети магазинов
DURACELL Коммерческое предложение для сети магазинов Акция 20+1, Петровская Слобода
Акция 20+1, Петровская Слобода Рынок лидогенерации. Интернет-рынок в России. Понятия и термины СРА-рекламы. Процедура по работе с партнерской сетью
Рынок лидогенерации. Интернет-рынок в России. Понятия и термины СРА-рекламы. Процедура по работе с партнерской сетью Научное шоу Открывашка. Выпускной в детском саду
Научное шоу Открывашка. Выпускной в детском саду Adversting
Adversting Сервисная компания ТатПром-Холдинг. Производство оборудования для нижнего заканчивания скважин
Сервисная компания ТатПром-Холдинг. Производство оборудования для нижнего заканчивания скважин Invenda Intel
Invenda Intel Эффективность предпринимательской деятельности. Тема 8
Эффективность предпринимательской деятельности. Тема 8 Transactional Replication
Transactional Replication Семинар “Желание, власть и любовь”
Семинар “Желание, власть и любовь” Moda International Fashion Group
Moda International Fashion Group Уміння продавати
Уміння продавати База отдыха и рыбалки на НГ
База отдыха и рыбалки на НГ Рекламное воздействие и ценовые модели размещения рекламы в интернете
Рекламное воздействие и ценовые модели размещения рекламы в интернете Сходства и различия рекламы и PR
Сходства и различия рекламы и PR Большой и современный жилой комплекс Ярославский
Большой и современный жилой комплекс Ярославский Смазочно-охлаждающие жидкости (СОЖ)
Смазочно-охлаждающие жидкости (СОЖ) Компания Atomy
Компания Atomy Phenicoptere
Phenicoptere Мастерство переговоров. Тренинг Стратегия и тактика эффективных переговоров
Мастерство переговоров. Тренинг Стратегия и тактика эффективных переговоров Петербургский клуб Природного земледелия. Бесплатные лекции для садоводов и продажа лучших товаров для Природного земледелия
Петербургский клуб Природного земледелия. Бесплатные лекции для садоводов и продажа лучших товаров для Природного земледелия Разработка комплекса маркетинга. Разработка товара. Установление цен на товары
Разработка комплекса маркетинга. Разработка товара. Установление цен на товары Как перестать беспокоиться и начать путешествовать
Как перестать беспокоиться и начать путешествовать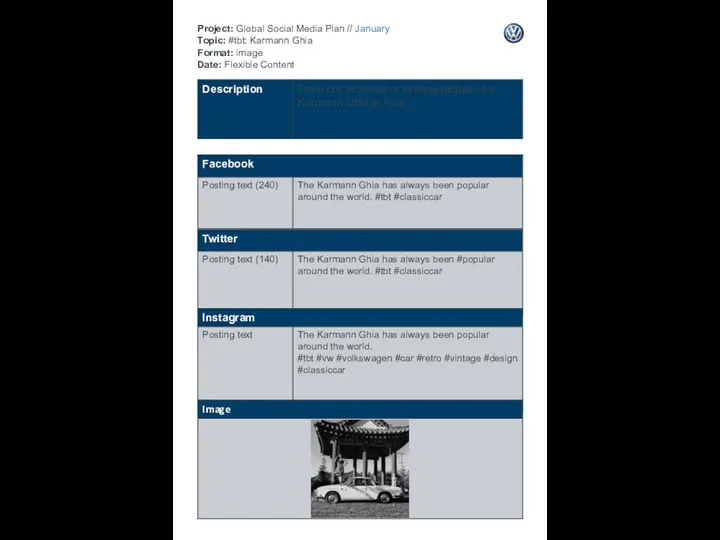 Project: Global Social Media Plan
Project: Global Social Media Plan Школьная Форма
Школьная Форма